Lecture 4 - Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
True
True or False: A physician can ultrasound anything (even eyeballs) if they know anatomy.
During ultrasonography, high-frequency sound waves are produced by a transducer. These waves either penetrate the tissue or don't. If they penetrate the tissue, they return (bounce back) or fail to return differently based on the type of tissue. Crystals in the transducer convert sound waves to an electric current, which is converted to an image in the ultrasound machine.
During ultrasonography, h_____-f______ s_______ waves are produced by a t_________. These waves either p________ the tissue or don't. If they p___________ the tissue, they r______ (bounce back) or fail to r_______ differently based on the t______ of tissue. C_______ in the t__________ convert s_______ waves to an e________ current, which is converted to an i_________ in the ultrasound machine.
False. Ultrasound waves do not go through air, so an ultrasound of a non-fluid-filled lung will not be helpful.
True or False: Ultrasounding a healthy lung is a superb use of your client's money.
When the sound waves emitted from the transducer penetrate pure fluid, they do not return to the transducer. If they hit something that is not pure fluid, they return and translate to differing shades of greyscale.
When the sound waves emitted from the transducer penetrate p_____ f_______, they do not return to the transducer. If they hit something that is not p_____ f______, they return and translate to differing s______ of g________.
The greyscale image produced from ultrasonography is dependent on how dense (lacking in water) the tissue is.
The greyscale image produced from ultrasonography is dependent on how d______ (lacking in w_______) the tissue is.
All sound waves bounced back to the machine (extremely dense material)
