Functional Human Anatomy Exam 2 Material
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
Cervical Plexus
innervates neck & diaphragm
nerve roots from C1 to C4 (sometimes contribution from C5) spinal nerves
Brachial Plexus
innervates pectoral girdles & upper limbs
nerve roots from C5 to T1 spinal nerves
Lumbar Plexus
innervates lower limb & pelvic girdle
nerve roots from T12 to L4 spinal nerves
Sacral Plexus
innervates lower limb & pelvic girdle
nerve roots from L4 to S4 spinal nerves
Nerve Plexus
network of nerves originating from ventral rami of the spinal cord (branches that extend from the spinal nerves after they emerge from the spinal cord)
Spinal Nerve Groupings
8 pairs of cervical spinal nerves
12 pairs of thoracic spinal nerves
5 pairs of lumbar spinal nerves
5 pairs of sacral spinal nerves
1 pair of coccygeal spinal nerves
31 pairs total
Spinal Nerve Components
dorsal and ventral roots come together to form a spinal nerve, which further splits into a dorsal ramus & a ventral ramus
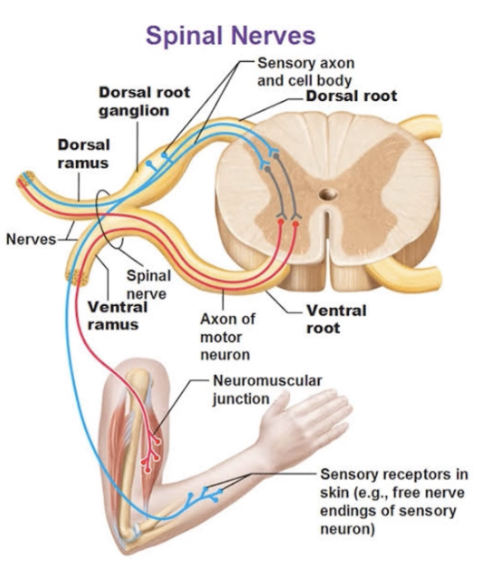
Dorsal Root Fibers
only sensory incoming fibers
Ventral Root Fibers
only motor outgoing fibers
Dorsal Rami
takes in sensory signals from skin of your back & sounds out motor signals for back muscles
sends fibers to and from skin of back, deep back muscles, and joints between adjacent vertebrae
Ventral Rami
take in sensory signals from everything besides skin of back & sends out motor signals to all plexuses
Type of Fibers in Spinal Nerve
both sensory & motor
remember that a spinal nerve is formed from ventral & dorsal roots combining
spinal nerve divides laterally into dorsal & ventral rami
Rami Fibers
both ventral and dorsal ramis have sensory AND motor fibers
it is the roots that only have one of each (dorsal = sensory & ventral = motor)
Plexuses are nerves formed by?
ventral rami of our spinal nerves
Nerves from Cervical Plexus
Lesser Occipital Nerve
Ansa Cervacalis
Greater Auricular Nerve
Transverse Cervical Nerve
Phrenic Nerve - sensory & motor for diaphragm
Supraclavicular Nerve
Nerve to Rhomboids & Serratus
Cranial Nerves (CN XI accessory & CN XII hypoglossal)
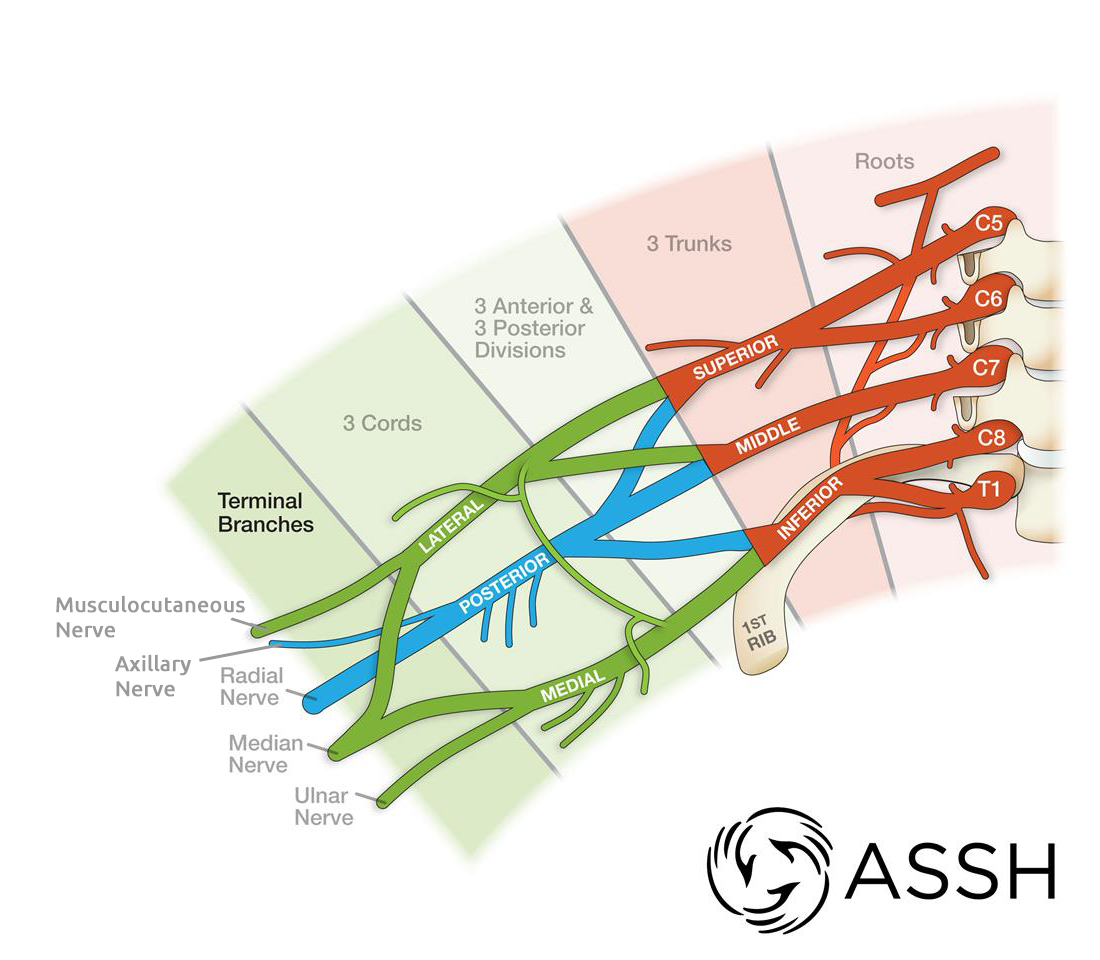
Terminal Nerves from Brachial Plexus
Musculocutaneous Nerve
Axillary Nerve
Median Nerve
Radial Nerve
Ulnar Nerve
MAMRU ABBREVIATION
These Terminal Nerves continue down the upper limb for a considerable distance. They are providing motor innervation to the muscles of the upper limb. They provide sensory innervation to the skin of the upper limb
Nerves from Lumbar Plexus
Iliohypogastric Nerve
Ilio-inguinal Nerve
Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve
