Crystal Structures EMA3050
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
cubic crystal structure
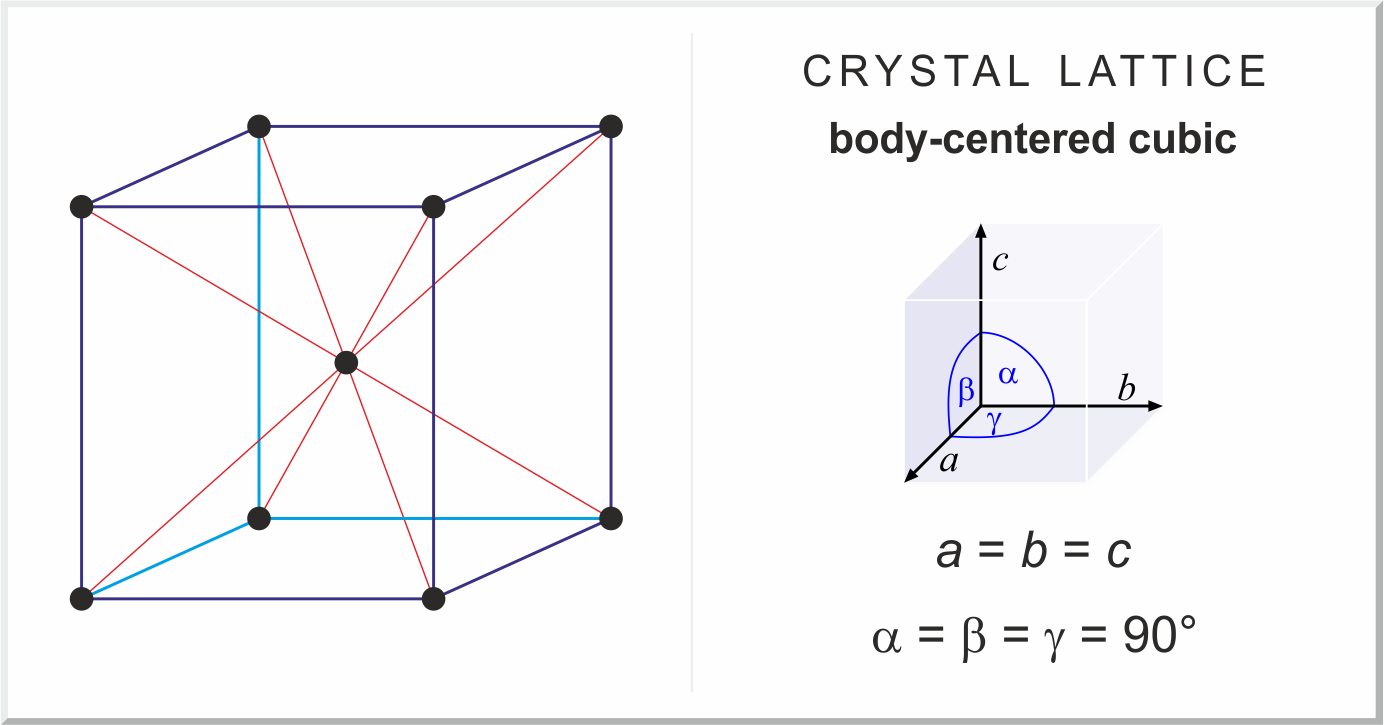
tetragonal crystal structure
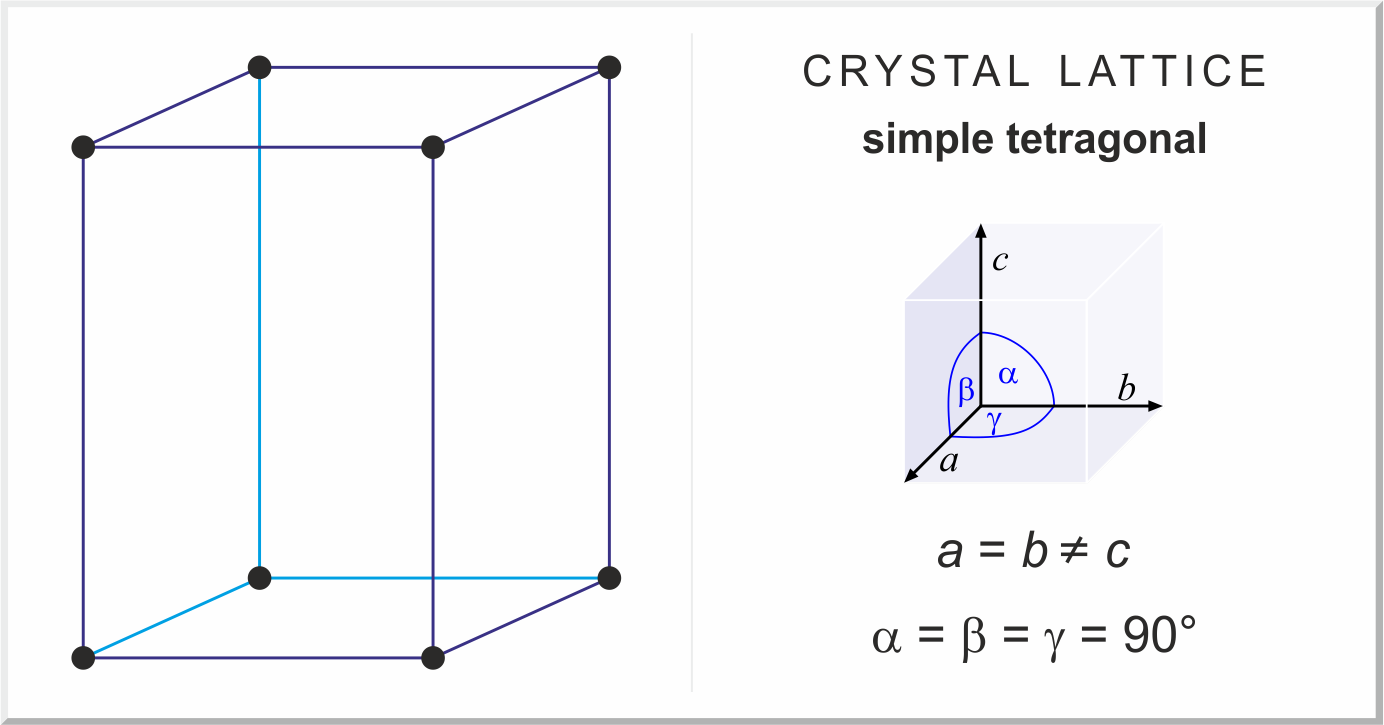
orthorhomic crystal structure
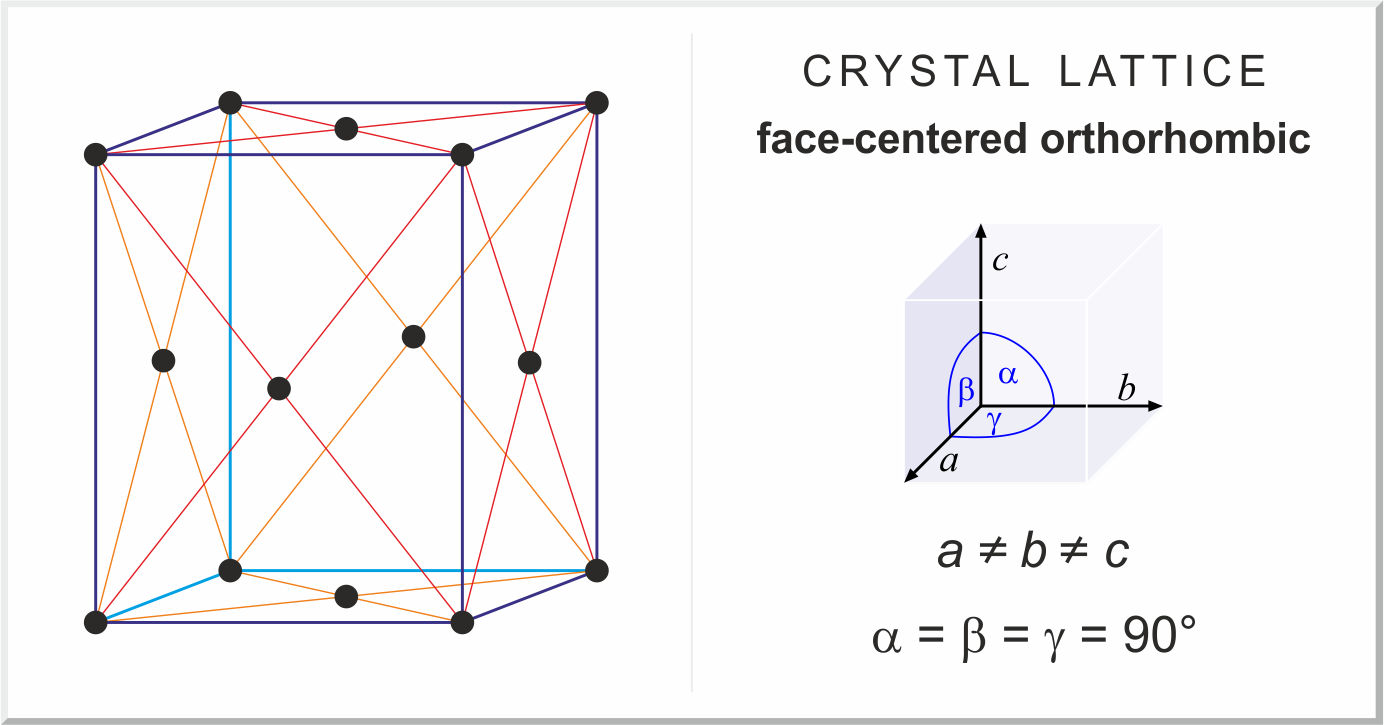
hexagonal crystal structure
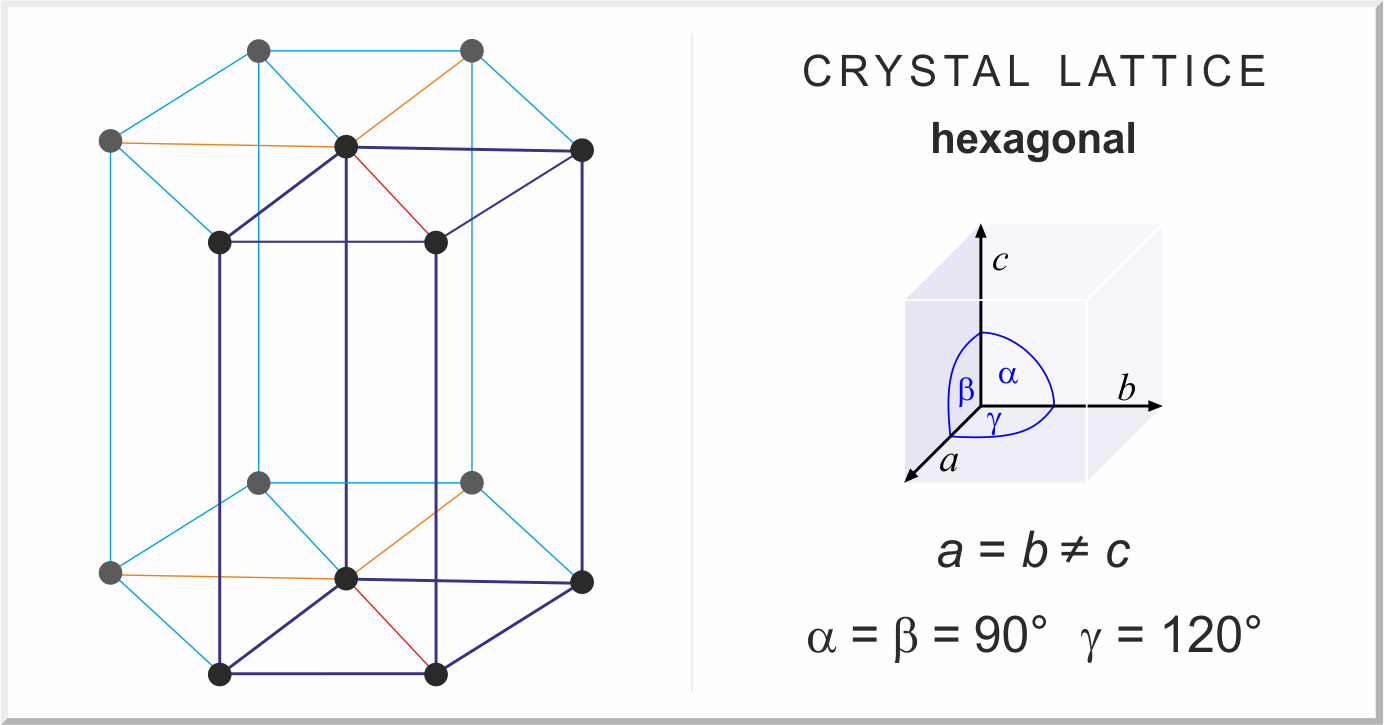
Monoclinic crystal structure
