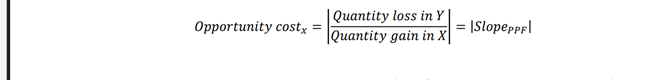Production Possibilities Frontier and Trade Concepts
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts about the Production Possibilities Frontier and the principles of international trade, including theories, implications of specialization, and the evolution of trade.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What does the PPF show?
The combinations of two goods an economy can produce using all resources and technology efficiently.
What are the two main assumptions of a basic PPF model?
Only two goods/services are produced, and there is one key resource (like labor).
What do points on the PPF represent?
Productive efficiency — you can’t produce more of one good without producing less of another.
What do points inside the PPF represent?
Inefficient production — some resources are not fully used.
What do points outside the PPF represent?
Unattainable levels of production with current resources and technology.
What does the slope of the PPF represent?
The opportunity cost of one good in terms of the other.
What does a straight-line PPF mean?
Constant opportunity cost — resources are equally good at producing both goods (homogeneous resources).
What does a bowed-out (concave) PPF mean?
Increasing opportunity cost — resources are specialized for different tasks.
What causes the PPF to shift outward?
Better technology or more resources → higher productive capacity → more of both goods can be produced.
What causes the PPF to shift inward?
Loss of resources or technology → less productive capacity.
If a country moves from a point inside to a point on the PPF, what happens?
The country improves efficiency by using resources more fully.
A new technology helps produce both cars and food faster. What happens to the PPF?
It shifts outward — economic growth.
If workers trained in car manufacturing are used in farming but are inefficient, what shape will the PPF be?
Bowed-out, because of increasing opportunity cost (specialization).
How did trade evolve over time?
From simple barter systems to complex Global Value Chains (GVCs) where production is spread across countries.
What is a Global Value Chain (GVC)?
A system where production steps for one product occur in different countries.
What is the key idea behind modern trade?
International linkage and cooperation increase global efficiency.
Why do countries trade according to Ricardo?
Because of differences in technology → Comparative Advantage.
What does the Heckscher–Ohlin Theory say about trade?
Countries trade based on differences in natural resources and factor endowments.
Name three additional reasons for trade besides comparative advantage.
Differences in consumer demand, economies of scale, and government policies.
What does 'increasing returns to scale' mean?
Producing more reduces the average cost per unit — large-scale production is more efficient.
Why might a small country import cars instead of producing them?
Because other countries can produce them at lower opportunity cost (comparative advantage).
Who are Frank and Ruby in the trade model?
Ruby is better at producing meat (rancher), Frank is better at producing potatoes (farmer).
What happens when Frank and Ruby specialize and trade?
Both can consume more than they could without trade.
What does this model show about trade?
Specialization and exchange increase total consumption possibilities.
If Ruby produces only meat and Frank only potatoes, why can both eat more after trading?
Each focuses on their comparative advantage, increasing efficiency and total output.
Cách tính opportunity cost?