Unit 8.2 - Strategic Positioning: Choosing how to compete
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Strategic positioning
The view people take of a business that results from the business's strategic decision making (how a business is perceived compared to competitors)
General features of strategic positioning
- Arise from the planned activities of the business based on their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats
- Should provide a sustainable competitive advantage
- Therefore a position easily replicated by competitors is not strategic positioning
- Usually based on two key factors
costs: Offering competitive prices
Differentiation: Offering unique and perceived high value benefits
Porter's generic competitive strategies (description/definition)
highlighted that a low cost or differentiation strategy could be aimed at the market as a whole (mass) or at a small part (niche) of the market (focus strategy).
He described the amount of the market targeted as the competitive scope of the business. A broad scope targets the market as a whole (mass) where a narrow scope focuses on a niche.
Porter's generic competitive strategies (diagram)
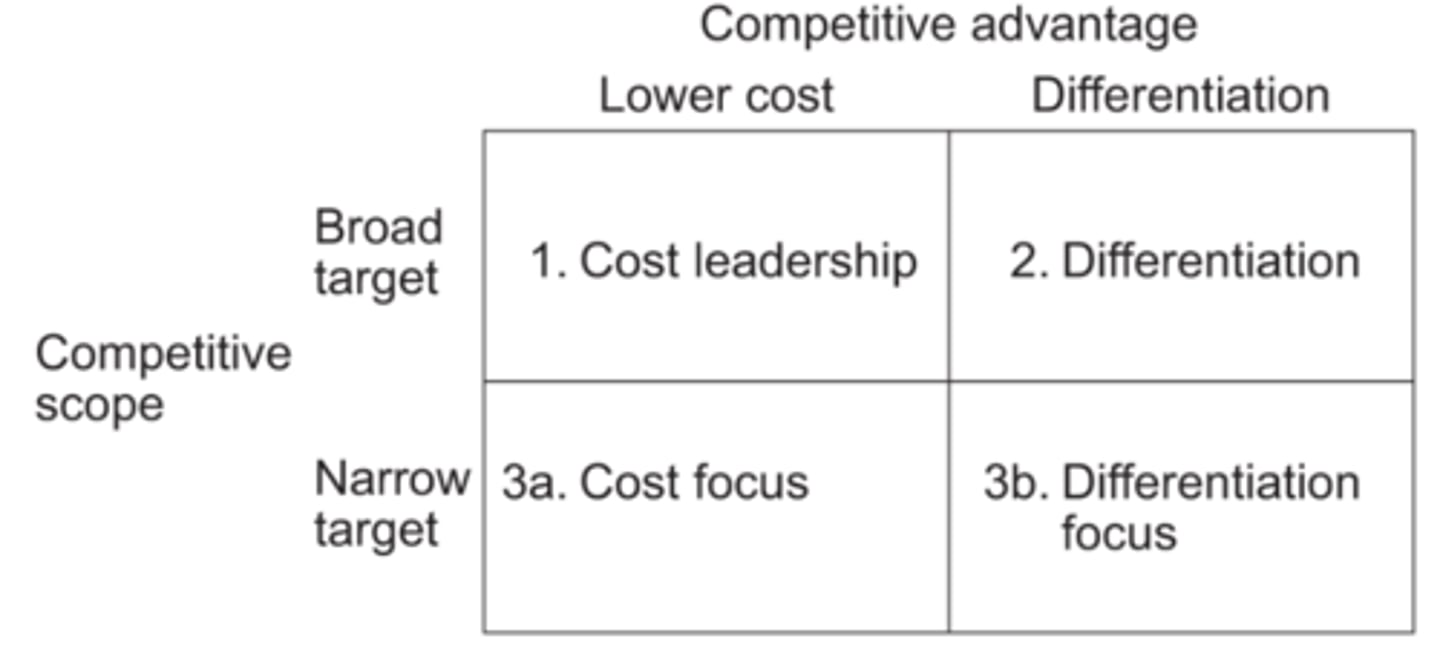
Low cost/cost leadership (Porter's strategies)
Business wishes to become lowest cost producer in an industry
- Tends to have standardised and mass produced products
How to achieve:
Economies of scale
Better technology
Research and development
Owning suppliers or sourcing suppliers cheaper
Efficient distribution channels
Lean production methods
Improvements in productivity
But:
Likely competitors will be able to copy these in the medium term, permanent cost leadership is difficult to achieve
Differentiation leadership (Porter's strategies)
A degree to which consumers see one brand as being different to another, this can benefit firms in two way:
- Increase sales volume
- Charge higher prices
How to achieve:
- Superior performance (features, benefits, reliability, durability)
- Branding (strong customer recognition, brand loyalty)
- Industry wide distribution across all major channels (widely stocked by retailers)
- Consistent and clever promotion (often dominated by adverts, sponsorships)
- After-sales service
But:
- Will result in higher cost wither in production, marketing or HR
- May need to find ways to protect USP i.e through patents
Focus (Porter strategies)
concentrates on one segment or a few within the market (niche markets). The target segment may be different from the rest of the market and poorly served by the main businesses
The focus can then be cost based or differentiation based
Cost focused strategy (Porter forces)
- business seeks a lower-cost advantage in just one or a small number of market segments.
