Unit 2: The Living World - Biodiversity
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Biodiversity
The diversity of life forms in an environment

Genetic Diversity
A measure of the genetic variation among individuals in a population

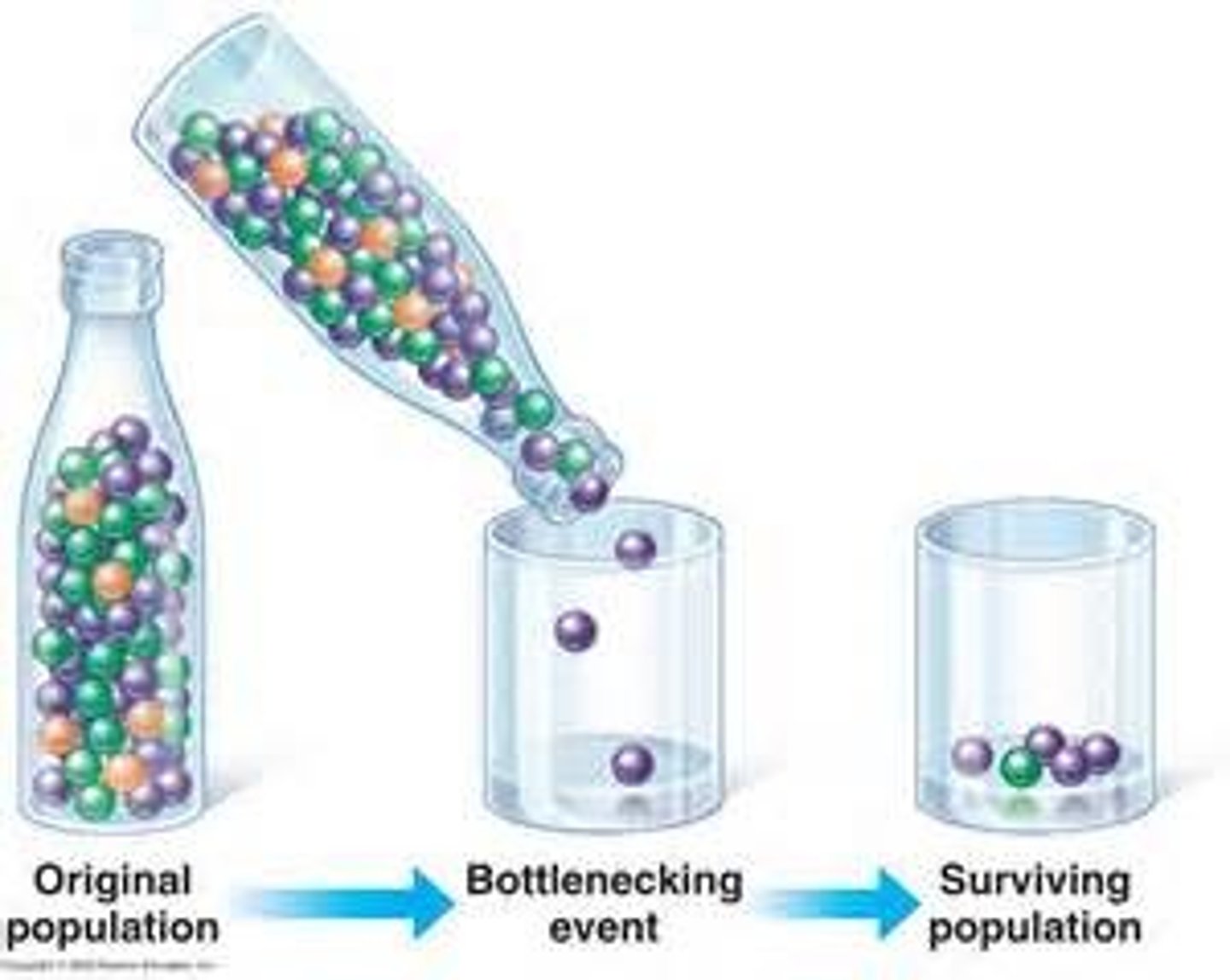
Population bottleneck
When a large population declines in number, the amount of genetic diversity carried by the surviving individuals is greatly reduced
Species Diversity
The number of species in a region or in a particular ecosystem
Habitat Diversity
The variety of habitats that exist within a given ecosystem

Specialists
Species that only live under a narrow range of biotic or abiotic conditions

Generalists
Species that can live under a wide range of abiotic or biotic conditions

Ecosystem Diversity
The variety of ecosystems that exist in a given region
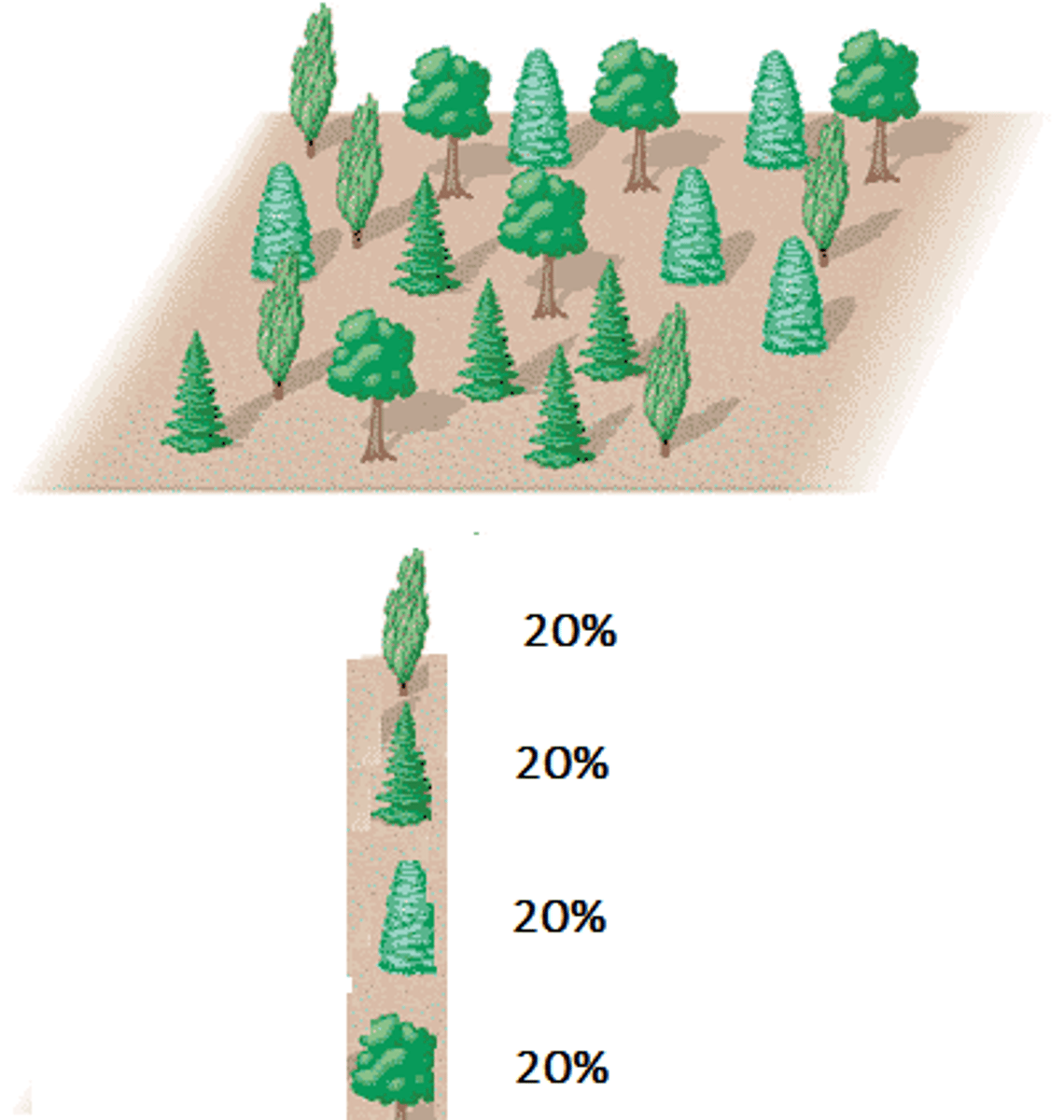
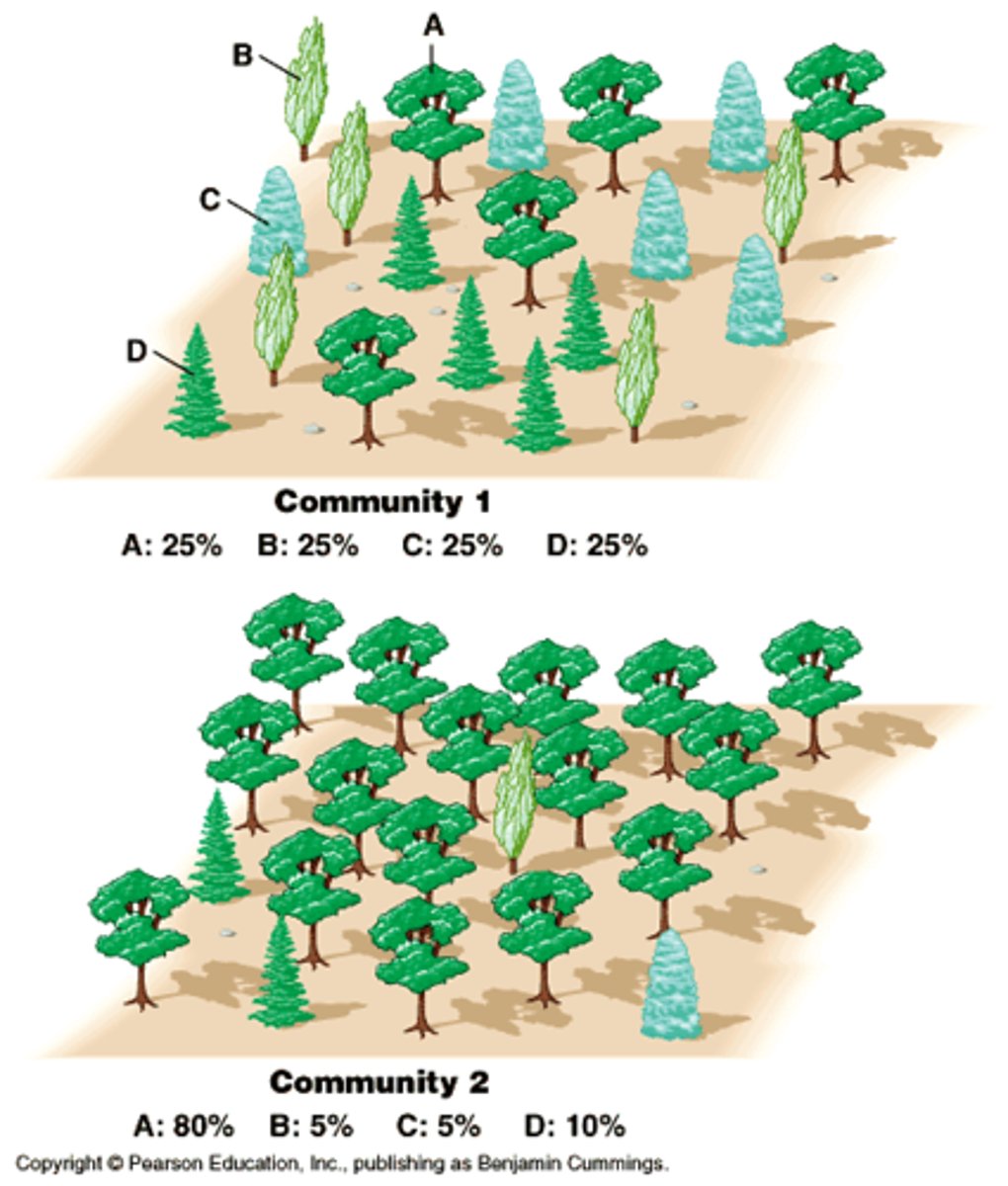
Species Richness
The number of different species in a given area
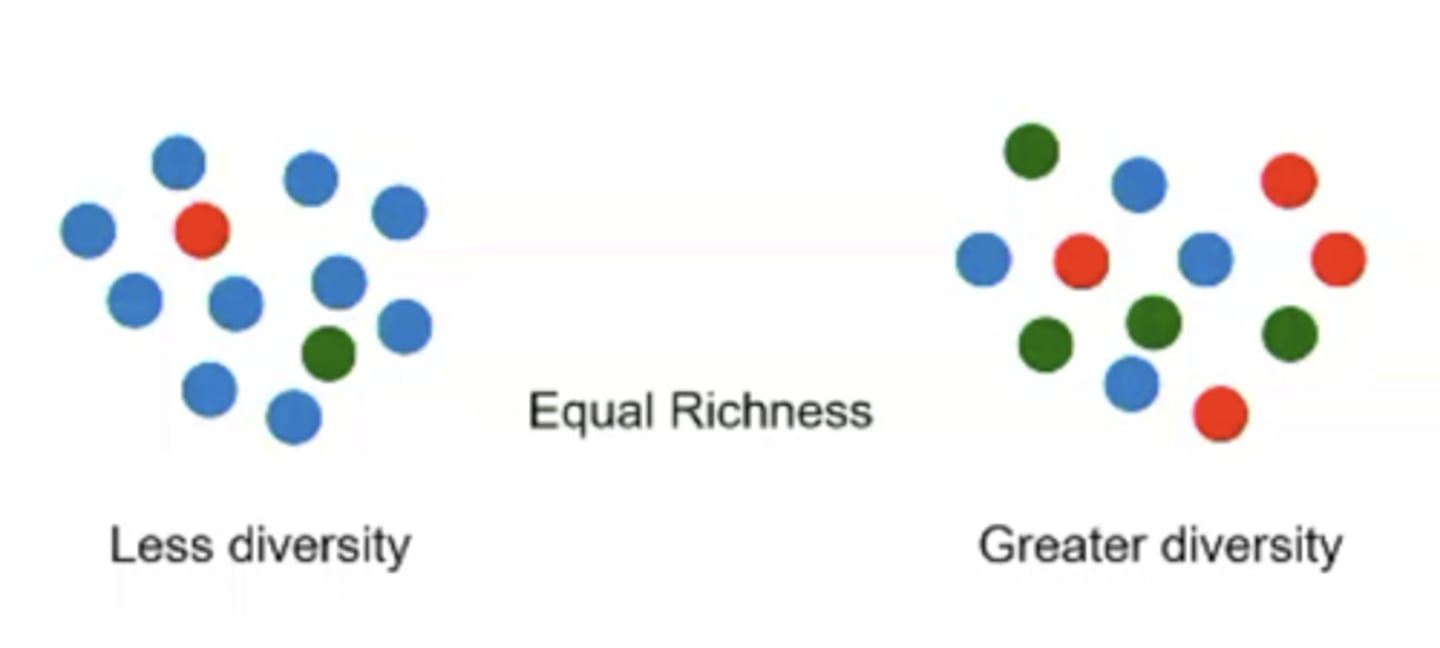
Species Evenness
The relative proportion of individuals within the different species in a given area
Ecosystem Services
The processes by which life-supporting resources such as clean water, timber, fisheries, and agricultural crops are produced

