Lesson 1 - Niche
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Is there anywhere life cannot be found?
Only in the most extreme environments where essential biological molecules cannot exist!
e.g., at the most extreme temperatures or pH
Life is everywhere!
Extremophiles are organisms that are able to live in extreme conditions
Life can be found…
In temperatures up to 121°C
In lakes with a pH >11
In pools with pH < 1
What is Ecology?
The study of how organisms interact with one another and their physical environment
The study of the processes influencing the distribution and abundance of organisms
Ex. Where is sugar maple found and why?
Where is sugar maple not found and why?
‘Ecology’ from Ancient Greek
oîkos 'house’
-logía 'study of
An Ecological Niche
The range of resources that an organism can use and the physical conditions that it can tolerate
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions that a species lives in
i.e., the range of resources and conditions allowing the species to maintain a viable population
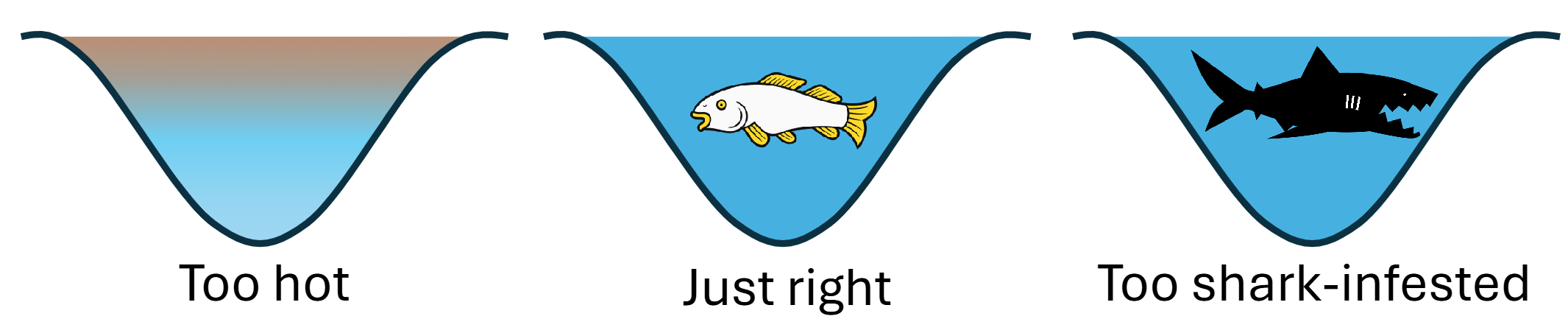
Abiotic Factors
Are the non-living, physical aspects that impact those organisms, such as temperature, mineral nutrients, wind, soils, and water quantity and quality.
Abiotic conditions help us to identify where organisms can potentially live.
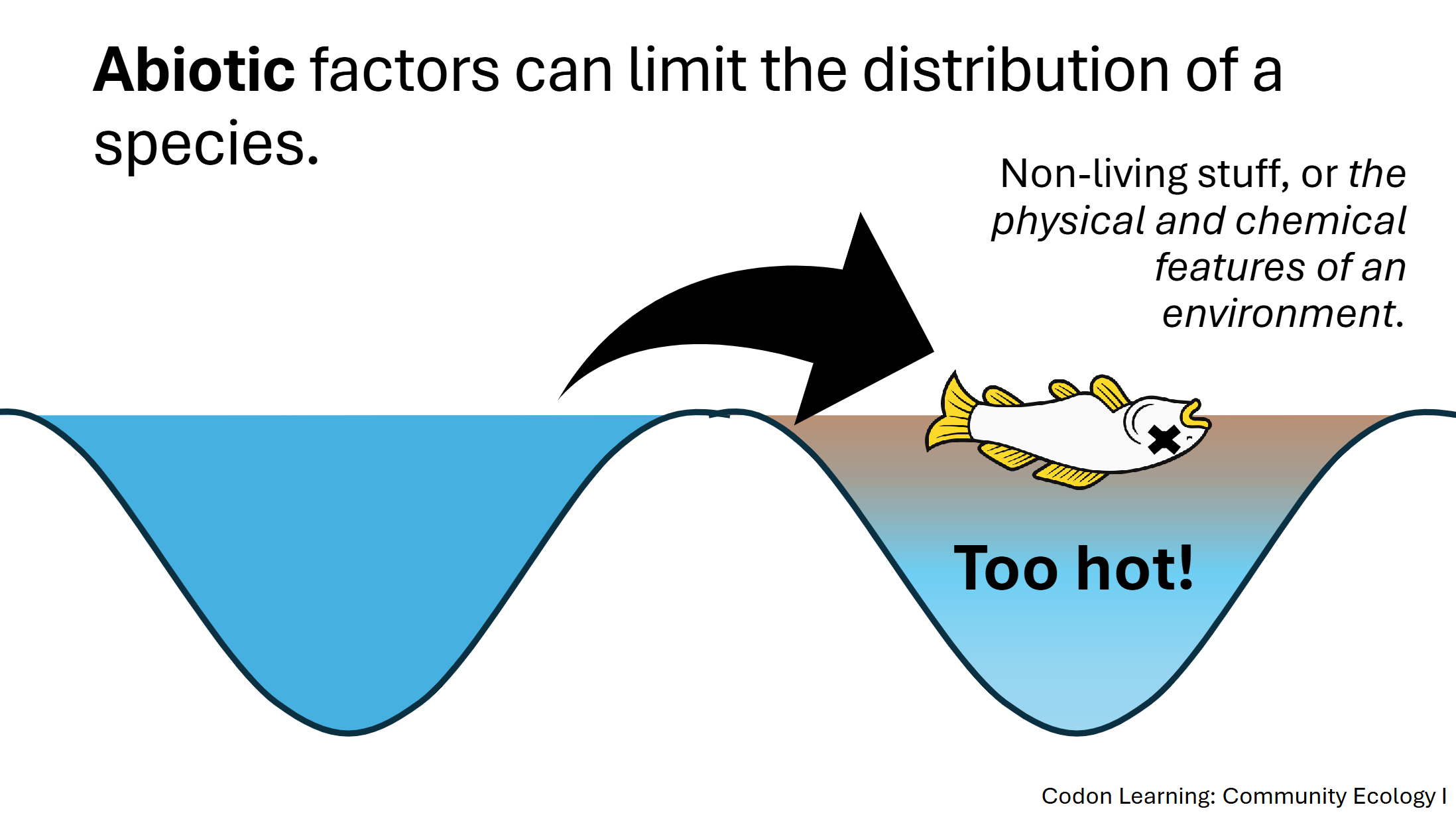
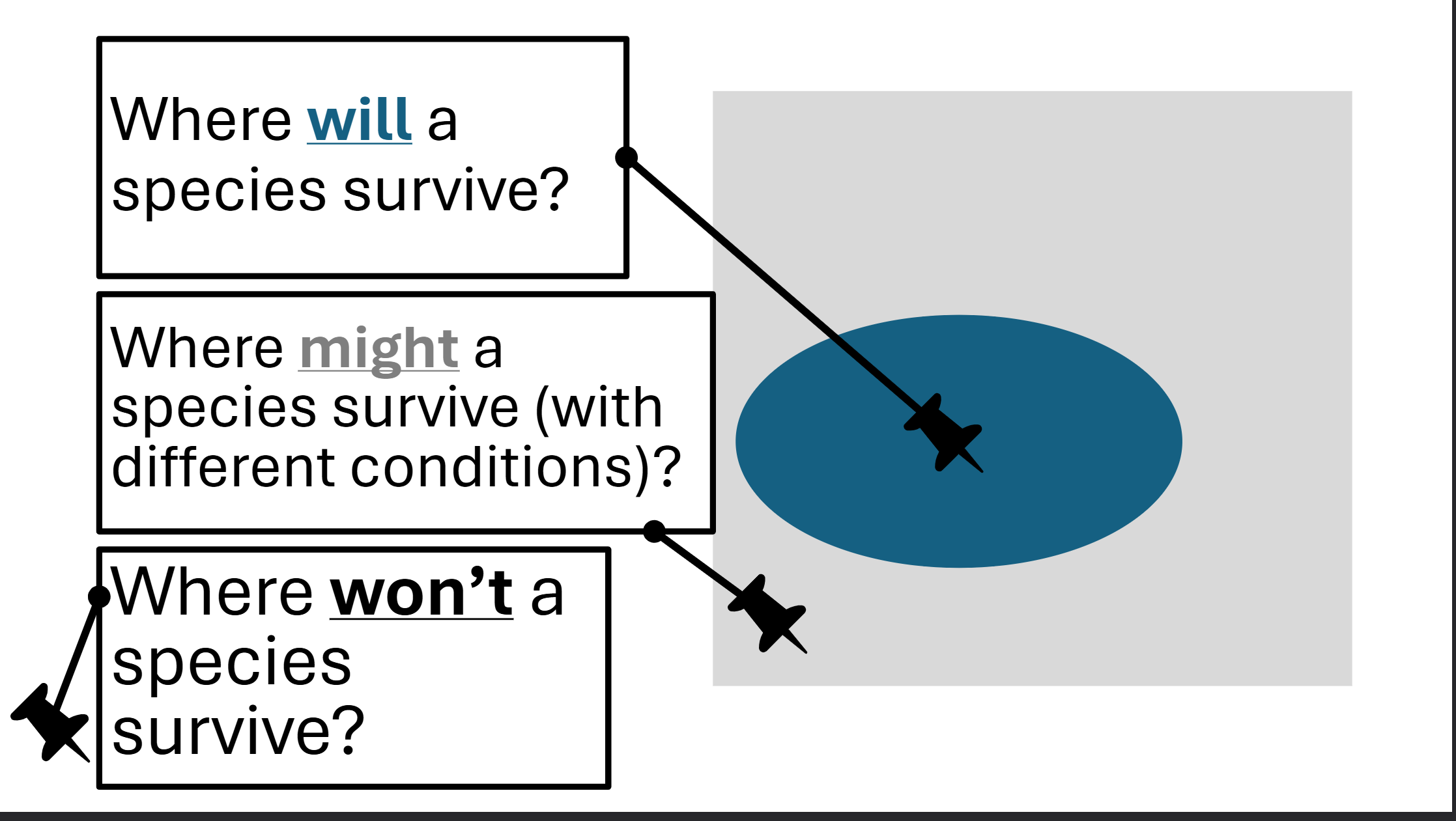
The Fundamental Niche
The possible range of conditions that a species can tolerate
Defines the locations where it is physically possible for a particular species to live
Help us to identify where organisms can potentially live!
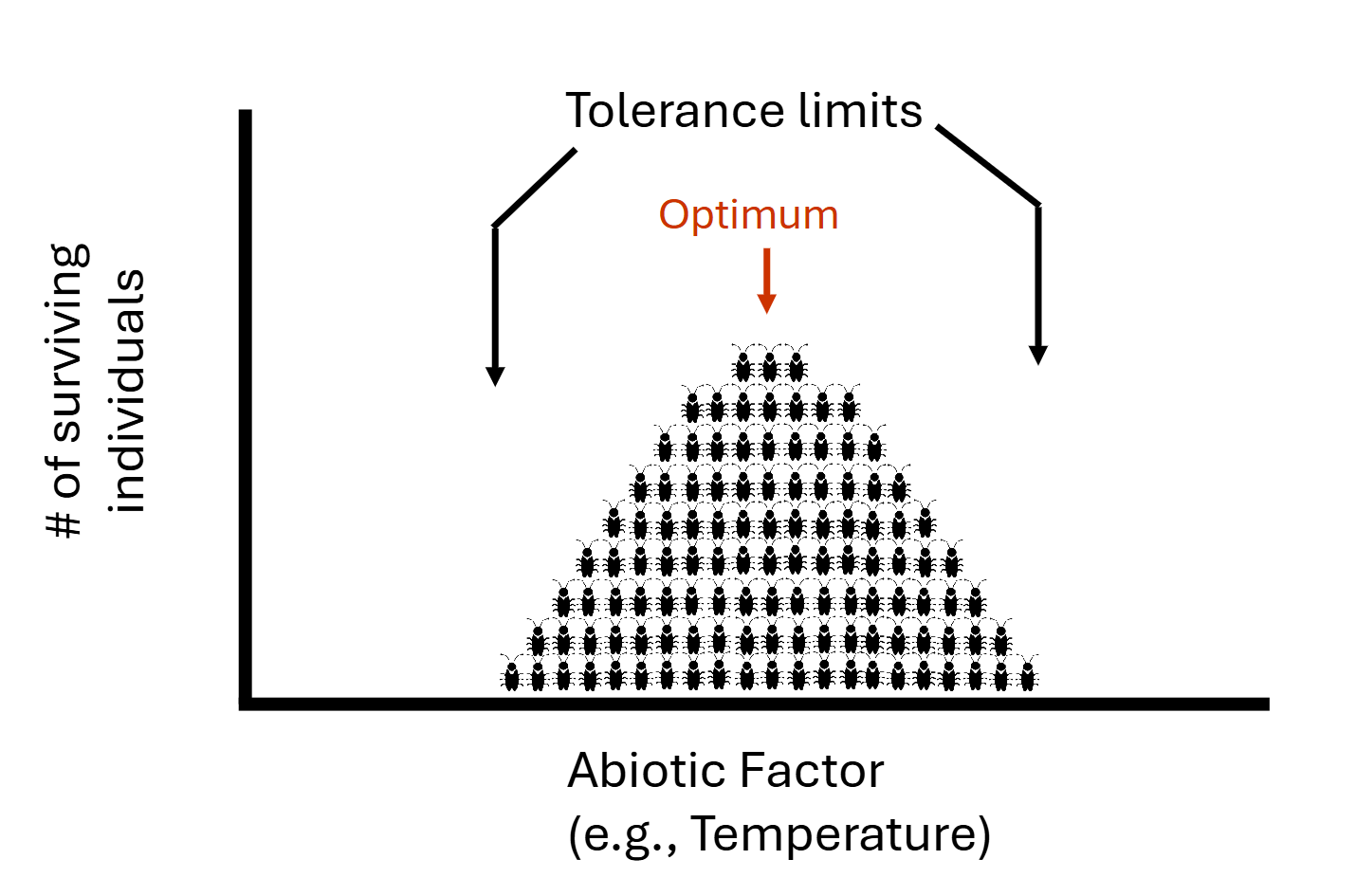
Range of Tolerance → refers to the range of environmental conditions within which an organism can survive, grow, and reproduce