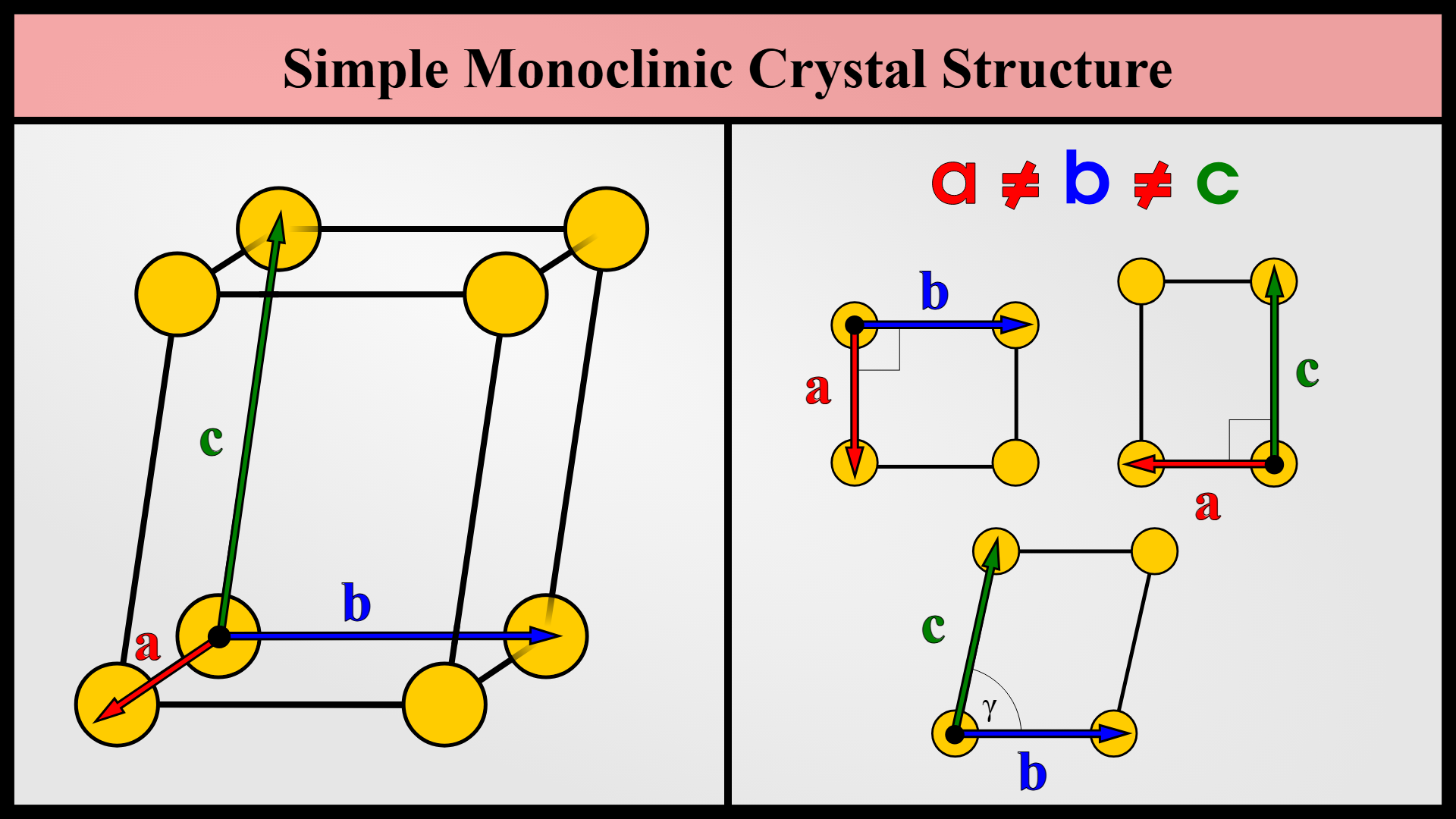
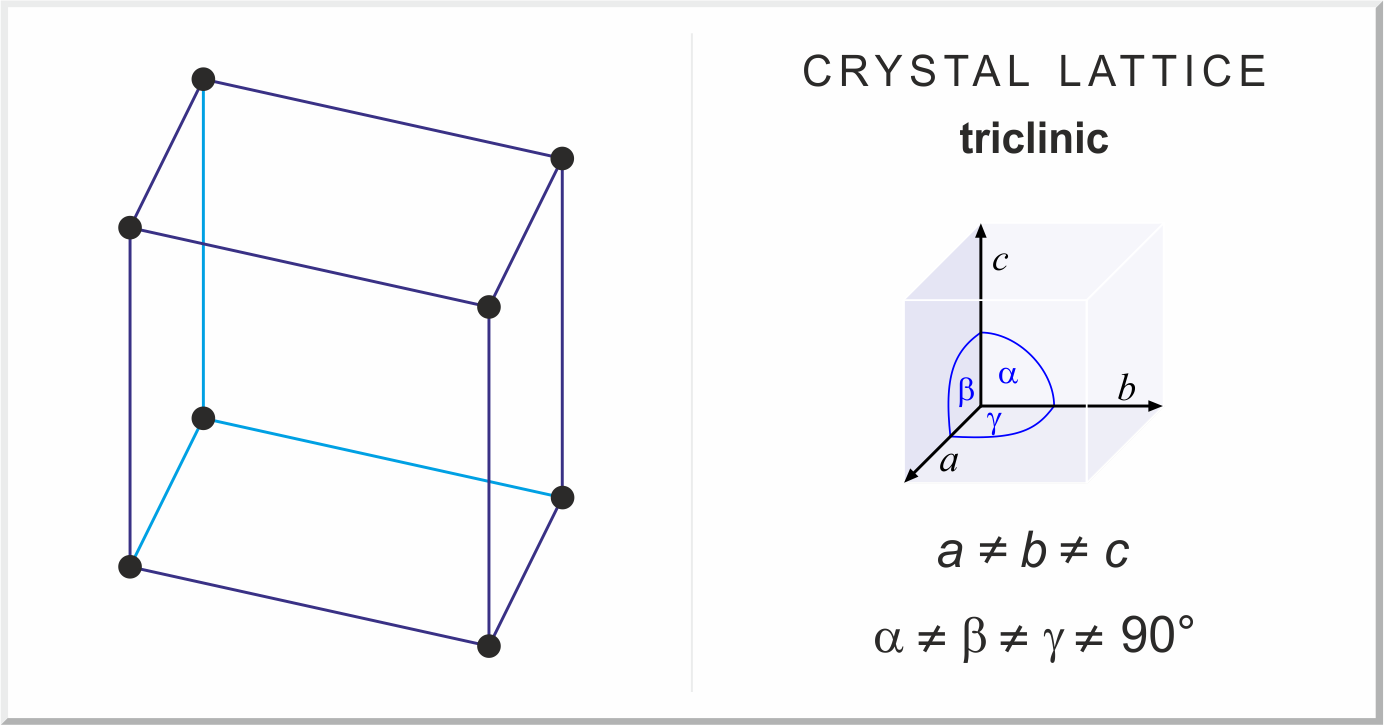
Triclinic crystal structure
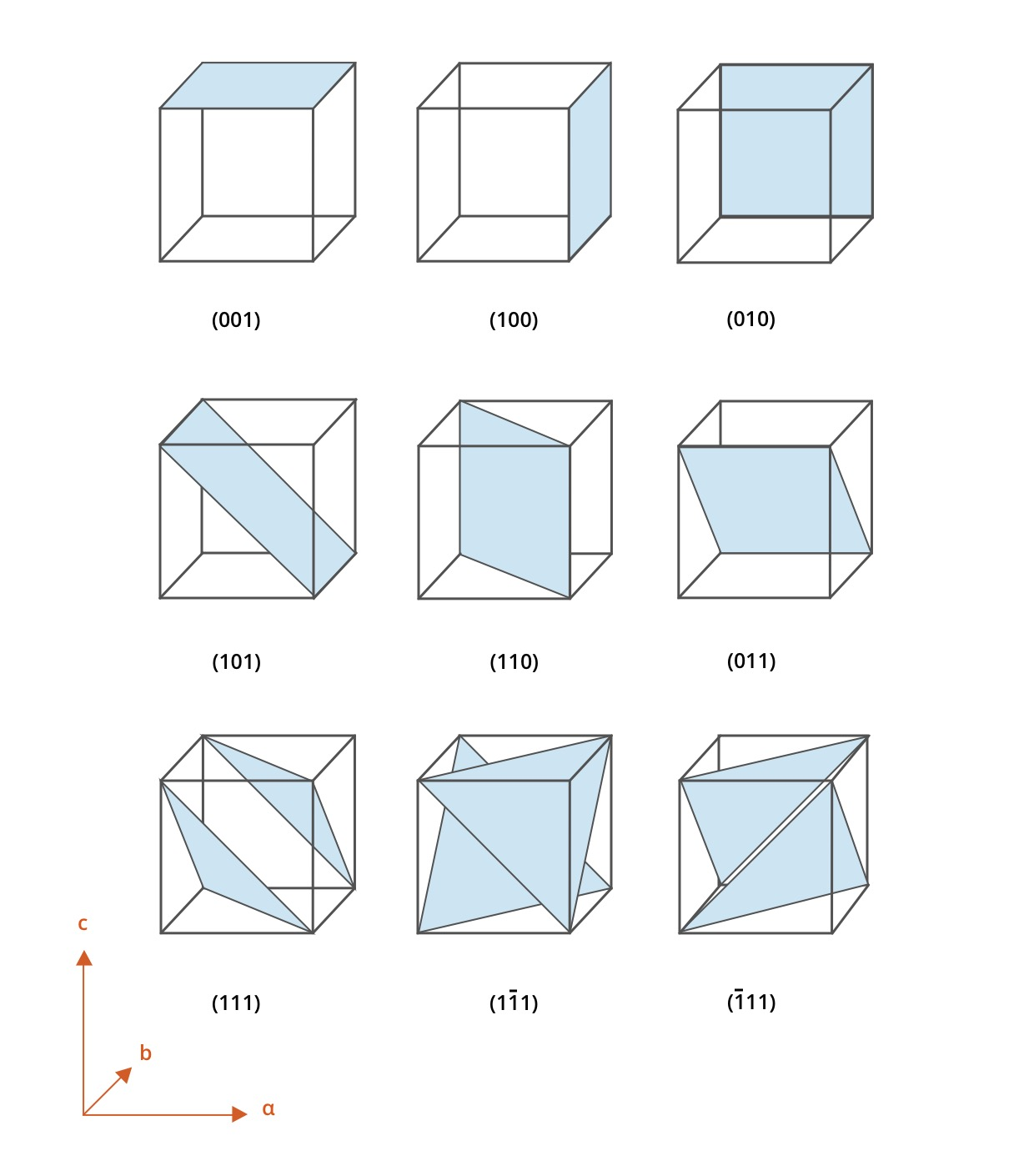
How to find crystallographic planes (for cubic)
Identify instersections → If it passes through the origin move the origin
Take reciprocals of intercepts
Clear fractions
Enclose in parenthesis
Find HCP vector
Find direction using a1 , a2 , and c