Provisioning Services
A good produced by an ecosystem that humans can use directly (food, fresh water, fiber, genetic products, etc)

Aquaculture
The farming of fish, shellfish, and seaweed

Regulating Service
The benefit provided by ecosystem processes that moderate natural phenomena (pollination, decomposition, water purification, erosion and flood control, carbon storage, climate regulation, etc)

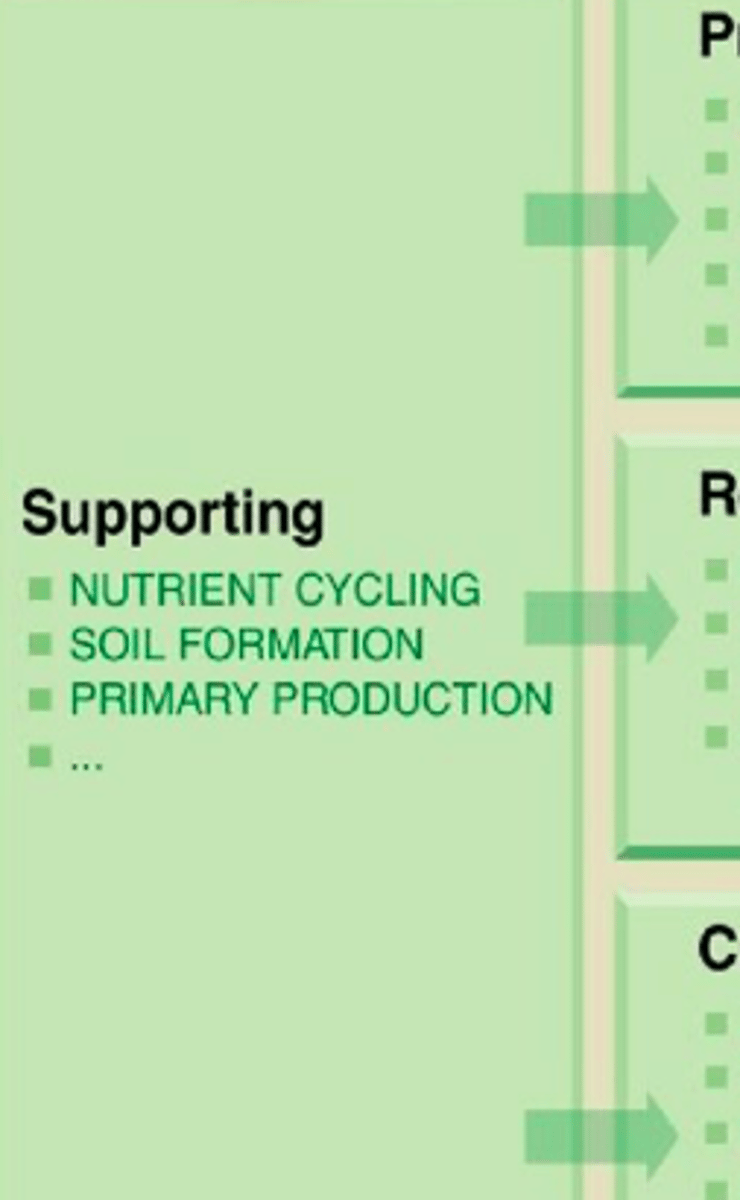
Supporting Service
Ecosystem services that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services (biomass production, oxygen production, soil formation, soil retention, nutrient cycling, water cycling, providing of habitats, etc)
Cultural Services
The non-material benefits people obtain from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, reflection, recreation, and aesthetic experience (walking, hiking, biking, and playing sports in green spaces; tourism; inspiration for art, culture, and design; spiritual experiences; etc