If an ultrasound image is white, what does that mean for the sound waves and density of the material?
Some sound waves bounced back (dense material)
If an ultrasound image is gray, what does that mean for the sound waves and density of the material?
All sound waves penetrated completely and did not bounce back (pure fluid material)
If an ultrasound image is black, what does that mean for the sound waves and density of the material?
Black
What does anechoic mean in ultrasonograph-ese?
Lighter
What does hyperechoic mean in ultrasonograph-ese?
Darker
What does hypoechoic mean in ultrasonograph-ese?
Same
What does isoechoic mean in ultrasonograph-ese?
Echogenicity of the tissue
What are you describing when using words like hyper-, hypo- and anechoic?
Bone or gas organ boundaries
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
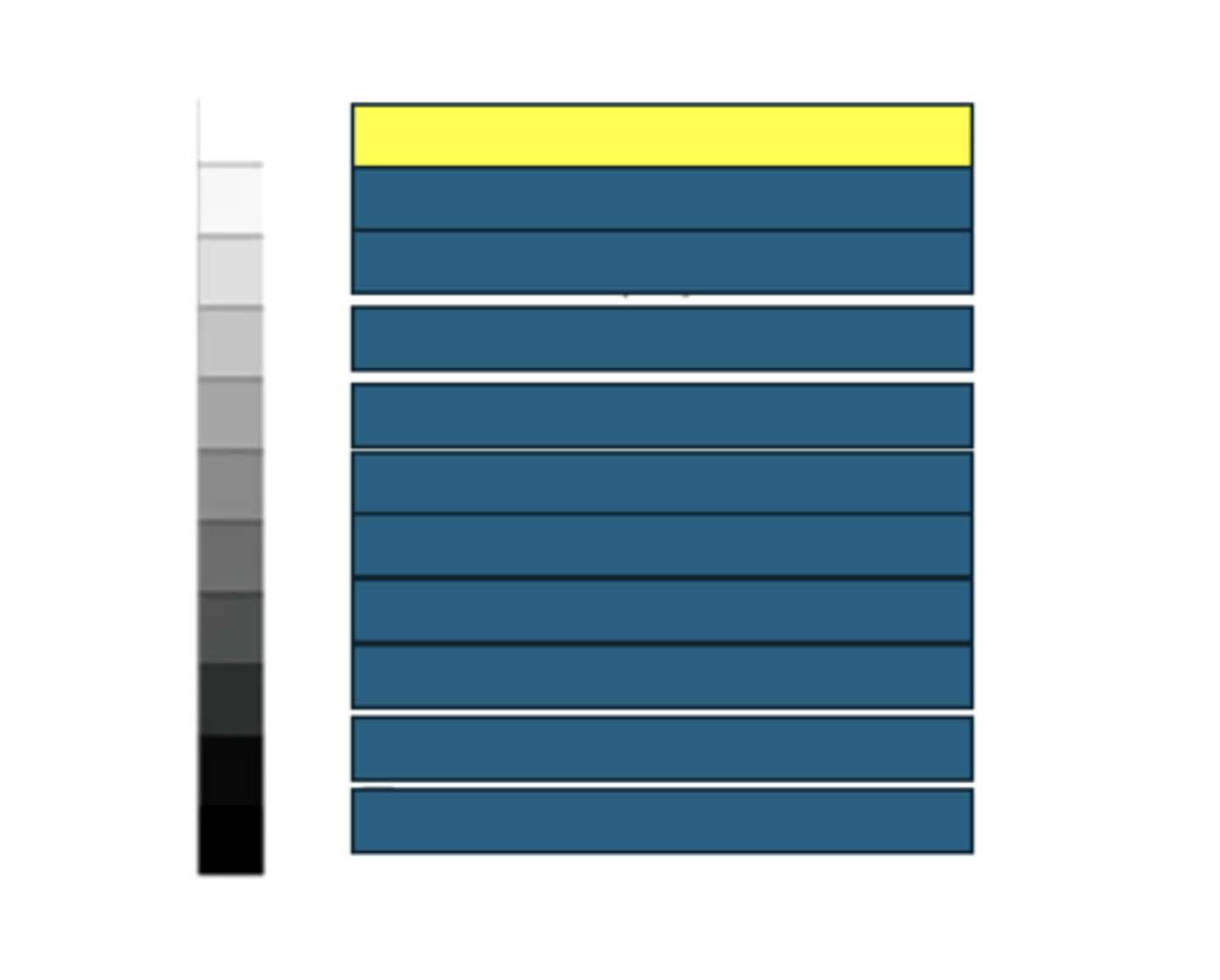

Structural fat and vessel walls
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
