Melatonin and Eicosanoids
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Sleep and wakefulness
Melatonin has a major role in regulation of ________ and ______________.
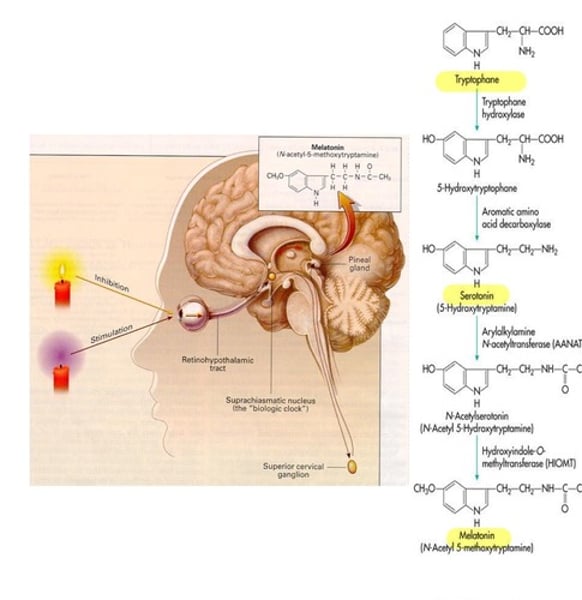
Pineal gland; 3rd
Melatonin is produced by the _________ gland, located behind the ____rd ventricle.
Tryptophan; serotonin
Melatonin is synthesized from _______________ with ____________ as an intermediate.
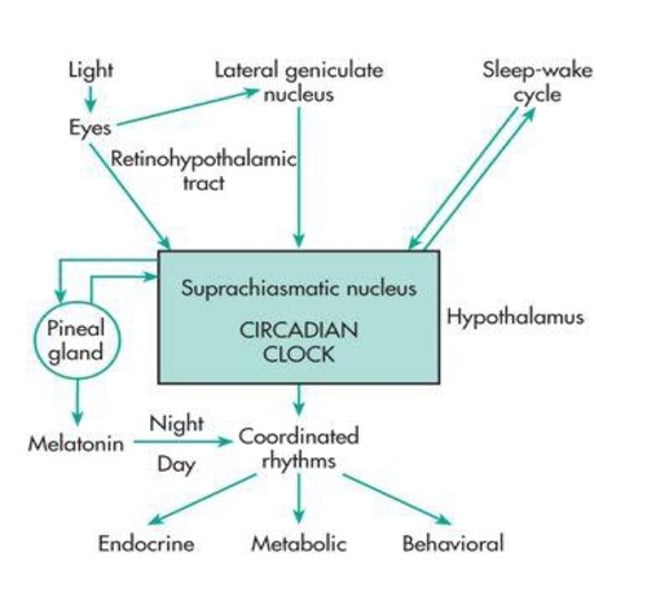
Blue light; supra-chiasmatic nucleus
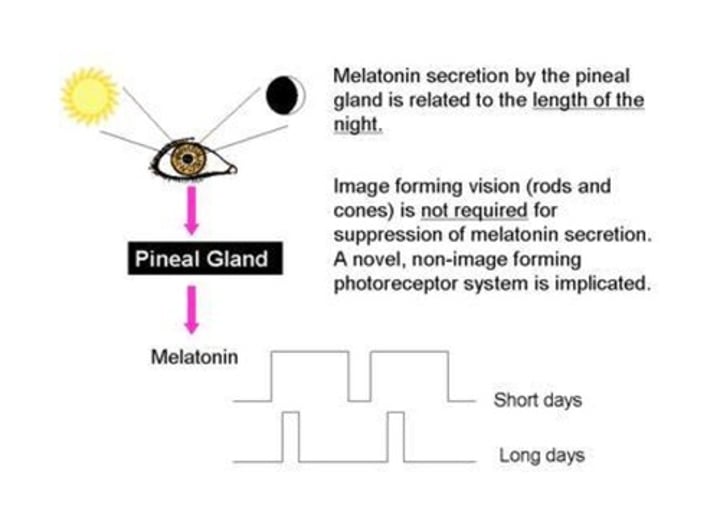
_______ light suppresses melatonin. Photic information from retina transmitted to hypothalamus and SNS via the ______-____________ nucleus, then to pineal gland.