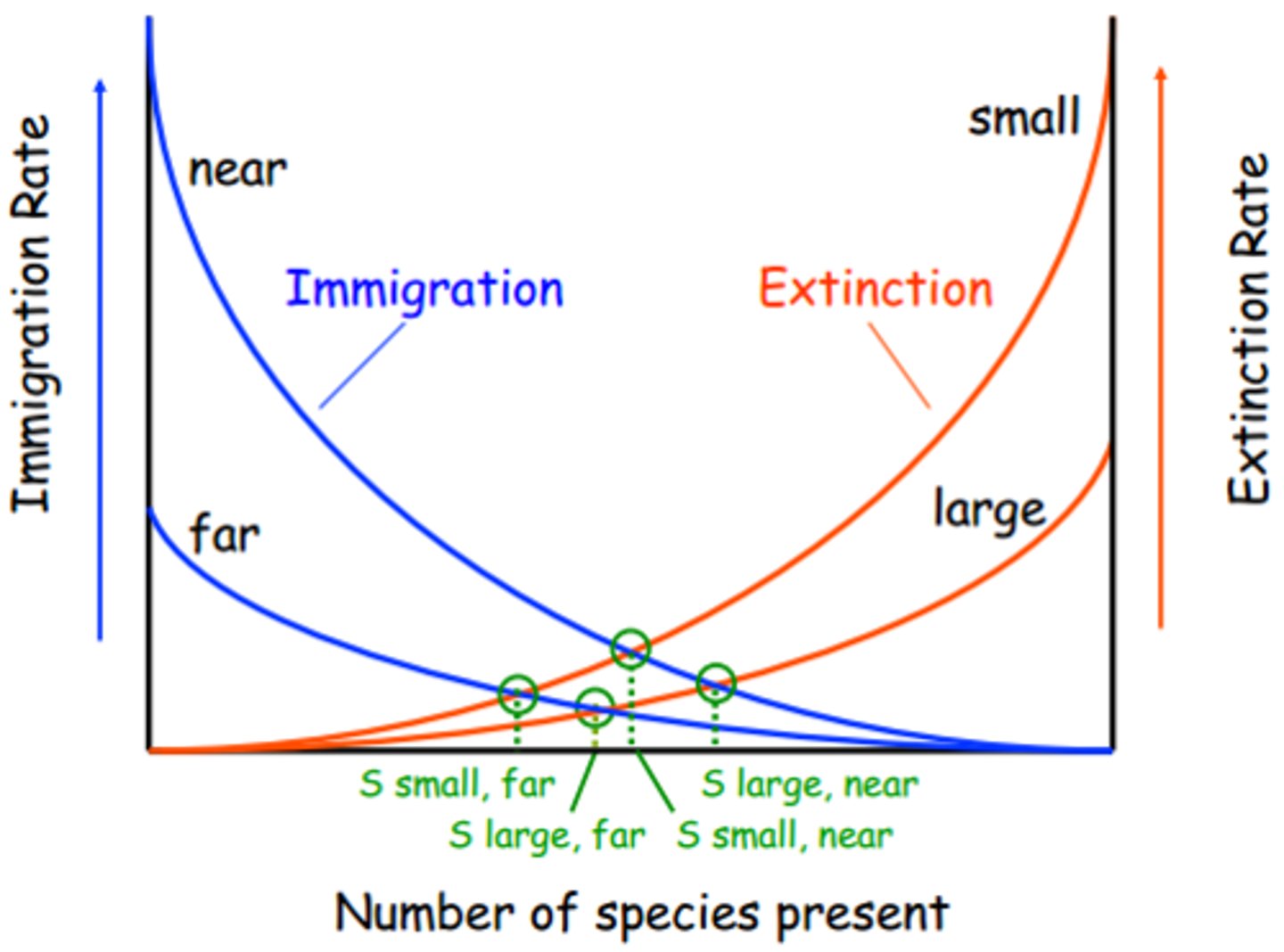
Island Biogeography
The study of how species are distributed and interacting on islands
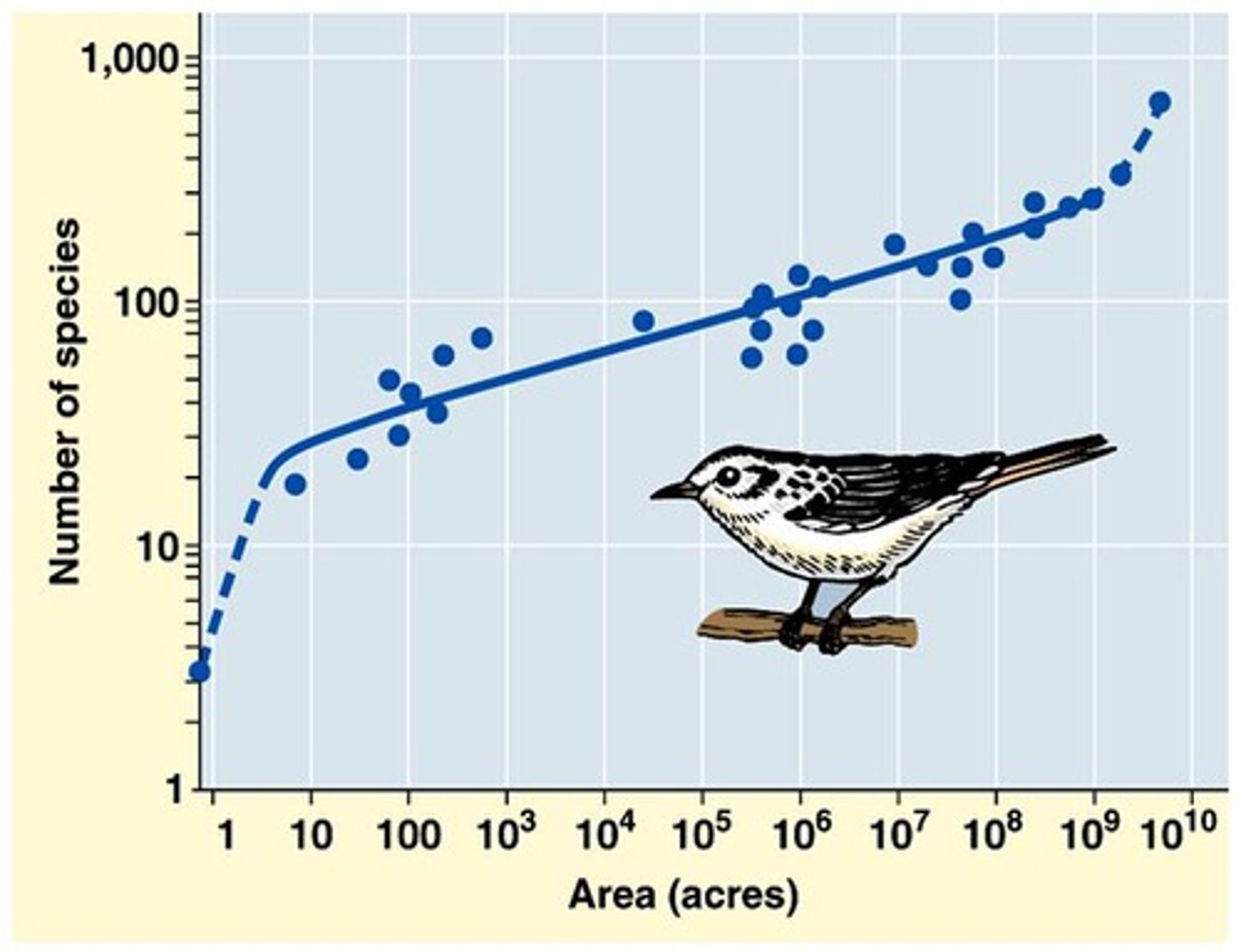
Species-Area Curve
A description of how the number of species on an island increases with the area of the island
Shannon-Wiener Diversity Index
a way of expressing the number of species in a community and each species relative abundance using a single value to determine the diversity of an ecosystem on a scale of 0-4, with zero being no diversity (i.e. a corn field), and 4 being maximum diversity (i.e. a tropical rain forest or coral reef)
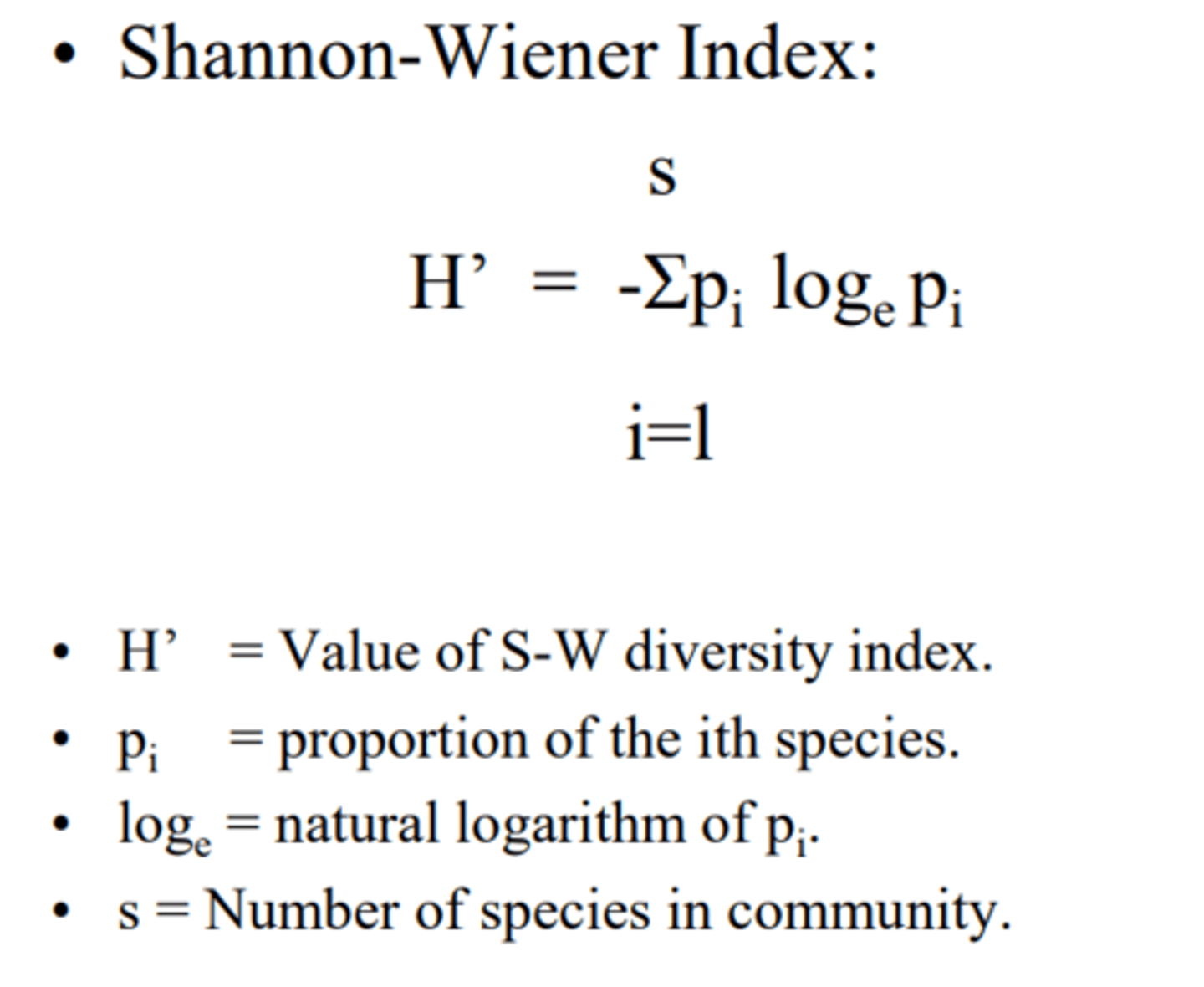
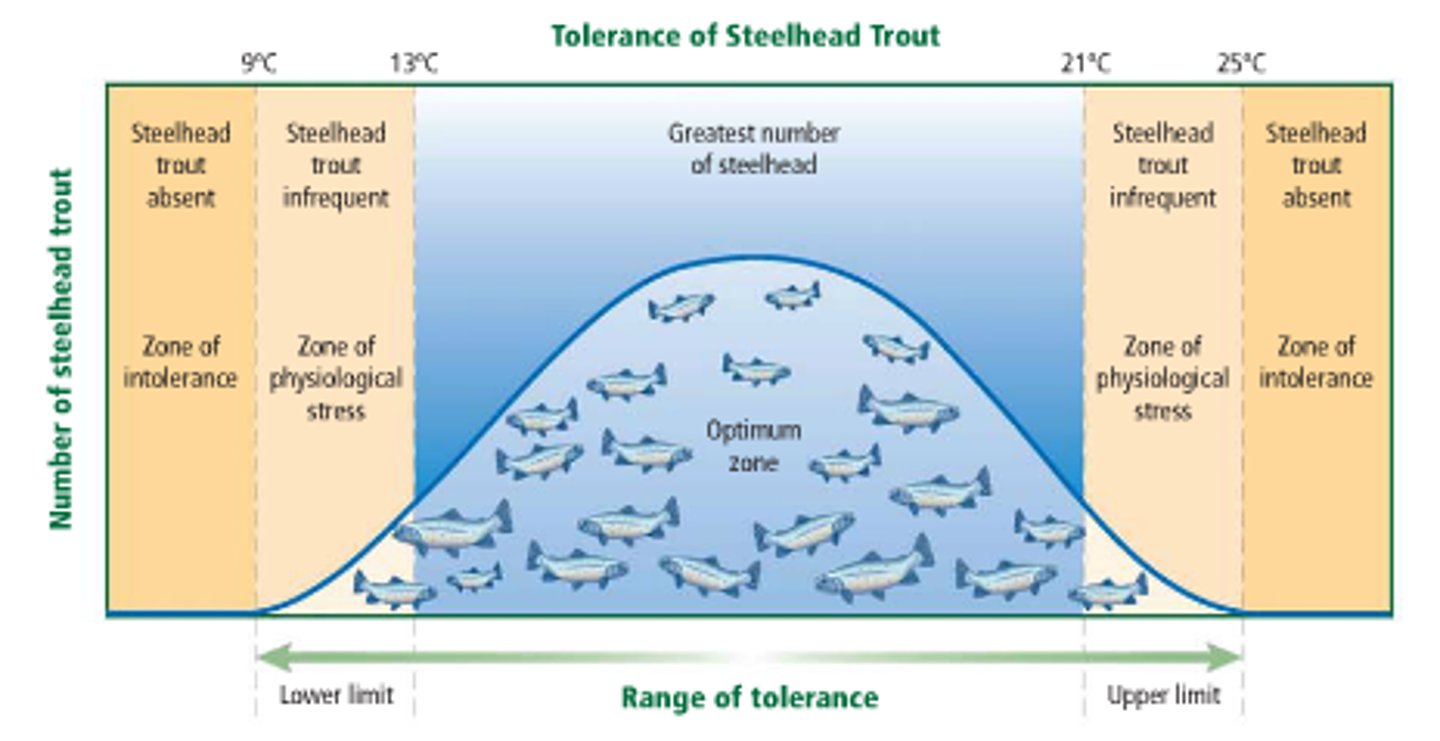
Ecological Tolerance (Fundamental Niche)
The suite of abiotic conditions under which a species can survive, grow, and reproduce
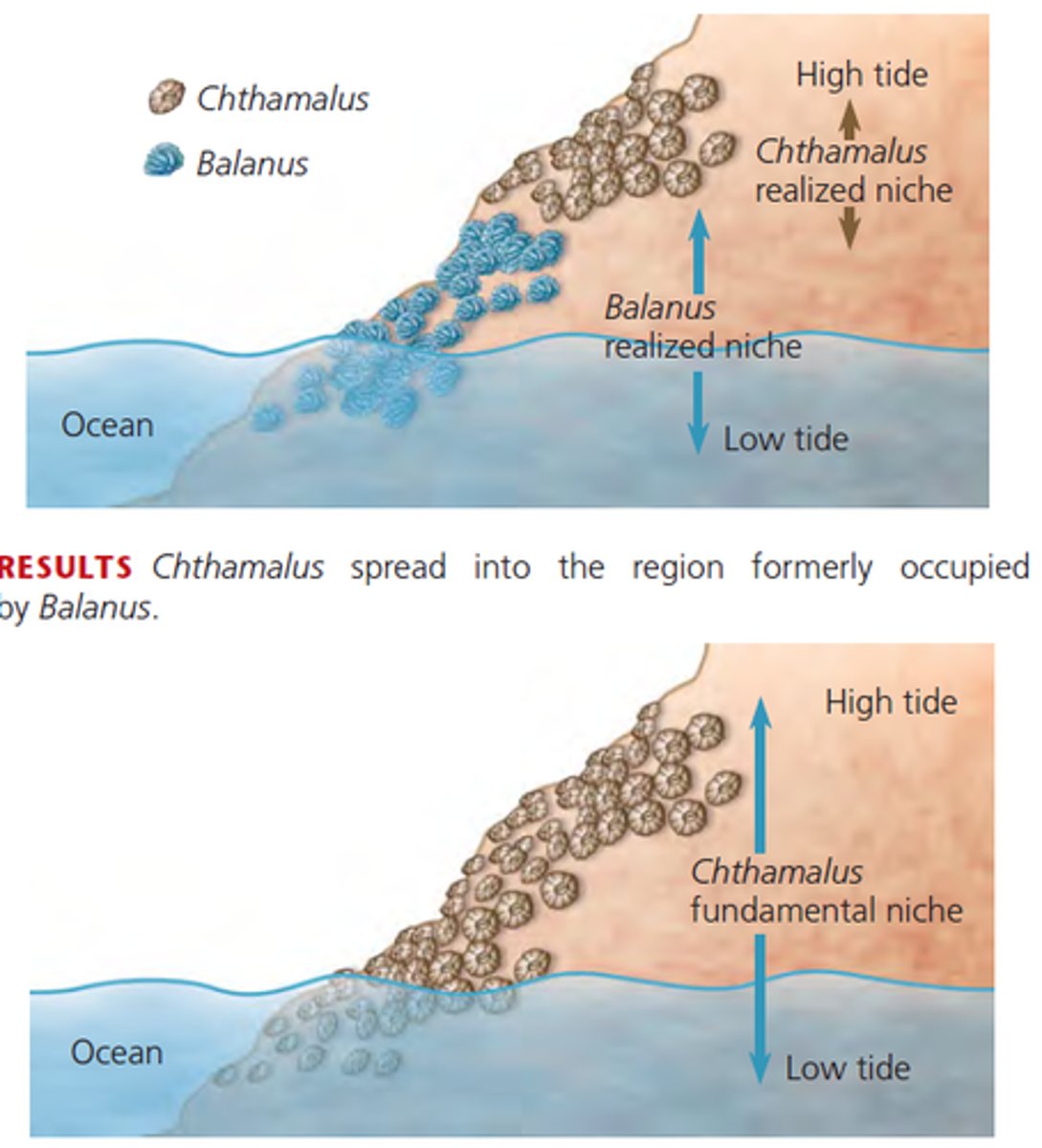
Realized Niche
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives
Geographic Range
Areas of the world in which a species lives