Find head point
Find tail point
take head - tail
Put in [h k i l] form where k = -(h+k)
![<ol><li><p>Find direction using a<sub>1 </sub>, a<sub>2</sub> , and c</p></li><li><p>Find head point </p></li><li><p>Find tail point</p></li><li><p>take head - tail</p></li><li><p>Put in [h k i l] form where k = -(h+k)</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bcb30146-5492-4a65-914b-124b598c3d7e.png)
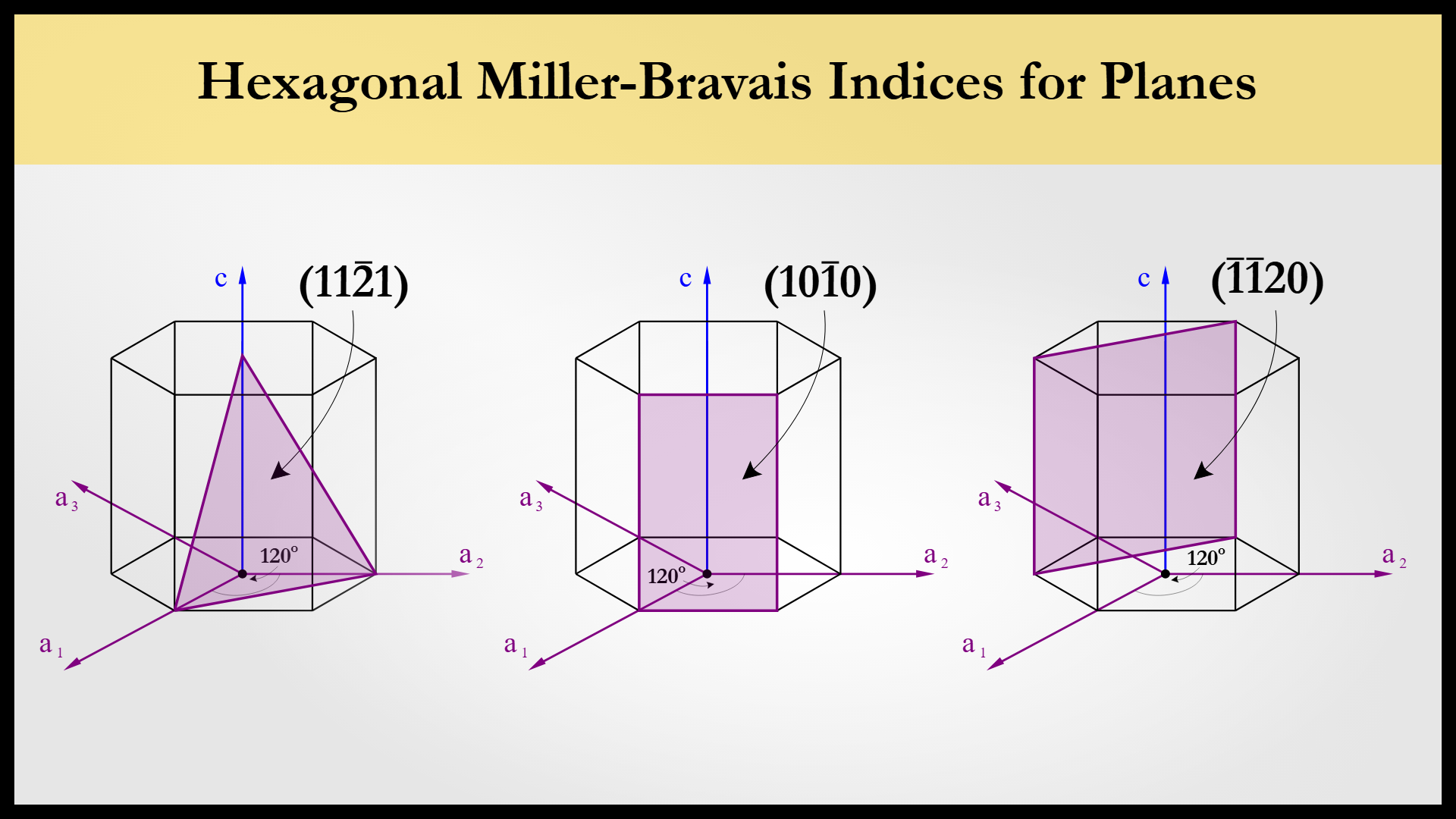
Fnd planes in hexgonal HCP
Use a1 , a2 , and c to find intercepts
Take reciprocal of intercept
Convert to 4 index (h k i l)
What is the coord number
number of nearest nieghbor atoms
APF of FCC and HCP
74%
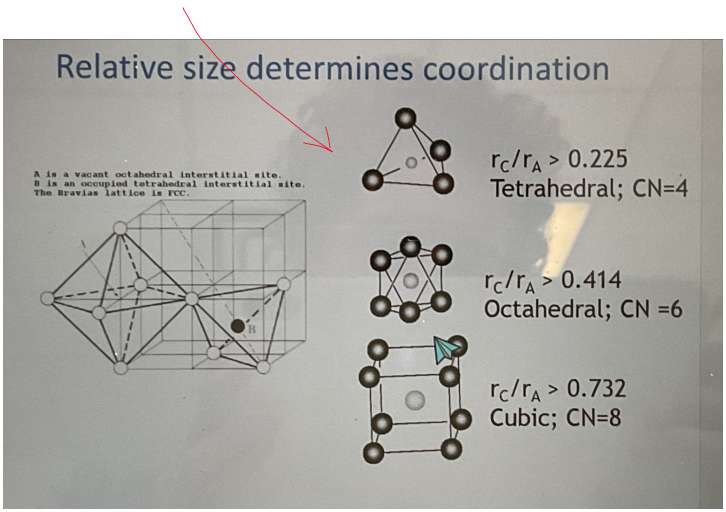
What can the ratio of atomic radii of cations to anions tell you about binary structures
