Chem 7L Final Exam Experiments 1-5 Review
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Limiting and excess reagents for Expt 2?
Al^(3+) served as the limiting reagent while 8 hydroxiquinoline (3hq-) was the excess reagent. For every 1 Al^(3+) theres 3 hq- moles (Expt 2)
Purpose of NH4CH3COO in Experiment 2?
Ammonium Acetate acts as a buffer to maintain the PH of 4, preventing unwanted side products like Al(OH)3
Additionally, it helps bind hq ligand to Al3+ by solubilizing it
Expt 2 Precipitation for 15 minutes instead of 1 hour, what does it do to Al^(3+) concentration?
Al^(3+) concentration is artificially lower, starting material couldn’t react in time to make precipitate, decreasing yield;(experimental/theoretical)*100, and keeping some Al^(3+) in the solution.
Gravimetric Analysis Experiment 2
Quantitive analysis of mass, by converting a soluble analyte to an insoluble product.
Experiment 3 reasons for a lower molecular weight of unknown acid?
Excess NaOH titrant inputted, leading to darker endpoint color
Molecular weight acid is inversely proportional to moles of NaOH titrated
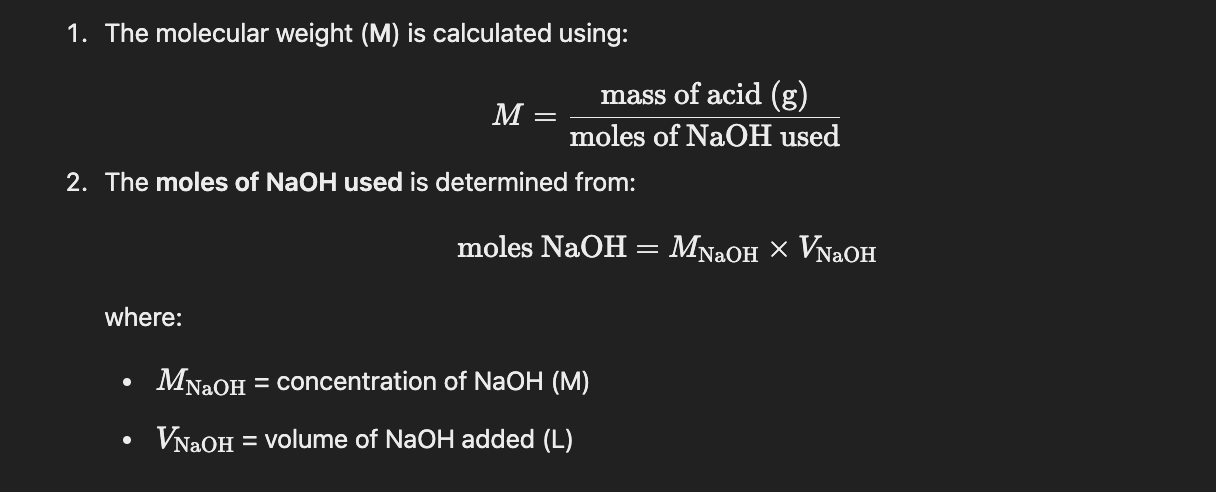
How did we select the right indicator for the weak acid strong base titration NaOH into KHP in experiment 3?
NaOH into KHP titration has PH greater than 7 @ equivalence point, therefore pKa of indicator should be greater than 7 to signal at endpoint
Initial ph of weak acid is irrelevant
What were the starting materials and desired products for experiment 2?
Starting material; Aluminum Nitrate
Desired product; Aluminum 8 hydroxyquinoline
Goal; find Al^(3+) concentration from the formed precipitate
In Experiment 3 you have 200mg unknown acid inside 80mL h20(l), where you dispense 4mL NaOH to reach endpoint. Find mass of acid for 16mL of NaOH?

Ratio of new/old for grams of acid then ml of titrant NaOH.
What leads to a low pKa in experiment 3?
If you titrate a weaker acid (higher pKa), the equivalence point pH will be higher.
If you titrate a stronger acid (lower pKa), the equivalence point pH will be lower.
The equivalence point volume depends on the initial concentration of the acid and NaOH used, not on pKa. (M1V1)=(M2V2)
½ the way to eq point ph=pka, [HA]=[A^(-)]
pKa=1/2 volume NaOH towards eq point
Experiment 4’s limiting and excess reagents for green product?

Oxalate acts as a binding ligand
Hydrogren Peroxide oxidizes Fe²+ to Fe³+
Experiment 5 Uranium emitting photons, identify the transition that has the smallest wavelength.
Ex) ni=4,nf=2 takes MORE energy than ni=2,nf=4 or ni=2,nf=5 |
The higher you go during energy transitions the smaller the wavelength
λ(v)=C

-Ethanol is a poor solvent therefore, products can precipitate and impurities dissolve
-Heating increases solubility to dissolve sample in solution
-2 days allows SLOW cooling and pure crystal formation
(Expt 4) You mistakenly add water to green crystal solution instead of sodium acetate 4.7 pH buffer, causing bpy bidenate ligand to not bind to Iron. What are some functions this buffer would’ve served?
-Preventing Fe²+ from oxidizing to Fe³+
-Induces bpy and Fe²+ binding to form complex
Due to accidental water addition mass % iron would be low due to Fe²+ ions failing to bind, lowering absorbance
(Expt 4) Green crystals dissolved in water, you add sulfuric acid, calcium chloride and make it a precipitate. Whats the precipitate and supernatant?
Crystals in water releases Fe² and oxalate ions
H2SO4 Sulfuric acid; solubilizes Fe²+, liquifying it
Calcium chloride forms calcium oxalate precipitate
Supernatant; Fe²+, Precipitate; CaC2O4
Expt 4 Calibration Curve Recap
y-int was near zero
x axis was iron concentration
y axis was absorbance of iron
Which has more spectral emission lines hydrogen or helium and why?
-Spin states of helium are more than that of hydrogen
-Quantum number support for hydrogen is higher because of that extra electron
-Shielding of the electrons in helium leads to more spectral lines
-Helium supports triplet and singlet state and hydrogen supports singlet only
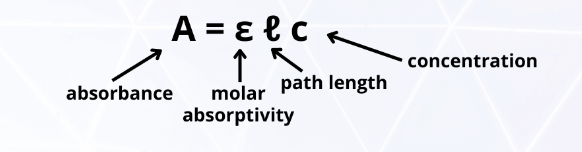
Absorbance and % T proportionality
Abs↑ %T↓
Pathlength and %T proportionality
Pathlength↑ %T↓
At ½, 2/3, 1/3, eq point identify pKa equation
½ eq point pka=ph
1/3 eq point pka=ph-log(0.5)
2/3 eq point pka=ph-log(2)