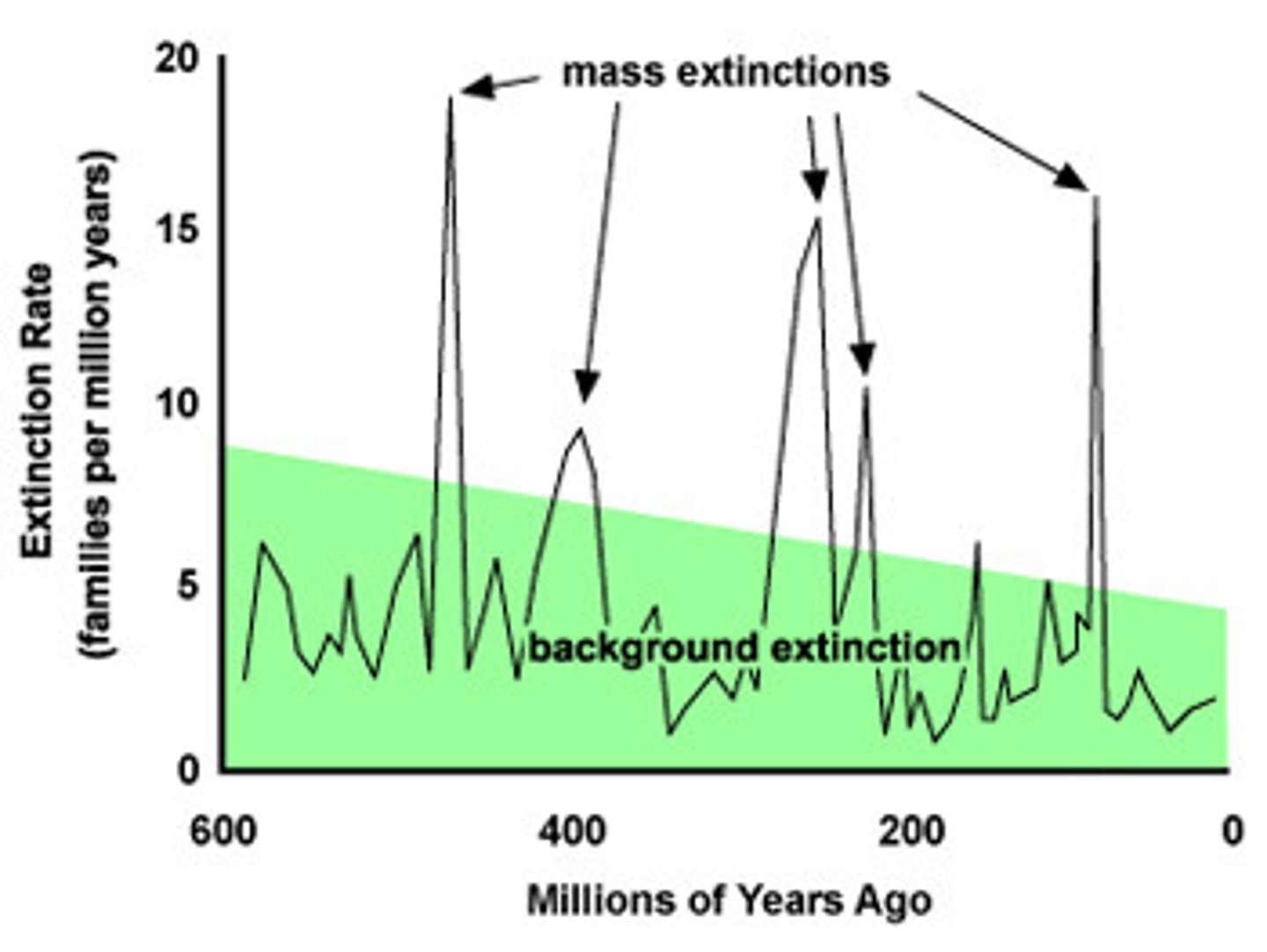
Mass Extinction
A large number of species that went extinct over a relatively short period of time
Periodic Disruption
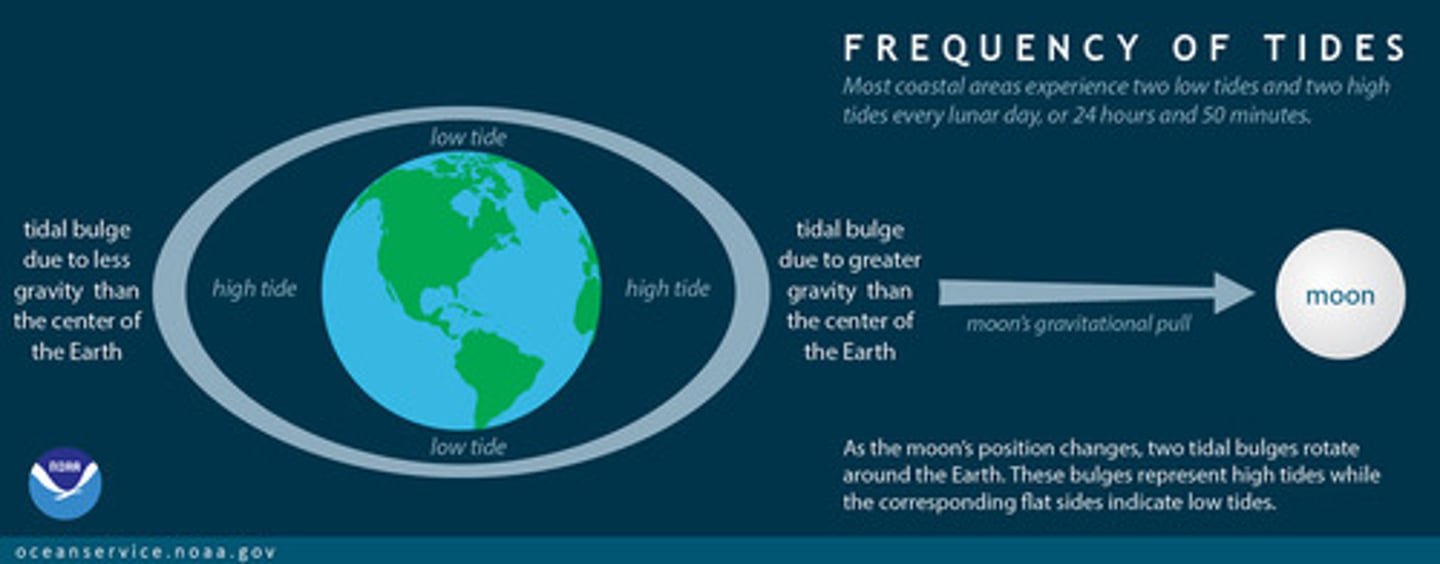
Occurring regularly, such as the cycles of day and night or the daily and monthly cycles of the moon's effect on ocean tides
Episodic Disruption
Occurring somewhat regularly, such as cycles of high rain and low rain that occur every 5-10 years
Random Disruption
Occurring with no regular pattern, such as volcanic eruptions or hurricanes

