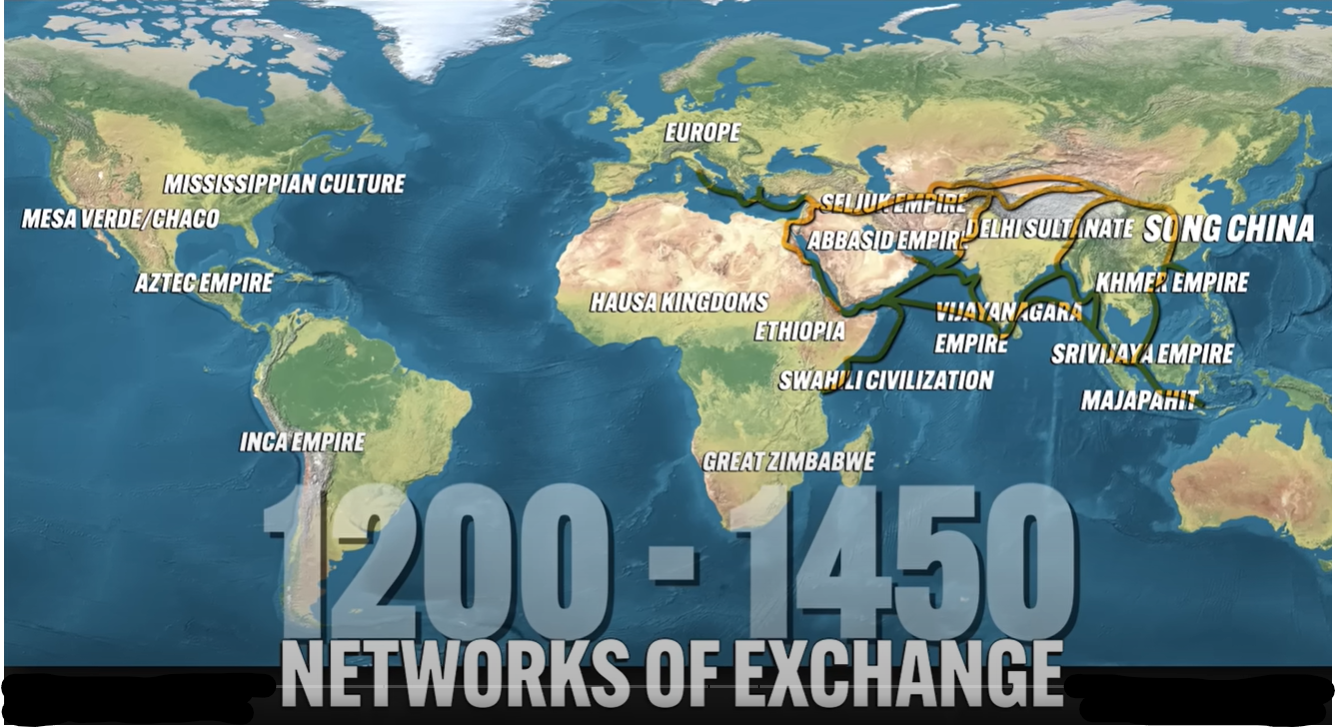
UNIT 2: Networks of Exchange c. 1200 - 1450
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Unit 2
Networks of Exchange
c. 1200 - 1450
how various states are connected to one another
Networks of Exchange
merchants and traders carried goods for sale across these routes
religion, culture, and language were also transferred
Major Networks of Exchange
Silk Roads + Indian Ocean Network + Trans-Saharan Trade
during c. 1200 - 1450: these networks increased in geographic scale
Silk Road
stretched across Eurasia (Europe + Asia)
powerful trading cities emerged because of their location along these routes: Samarkand + Kashgar
Luxury Goods:
Chinese silk and porcelain
Innovations:
transportation:
Caravanserai: provided safety and shelter along the route to travelers
significant place for the spreading of religion and technology
commercial:
Money Economies: paper money to exchange goods
Credit: Banking Houses (the transfer of money and goods)
Indian Ocean
Transportation:
Monsoon Winds: predictable wind patterns that allowed for more efficient travel (utilizing sail boats)
Magnetic Compass (direction)
Ship Designs: Chinese “Junk” (large cargo capacity)
Luxury Goods:
textiles
spices
bulk goods (ships can carry heavier cargo)
Indian Ocean: Swahili City States
Swahili City States: a collection of independent city-states along Africa’s EAST coast
gold, ivory, enslaved people
