REFLEX PHYSIOLOGY & GENERAL SENSES
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Reflex
automatic response to a stimulus
Maintain balance and posture, Protect us from danger or injury, Carry out routine activities like chewing or walking
most neural reflexes are designed to
Reflex Arc
1.Receptor
2.Sensory Relay
3.Integration
4.Motor Command Relay
5.Effector
1st step of reflex arc
receptor
2nd step of reflex arc
sensory relay
3rd step of reflex arc
integration
4th step of reflex arc
motor command relay
5th step of reflex arc
effector
monosynaptic
fast and integrated in the spinal cord
polysynaptic
contain at least one interneuron, most reflexes
knee jerk
example of monosynaptic
monosynaptic v polysynaptic
based on the number of neurons involved
somatic
voluntary and involves skeletal muscle
autonomic
involuntary and involves smooth muscles, glands, or visceral organs
Acquired Reflexes
learned through experience, ex driving walking and skiing
general stimuli
temperature, pH, pressure
special stimuli
vision, hearing, equilibrium, taste, smell
Exteroceptors
monitor external conditions, (heat, cold, touch, pain, pressure)
Interoceptors
monitor internal conditions (chemoreceptors, visceral stretch receptors, proprioceptors)
Chemoreceptors
interoceptor that monitors blood PH
Visceral Stretch Receptors
interoceptor thats a distension of visceral organs