Defines fundamental niche!
Ex. In a dry environment, for example, humans die if they are exposed to temperatures above 57°C (130°F)
Biotic Factors
Are the organisms present—the ones that do the eating and competing and beneficial exchanging
Ex. Food availability, rates of reproduction, competition, predators, parasites etc
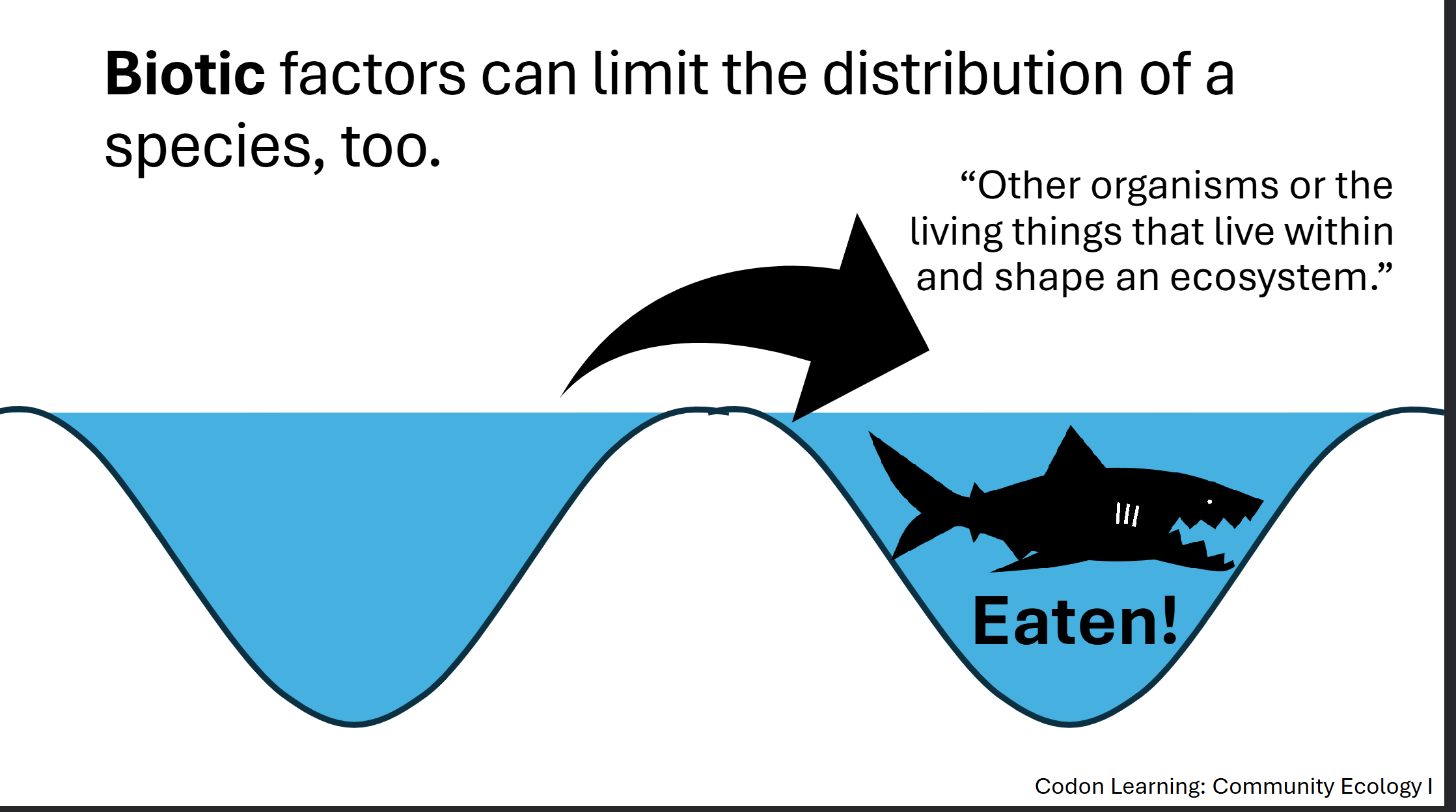
Realized Niche
Spaces within the fundamental niche where the biotic factors are also sufficient – and thus where the species could survive
No species occupies its entire fundamental niche → more limited range of conditions
These biotic interactions can include:
Predation or herbivory (literally, "plant eating") that eliminates a species from certain areas;
Diseases caused by parasites;
Mutualisms involving a strong and beneficial interdependence between two species;
Competition for space, nutrients, water, nesting sites, or other resources.