Light; darkness
Secretion of melatonin is regulated and inhibited by __________, but stimulated by _____________.
Norepinephrine; beta-adrenergic
Melatonin is stimulated by darkness by retinal photoreceptors releasing ________________, which activated _______-adrenergic receptors in the pineal gland.
Serotonin
The activation of beta-adrenergic receptors in pineal gland cause ______________ to be converted to melatonin.
Hyperpolarized; Blind
Melatonin is inhibited by light by retinal photoreceptor cells becoming ________________, which inhibits release of norepinephrine. _________ can still have light-induced suppression of melatonin as long as light is coming through their retina.
Supra-chiasmatic nucleus
Circadian rhythm of melatonin secretion is controlled by an endogenous pacemaker in the _______-______________ nucleus.
Lighting; modify; suppress
Environmental ___________ alters timing of circadian rhythm. Day-night cycles can ___________ rhythm. Brief pulses of light ____________ melatonin.
2-4 AM
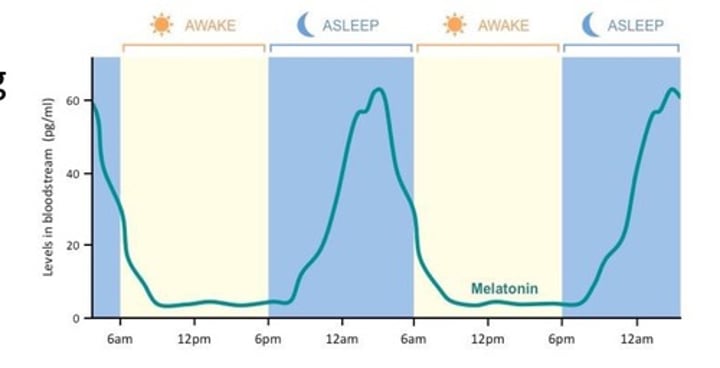
Secretion of melatonin usually begins at dusk and peaks at ___-___ AM.
Time zones; night-shift
Shifts in melatonin secretion after flights across ______ zones and in ________-shift workers.
1-3 years old; declines
Melatonin increases until __-__ years old in humans, then it _____________.
MT1 and MT2
Melatonin activates ______ and ______ receptors, which are G-protein coupled receptors.
Reproduction
Melatonin regulates/affects sleep, circadian rhythm, mood, sexual maturation and ________________, and aging.
Anti-inflammatory
Melatonin may have ______-______________ effects on immune system. Results in immunocompetent cells with a high affinity for melatonin receptors.
Cancer; enhances
May have beneficial effects on __________, since removing pineal gland ____________ tumor growth.
Damage; free radicals
Melatonin affects aging by decreasing cell ____________ due to free ____________.
Speed; duration/quality
Melatonin affects _________ of falling asleep and _____________/__________ of sleep.
Mood; depression
Abnormal circadian rhythms implicated in _______ disorders. Can cause ____________ and seasonal affective disorder.
Bright-light
___________-_________ therapy can decrease depression and help SAD.
Reproductive; increases
Hours of darkness/season linked to _______________ activity. Melatonin _______________ during long winter nights.
GnRH; estrous
When melatonin decreases, ________ starts to increase, causing more __________ cycles.
Puberty; pituitary-gonodal axis
Decreases in melatonin at ____________. Melatonin decrease activates the pituitary-____________ axis.
Ovarian; progesterone
Melatonin may affect sex steroid hormone synthesis and modulate ___________ function. Melatonin receptors on ovaries stimulate progesterone synthesis.
Alopecia X; decrease
Melatonin is used to treat __________ ___ in dogs because it may _____________ GnRH, which decreases LH/FSH effects on adrenal androgen precursors.