Resistance
In an ecosystem, a measure of how much disruption can affect the flows of energy and matter
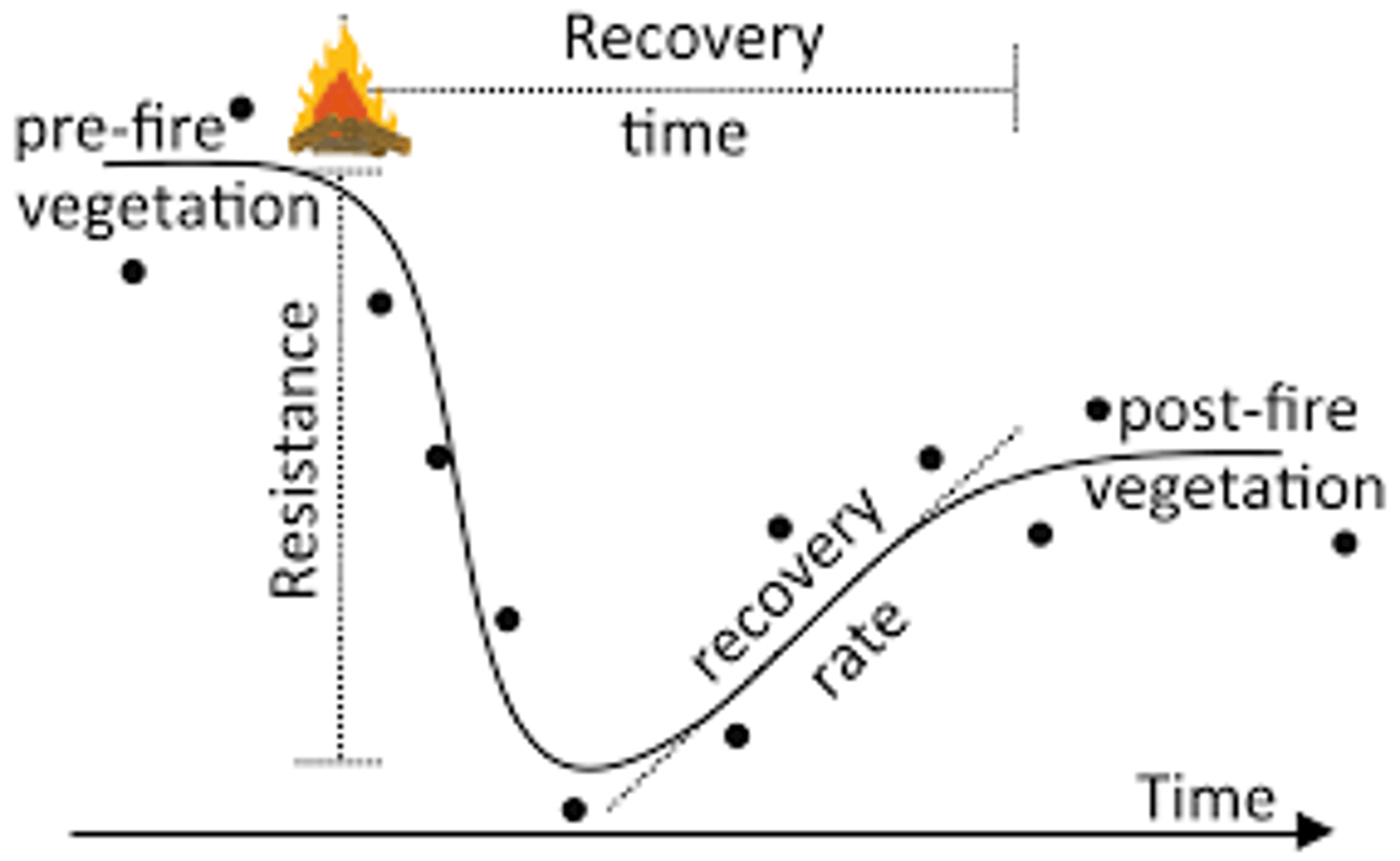
Resilience
The rate at which an ecosystem returns to its original state after a disturbance