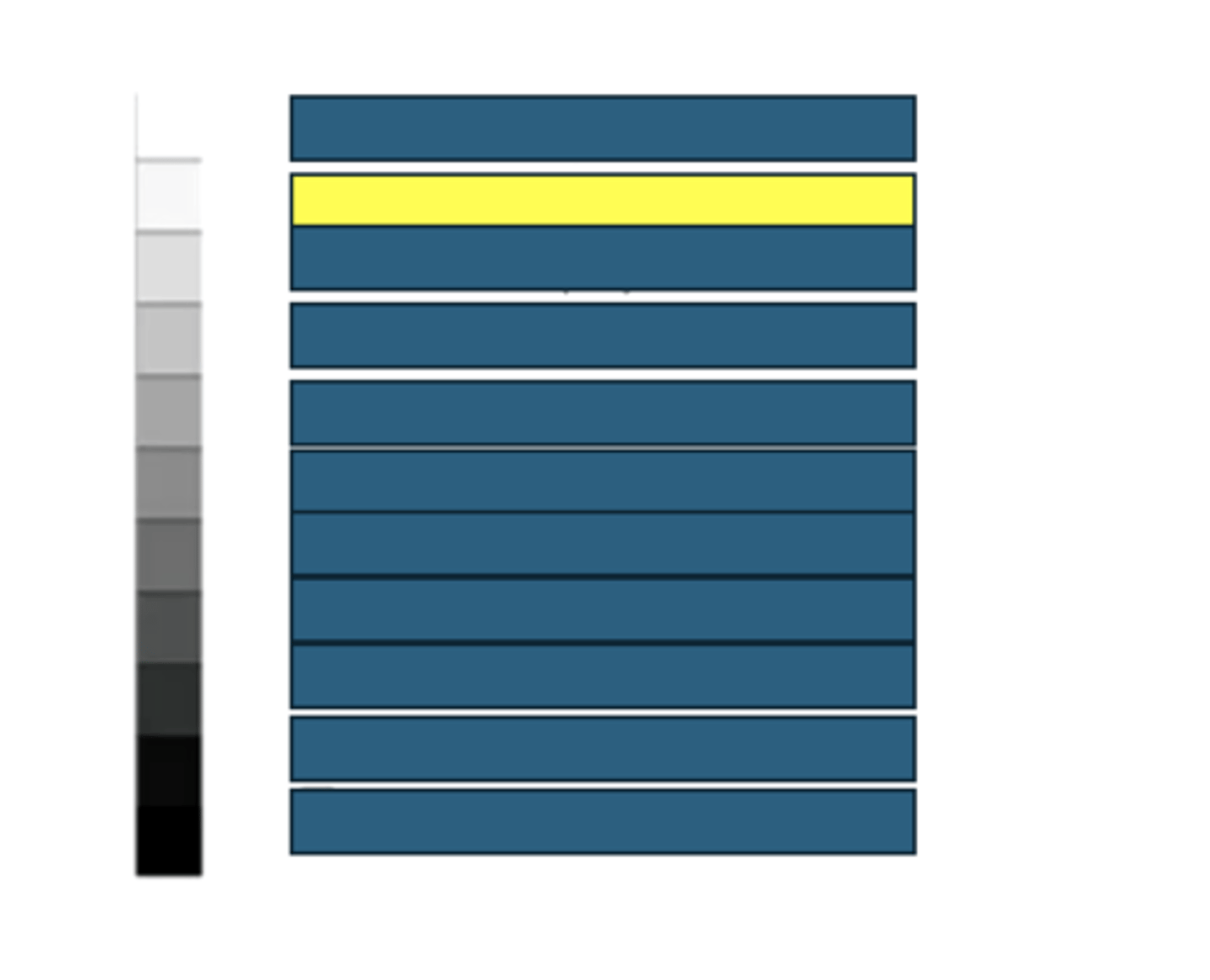
Renal sinus fat
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
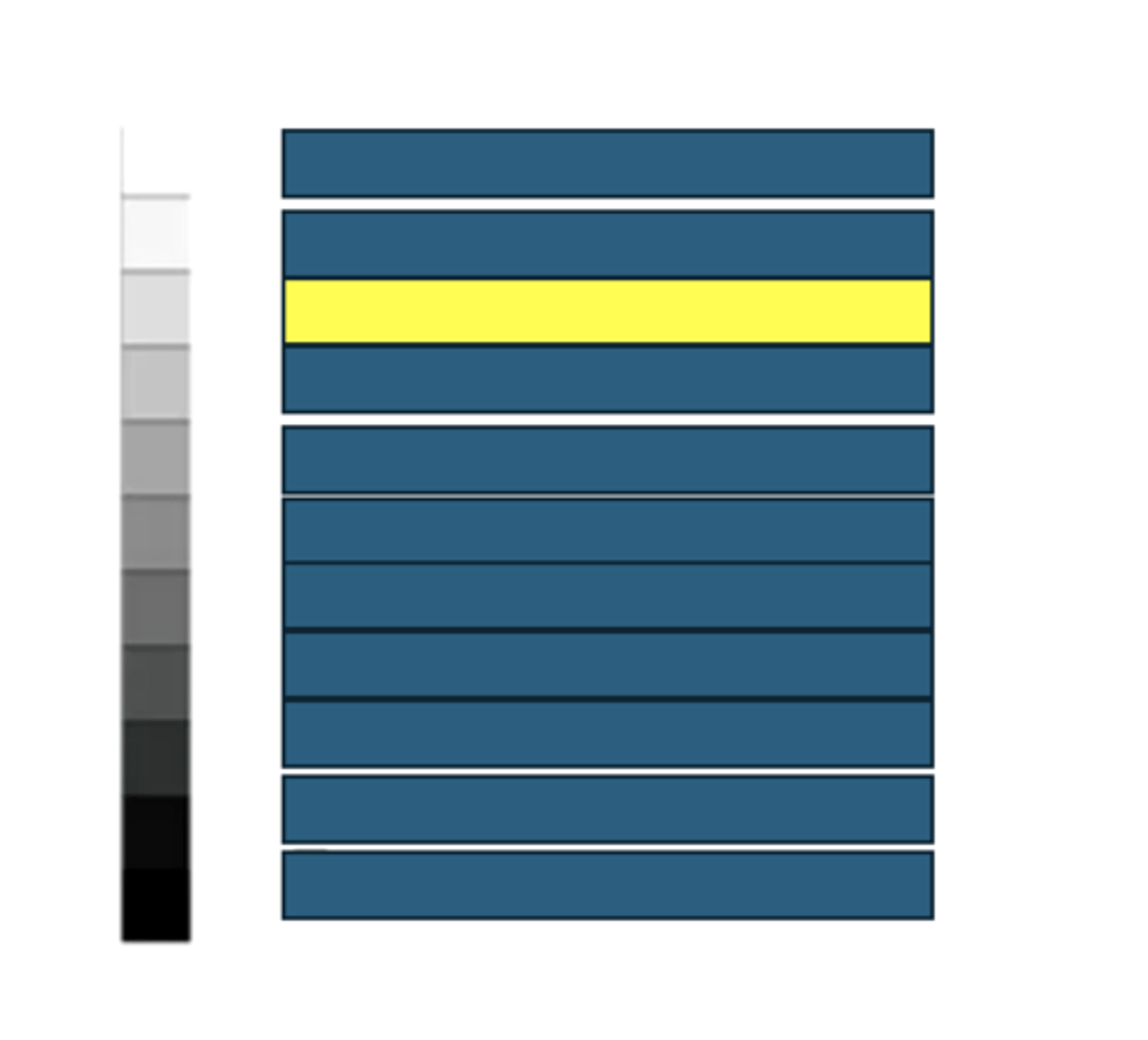
Prostate
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
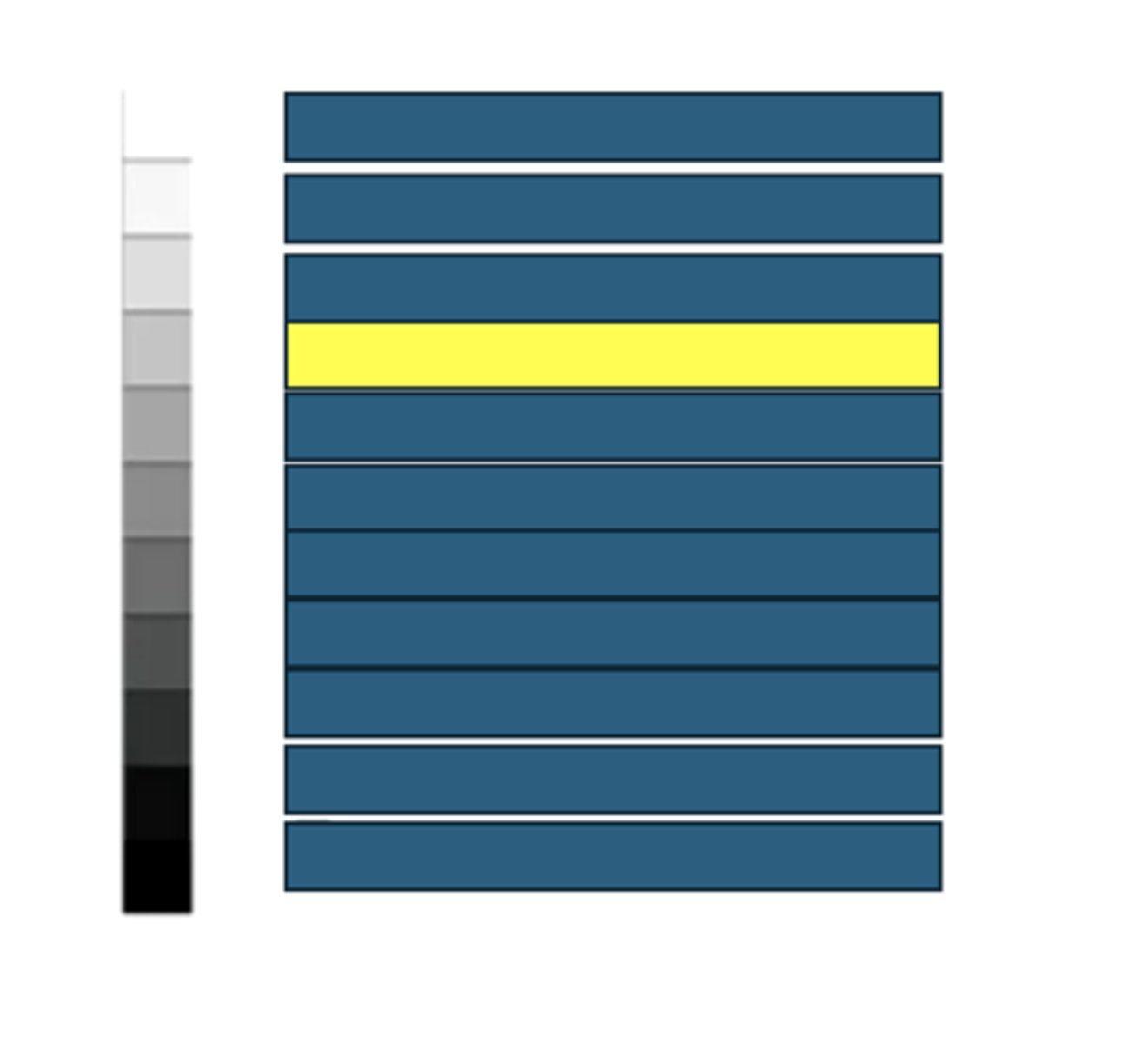
Spleen
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
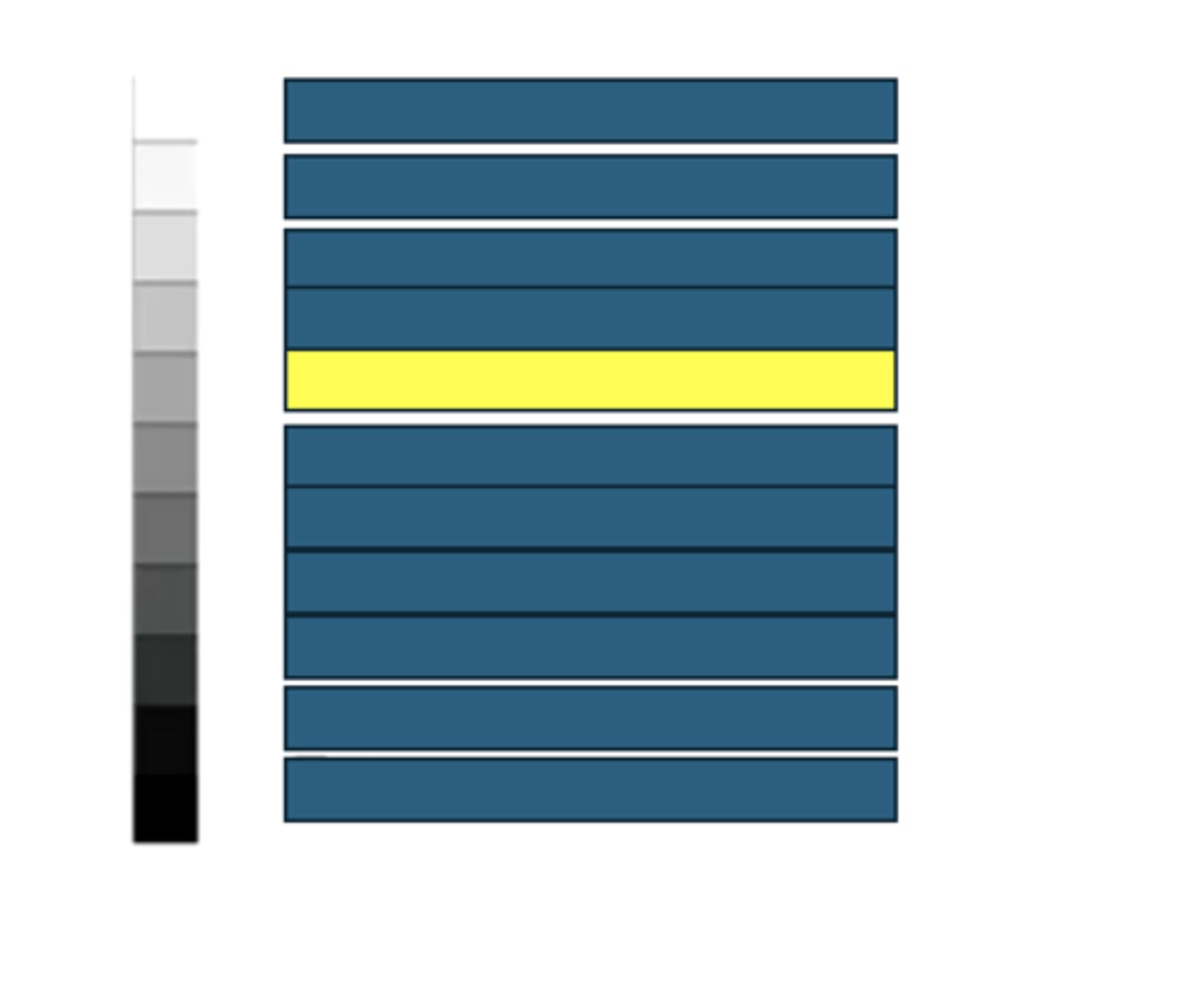
Storage fat
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
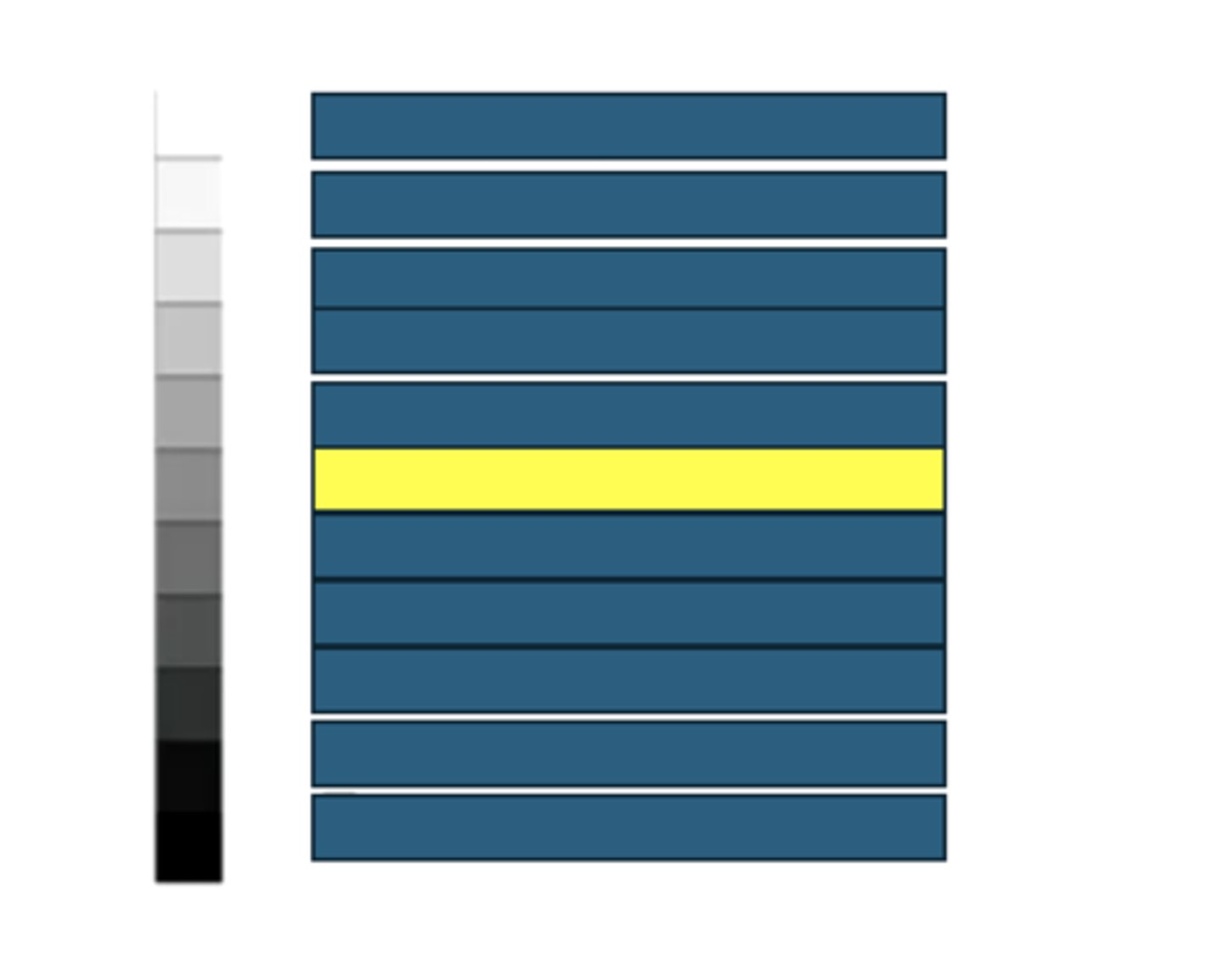
Liver
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
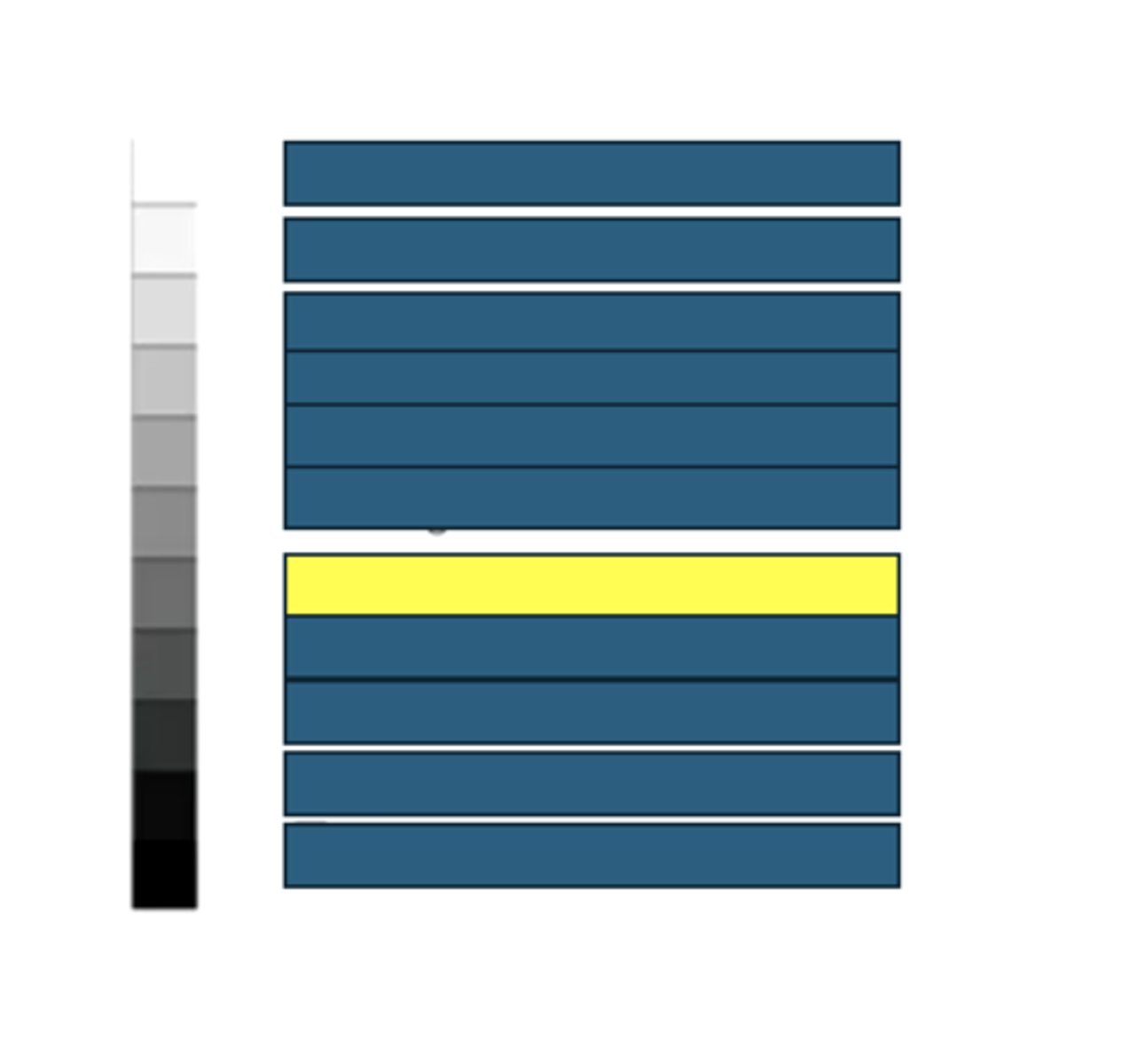

Renal cortex
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
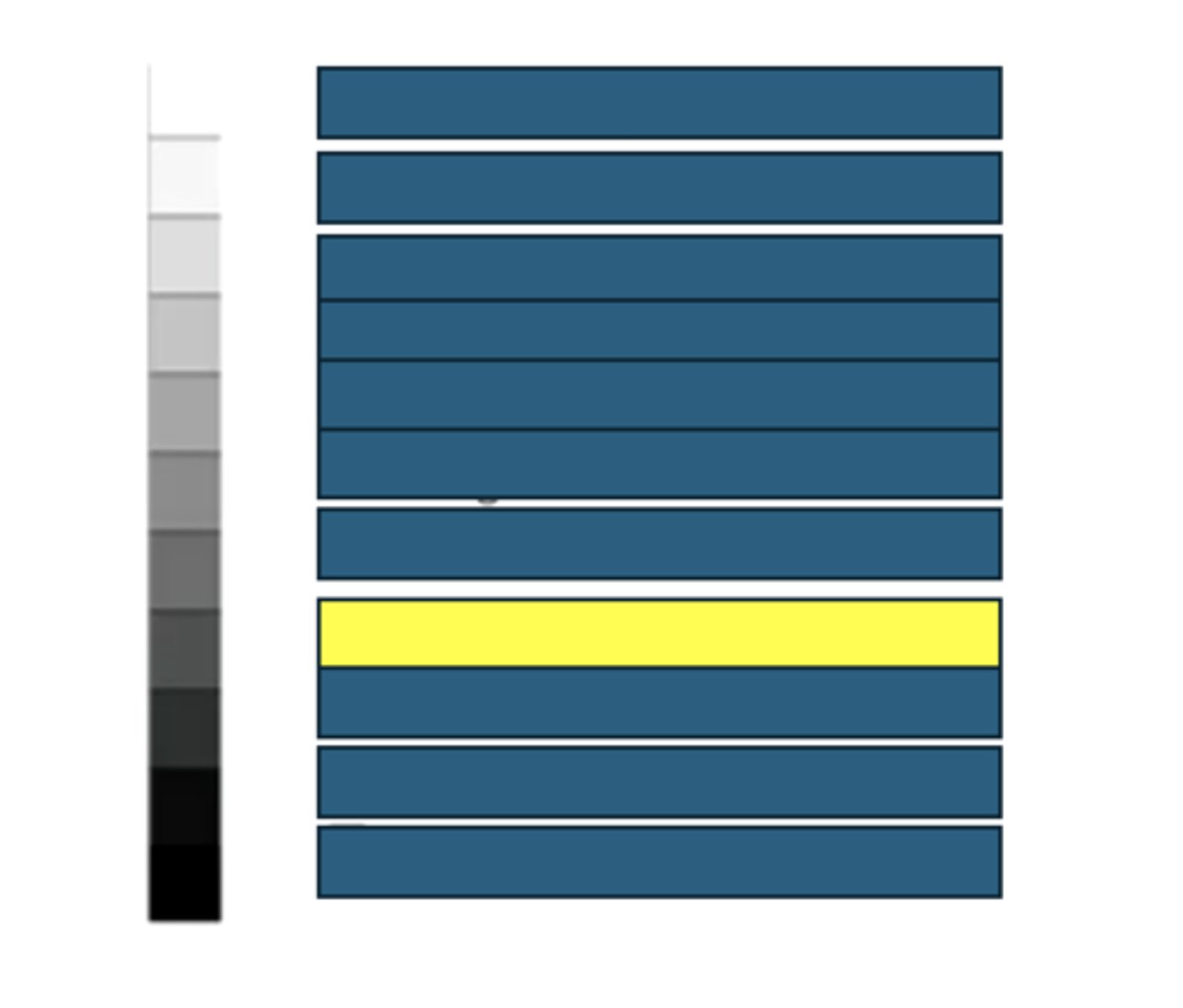
Muscle
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
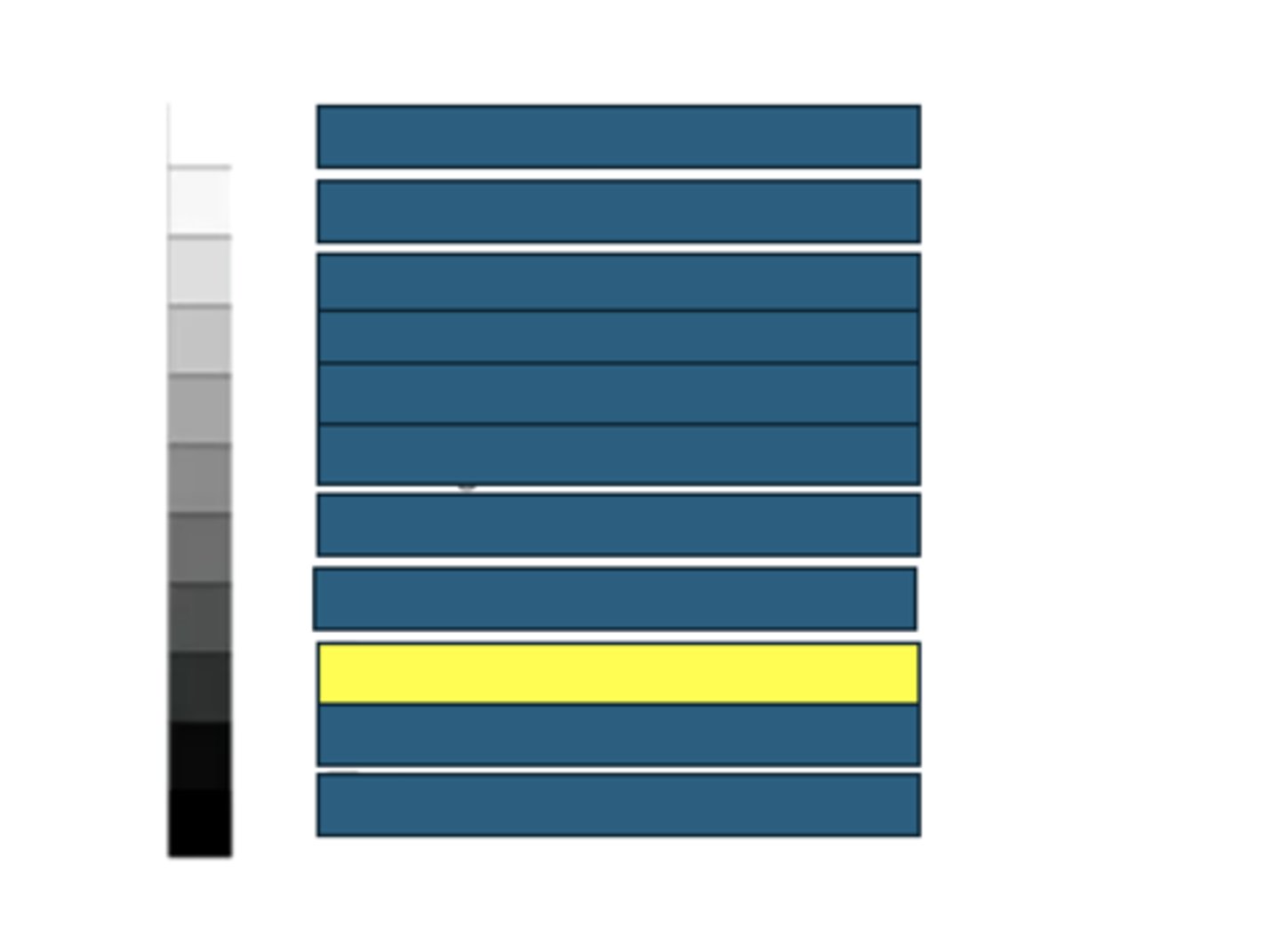
Renal medulla
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
Bile and Urine
What kind of structures/tissues/fluids would have this echogenicity on an ultrasound?