Genitofemoral Nerve
Femoral Nerve - supplies quad muscles
Obturator Nerve - supplies groin muscle
Sacral Plexus Nerves
Superior/Inferior Gluteal Nerves
Sciatic Nerve - largest nerve in the human body
provides motor innervation to muscles of foot, leg, and posterior thigh & sensory innervation to the same areas
splits into two along popliteal fossa (back of the knee): tibial & common fibular nerves
Posterior Femoral Cutaneous Nerve
Pudendal Nerve
Piriformis Muscle
small muscle in deep gluteal region
sits right on top of sciatic nerve, so tightness of this muscle can impinge the nerve, which results in sciatica (weakness/pain in legs or parasthesia - tingling, numbness, or burning in the skin)
5 Major Regions of Brachial Plexus
Brachial Plexus originates from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1
Regions Medial to Lateral (Read The Darn Cadaver Notes):
Ventral Rami of Spinal Nerves (Roots of Brachial Plexus) - Trunks - Divisions - Cords - Terminal Nerves
Brachial Plexus Trunks
3 trunks within brachial plexus
superior trunk forms from C5 & C6 ventral rami
middle trunk forms from C7 ventral rami
inferior trunk forms from C8 & T1 ventral ram
Brachial Plexus Divisions
each trunk (inferior, middle, superior trunks) splits into two divisions (anterior & posterior divisions)
Brachial Plexus Cords
all three posterior divisions combine to form posterior cord
anterior divisions from superior & middle trunks form the lateral cord
continuation of anterior division of inferior trunk forms the medial cord
Brachial Plexus Nerves (FORMATION, not the actual nerves)
nerves of brachial plexus arise form one or more trunks/cords
Dermatome
an area of skin supplied by a single sensory nerve root
there can be significant overlap between adjacent dermatomes
Reflex
immediate involuntary motor response/action
Steps of Reflex Arc
reflex arc - neural wiring of single reflex - no conscious control
begins @ sensory receptor and ends @ peripheral effector
1 - stimulation & activation of sensory receptor
2 - activation of a sensory neuron - sends signal in from dorsal root/horn
3 - information processing in CNS - interneuron sends message through to motor neuron immediately, does not wait for brain signaling
4 - activation of a motor neuron - impulse sent out via ventral root/horn
5 - response by effector
Stretch Reflex
particular form of reflexes
occurs when a muscle is stretched and creates an involuntary motor response
muscle spindles in a muscle initiate stretch reflex
clinically, this is usually created by striking a muscle with a reflex hammer (patellar reflex!)