Anxiety and seizure activity
Melatonin decreases ____________ and ____________ activity.
Sedation and incoordination
Short-term side effects of melatonin are minimal and include ____________ and __________________.
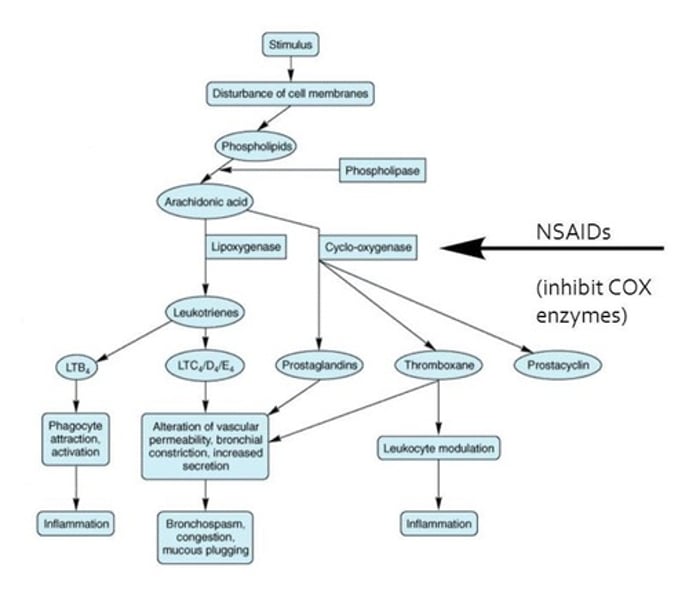
Eicosanoids
What is the group of signaling molecules synthesized by oxidation of 20-carbon essential fatty acids (EFA)?
Inflammatory
When consuming EFAs in diet, they affect _____________ pathways.
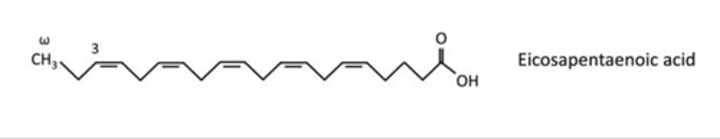
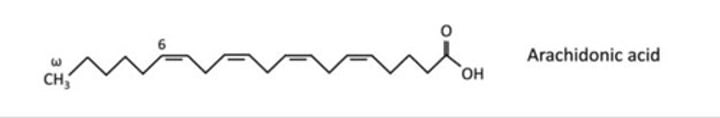
Arachidonic acid and Eicosapentaenoic acid
What are the 2 precursors of Eicosanoids?
Actions
Balance between each type of eicosanoids (omega-3 and omega-6) determines actions.
Less inflammatory
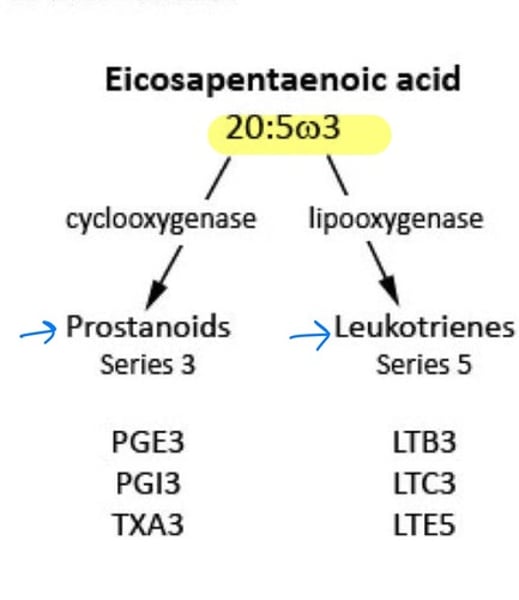
Omega-3 EFAs yield eicosapentaenoic acid, which is ______ inflammatory.
Pro-inflammatory
Omega-6 EFAs yield arachidonic acid, which is ______-inflammatory.