- Product will be basic - perhaps a similar product to the higher-priced and featured market leader, but acceptable to sufficient consumers.
Differentiation focus strategy
- business aims to differentiate within just one or a small number of target market segments.
- The special customer needs of the segment mean that there are opportunities to provide products that are clearly different from competitors who may be targeting a broader group of customers.
- Typical niche marketing strategy used by small firms who can establish themselves in these markets achieving higher prices to maintain their profitability
Bowmans strategic clock (Last exam Y13 2024)
- Bowman's model plots the options open to a business
- Bowman's Strategic Clock is a model that explores the options for strategic positioning
- The purpose of the clock is to illustrate that a business will have a variety of options of how to position a product based on two dimensions - price and perceived value.
- From this, it is possible to analyse the strategic positioning a business has now and where it may want to be in the future.
8 Options on Bowman's strategic clock (Last exam Y13 2024)
1) Low price & Low added value
2) Low price/perceived added value
3) Hybrid
4) Differentiation
5) Focused differentiation
6) Increased price & standard product/risky high margins
7) Monopoly pricing/increased price & low value
8) Loss of market share/low price & standard product
Low price & Low added value (Bowmans strategic clock)
This is not a very competitive position for a business. The product is not differentiated and the customer perceives very little value (inferior good), despite a low price. The only way to remain competitive is to sustain low prices and hope no one undercuts you
Low price/perceived added value (Bowman's strategic clock)
Businesses positioning themselves here look to be the low-cost leaders in a market but products not seen as inferior. A strategy of cost minimisation is required for this to be successful, often associated with economies of scale. Profit margins on each product are low, but the high volume of output can still generate high overall profits. Competition amongst businesses with a low price position is usually intense - often involving price wars.
Hybrid (Bowman's strategic clock)
involves some element of low price (relative to the competition), but also some product differentiation. The aim is to persuade consumers that there is good added value through the combination of a reasonable price and acceptable product differentiation. This can be a very effective positioning strategy, particularly if the added value involved is offered consistently.
Differentiation (Bowmans strategic clock)
Offer customers the highest level of perceived added value. Branding plays a key role in this strategy, as does product quality. A high quality product with strong brand awareness and loyalty is perhaps best-placed to achieve the relatively high prices and added-value that a differentiation strategy requires.
Focused differentiation (Bowmans strategic clock)
aims to position a product at the highest price levels, where customers buy the product because of the high perceived value. This the positioning strategy adopted by luxury brands, who aim to achieve premium prices by highly targeted segmentation, promotion and distribution. Done successfully, this strategy can lead to very high profit margins, but only the very best products and brands can sustain the strategy in the long-term.
Increased price & standard product/risky high margins (Bowmans clock)
High risk positioning strategy that you might argue is doomed to failure - eventually. With this strategy, the business sets high prices without offering anything extra in terms of perceived value. If customers continue to buy at these high prices, the profits can be high. But, eventually customers will find a better-positioned product that offers more perceived value for the same or lower price. Usually happens when managers misjudge benefits on offer or product is first introduced
Monopoly pricing/increased price & low value (Bowmans clock)
Can only really exist if a business has no competition (why is it's called monopoly pricing), but in another type of market this strategy will fail as they are offering the lowest benefits but still charging a high price
Loss of market share/low price & standard product
This position is a recipe for disaster in any competitive market. Setting a middle-range or standard price for a product with low perceived value is unlikely to win over many consumers who will have much better options (e.g. higher value for the same price from other competitors).
