Geo-physical science- projectile motion
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Projectile
any object that moves the air or through space under the influence of gravity
Example of a curved path of projectile (parabola)
a stone thrown horizontally curves downward due to gravity
Projectile curves are a result of what two components?
constant motion horizontally
accelerated motion vertically
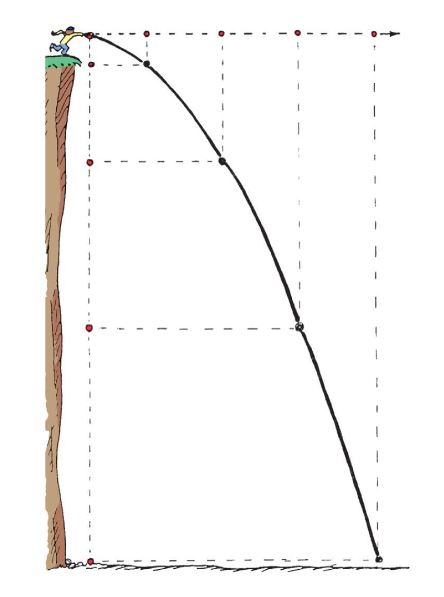
Projectile motion is a combination of a _______ component and a ________ component.
horizontal, vertical

In a parabola, only the ________velocity component changes with time. The _________ component remains constant.
vertical, horizontal
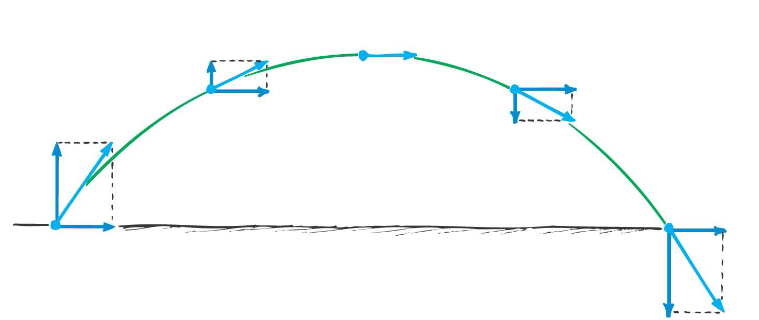

The velocity of a typical projectile can be represented by horizontal and vertical components. Assuming negligible air resistance, the horizontal component along the path of the projectile…
remains the same

When no air resistance acts on a fast-moving baseball, its acceleration is…
downward, g
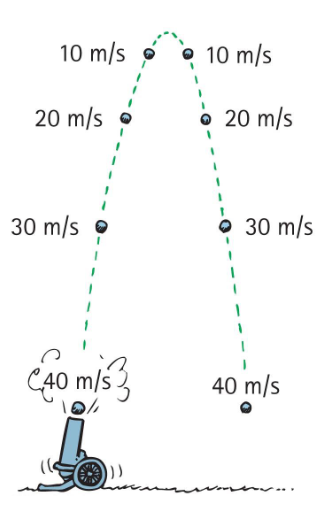
Projectile altitude and range- for equal launching speeds, the same range is obtained from two different projection angles — a pair that add up to ___.
90°
Example: Same range occurs for a 75° launch and a ___ launch of the same initial.