PG
Eicosanoids have a 2 letter abbreviation = _____
PGE
Eicosanoids have one A-B-C letter = ______
PGE2
Eicosanoids have a subscript indicating number of double bonds = _______
5; 3; 5
Omega-3 FAs yield eicosapentaenoic acid (has ___ double bonds) and contains prostanoids with ___ double bonds and leukotrienes with ___ double bonds.
4; 2; 4
Omega-6 FAs yield arachidonic acid (has ___ double bonds) and contains prostanoids with ___ double bonds and leukotrienes with ___ double bonds
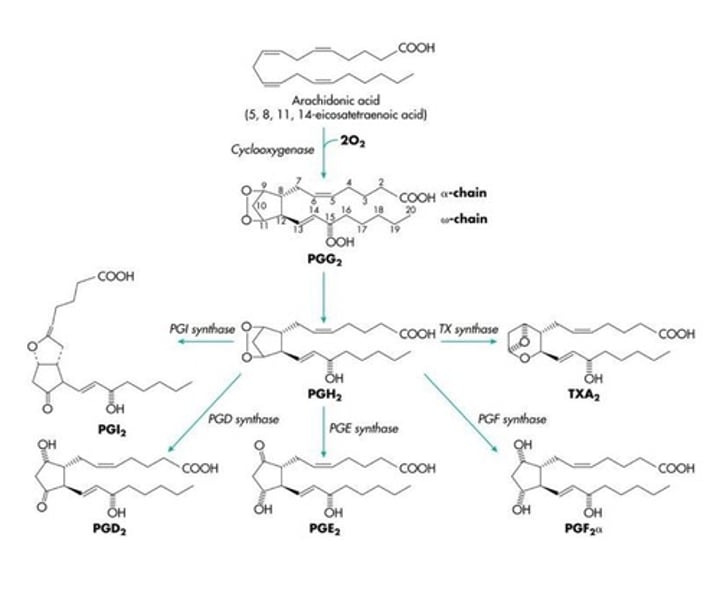
Cyclopentane ring
Prostaglandins A-I differ in substituents on the ______________ ring.
a,B-unsaturated ketones
PGAs are a,B-________________ ketones.
B-hydroxyl ketones
PGEs are B-____________ ketones.
1,3-diols
PGFs are 1,3-_______.
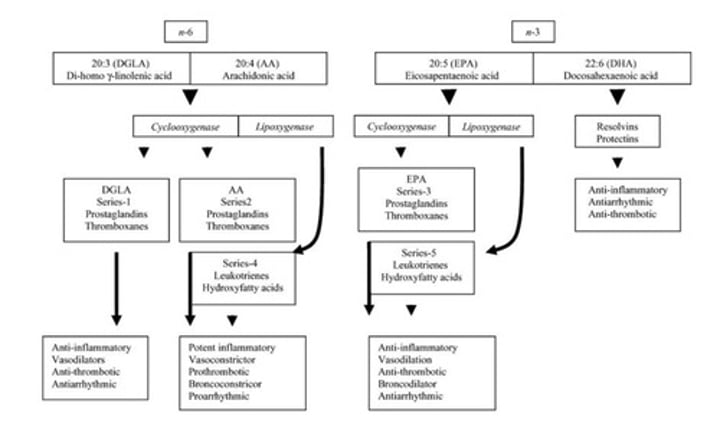
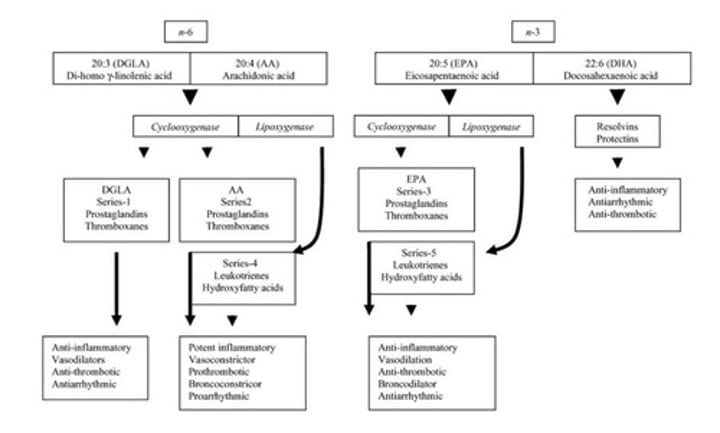
Lessen; arachidonic acid
Major function of EPA cascade is to ____________ inflammatory effects of ______________ acid prostanoids.