Proprioceptors
interoceptor that deals with postural information
TWO broad classes of receptors
general and special
Free (naked) Nerve Endings
Dendrites terminate in epidermis/dermis junction of skin and mucosal epithelium, Detect pain (extreme temperature)
Merkel Cells
associated with free nerve endings, located in the stratum germinitivum (basale), detect light touch/ sustained pressure
Encapsulated Receptors
Ex. Meissner’s Corpuscles, Pacinian Corpuscle
Meissner’s Corpuscle
type of encapsulated receptor, more superficial, detects light touch
Pacinian Corpuscle
type of encapsulated receptor, more deep, detects forceful pressure, vibration
Free nerve endings
—•terminate basically at the surface of skin or mucosa and detect pain (more superficial and detect pain)
merkel cells
—reside at the deepest layer of the epidermis and detect touch (deeper and detect touch)
Meissner’s Corpuscles
superficial
Pacinian Corpuscles
deep (since they are deeper it takes more force to activate)
1
merkel disk
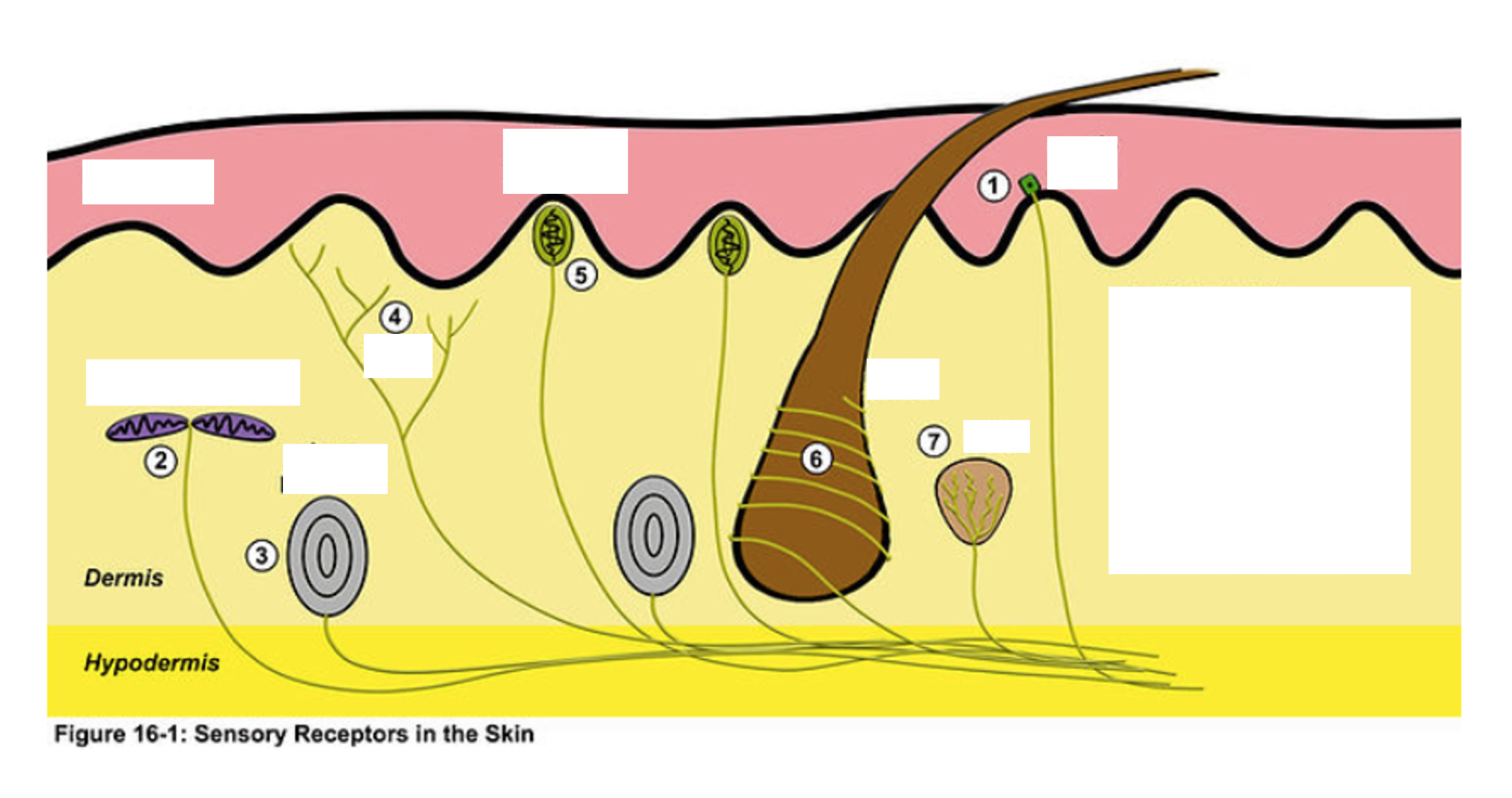
2
ruffini corpuscle
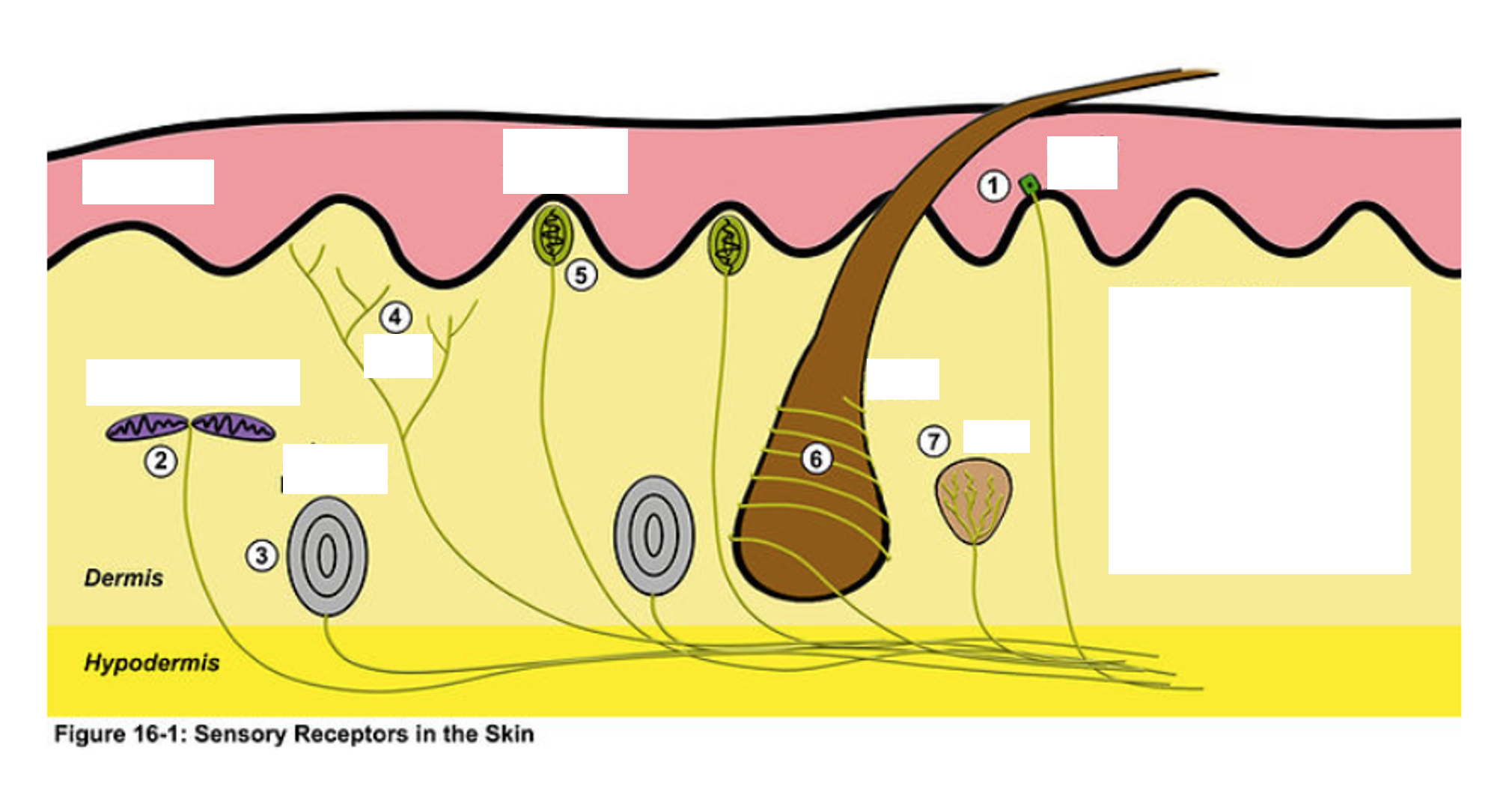
3
Pacinian Corpuscle
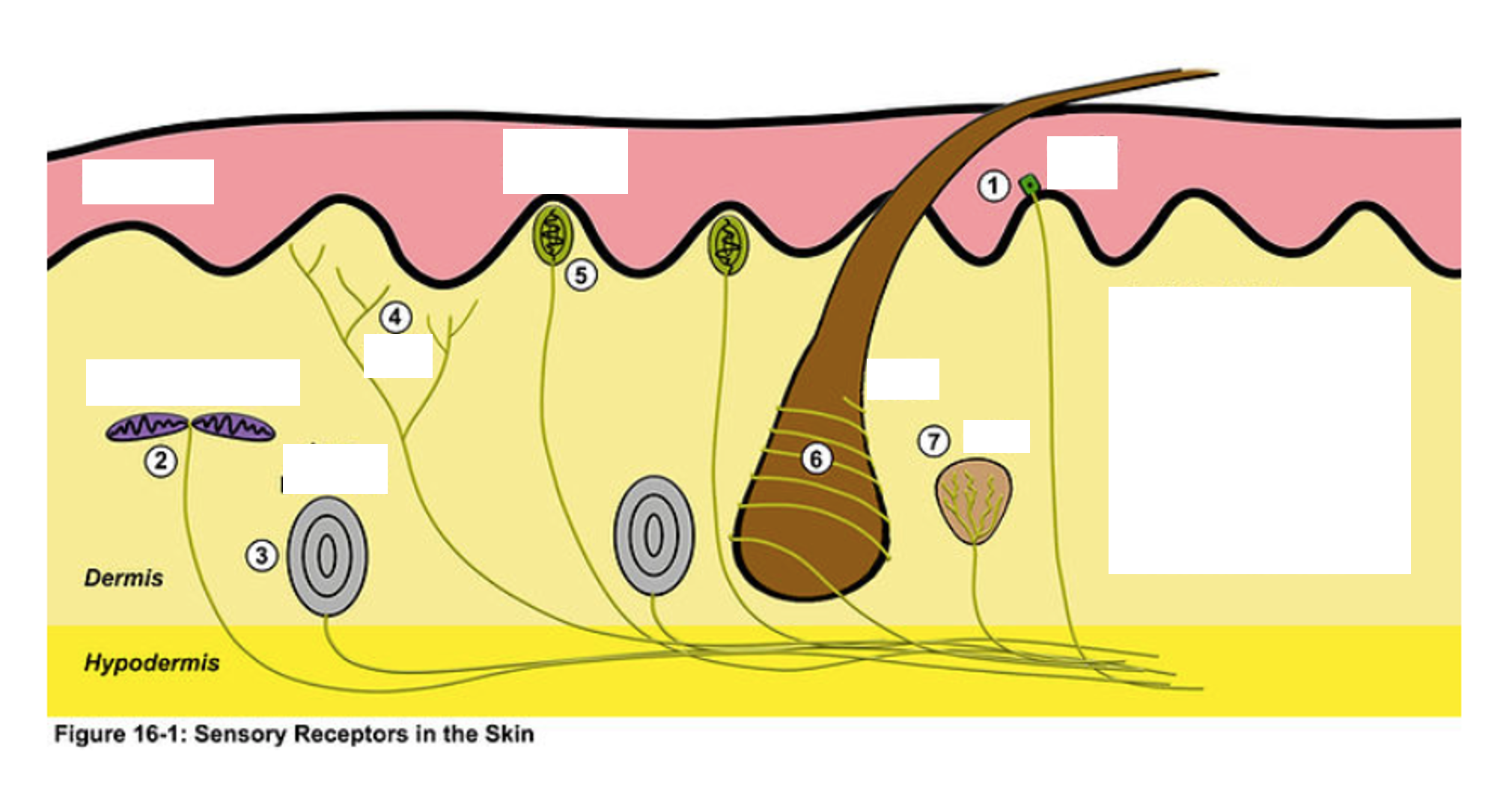
4
Nociceptor (free nerve endings)
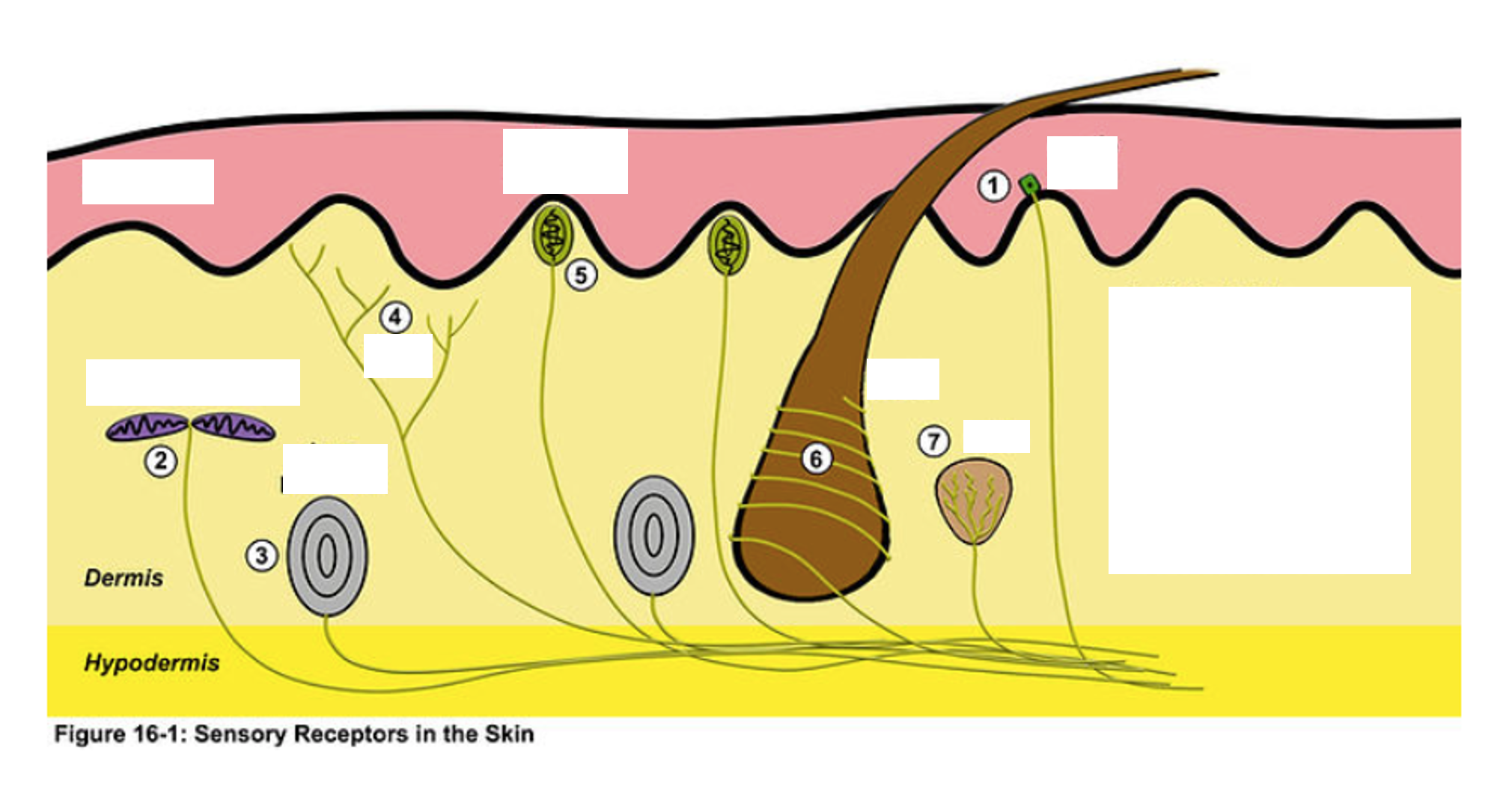
5
Meissner’s corpuscle
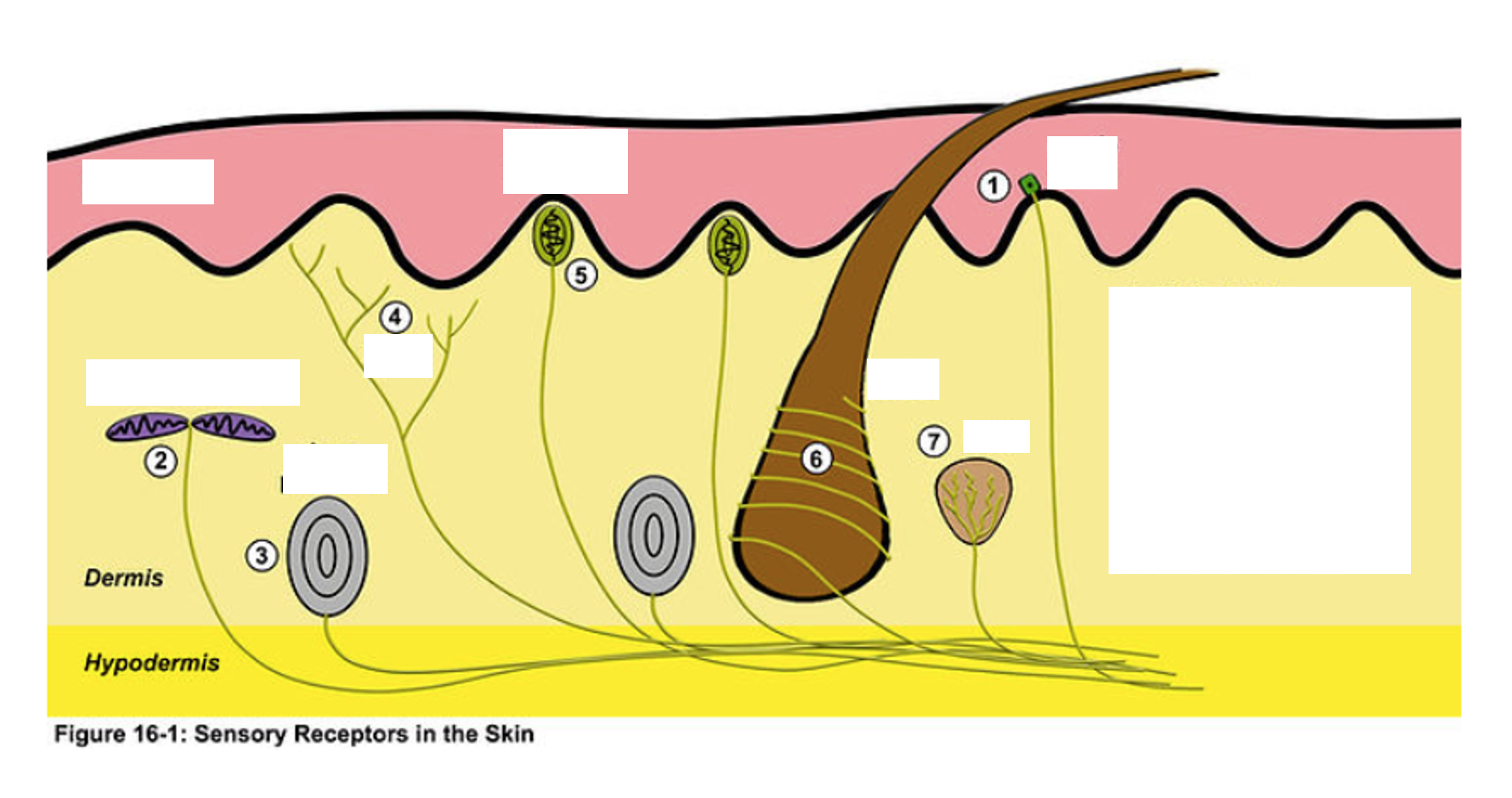
6
Root Hair Plexus
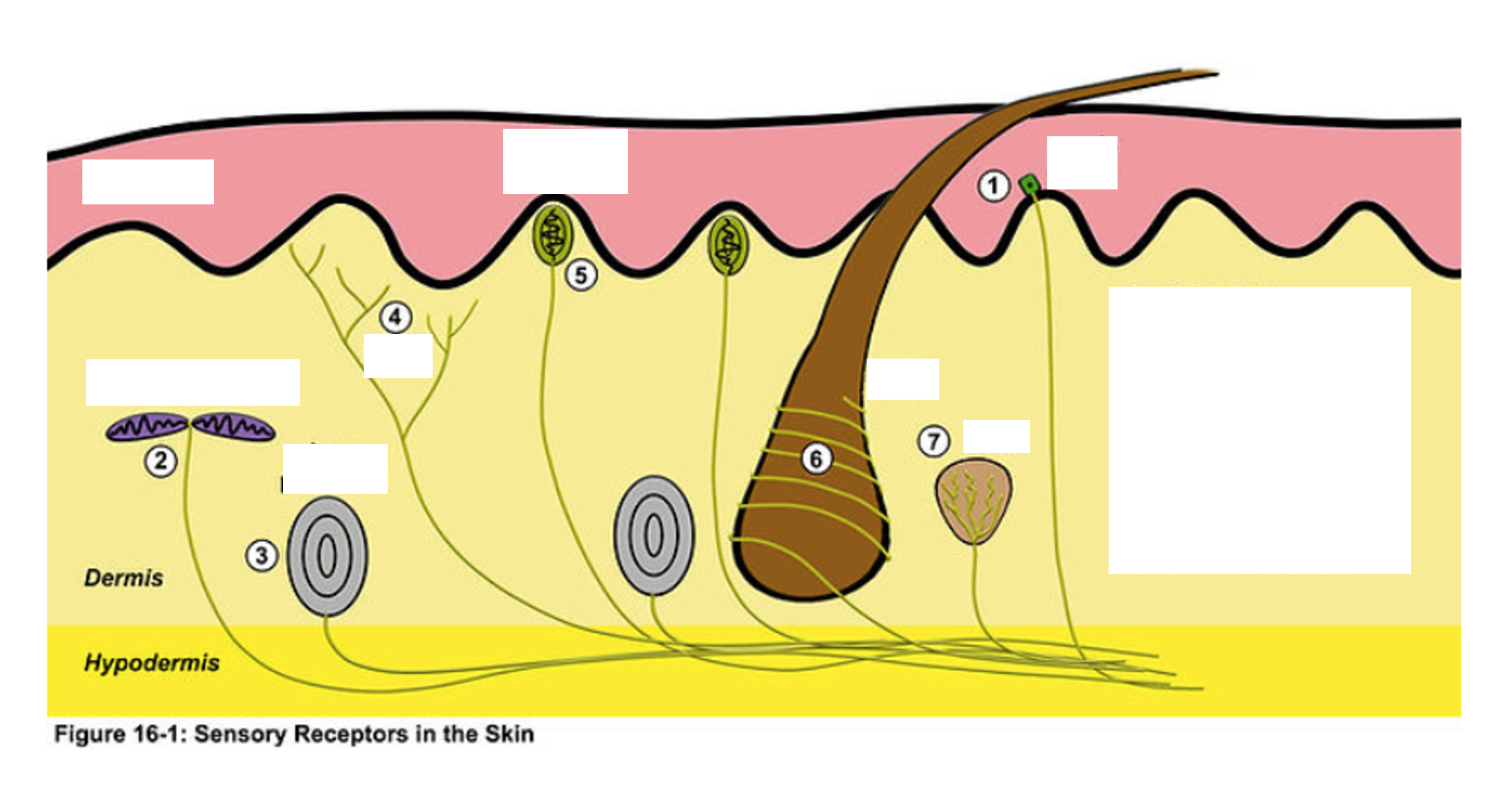