process:
stimulus activate sensory receptors & muscle spindle fibers are stretched
activation of a sensory neuron
information processing in CNS
activation of the motor neuron
response by effector - muscle contracts
Muscle Spindles
initiate stretch reflex
sensory receptors inside of our muscles that detect when a muscle is stretched
help to prevent overstretching of a muscle and help to maintain posture of the body, especially when supporting large loads
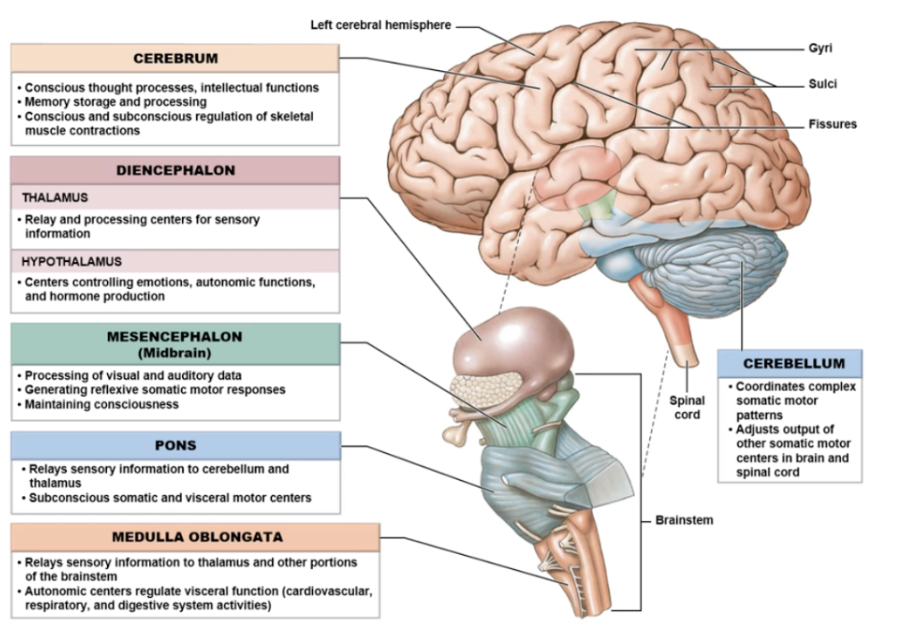
Meningeal Layers of Brain (superficial to deep)
Epidural space - dura mater - subdural space - arachnoid mater - subarachnoid space (CSF) - pia mater
Brainstem structures (inferior to superior)
medulla oblongata
pons
midbrain (mesencephalon)
Six Major Regions of Brain
Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Medulla Oblongata, Pons, Mesencephalon, Diencephalon
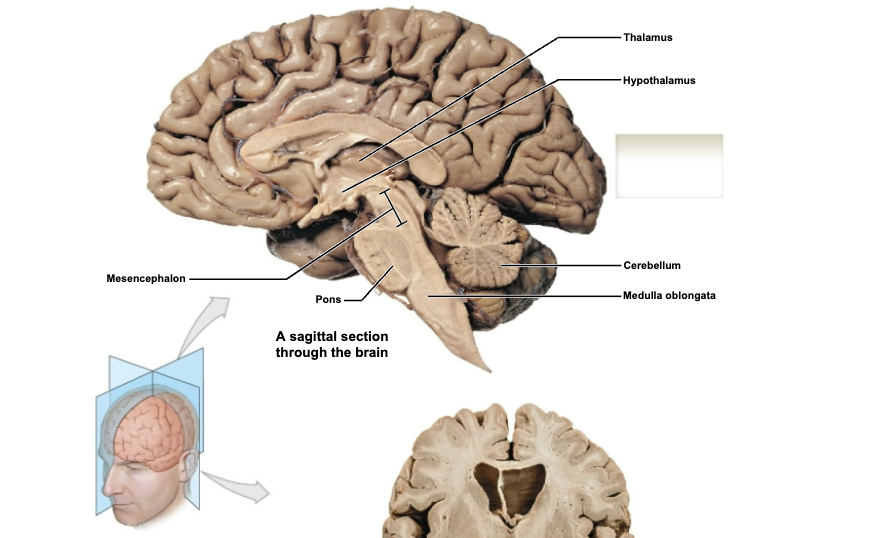
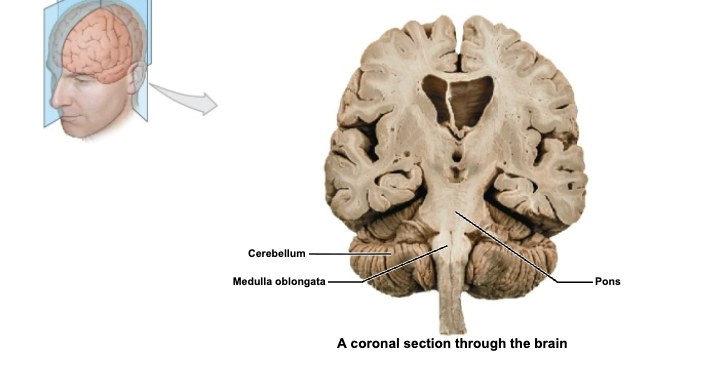
Medulla Oblongata
most inferior segment of brainstem
connects brainstem with spinal cord
essential to survive - plays a role in regulating visceral functions like cardiovascular system impulses
Pons
middle section of brainstem
allows for communication between cerebrum & cerebellum
several cranial nerves emerge here
Mesencephalon (midbrain)
most superior segment of brainstem
maintains consciousness
motor pathways; alertness; vision & hearing regulation
Cerebrum
two hemispheres (left & right) split by longitudinal tissue connected by corpus callosum (white matter)
controlateral control (opposite side)
sensory processing & motor output to skeletal muscles
conscious thought processes - logic, reasoning, planning
memory storage
Cerebral Cortex
gray matter of cerebrum
gyri - wormy-like formations of brain
sulci - crevices between gyri
Four Lobes of Cerebrum
Frontal - mainly motor output - higher coginitive functions, planning, reasoning, and memory - primary motor cortex: initiates voluntary movement
Parietal - sensory input mainly - primary somatosensory cortex: processes touch
Temporal - processing info from hearing (speech & language comprehension) - olfactory (smell) & gustatory (taste) cortex
Occipital - visual cortex