Ecological Niche
Includes both biotic and abiotic factors
Fundamental Niche
All the possible dimensions in which a species can survive in principle
Potential range based on tolerances
Realized Niche
The dimensions in which a species
survives after the effects of biotic
interactionsMore conditions = narrower range
Hypothesis and Null Hypothesis
A proposed explanation for something that researchers have observed
Are testable because they make predictions
The “If” Part
Ex. Sugar maples do not grow well in grassy fields because sugar maples and grass experience intense competition for nitrogen in the soil.
A null hypothesis states the "not" or "no-effect" contrast to the hypothesis being tested.
Every hypothesis has a corresponding null hypothesis.
Ex. Fever-is-adaptive-for-the-host hypothesis → Fever is not adaptive for the host

Predictions
A statement of an outcome that should occur if a hypothesis is correct
The “Then” statement
“If my tomatoes haven't germinated because they need more time, then I should start to see some seedlings emerging if I wait a few more days."
Ex. Removing the grass from Johnston Green will increase the survival of sugar maples planted there.

Treatment Group vs Control Group
Treatment Group
A group that experiences experimental conditions that conform to the mechanism proposed in the hypothesis
Control Group
A group that represents the normal or no-treatment condition
Serves as a comparison to the treatment group
Outcome Variable
The variable that is measured in an experimental or observational study. It represents a quantity that is relevant to the hypothesis being tested.
Ex. Testing the hypothesis that a new medication can improve symptoms in humans with chronic high blood pressure → Blood Pressure measured over time