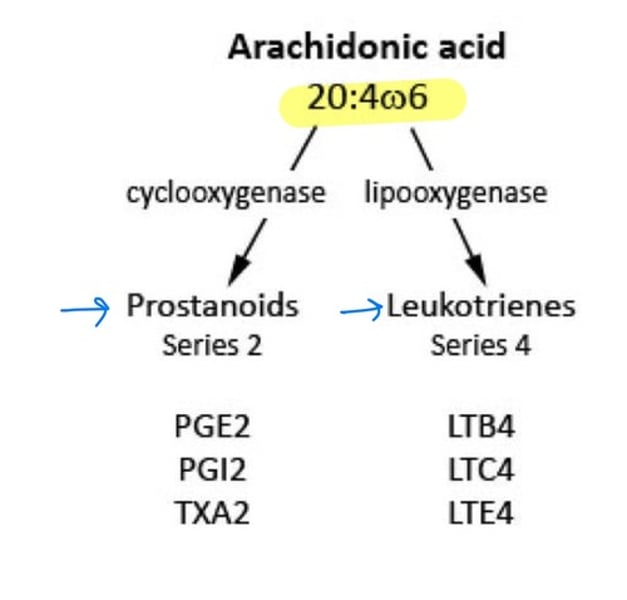
Prostaglandins (PG), prostacyclins (PGI), thromboxanes (TX)
What are the 3 prostanoids in the AA cascade?
Leukotrienes (LT) and Lipoxins (LX)
AA cascade also contains what other 2 substances?
Stimulate; inhibit
Overall effects of AA cascade are to ____________ inflammatory responses, modulate pain and fever, reproductive functions, __________ gastric acid secretion, blood pressure regulation, and platelet activation/inhibition.
Cats; delta 6-desaturase
________ can't convert linoleic acid to arachidonic acid due to low _________ __-_____________ enzyme.
Omega-3; prostanoids
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) cascade is formed from ___________-___ EFAs and form mostly _______________.
Phospholipase A
What releases arachidonic acid from phospholipids in cell membrane?
COX1 and COX2
Arachidonic acid will be oxygenated by cyclooxygenase (_________ and _________) to make prostanoids.
Omega-6
Arachidonic acid (AA) cascade is formed from ____________-____ FAs.
5LOX
Arachidonic acid will be oxygenated by lipooxygenase (________) to make leukotrienes.
Short; inflammation
Major actions of prostanoids derived from arachidonic acid: Local hormones with autocrine or paracrine action, ________ half-life (seconds to minutes), mediated by specific receptors, mediate _________________ (except for lipoxins).
PGE2
What prostanoid derived from arachidonic acid controls smooth muscle contraction, brochoconstriction, pain, heat, and fever?
PGI2
What prostanoid derived from arachidonic acid controls vasodilation and inhibits platelet aggregation?
Linoleic acid (18 C EFA) and Gamma linolenic acid
What are the 2 dietary precursors of arachidonic acid?
TXA2
What prostanoid derived from arachidonic acid controls vasoconstriction and stimulates platelet aggregation?
Inhibit; decrease
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ___________ prostanoid formation, and therefore ___________ inflammation, redness, swelling, pain, and heat.
Firocoxib (Previcox), deracoxib (Deramaxx), meloxicam (Metacam), piroxicam (Faldene), celecoxib (Celebrex)
What 5 NSAIDs inhibit only COX2 and have less side effects?
Aspirin, carprofen (Rimadyl), flunixin (Banamine), phenylbutazone, ibuprofen, naproxen
What 6 NSAIDs inhibit COX1 and COX2?