Central Sulcus
splits precentral (frontal) & postcentral (parietal) region
Cerebellum
little brain
balance; coordination; smooth, controlled motor function/movement
get info from visual & auditory cortex to help with balance
Diencephalon
superior to brainstem
attaches brainstem to cerebrum
3 divisions - epithalamus, thalamus, and hypothalamus divisions
Epithalamus Division of Diencephalon
has pineal gland (endocrine): secretes melatonin which regulates sleep cycles
acts as a bridge between limbic system and other parts of the brain
Thalamus Division of Diencephalon
sensory information relayed & processed here
Hypothalamus Division of Diencephalon
hormonal release
connection between the nervous and endocrine systems
intimate connection to pituitary gland - sends out regulatory hormones to it
controls emotion, autonomic functions, and hormone production
Basal Ganglia
a series of deeply located brain structures that coordinate movement in the body
receive info from cerebrum and brainstem
Limbic System
group of structures that regulate emotions - emotional brain
limbic structures:
olfactory bulb & tract - sense of smell
amygdala - memory, decision makaing, emotion
hippocampus - memory & learning
thalamus
hypothalamus - connects endocrine & nervous systems
LABEL
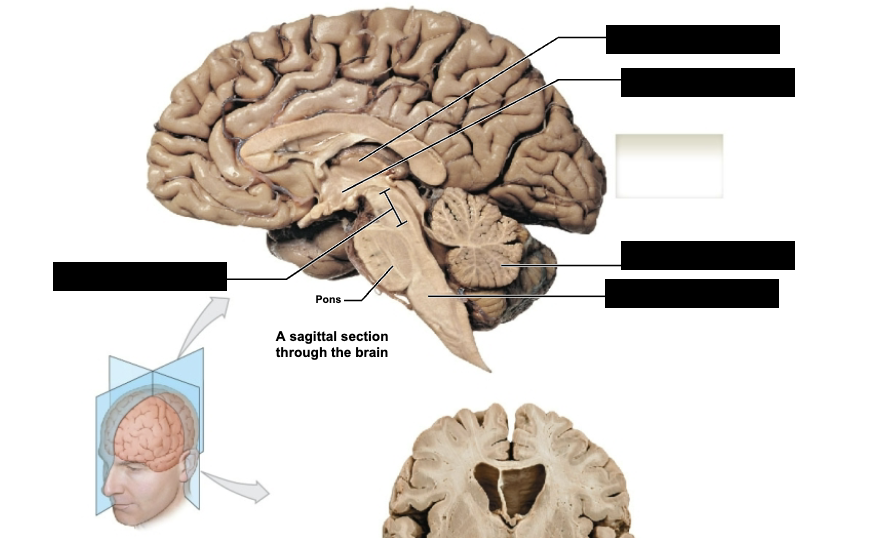
label sagittal section through brain
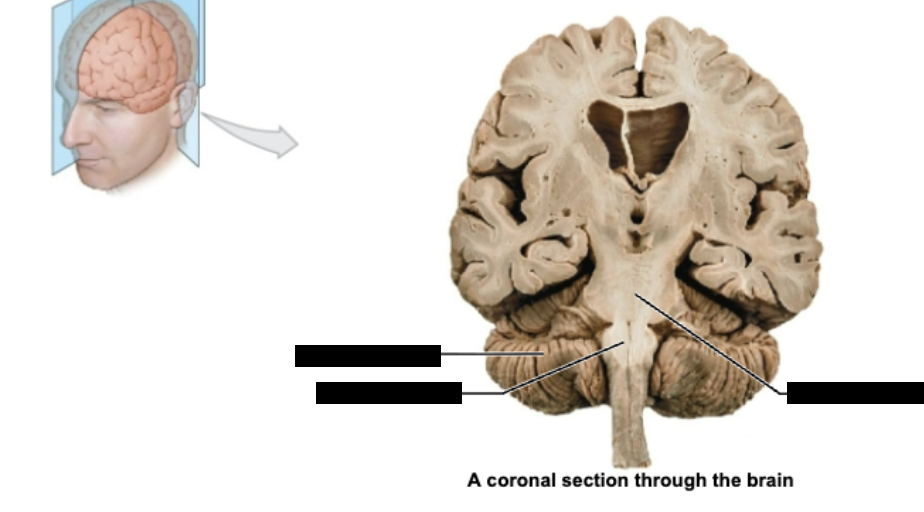
label coronal section through brain
Ventricular System of the Brain
hollow spaces and channels that contain and move cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
help to cushion and nourish the brain
general flow of CSF is moving down in an inferior diection
Chronological Passageway of CSF in Ventricular System
CSF produced by choroid plexus (specialized tissue made up of ependymal cells lining ventricles) in the two lateral ventricles found in cerebral hemispheres
CSF flows from lateral ventricles through interventricular foramina into third ventricle
CSF passes through narrow cerebral aqueduct into fourth ventricle
CSF is further produces in fourth ventricle by choroid plexus
CSF exits ventricle through three openings into subarachnoid space
CSF production
