Honors Biology Unit 6 SCHS
1.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Last updated 8:10 PM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
What is genetics?
Genetics is the study of biological inheritance patterns and variation.
2
New cards
What are Mendel’s three key decisions?
Control over breeding, use of purebred plants, observation of either or traits. Pea plants Reproduced quickly.
3
New cards
What is the P generation?
Parental generation.
4
New cards
What is the F1 generation?
The offspring resulting from a parental cross are referred to as the first filial generation (or F1 generation).
5
New cards
What is the F2 generation?
The result of a cross between two F1 individuals.
6
New cards
What is the law of segregation?
Organisms inherit two copies of each gene, one from each parent. Organisms donate only one copy of each gene in their gametes (two copies of each gene segregate, or seperate, during gamete formation.
7
New cards
What are Mendel’s three conclusions?
Traits are inherited as discrete units, and the other two are collectively called the law of segregation.
8
New cards
What is a gene?
A piece of DNA that provides a set of instructions to a cell to make a certain protein.
9
New cards
How many alleles do you have for each gene?
Two.
10
New cards
What does homozygous mean?
Two of the same allele.
11
New cards
What does heterozygous mean?
Two different alleles.
12
New cards
What is a genome?
All the organism’s genetic material.
13
New cards
What is a genotype?
The genetic makeup of an organism for a particular gene (e.g. RR).
14
New cards
What is a phenotype?
If R is dominant, RR=Rr.
15
New cards
What is a dominant allele?
If R is dominant, RR=Rr. Capital letter is always dominant.
16
New cards
What is a recessive allele?
Only expressed if have two copies of recessive present. Lowercase letter always represents.
17
New cards
Type AB blood would react with antibodies…
None.
18
New cards
Proteins differ from one another because…
they have a different number of amino acids, they each have their own unique 3d shape, they are composed of different amino acids.
19
New cards
What type of cell division results in 4 haploid cells?
Meiosis.
20
New cards
Mutations that affect multiple genes usually take place during…
Meiosis
21
New cards
How many chromosomes would a normal human karyotype have?
46
22
New cards
Why do some enzymes stop working when the temperature increases?
They denature, the shape of the active site may be altered, their 3d shape is altered.
23
New cards
Determine the Amino Acid Sequence from the following mRNA sequence: UUUCCAGCU
Phe-Pro-Ser.
24
New cards
Mutuations in the DNA sequence of a gene _______ affect the expression of the gene.
May or may not.
25
New cards
Sex Linked genetic disorders are more likely in men than women because…
men only have a single x chromosome.
26
New cards
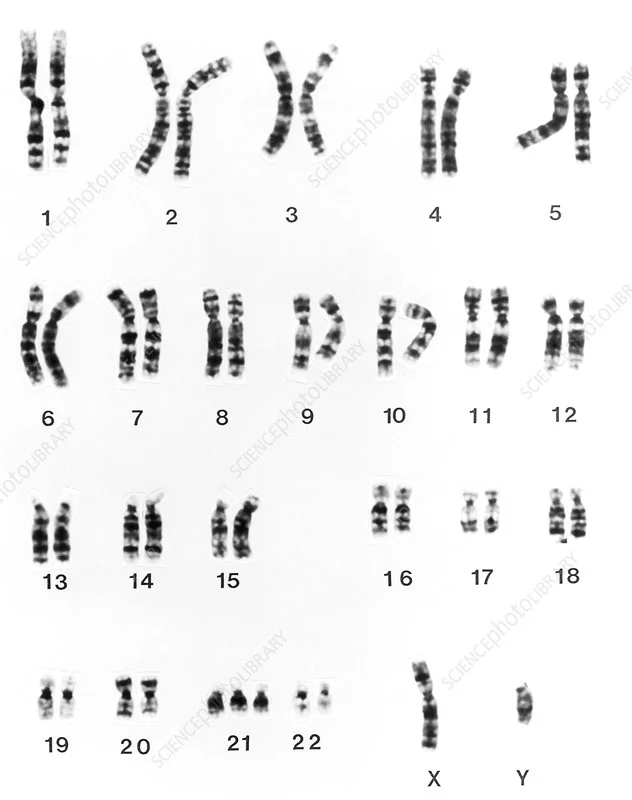
The correct notation for theis karyotype is…
47XY+21
27
New cards
What is used to match chromosomes when preparing a karyotype?
beinding patterns, length of chromosome, and centromere position.
28
New cards
Human eye color is an example of what kind of inheritance?
Polygenic
29
New cards
What would be the phenotypic ratio in the following genetic cross: TT and tt?
4:0
30
New cards
In a monohybrid cross, if all the offspring are heterozygous, the parents must be both…
homozygous
31
New cards
What would be the possible phenotypes of the cross AB and O?
A, B
32
New cards
What would be the posible gametes for the following genotype: BbTt?
BT, Bt, bT, bt
33
New cards
What factors affect an organisms phenotype?
the organism´ s epigenome, the organisms genotype, and the environment.
34
New cards
Which of the followimng factors affect an organisms genotype: The environment, An organisms genotype, the organisms epigenome?
None of the listed.
35
New cards
Genes found on the same chromosome are called…
linked genes
36
New cards
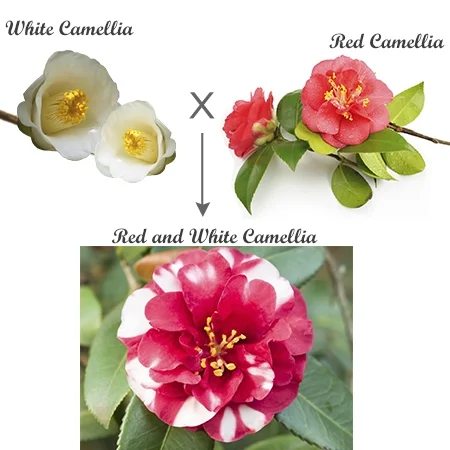

This image shows what type of inheritance?
co-dominance.
37
New cards
the first 22 pairs of chromosomes are called…
both homologous and autosomes.
38
New cards
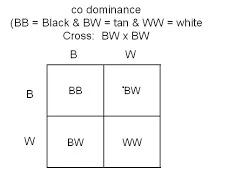
What would be the genotypic ratio in this genetic cross?
1:2:1
39
New cards
The number of chromosomes in gametes are termed…
haploids
40
New cards
What would be the female
parent´ s genotype be?
parent´ s genotype be?
41
New cards
a gene that maintains its epigentic tag, s when it becomes an embryo is called an…
imprinted gene
42
New cards
Which of the following blood types results in different phenotypes: IAi and IAIA, IAIB and IAIA, IBIB and IBi, all of the listed?
IAIB and IAIA
43
New cards
Genes carry instructions for assembling…
proteins
44
New cards
What would be the expected genotype ratio from a cross between two homozygous recessive parents?
0:4 not 4:0.
45
New cards
Albinism(the lack of all other pigments is an example of…
epistasis.
46
New cards
What % of the offspring would have a disorder if it is a dominant disorder in a cross between Ss and Ss?
75%
47
New cards
What is co-dominance? Give an example.
\n When both traits are expressed. (Ex. Red and white flower.)
48
New cards
What is incomplete dominance?
A blending of traits. Red+White=Pink.