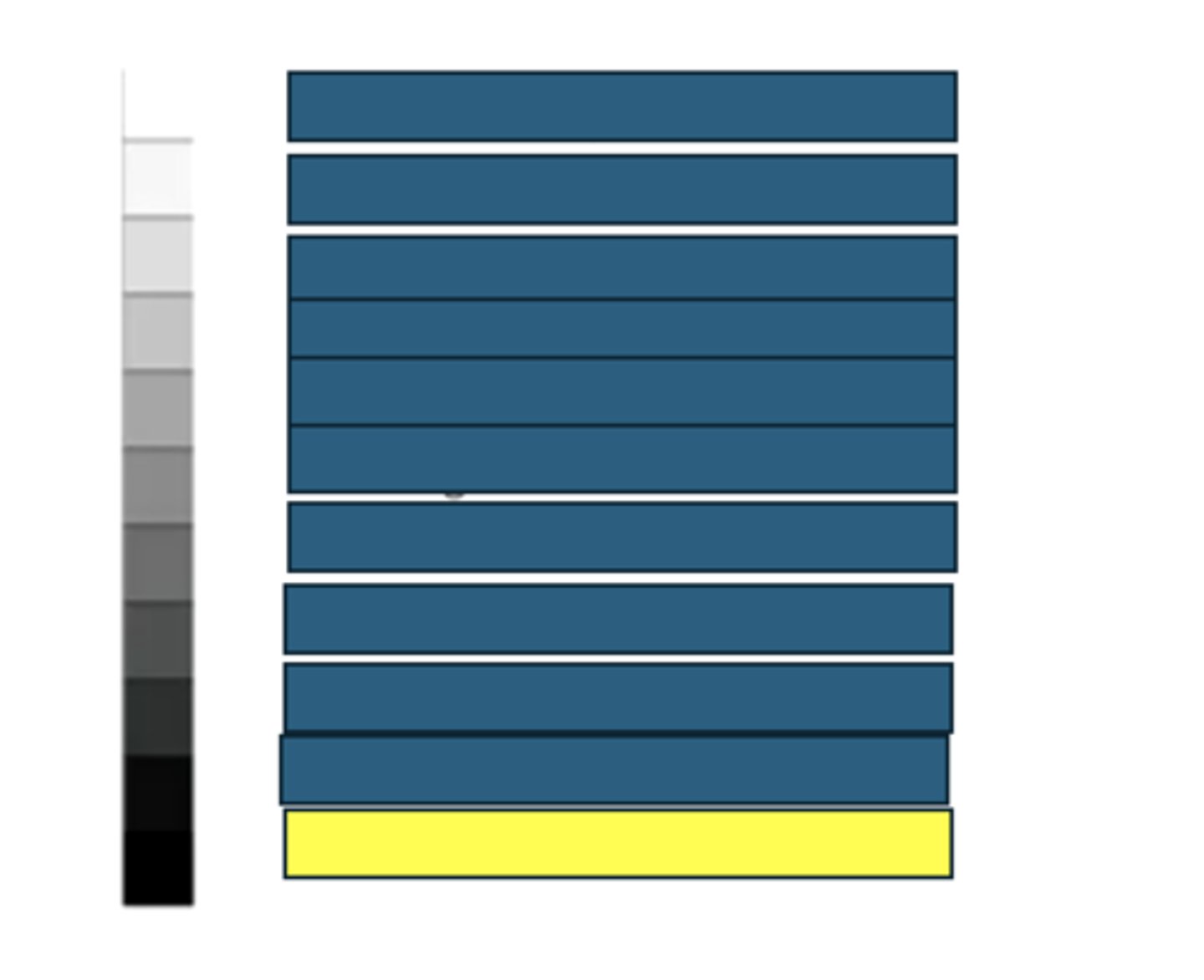

False. The probe's location should always correspond to the top of the image.
True or False: When showing your friends your hip and trendy ultrasound pic you're about to upload to your vinsta (veterinary insta), you can situate the probe's location anywhere on the image as long as it is clearly marked.
Artifacts in ultrasonography include the following:
- Acoustic shadow
- Acoustic enhancement
- Reverberation
- Mirror image
- Slice thickness
- Edge shadowing
Artifacts in ultrasonography include the following:
- Acoustic s______
- Acoustic e_______
- R____________
- M______ image
- S_______ thickness
- E________ shadowing
Acoustic shadow is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when the ultrasound waves cannot penetrate a structure, making everything beneath that structure a shadowy artifact
Acoustic shadow is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when the ultrasound waves cannot p________ a structure, making everything b_______ that structure a s________ artifact
Acoustic enhancement is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when the sound waves penetrate pure fluid very quickly, but then run into a soft tissue structure beneath the fluid. The quickness with which the waves approached the soft tissue causes them to bounce back more harshly, creating an artificially bright soft tissue structure deep to the pure fluid structure.
Acoustic enhancement is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when the sound waves penetrate p_____ f_______ very quickly, but then run into a soft tissue structure b_____ the f_____. The q__________ with which the waves approached the soft tissue causes them to bounce back more h______, creating an a________ b______ soft tissue structure d_____ to the p____ f_____ structure.
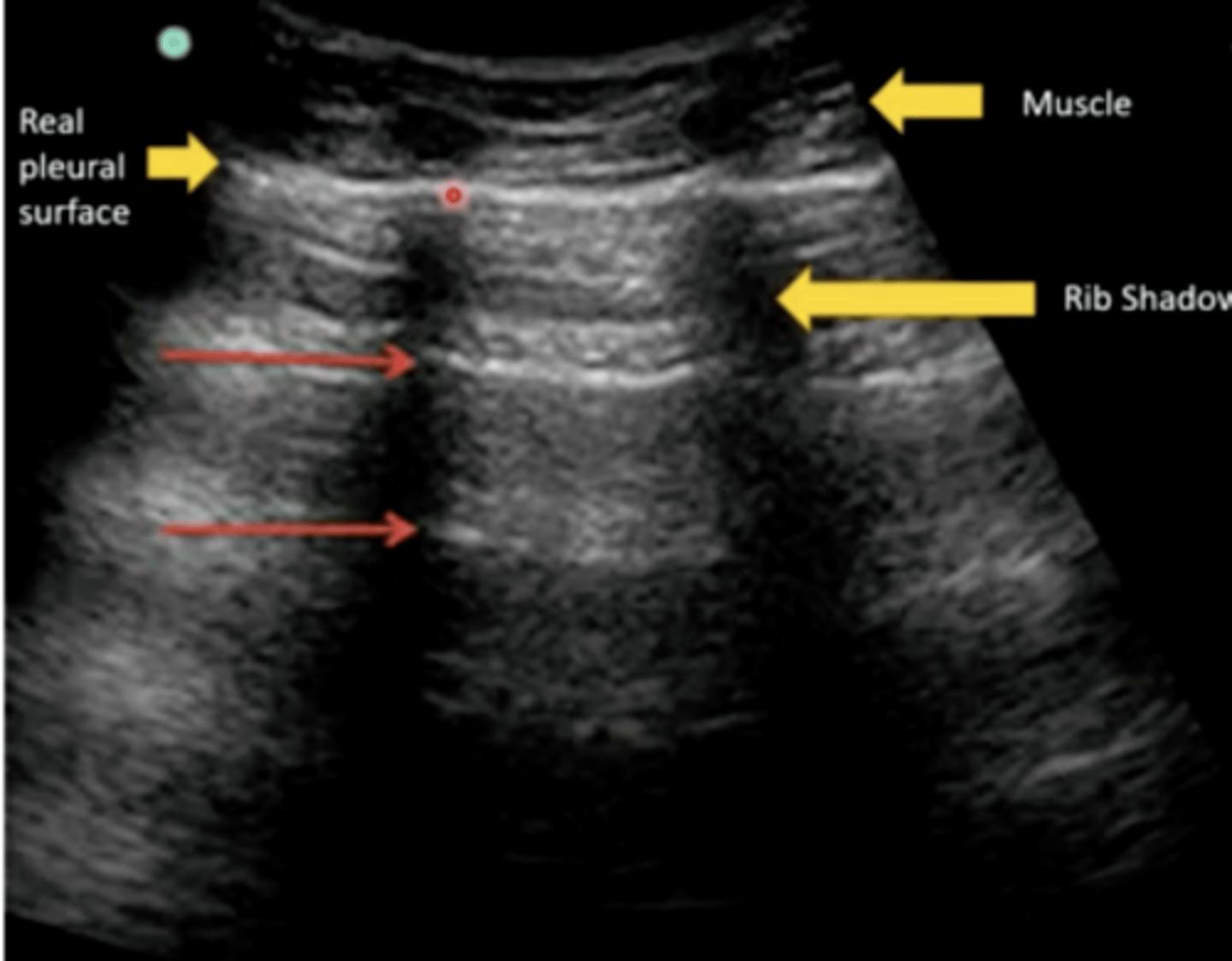
Reverberation is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when sound waves reflect multiple times between two structures. Reverberation can create a mirror image. Reverberation is most commonly seen in the lungs.