15°
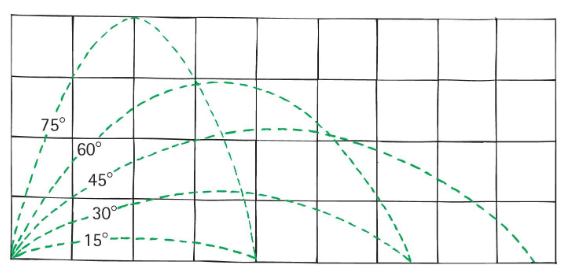
A ball tossed at an angle of 30° with the horizontal will go as far downrange as one tossed at the same speed at an angle of
60°
With air resistance, both range and altitude on projectiles are ______
decreased
Without air resistance, the speed lost on projectiles going up is __________ as the speed gained while coming down
the same
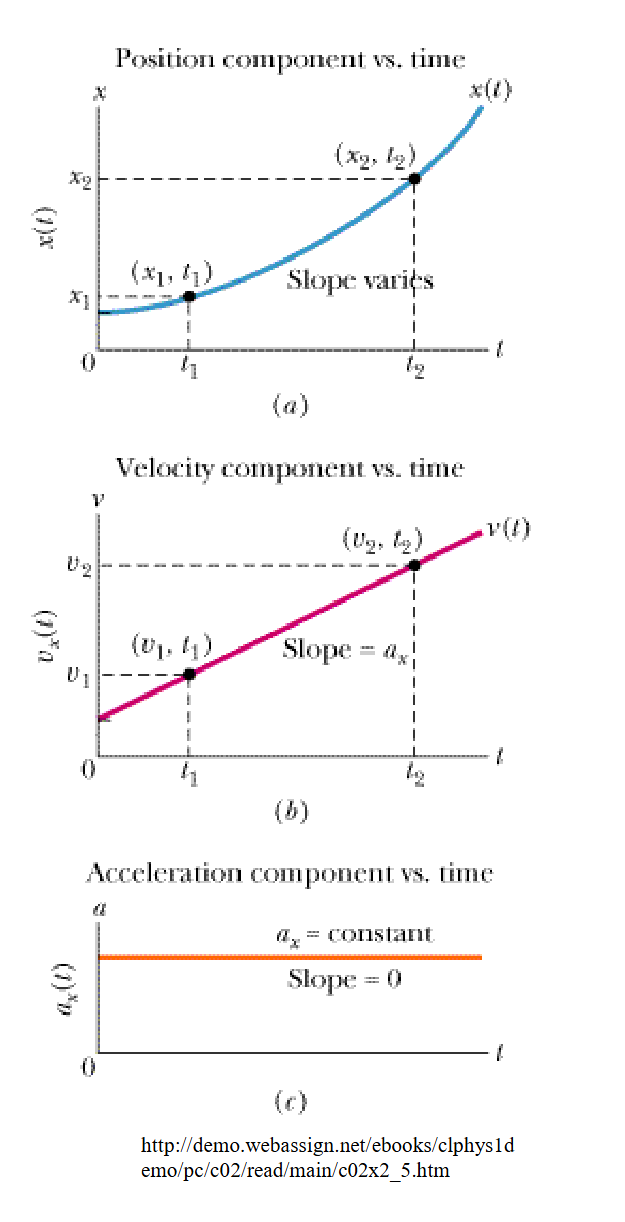
Comparison of change of position, velocity, and acceleration
(see picture)
Example of predicting position as a function of time
emergency plane landing
Equation for free fall (?)
Equals 9.8 m/s2. It is only under the influence of gravity.
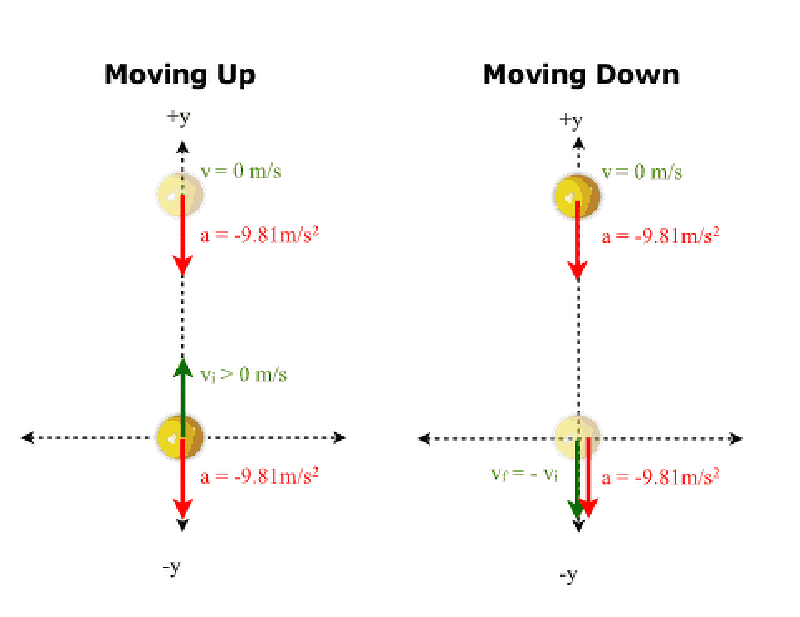
In our lab experiment, then the motion sensor was pointing downward, what did the plotted computer data show?