made by ependymal cells of choroid plexus
Cranial Nerves
12 pairs of them
general rule: as you increase in cranial nerve number, you are heading farther posteriorly and inferiorly
CN I
Olfactory Nerve
sensory only
sense of smell
CN II
Optic Nerve
sensory only
taking in visual information
CN III
Oculomotor Nerve
motor; controlling muscles that move eyeball superiorly, inferiorly, medially
one of three nerves that control extra-ocular muscles
CN IV
Trochlear Nerve
motor; controlling muscles that move eyeball superiorly
one of three nerves that control extra-ocular muscles
CN VI
Abducens Nerve
motor; controlling muscles that move eyeball laterally
one of three nerves that control extra-ocular muscles
CN V
Trigeminal Nerve
both motor & sensory
sensation to face
motor innervation of mastication (chewing)
CN VII
Facial Nerve
sensory & motor
muscles of facial expression, part of tongue (anterior 2/3 of it for taste), salivary glands
vulnerable during removable of parotid gland (near ear)
CN VIII
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
sensory only
2 divisions: vestibular & cochlear divisions
vestibular division: balance & sense of position in space
cochlear division: auditory input
CN IX
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
sensory & motor
taste & swallowing functions
sensory for posterior 1/3 of tongue for taste
controlling muscles for swallowing and speech
CN X
Vagus Nerve
sensory & motor
longest and most complex cranial nerve
primarily heart & digestive regulation through parasympathetic nerve signaling
CN XII
Hypoglossal Nerve
motor only
muscles of tongue (except palatoglossus, which is innervated by vagus)
when affected, tongue will deviate to one side when projected forward
CN XI
Accessory Nerve
motor only
innervates sternocleidomastoid & trapezius
neck & back movement
Autonomic Nervous System
functions outside of our conscious awareness
controls all actions occurring in the background to keep the body working normally
oversees cardiovascular, respiratory, endocrine, urinary, digestive, and reproductive functions
has both efferent & afferent nerve fibers
Efferent Portion of ANS
sends signals to our internal organs
has two divisions