Reverberation is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when sound waves r______ multiple times between t______ structures. Reverberation can create a m________ i___________. Reverberation is most commonly seen in the l_________.
Mirror images are ultrasonography artifacts that occur when the ultrasound waves hit a strong reflector structure and duplicates the image on the opposite side of the reflector when the waves travel back to the probe. Mirror images are most common at the thorax/abdomen interface due to the diaphragm being a strong reflector structure.
Mirror images are ultrasonography artifacts that occur when the ultrasound waves hit a s_______ r__________ structure and d________ the image on the opposite side of the r________ when the waves travel back to the probe. Mirror images are most common at the t______/a_______ interface due to the d_________ being a s________ r_________ structure.
Slice thickness is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when a 3D structure filled with fluid (like the bladder or gall bladder) causes the ultrasound waves to bend and create a false sludge in the anechoic space on the 1D image made by the machine.
Slice thickness is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when a 3___ structure filled with f______ (like the b________ or g_____ b_______) causes the ultrasound waves to b_______ and create a false s_______ in the anechoic space on the 1___ image made by the machine.
Edge shadowing is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when ultrasound waves penetrate a curved structure and bend, creating dropout (black lines) of the waves deep to the structure.
Edge shadowing is an ultrasonography artifact that occurs when ultrasound waves penetrate a c______ structure and b_________, creating d_________ (black lines) of the waves d________ to the structure.
Probe, because it has non-durable crystals contained in it that are very sensitive to being dropped
What is the most expensive part of the ultrasound setup and why?
Linear probe; we can use it on equine tendons
What kind of ultrasound probe shoots sound waves in a straight line, and what is an example of the kind of tissue we ultrasound using this probe?
Curvilinear probe; we can use it on the abdomen and thorax
What kind of ultrasound probe shoots sound waves in a sector shape, and what is an example of the kind of tissue we ultrasound using this probe?
The frequency of the ultrasound probe (in mHz) changes the resolution and depth of the image
The frequency of the ultrasound probe (in m___) changes the r________ and d______ of the image
Increasing the frequency of the ultrasound probe translates to less depth into the tissues but a higher resolution. Decreasing the frequency of the ultrasound probe translates to more depth into the tissues but a lower resolution.
Increasing the f__________ of the ultrasound probe translates to l______ depth into the tissues but a h________ resolution. Decreasing the f________ of the ultrasound probe translates to m______ depth into the tissues but a l________ resolution.
Higher frequency (less depth, more resolution)
What frequency (higher or lower) would you want to ultrasound the equine tendon with?
Lower frequency (more depth, less resolution)
What frequency (higher or lower) would you want to ultrasound the equine abdomen with?
Bones and lungs
What are the only two structures in the body for which ultrasound is useful only in pathologic conditions (i.e., the ultrasound is only useful when these two tissues are NOT normal)?
Ultrasound imaging in two planes (transverse and longitudinal) is useful for lesion description. The transverse plane tells the ultrasonographer the location of the lesion, whereas the longitudinal plane describes its length.
Ultrasound imaging in two planes (t_______ and l___________) is useful for lesion description. The t_________ plane tells the ultrasonographer the l_________ of the lesion, whereas the l_______ plane describes its l_________.
Doppler mode is the real-time imaging of a structure in ultrasonography. It can be used for heartbeat and direction of fluid flow.
D_________ mode is the real-time imaging of a structure in ultrasonography. It can be used for h_______ and direction of f______ f_______.
Computed Tomography (CT) is an X-ray-based imaging technique that occurs in a tube. Radiographs are taken all around a structure in a tube, and a computer program generates a 3D slice image.
C________ T_________ (CT) is an __-r____-based imaging technique that occurs in a t_______. R__________ are taken all around a structure in a t________, and a computer program generates a 3____ s________ image.
Radiation safety is especially important when performing a CT, since an increased amount of x-rays are needed to create the 3D image.
Radiation s_________ is especially important when performing a CT, since an increased amount of __-r_____ are needed to create the 3____ image.
Compared to radiographs, CT produces intense detail due to the lack of superimposition in CT (as opposed to radiography).
Compared to radiographs, CT produces intense detail due to the lack of s_____________ in CT (as opposed to radiography).
An animal is always anesthetized or heavily sedated for a veterinary CT. In equine medicine, the size of the CT machine gantries (entranceways) usually limit the image to that of the carpus, tarsus, digit or head.
An animal is always a________ or heavily s_______ for a veterinary CT. In equine medicine, the size of the CT machine g_______ (entranceways) usually limit the image to that of the c_____, t_______, d______ or h________.
Standing CT's, which produce images that do not have the same high quality as a typical, gantry-style CT machine
If a horse is lame on its leg and the veterinarian is worried about anesthetizing it (for fear of it having trouble rising post-anesthesia), what is an option to obtain a CT image?
CT is an extremely useful imaging modality for the following:
- Detailed evaluation of bone
- Imaging the head, spine and abdomen (however, soft tissue structures must have contrast solution injected into them)
- Finding tiny lesions not able to be detected by radiography
CT is an extremely useful imaging modality for the following:
- Detailed evaluation of b______
- Imaging the h____, s_____ and a______ (however, soft tissue structures must have c_______ s_________ injected into them)
- Finding tiny l_________ not able to be detected by radiography
In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a strong magnet is applied to tissues, and the hydrogen protons (found in water in the tissues) are excited by a radio frequency pulse. When the pulse is removed, the protons relax and emit a signal, making an image.
In m_______ r________ i________ (MRI), a strong magnet is applied to tissues, and the h_______ protons (found in w______ in the tissues) are excited by a r______ f________ p________. When the p_____ is removed, the protons r_____ and emit a s_____, making an image.
True
True or False: Special attention must be paid to removing all metal (including horseshoes and metallic anesthesia equipment) during an MRI.
There are specific MRI sequences used to image structures to look for lesions.
There are specific MRI s________ used to image structures to look for l________.
Air and bone
What are the only two structures whose hydrogen protons do NOT emit a signal in an MRI?
Each sequence of an MRI creates a different greyscale. Thus, two or more sequences are performed when looking for a lesion.
Each sequence of an MRI creates a different g________. Thus, t_____ or more sequences are performed when looking for a lesion.
MRI is often preferred to CT when imaging soft tissue and cartilage, since the physician does not have to inject contrast solution.
MRI is often preferred to CT when imaging s_____ t_______ and c_________, since the physician does not have to inject contrast solution.
CT is often preferred to MRI when imaging bone, since it does not contain as many hydrogen protons and does not emit a clear signal.
CT is often preferred to MRI when imaging b________, since it does not contain as many hydrogen protons and does not emit a clear signal.
When MRI is used to image bone, it shows a negative image since bone is black.
When MRI is used to image bone, it shows a n________ image since bone is b________.
In small animal practices, MRI is used to image the following:
- Neuroimaging
- Musculoskeletal
- Tumor staging
- Abdomen
- Cardiac
In small animal practices, MRI is used to image the following:
- N__________
- M__________
- T________ staging
- A___________
- C_________
False. MRI's create a 3D image.
True or False: MRI creates a 2D image from a 3D object.
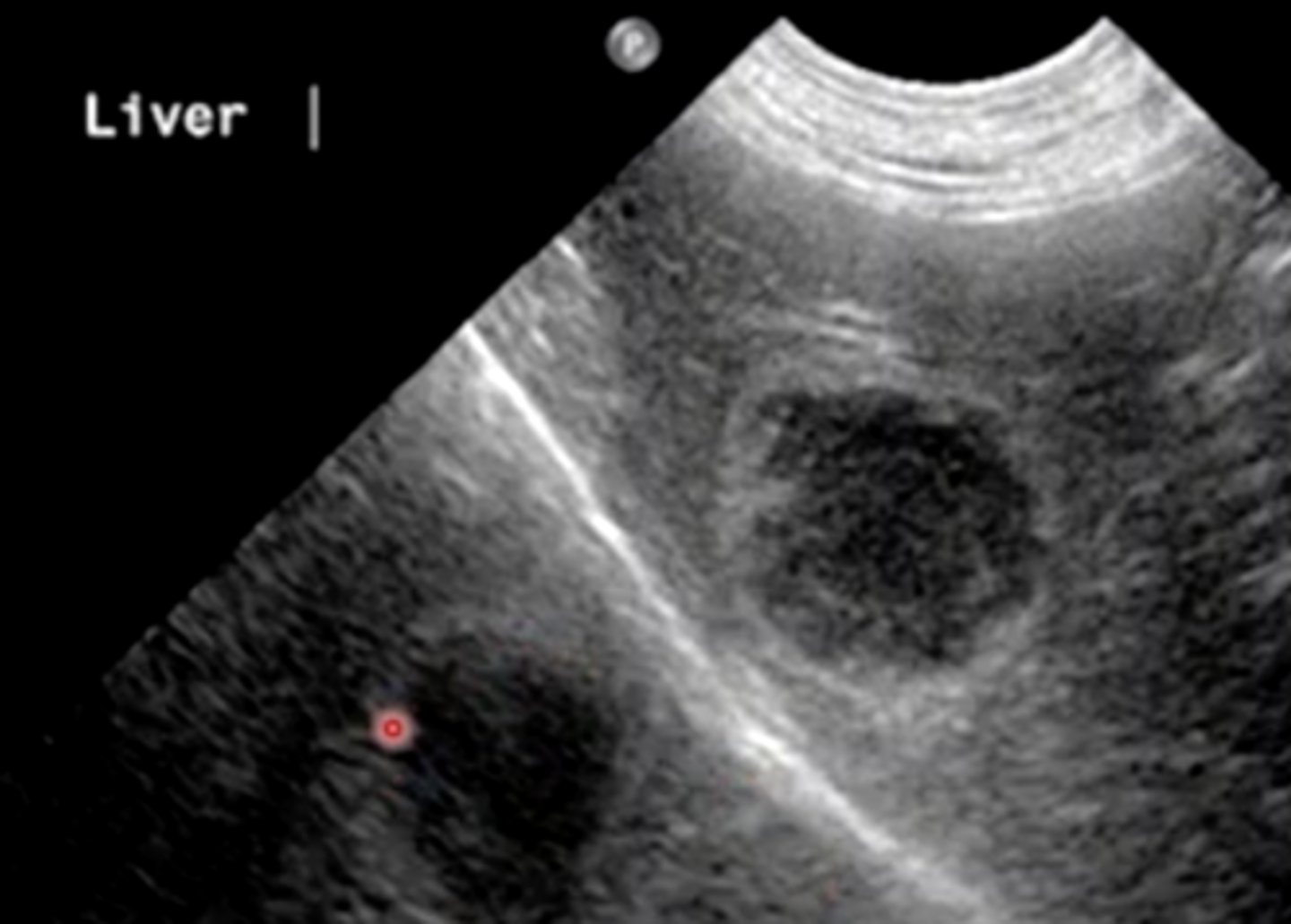
Mirror image
You are performing an ultrasound of the liver when you see this image. What artifact is this? (Hint: think of the interface at which the liver is located).