Islamic: larger trading in Dar-Al Islam
Swahili language emerged (native Bantu + Arabic)
Diasporic Communities
settlement of ethnic people in another location (separate from their homeland)
(Indian Ocean: e.g
Arab and Persian communities established in East Africa)
Trans-Saharan Route
Transportation Technology:
Camel Saddles: larger cargo and more suitable for long term travel
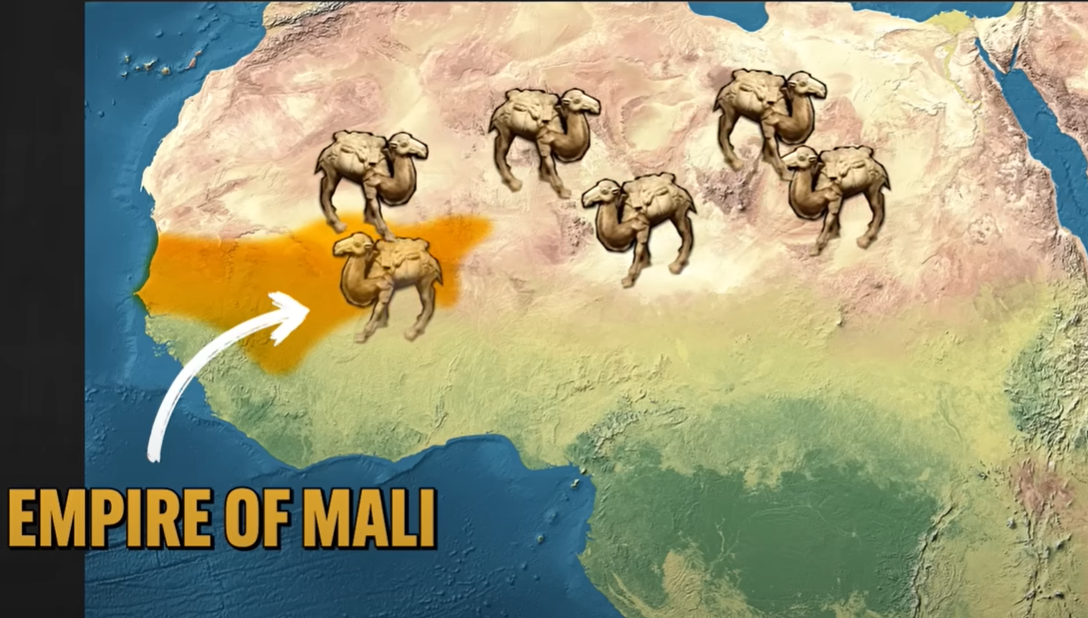
Empire of Mali: Trans-Saharan Network
gained extreme prosperity through trade (gold and taxing of merchants)
Mansa Musa: monopolized trade and facilitated growth

Effects of Connectivity through Trade
Cultural:
spread of religions and beliefs:
Buddhism originated in South Asia or India but got transferred into China
House of Wisdom:
Greek and Roman scripts were translated into Arabic
gunpowder: explosive weaponry (originated in China)
Environmental:
crops: champa rice
disease: BUBONIC PLAGUE:
Created in China due to rats and declined large amounts of the population


Mongol Empire
established the largest land-based empire of all time
based on the SILK ROAD
replaced powerful empires across Eurasia (e.g: Song Dynasty + Abbasid Empire fell to the Mongols)
Four Khanates: maintain unity and effectively govern the large empire
increased the safety of merchants along the Silk Road
Pax Mongolica: the period of relative peace and stability that existed within the vast Mongol Empire