displacement, velocity, and acceleration
Projectile motion
Motion under the influence of gravity near Earth’s surface has essentially constant acceleration whose magnitude is g=9.8m/s2, and whose direction is downward.
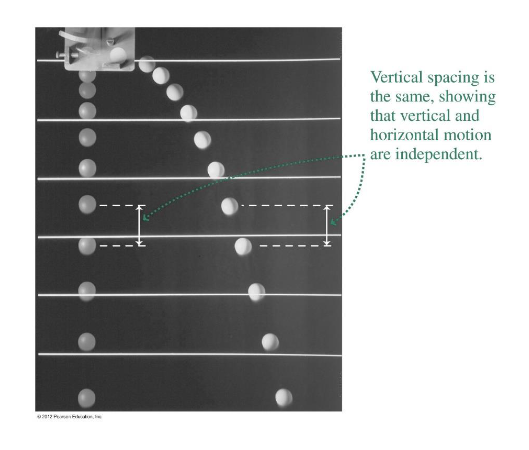
Horizontal and vertical motions are _______
independent
Equations for projectile motion, in a coordinate system with y axis vertically upward.
(see picture)
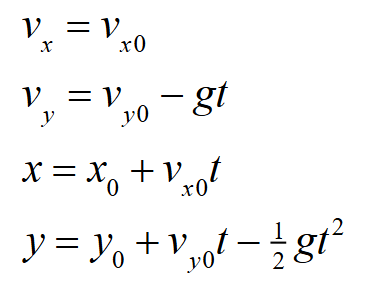
___ is like our falling projectile. But we have a ___ world (like going from a photograph in 2-D to a sculpture in 3-D)
2-D, 3-D
Vectors
show direction and magnitude (or quantity)
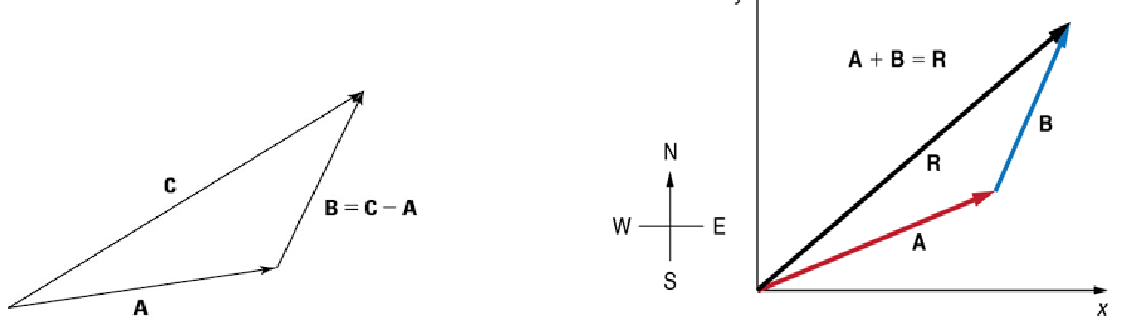
We can add, subtract, or multiply _______
vectors
Any change in velocity is an __________ (again, NOT just speeding up)
acceleration
A car driving around a corner … even at the same _____ … is acceleration.
speed
What is circular motion?
One of the most important types of motion in the universe. Acceleration motion. Uniform circular motion is accelerated, even if the same speed, because it is changing direction.
Circular motion is…
accelerated motion
Examples of circular motion
Car wheel turning. Both wheel and car turning, therefore two accelerations.
Airplane turning
Hands on a clock
Earth orbiting the sun
Bicycle wheels turning (and pedals)
Equation for circular motion
a = ∆v / ∆t