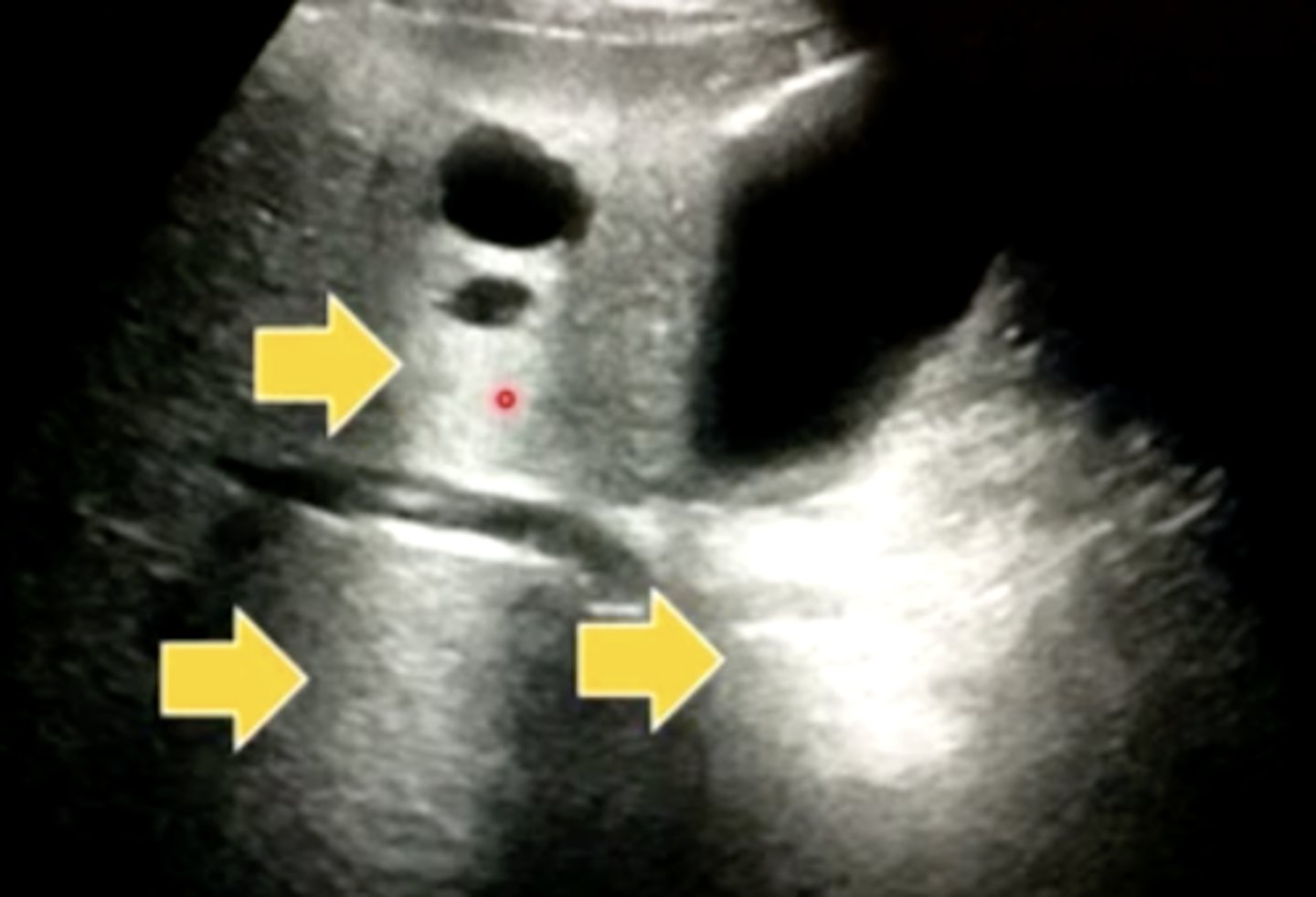
Acoustic enhancement
An experienced ultrasonographer tells you these soft tissue structures (deep to the anechoic areas of pure fluid) are artificially bright. What artifact is that called?
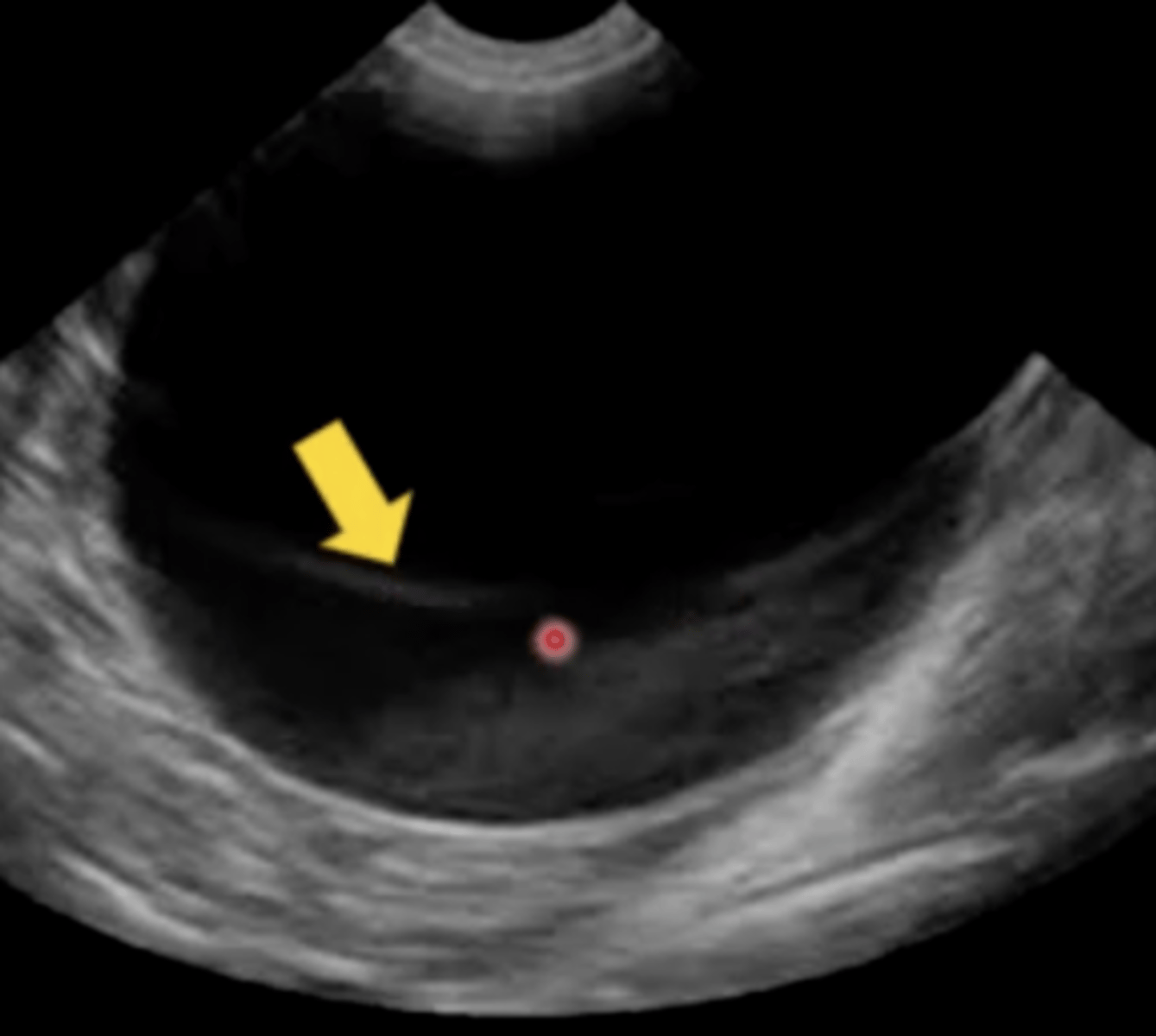
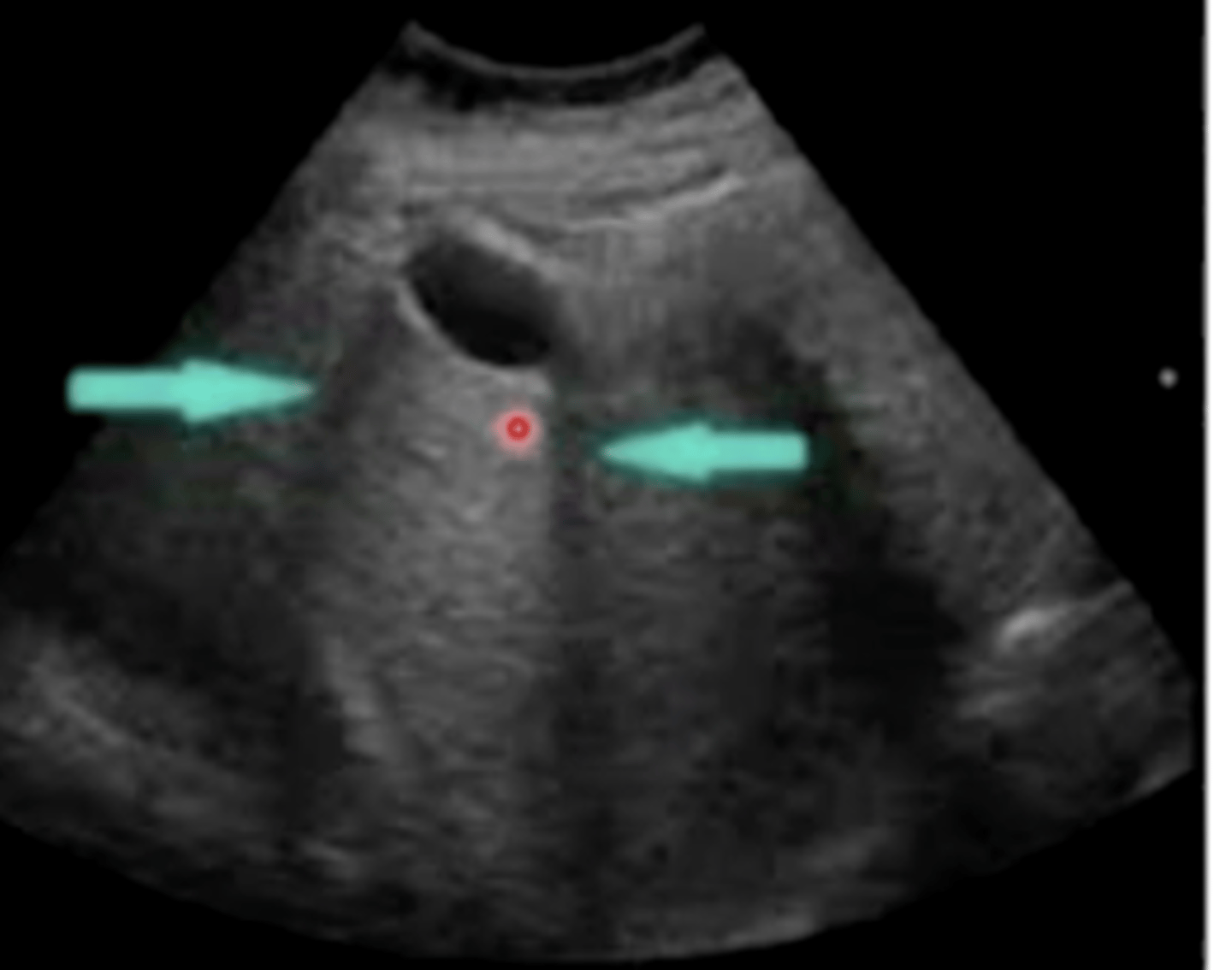
Slice thickness
It's Bring Your Husband to Work day, which is your least favorite national holiday (but clinic law states you must abide by it). You bring your idiot husband, who takes one look at this ultrasound of a Labrador bladder and absolutely freaks out at the amount of sludge present at the bottom. He's a neurosurgeon who trained at John Hopkins and thinks he knows everything, and he says that thickness looks like cancer formation. You pop your knuckles and prep to blow his mind with your knowledge of ultrasound artifacts. What artifact do you tell him this is?