sympathetic - fight or flight
parasympathetic - rest & digest
Afferent Division of ANS
visceral sensory receptors within internal organs
send information about internal environment to body
Somatic Nervous System
sends fibers to and from the skeletal muscle, our skin, and major joints
has efferent & afferent neurons
somatic motor neruons do not involve ganglia
Vital Functions of Autonomic Nervous System
stimulates smooth muscle found in body’s organs and blood vessels
influences glandular activity (upregulating/downregulating)
acting upon the conducting tissue of the heart
transmitting reflex & pain signals (sensory) information from organs, blood vessels, etc
influences lung & heart activity
influences activity of digestive tract
Sympathetic NS
fight or flight
energy consuming
essential for responding to internal and external stresses
AKA thoracolumbar division
Parasympathetic NS
rest and digest
energy conserving
essential for maintaining bodily functions during low activity and stress
AKA craniosacral division
Ganglia
essential element of the physical setup of the autonomic pathways
sympathetic & parasympathetic fibers rely on two neurons arranged in series
there is a preganglionic neuron and a postganglionic neuron
these neurons are in proximity at a ganglion
ganglion refers to clusters of neuronal cell bodies located outside the central nervous system
Preganglionic Neuron
short in sympathetic, long in parasympathetic
cell body is in the gray matter of the central nervous system
axons are within ganglia
Postganglionic Neuron
long in sympathetic, short in parasympathetic
cell body is peripherally located - outside CNS, inside ganglia
Sympathetic Ganglia
close to spinal cord
short preganglionic neuron that secretes acetylcholine (ACh) & long postganglionic neuron that secretes norepinephrine (NE)
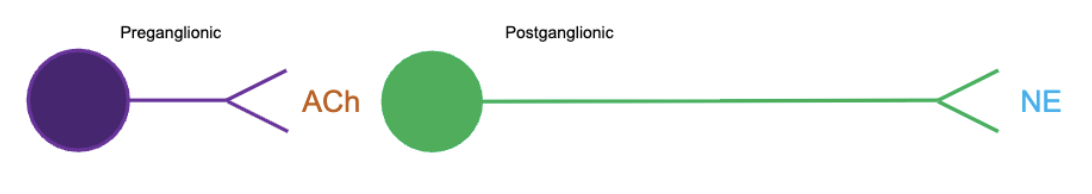
Parasympathetic Ganglia
farther away from spinal cord
long preganglionic neuron that secretes ACh & short postganglionic neuron that secretes ACh
for the most part, these ganglia are adjacent to or within the walls of their effectors

Sympathetic Preganglionic Neurons
cell body originates in lateral horn of the gray matter in the spinal cord from T1 through L2 levels
