4.3 - Genetic diversity can arise as a result of mutation or during meiosis
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is a mutation?
An alteration to the DNA base sequence.
Often arise spontaneously during DNA
replication.
Why might a mutation not lead to
change in the amino acid sequence?
● Genetic code is degenerate so
mutation may end up coding for same
amino acid as the original triplet.
● Mutation may occur in intron.
What is a substitution mutation?
When a nucleotide in the DNA sequence
is replaced by another. This is more
likely to be a quiet mutation, meaning no
change occurs in the amino acid
sequence.
What is a deletion mutation?
When a nucleotide in the DNA sequence
is lost. This is more likely to be harmful
and significant, as it leads to a frame
shift which means the entire amino acid
sequence will be different.
What is a mutagenic agent? Give
examples of this.
Factors that increase the rate of gene
mutation. X-rays, UV light, gamma rays,
certain chemicals e.g. in alcohol and
tobacco.
What is a polyploidy chromosome
mutation?
Where an individual has three or more
sets of chromosomes instead of two.
What is chromosome non-disjunction?
When chromosomes fail to separate
correctly in meiosis, resulting in gametes
with one more or less chromosome than
normal.
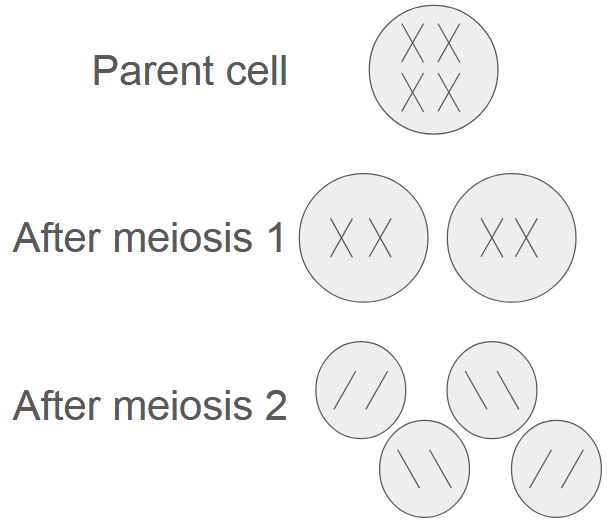
What is meiosis?
A form of cell division that produces four
genetically different haploid cells (cells
with half the number of chromosomes
found in the parent cell) known as
gametes.
How does meiosis differ from mitosis?
● Meiosis produces four genetically different
cells with half the number of chromosomes
as the parent cells.
● Mitosis produces two genetically identical
cells with the same number of
chromosomes as the parent cells.
What happens during meiosis Ⅰ?
1. Homologous chromosomes pair to form bivalents.
2. Crossing over (exchange of sections of genetic
material) occurs at chiasmata.
3. Cell divides into two. Homologous chromosomes
separate randomly. Each cell contains either
maternal or paternal copy.
What happens during meiosis Ⅱ?
1. Independent segregation of sister
chromatids.
2. Each cell divides again, producing 4
haploid cells.
Draw diagrams to show cells after each
stage of meiosis.
In which two ways does meiosis produce
genetic variation?
1. Crossing over during meiosis Ⅰ
2. Independent assortment (random
segregation) of homologous
chromosomes & sister chromatids
Result in new combinations of alleles.