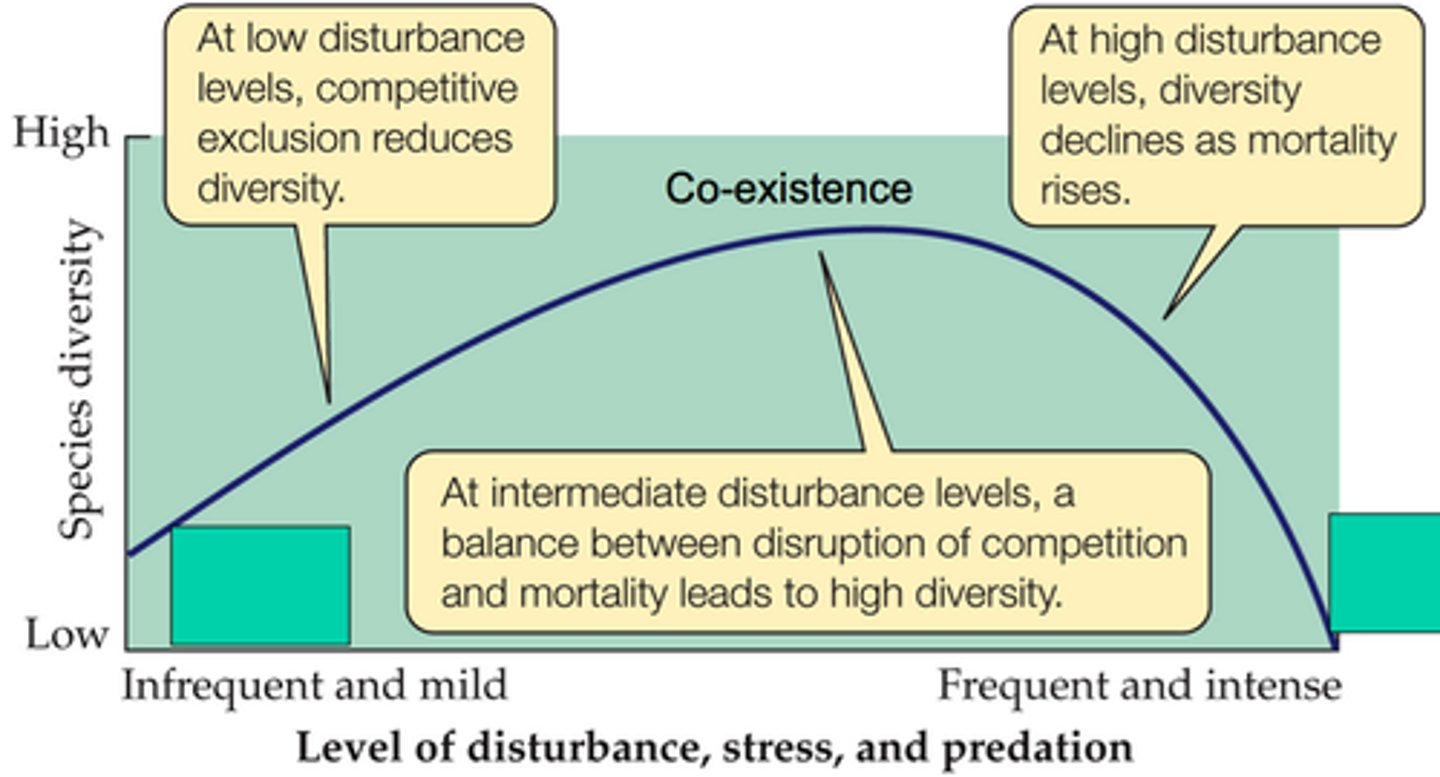
Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis
the hypothesis that ecosystems experiencing intermediate levels of disturbance will favor a higher level of diversity than those with high or low disturbance levels
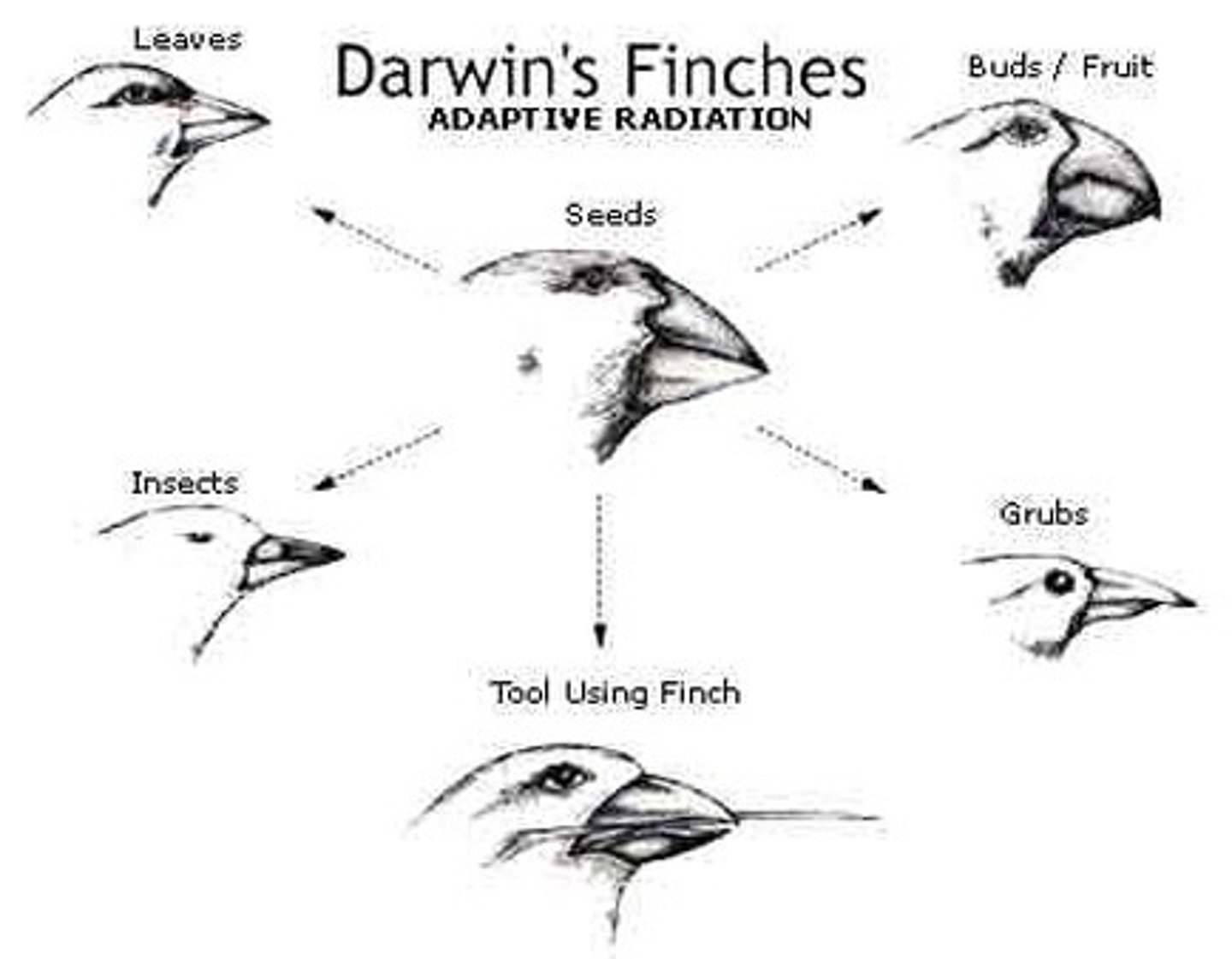
Evolution
A change in the genetic composition of a population over time
Microevolution
Evolution at the population level
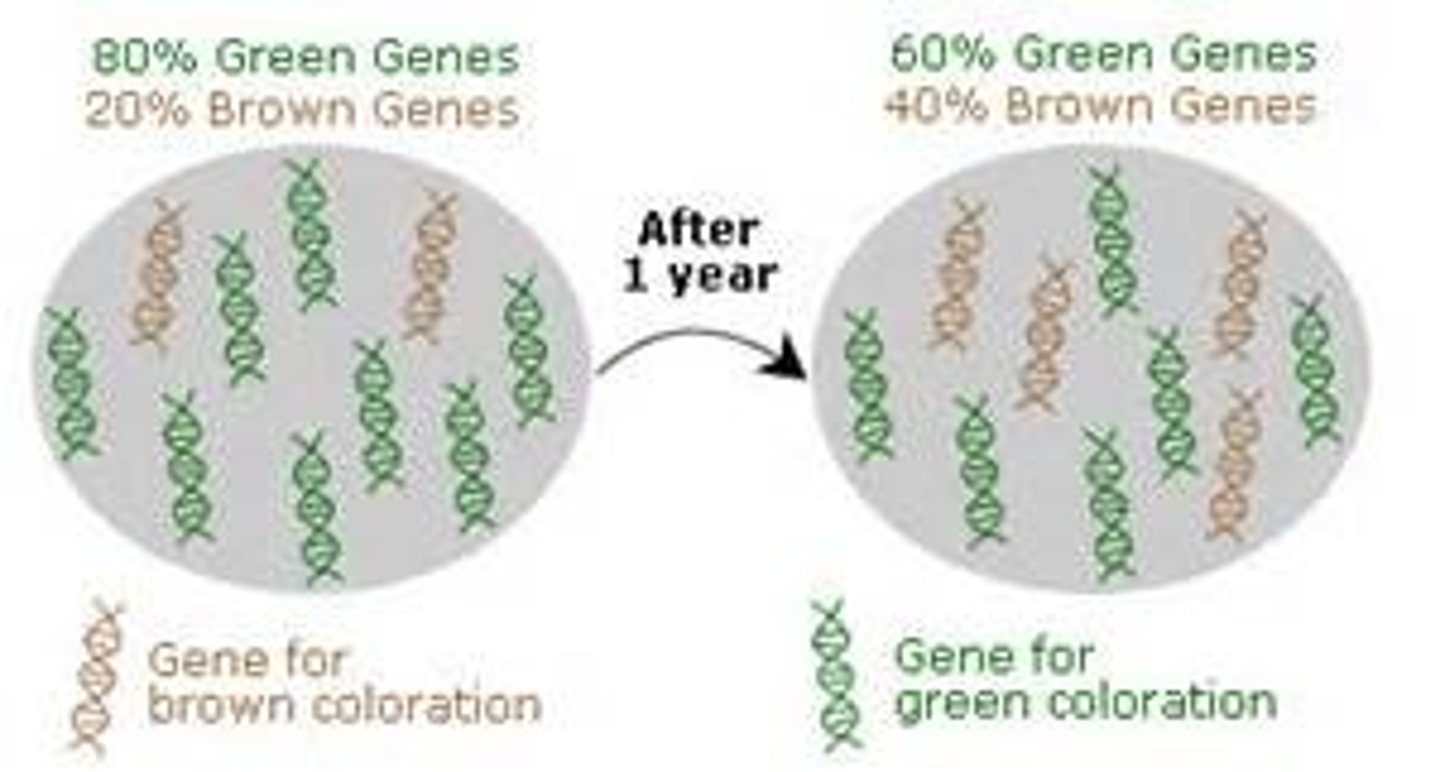
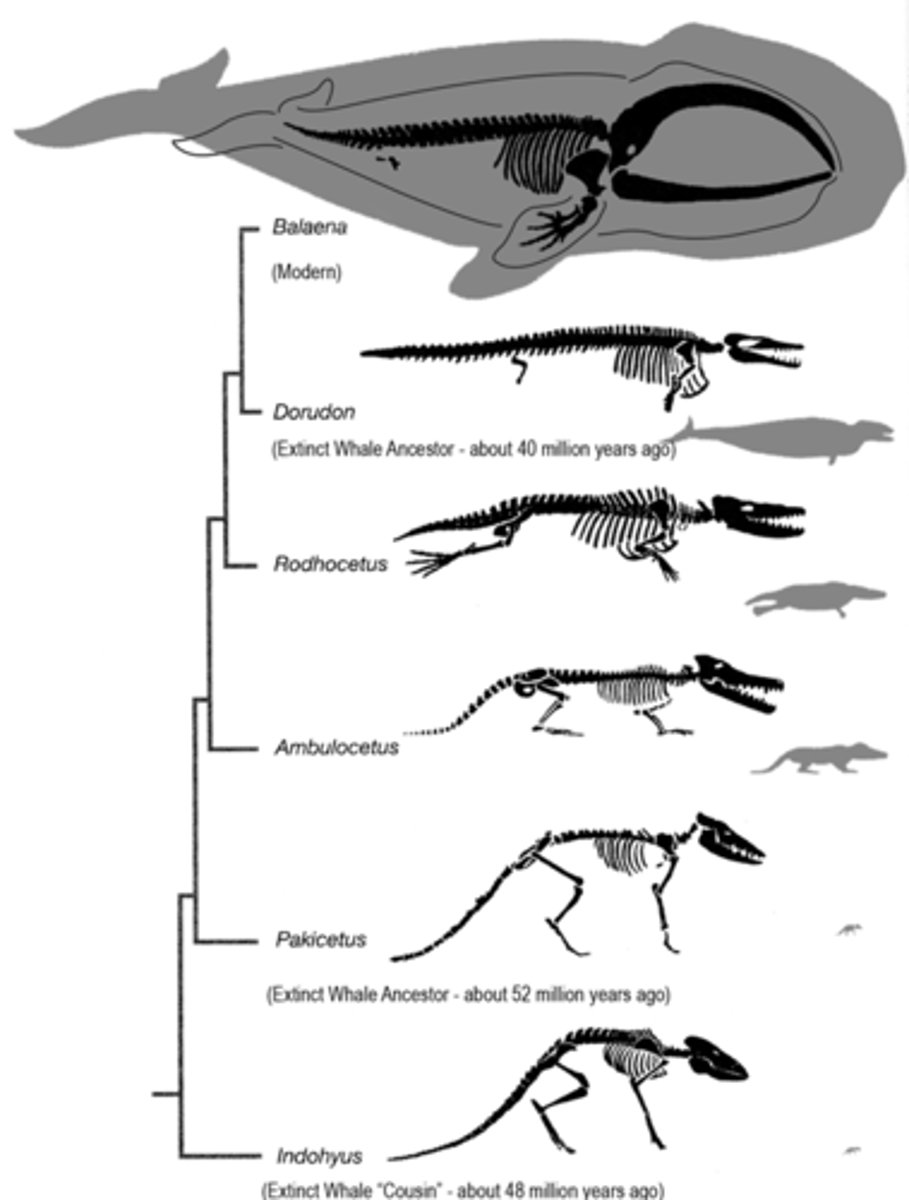
Macroevolution
Evolution that gives rise to new species, genera, families, classes, or phyla
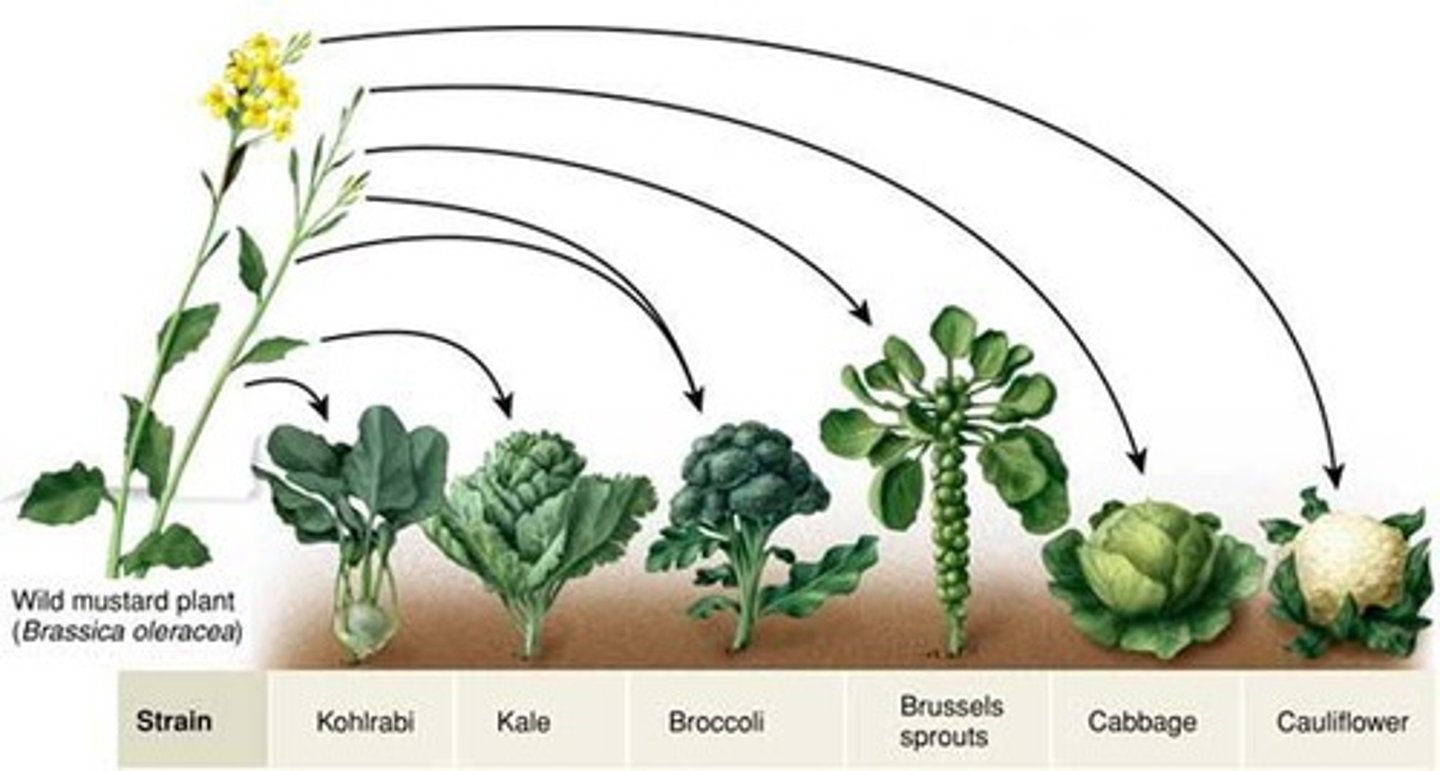
Artificial Selection
The process in which humans determine which individuals breed, typically with a preconceived set of traits in mind
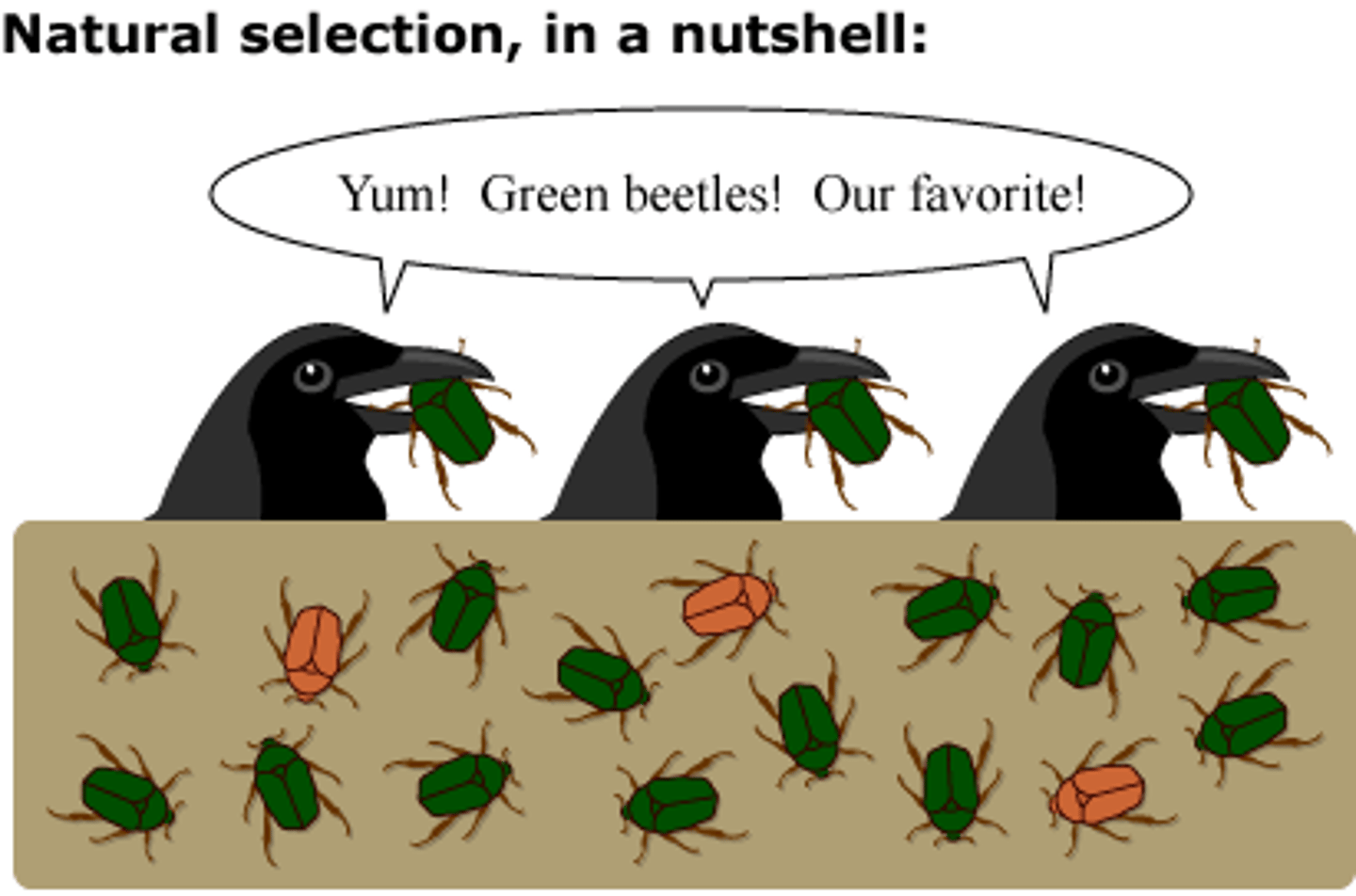
Natural Selection
The process in which the environment determines which individuals survive and reproduce
Fitness
An individual's ability to survive and reproduce