7
Krause End Bulb
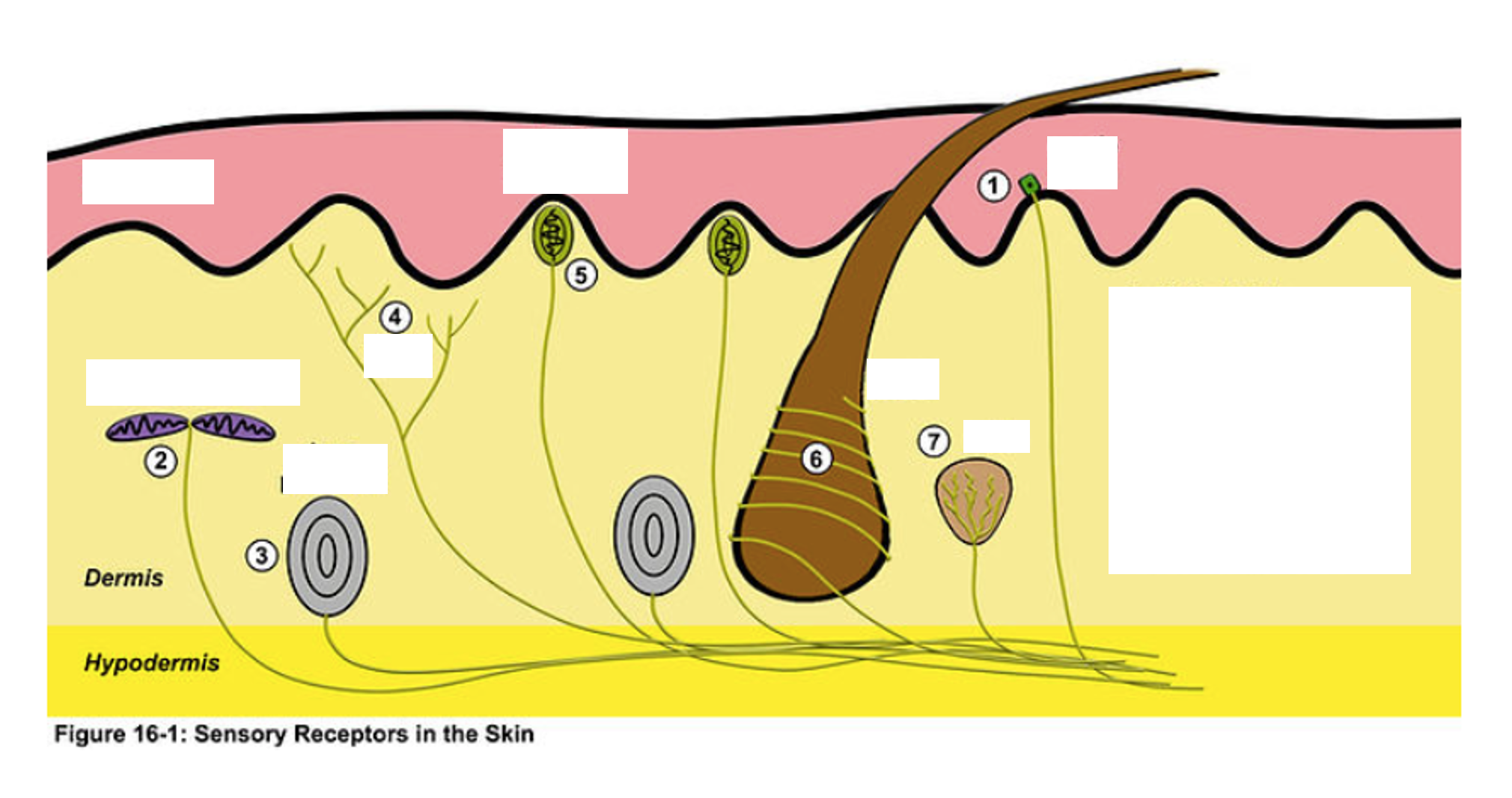
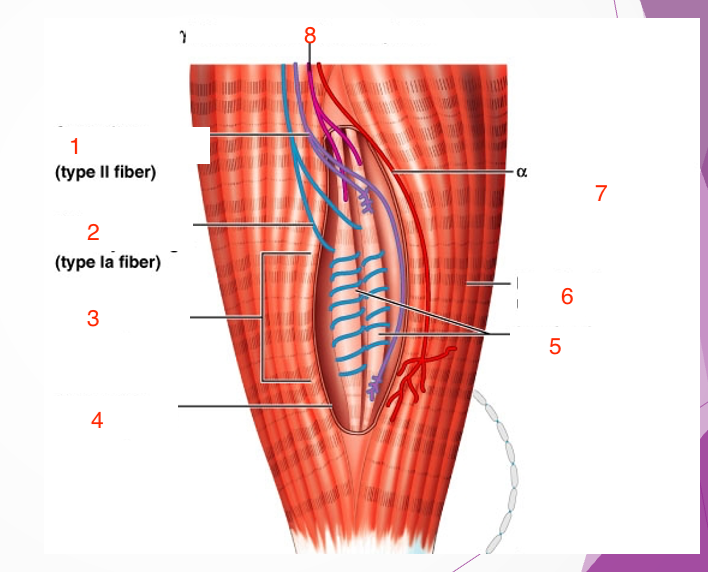
Muscle Spindle
uMonitor muscle position
uEnsure muscles are not overstretched
muscle spindle
Purpose of — is to monitor muscle position based on its state of stretch (prevents overstretching)
Intrafusal & Extrafusal Fibers
TWO types of muscle fibers in muscle spindle
intrafusal fibers
—-(proprioceptors): have a contractile and non-contractile region
extrafusal fibers
have contractile regions
intrafusal fibers
—located within extrafusal skeletal muscle fibers
sensory region
Intrafusal fiber innervated by sensory neuron dendrites wrapped around —
a-motor neurons
