SL Business Unit 2
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Stakeholder
An individual, group, or organization with a direct interest or involvement in the operations and performance of a business
Internal vs External (Stakeholders)
External Stakeholders own shares but are not directly involved in the daily operations of a business
Internal Stakeholders
Employees, Managers/Directors, Shareholders/Stockholders
2 objectives of shareholders
Maximize dividends (proportion of the profits given to them)
Achieve capital gain (a rise in the value of shared)
External Stakeholders
Customers, Suppliers, Financiers, Pressure Groups, Competitors, Government
Objectives of Suppliers
Regular contracts, good work relations with clients, clients pay on time
Objectives of Financiers
Long term relationships, ability of firm to repay debts
Objectives of Government
Avoid unfair practices, ensure correct corporate tax is paid, health and safety standards are met, compliance with the employment legislation
Conflict between stakeholders
Inability of an organization to meet all of its stakeholder objectives simultaneously (Due to differences in the varying needs of stakeholders)
Resolving stakeholder conflict
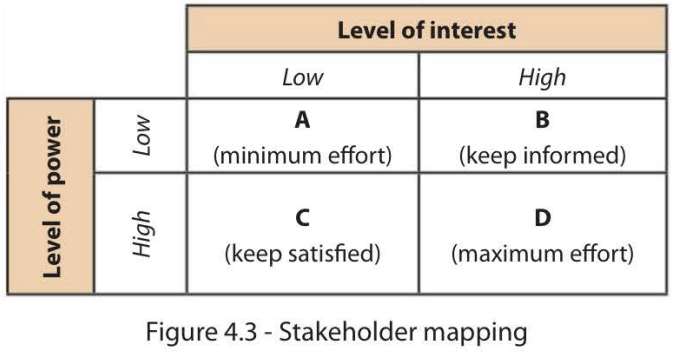
Stakeholder Conflict: Maximum Effort
For key stakeholders
Stakeholder Conflict: Mimimum Effort
Receive the lowest priority
Stakeholder Conflict: Keep Informed
Stakeholders can become highly disgruntled
Stakeholder Conflict: Keep Satisfied
via consultation on strategic decisions
Economies of Scale
When average costs of production decrease as the organization increases the size of its operations
Diseconomies of Scale
When an organization becomes too large - causing product inefficiencies affecting the whole industry (cost of product goes up)
Internal Economies of Scale
Technical, Financial, Managerial, Marketing, Purchasing
Internal Economies of Scale: Technical
Use sophisticated capital and machinery to mass produce. High fixed cost of equipment is spread out (reducing average cost of production)
Internal Economies of Scale: Financial
Borrowing large sums of money at lower rates of interest since they are seen as “less risky”
Internal Economies of Scale: Managerial
Sell products in bulk.
Benefit from:
Saves time
Transaction costs
Spread the high costs of advertising by using the same marketing campaigns
Internal Economies of Scale: Purchasing
Lower average costs by buying resources in bulk
External Economies of Scale
Technological Process, Improved Transportation, Regional Specialization
External Economies of Scale: Technological Process
Increases productivity levels
External Economies of Scale: Improved Transportation
Ensures to promote deliveries. Inefficiencies raise business costs and reduce profits.
External Economies of Scale: Regional Specialization
Particular locations have trustworthy reputations for producing certain goods. Industries benefit from specialists and thus reduces average cost for production.
Internal Diseconomies of Scale
Lack of control and coordination, poor working relationship, bureaucracy
Internal Diseconomies of Scale: Lack of control and coordination
Causes communication problems and add to firm cost without an increase in productivity. Increases Unit Cost
Internal Diseconomies of Scale: Poor working relationship
Senior managers become detached from workers lower down in the “hierarchy” Damaged communication flow and motivation.
Internal Diseconomies of Scale: Bureaucracy
Excessive admin paperwork/company policies. Decision making is more time consumer, communication is challenging. Increases Unit Cost
External Diseconomies of Scale
Higher rent, higher pay, traffic conjection
External Diseconomies of Scale: Higher rent
Add to fixed cost. Increases Unit Cost
External Diseconomies of Scale: Higher pay
Increases cost without necessarily increasing output. Raising average cost of production
External Diseconomies of Scale: Traffic Congestion
Too many businesses in one area → delayed deliveries, increased transportation cost, more competitiveness. Increases Unit Cost
Internal Growth (Organic Growth)
Business grows by using their own resources and capabilities to increase the scale of operations and sales revenue
Examples of Internal Growth
Changing prices
Effective promotions
Product innovation
Increased distribution
Pros/Cons of Internal Growth
Pro
Better control/ co-ordination
Inexpensive
Corporate culture
Less risky
Con
Diseconomies of scale
Restructure
Dilution of control and ownership
Slower growth
External Growth (Inorganic Growth)
Dealing with outside organizations rather than from an increase in the organization’s own business operations
Examples of External Growth
Mergers and Acquisitions
Acquisitions: when a company buys a controlling interest in another form with permission/agreement of the board of directors
Takeovers
When a company purchases a controlling stake in another company without permission or agreement
Joint Ventures
2+ businesses come together to form a separate entity (share costs, risk, control, etc)
Strategic Alliance
2+ businesses come together but do not form a separate entity (“project”, share costs, marketing, operations)
M&A Pro/Cons
Benefits: greater market share, economies of scale, diversification
Drawbacks: Redundancies (too many employees), conflict, culture clash, diseconomies of scale, loss of control
Strategic Alliances Pro/Cons
Benefits: Spreads costs/risks, relatively cheap, competitive advantage
Drawbacks: Rely heavily on goodwill of counterparts, large expenditure, culture clash
Multinational Companies
Organizations that operate in 2+ countries, with a head office based in the home country
MNC Pro/Cons
Pro
Creates jobs
Higher national income (GDP increases)
Knowledge/technology transfer
Increased competition
Con
Job losses
Repatriation of profits (negative for the country’s tax revenues)
Vulnerability
Social responsability
Competitive pressure
Reasons to become a MNC
Increased customer base
Cheaper production cost
Protectionist policies
Economies of scale
Brand development/value
Spreads risks
Reasons to stay a Small Business
Cost control, Loss of control, Financial risks, Government aid, Local monopoly power, Personalized services, Flexibility, Small market size
Reasons to become a Large Business
Economies of scale, Lower prices, Brand recognition, Brand reputation, Value-added services, Greater choice, Customer loyalty
Synergy
Creates greater output and improved efficiencies → why organizations seek to grown inorganically.
Joint Venture Pro
Benefit: Synergy, cost/risk spread, entry to foreign markets, relatively cheap, competitive advantage, high success rate
Franchising
an individual/business buys a license to trade using another company's products/name/brand/trademarks. Franchisee pays a license fee and royalty payments (based on sales revenues).
Benefits/Drawbacks for Franchisor
Benefits: Cheaper/Faster than internal growth, national/international presence, rapid growth with minimal effort, chances of success are increased
Drawbacks: risk in using name, difficult to control, difficult to meet standards, M&As are faster
Benefits/Drawbacks for Franchisee
Benefits: low start up cost, low risk, value-added services, large scale advertising, “their own bosses”
Drawbacks: overseen by franchisor, expensive, sales revenues are lost
Brand awarness vs Brand loyaly
Brand awareness is when customers recognize and recall your brand, while brand loyalty is when customers are dedicated to your brand and unwilling to switch to a competitor