Parasympathetic Preganglionic Neurons
cell body originates from cranial nerves III, VII, IX, X and from the sacral nerves S2-S4
Enteric Nervous System
3rd division of autonomic NS
found in walls of the digestive tract
Sympathetic Ganglionic Neuron Location
sympathetic chain ganglia (paired) - target visceral effectors in thoracic cavity, head, body wall, and limbs through innervation by postganglionic fibers
collateral ganglia (unpaired) - target visceral effectors in abdominopelvic cavity through innervation by postganglionic fibers
adrenal medulla (paired) - target organs and systems throughout body through release of hormones in blood stream
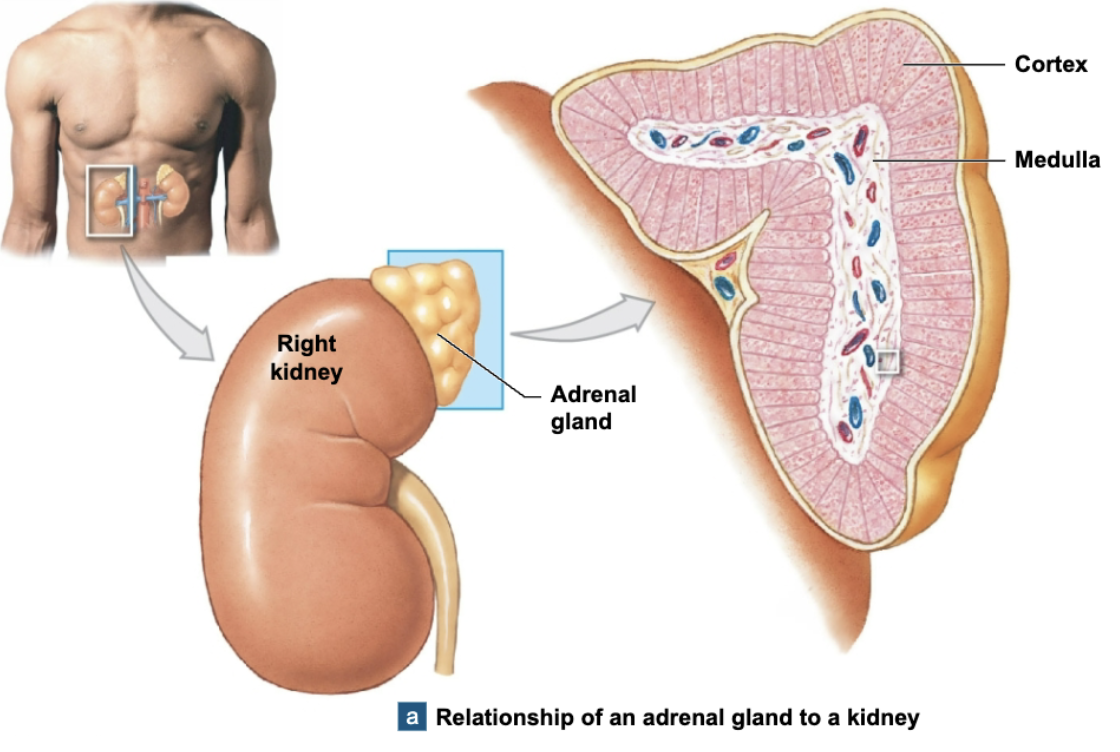
Adrenal Medulla
the internally located part of the adrenal gland, which sits directly above kidneys
releases neurotransmitters epinephrine (adrenaline) and norephinephrine (noradrenaline) into bloodstream (no postganglionic neuron)
Sympathetic Stimulation Effects
increased alertness
a feeling of energy & euphoria
increased cardiovascular & respiratory activity
elevation in muscle tone
mobilization of energy reserves
Parasympathetic Stimulation Effects
constriction of pupils
secretion of digestive glands
secretion of hormones promoting nutrient absorption
increased smooth muscle activity along the digestive tract
stimulation & coordination of defecation
contraction of the urinary bladder during urination
reduction in heart rate and force of contraction
constriction of respiratory passageways
sexual arousal
Dual Innervation
most vital organs are innervated by both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
two divisions often have opposite/antagonistic effects
label respiratory structures
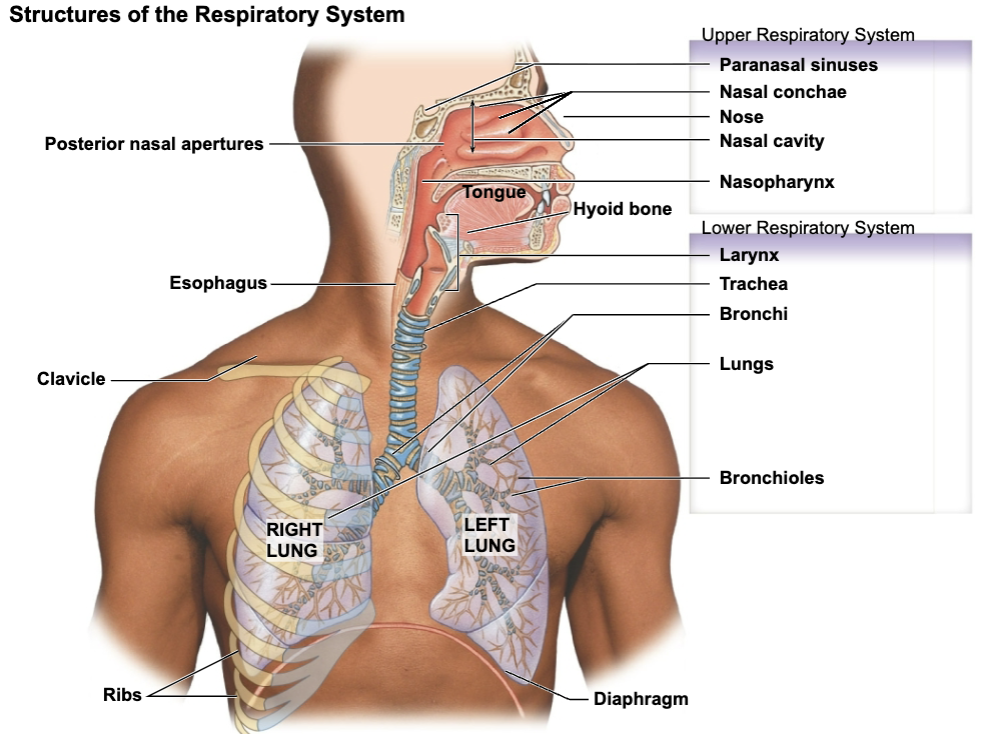
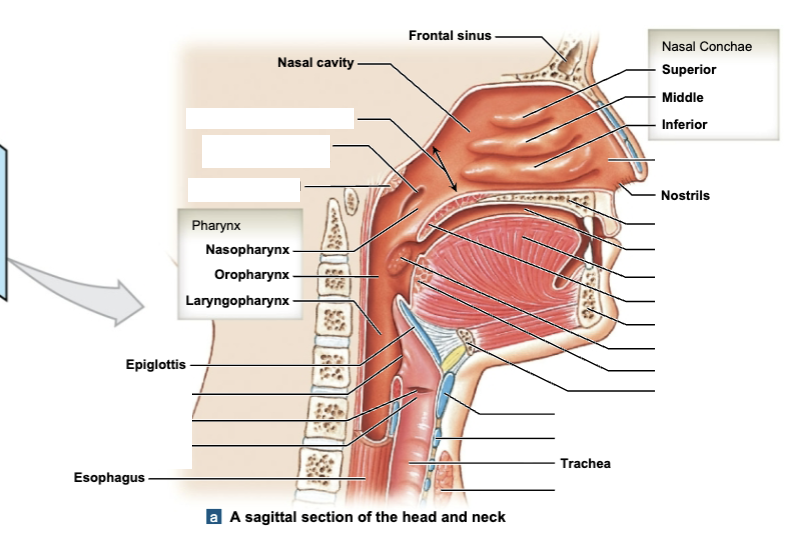
Upper Respiratory Tract
nose, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and pharynx
Lower Respiratory Tract
larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, bronchioles, and alveoli
Dividing Line between Upper & Lower Respiratory Systems
epiglottis
Conducting Zone
part of the airway from the nasal cavity going down towards the terminal bronchioles (full respiratory tract except for respiratory bronchioles & alveoli)