—innervate contractile region of extrafusal fibers
y-motor neurons
innervate contractile region of intrafusal fiber
sensory neurons
—sends continual impulses to CNS which sends signals back to extrafusal fibers via α-motor neurons
spindle is compressed
Muscle is contracted and —: frequency slows
fewer impulses
—sent to α-motor neurons and skeletal muscles relax
spindle is stretched
Muscle is extended and —: frequency increases
more impulses
—sent to α-motor neurons and skeletal muscles contract
willful muscle contraction
Brain sends impulse to γ-motor neurons in order to contract the intrafusal fibers which relieves compression of spindle
spindle length
determines frequency that alpha-motor neuron fires
intrafusal, extrafusal
We can willfully contract — fibers to reduce compression on spindle when we want to contract the — fibers
trandsucers
receptors are:
action potentials
the nervous system only speaks the “language” of ——- so we need to convert stimuli into ——.
Destination in the brain
How do we distinguish between action potentials?
Receptive fields
How do we distinguish stimuli?
2 point discrimination test
Ability for a person to detect two distinct points of contact on the skin as separate stimuli
Transducers
Convert stimuli to action potentials
destination
Action potentials are distinguished as unique by their ——- in the brain
action potentials
Different regions of the brain interpret ——- differently (pain vs. touch)
receptor fields
The smaller and denser the fields, the more sensitive (Hands, feet, face, genitals)
adaptation
Desensitization to constant stimuli is called
1
Secondary sensory endings (type 2 fiber)
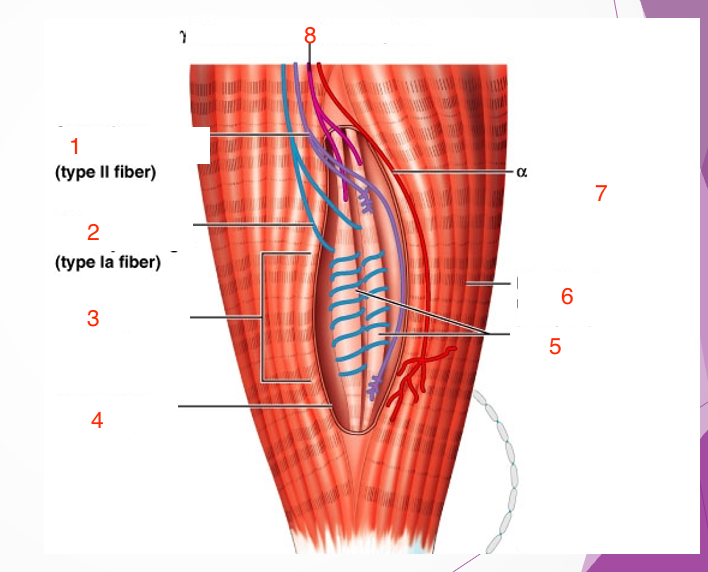
2
Primary sensory endings (type 1a fiber)
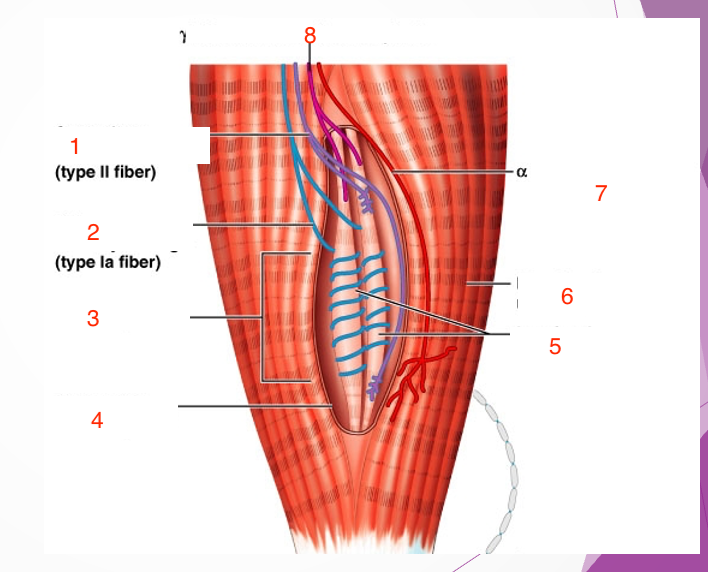
3
muscle spindle
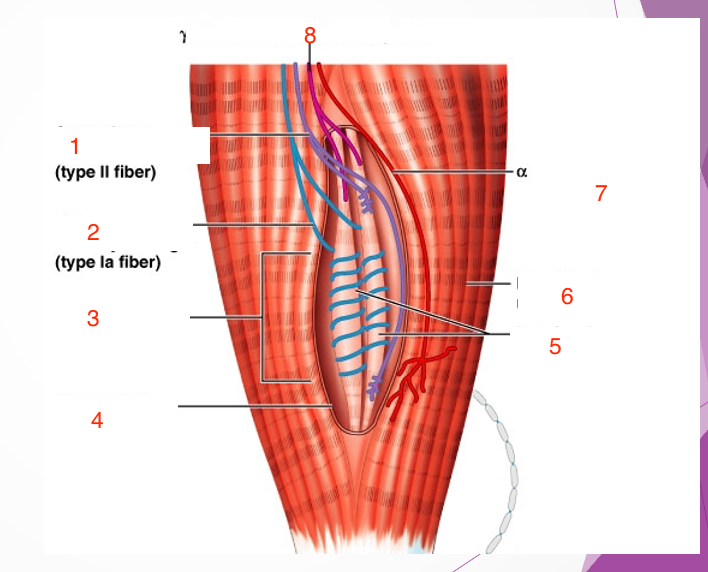
4
connective tissue capsule
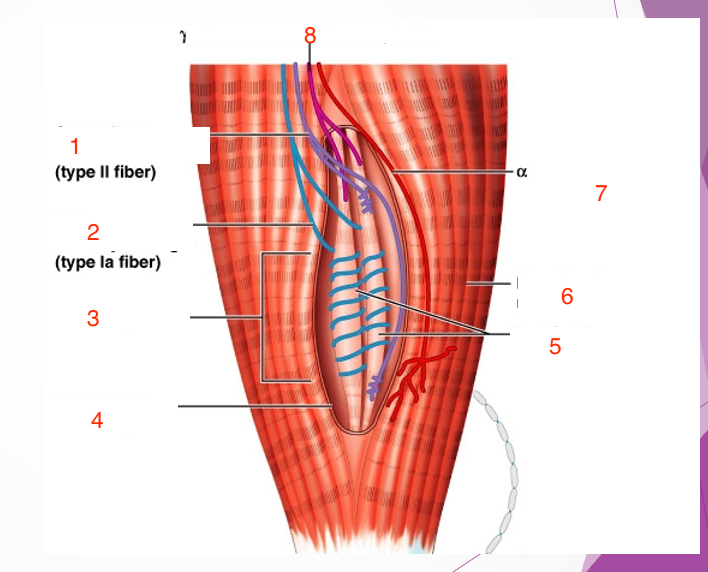
5
intrafusal muscle fiber
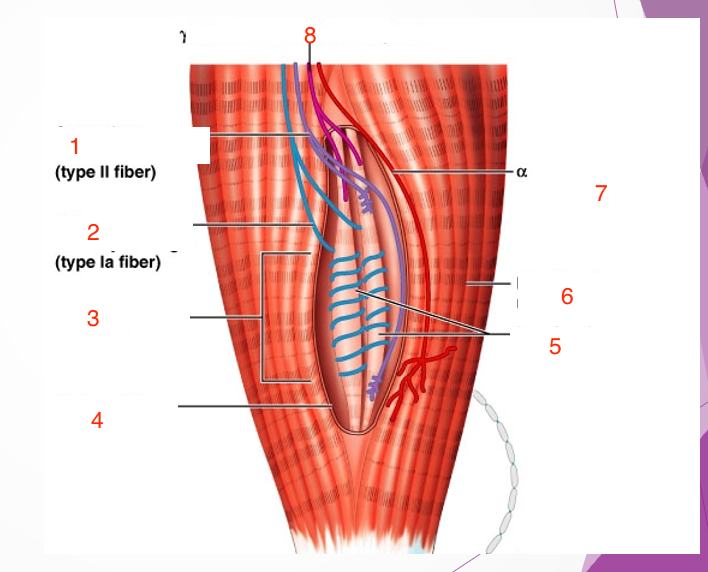
6
extrafusal muscle fiber
7
efferent motor fiber to extrafusal muscle fibers

8
efferent motor fiber to spindle