Adaptation
A trait that improves an individual's fitness

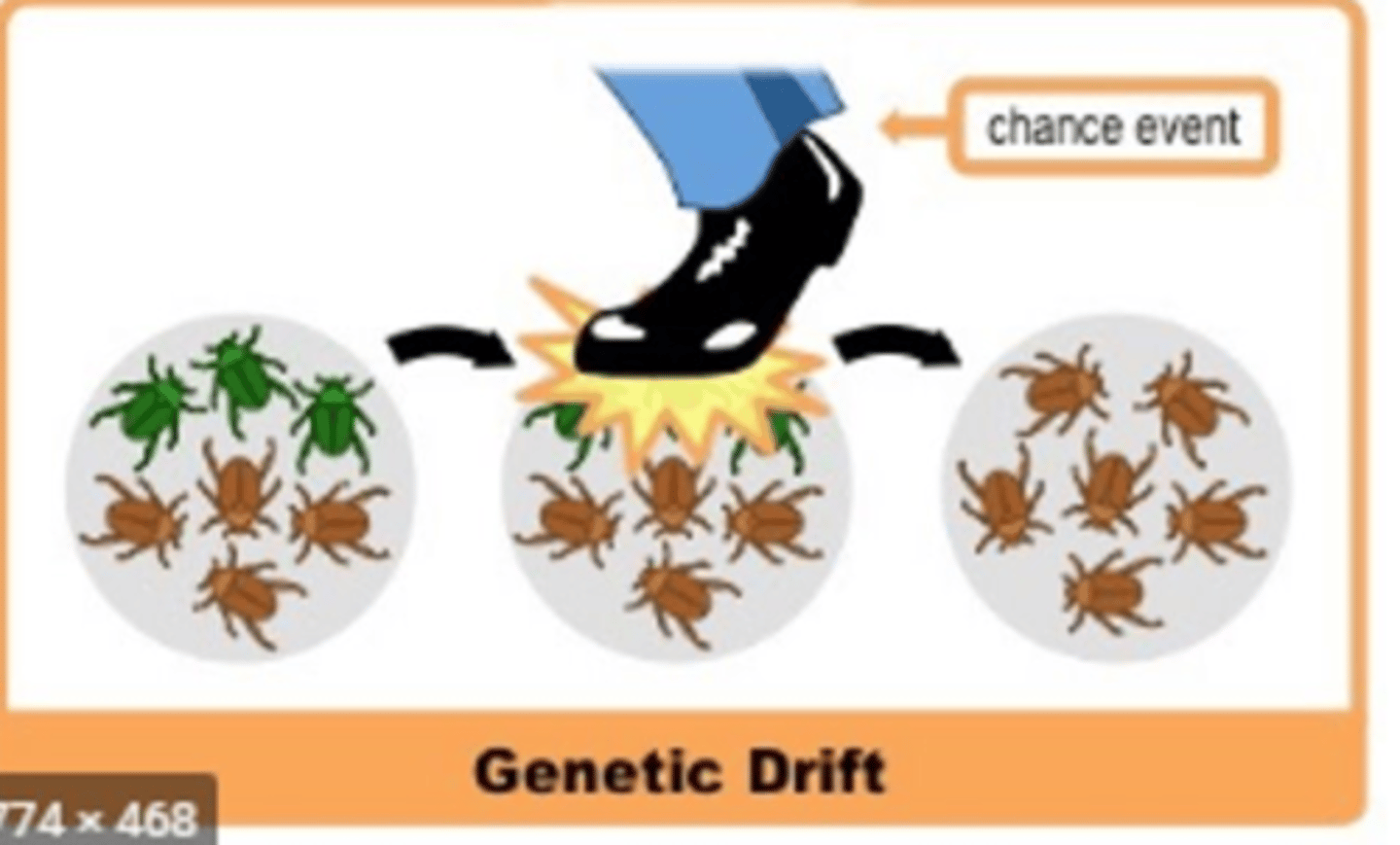
Genetic Drift
Random processes, such as natural disasters, that alter the genetic composition of a population over time, but the genetic changes are not related to differences in fitness among individuals
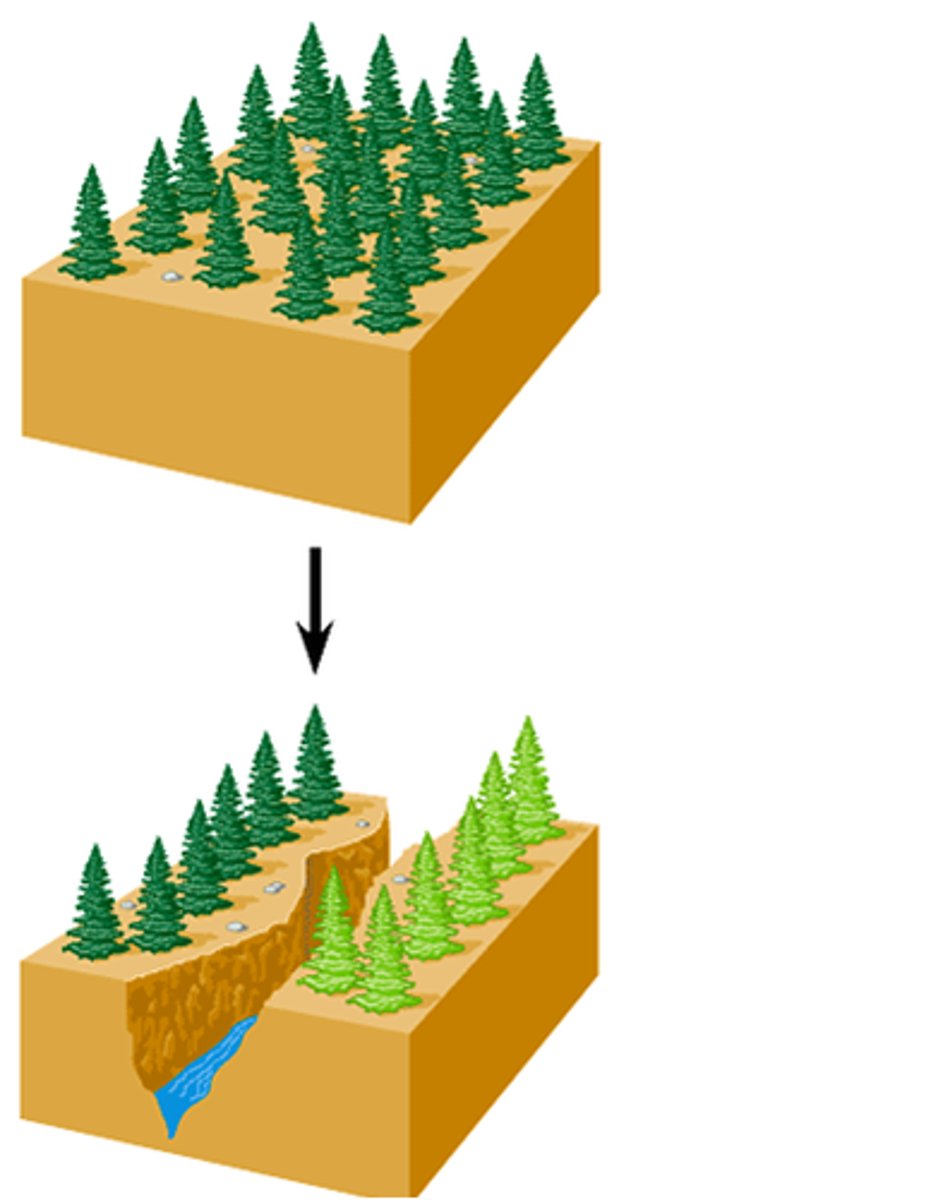
Allopatric Speciation
The process of speciation that occurs with geographic isolation
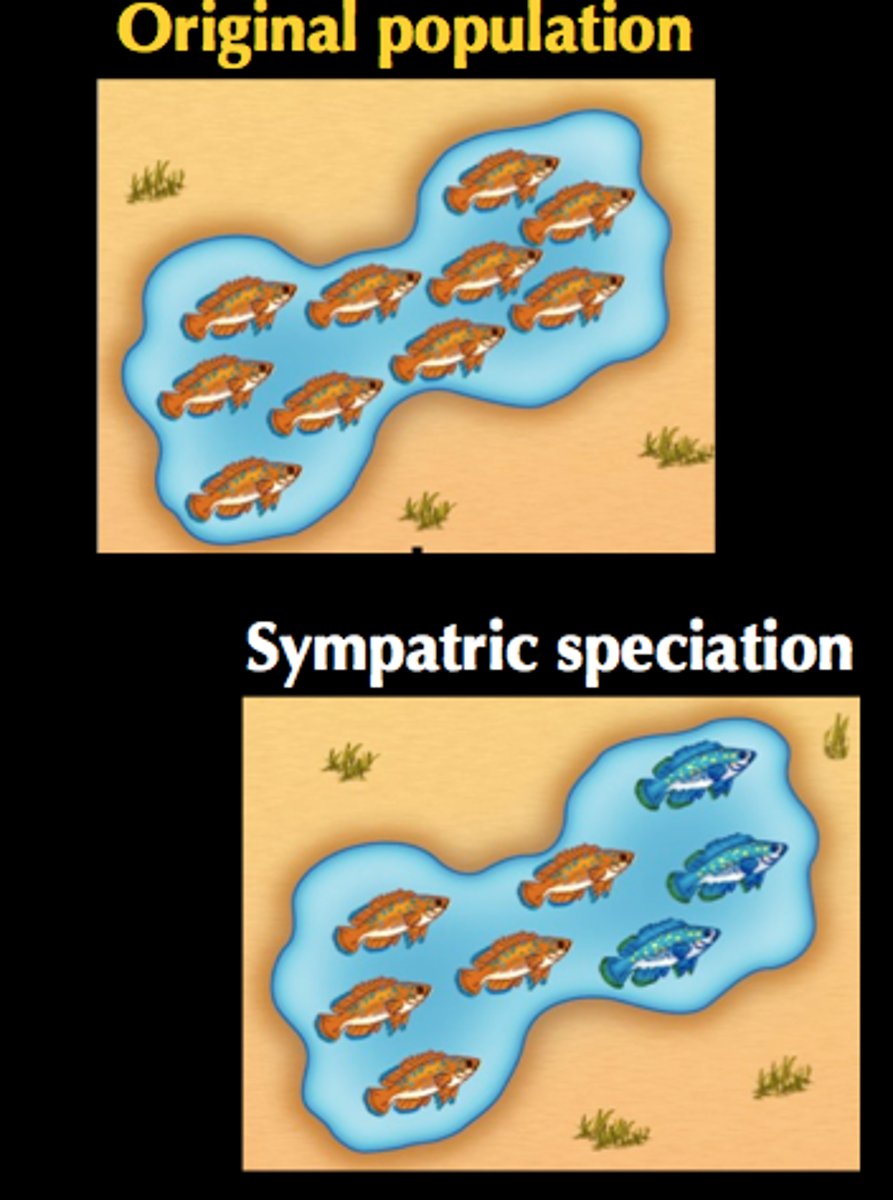
Sympatric Speciation
the evolution of one species into two species without geographic isolation
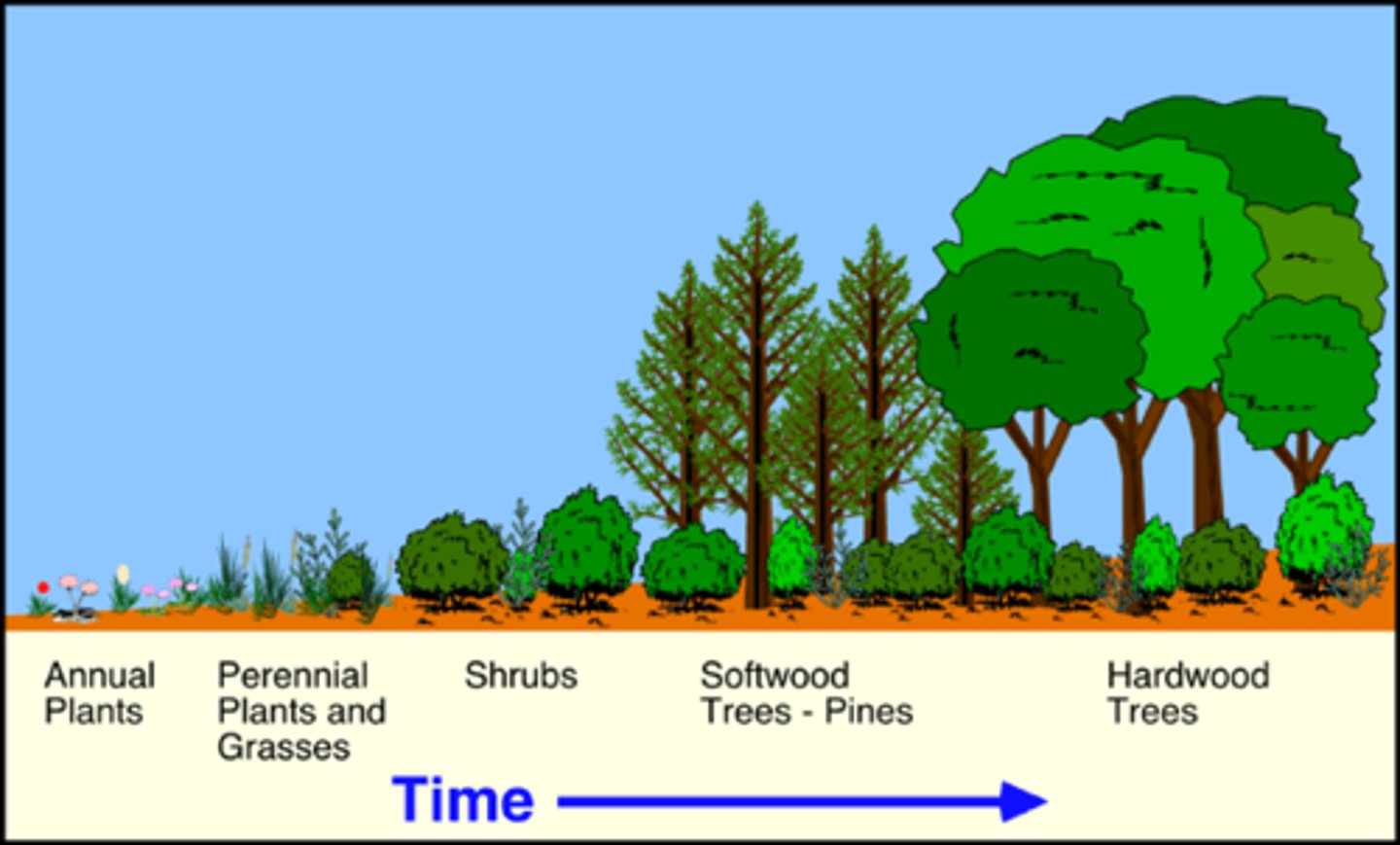
Ecological Succession
The predictable replacement of one group of species by another group of species over time
Primary Succession
Ecological succession occurring on surfaces with bare rock and no soil
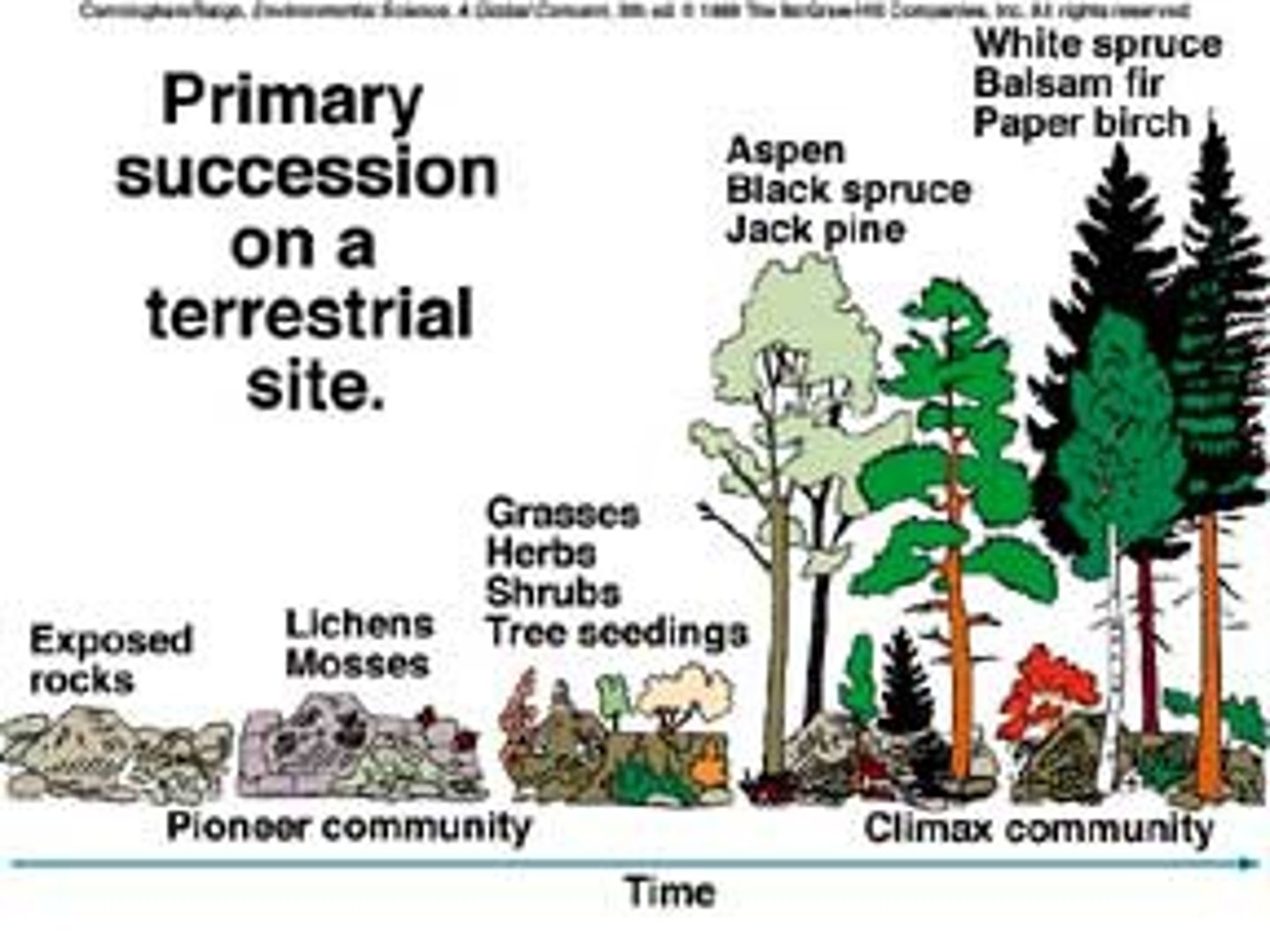
Pioneer Species
In primary succession, species that can survive with little or no soil and are the first to inhabit the exposed area (algae, lichens, mosses, bacteria, etc)