It can tell you the CN and thus the structure
(probably not on exam)
[NaCl]
[FCC] + octahedral (edge sharing)
![<p>[FCC] + octahedral (edge sharing)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8e99bfa7-ff4a-44ae-ba5a-f35239a6bba3.png)
[diamond] & [zincblend]
[FCC] + ½ tetrahedral (corner sharing)
Note: for diamond r = asqr(3)/4
![<p>[FCC] + ½ tetrahedral (corner sharing)</p><p>Note: for diamond r = asqr(3)/4</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/49b70227-ed75-4404-9fbe-a011a234d04e.png)
[flourite] , [antifluorite]
[FCC] + tetrahedral (edge sharing)
![<p>[FCC] + tetrahedral (edge sharing) </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/df54ee4c-0457-46e8-9e3b-08c902f965db.png)
[nickel arsenide]
[HCP] + ½ octahedral sites (corner sharing)
![<p>[HCP] + ½ octahedral sites (corner sharing)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/feb7f111-dd8c-4a37-b320-67f8c087999c.png)
[wurtzite]
[HCP] + ½ tetrahedral (corner sharing)
![<p>[HCP] + ½ tetrahedral (corner sharing)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cfb1feb9-d13c-4af2-a845-22d8c45535b5.png)
[rutile]
[HCP] + ½ octehedral sites (edge sharing)
![<p>[HCP] + ½ octehedral sites (edge sharing)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cae72060-931d-4043-b5bb-859b1447842d.png)
[corundum]
[HCP] + 2/3 octahedral sites (face sharing)
![<p>[HCP] + <sup>2</sup>/<sub>3</sub> octahedral sites (face sharing) </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b763b006-1e85-4377-8f04-bad7c89340ea.png)
What are Pauling’s Rules