pathway is merely directing air down towards lungs
no gas exchange taking place in this part of pathway (this happens in alveoli)
filtration, warming, and humidification of inhaled air
Respiratory System Functions
provides an area for gas exchange between the air and the blood
moves air to and from exchange surfaces of the lungs
protects the respiratory surfaces from dehydration
provides protection against invading pathogens
produces sound involved in verbal communication
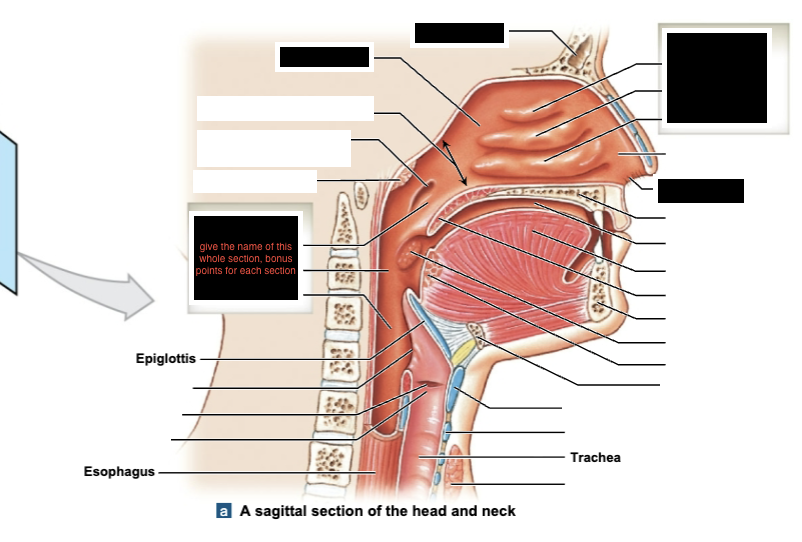
label black boxes of sagittal section of head and neck
Mucus (respiratory)
respiratory tract lined with epithelial tissue that secretes a sticky substance (mucus) which helps trap pathogens/dust/debris
epithelium is ciliated = has small fingerlike projections that move in a wavelike fashion
body wants to move the mucus upwards away from the longs
mucus can eventually be swallowed so the pathogens can be destroyed by the acidity in the stomach OR moved up to eventually be spit out
mucus plays a vital role in warming, humidifying, and filtering air within conducting zone in order to avoid damaging the delicate tissues farther down in the lungs
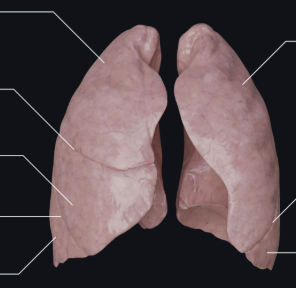
What view of the lungs is this?
anterior
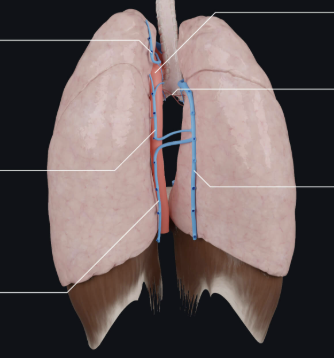
What view of the lungs is this?
posterior
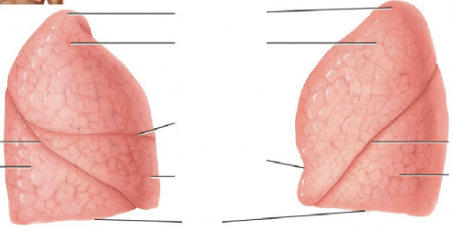
What view of the lungs is this?
lateral
3 lobes with transverse & oblique fissure - right lung
2 lobes with oblique fissure - left lung
Path of Air in Lungs
terminal bronchiole - respiratory bronchioles - alveolar ducts - alveolar sacs (visually resemble grape bunches)
alveolar sacs have numerous capillary beds which release carbon dioxide and then take on oxygen
oxygen is then distributed out to the body tissues
Bronchi Segments
primary, secondary, and tertiary segments
as you move deeper into lungs, you move into the tertiary segments
Major Cell Types that exist within lungs at alveolar level
Type I Alveolar Cells
Type II Alveolar Cells
Alveolar Macrophages
Type I Alveolar Cell
where gas exchange takes place in alveoli
form walls of alveoli