Secondary Succession
The succession of plant life that occurs in areas that have been disturbed but have not lost their soil
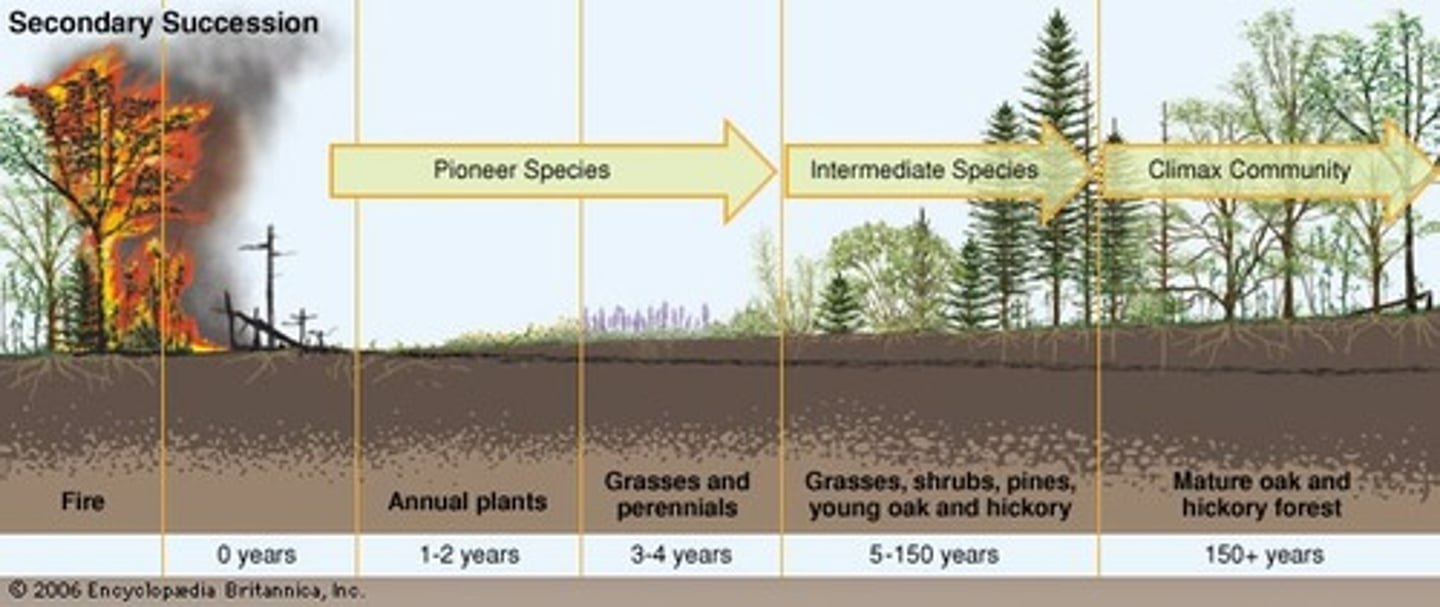
Climax Community
historically described as the final stage of succession; a stable, unchanging, "final" state of succession that will remain until a disturbance such as a fire disrupts the ecosystem
Keystone Species
A species that is not very abundant but has large effects on an ecological community

Indicator Species
A species that demonstrates a particular characteristic of an ecosystem