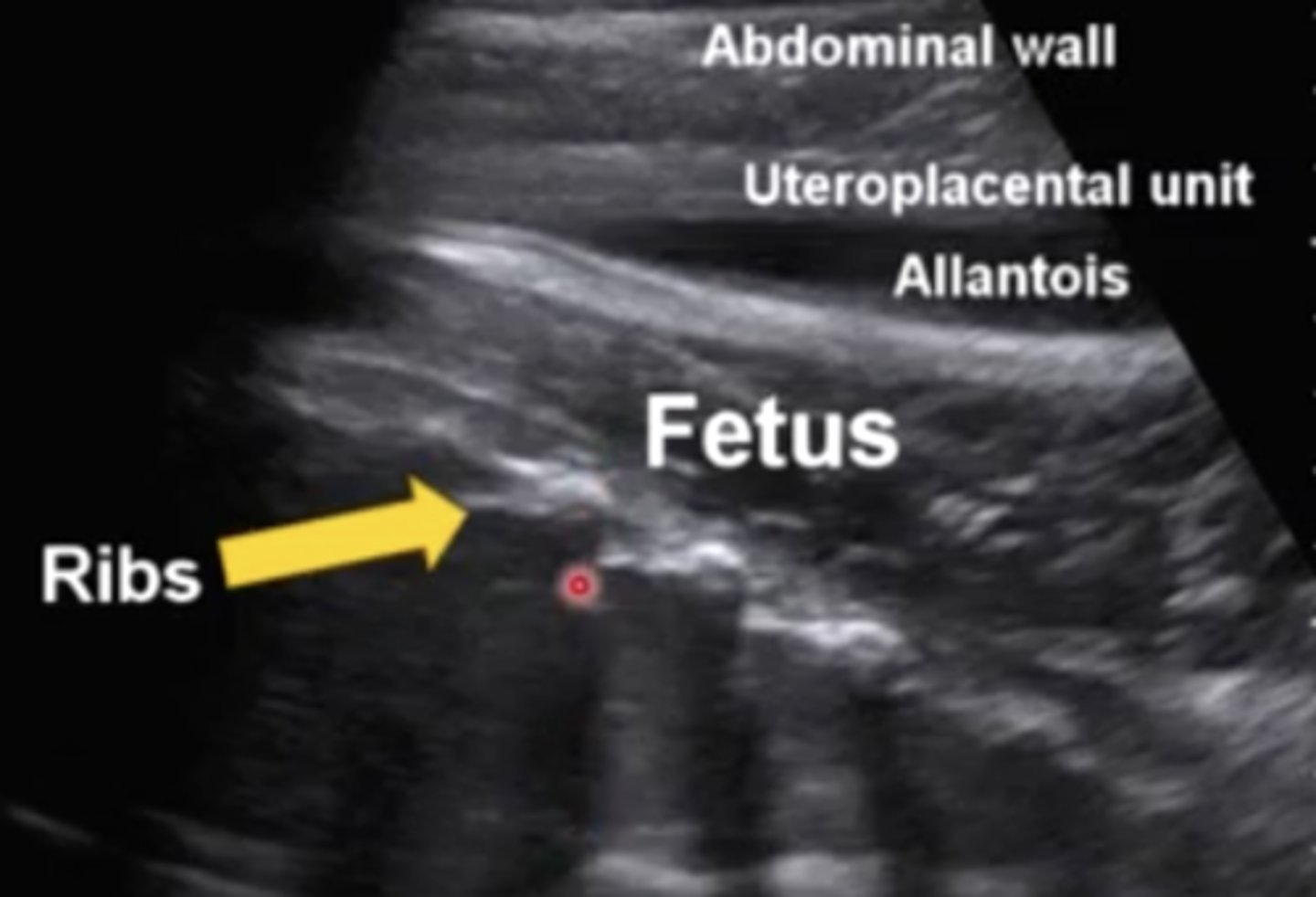
Acoustic shadow
In this ultrasound image, the ribs are casting what kind of artifact (you can't see anything below them)?
Edge shadowing
You are a surgical resident at a veterinary teaching hospital and wondering why you put yourself in this mess rather than happily spay and neuter for the rest of your life sans board certification. Your instructor asks you to name the artifact on an ultrasound of a gall bladder you guys are going to take out that afternoon. After taking a sip of your Coffee Mountain Dew Diet Coke Sludge Fest Surprise, what do you answer him?
Reverberation
You see this area of multiple reflections deep to the real pleural surface while performing ultrasonography of the lungs. What is this artifact called?