What are the non competitive strategies on Bowman's clock
6) Increased price & standard product/risky high margins
7) Monopoly pricing/increased price & low value
8) Loss of market share/low price & standard product
Bowmans clock (image)
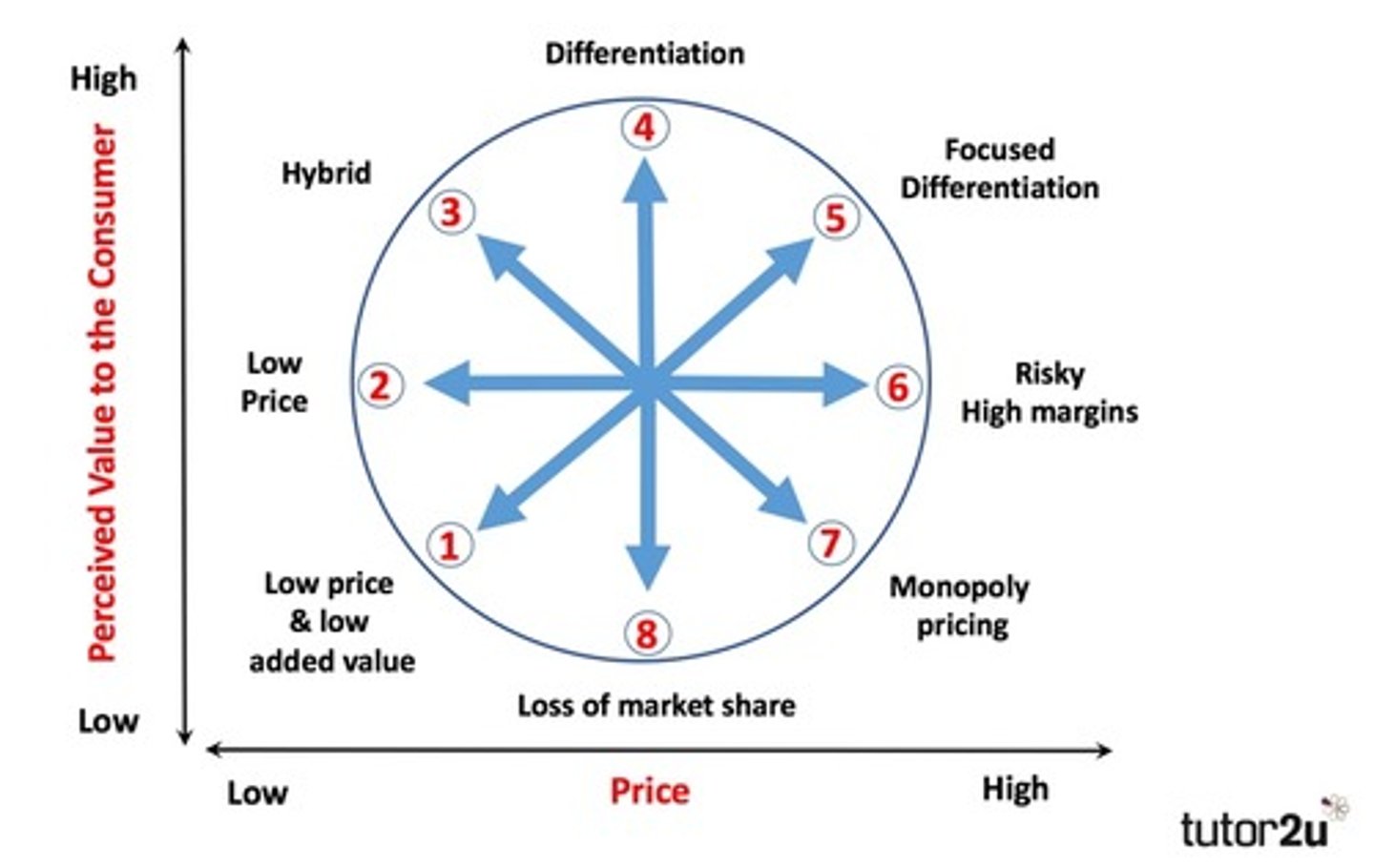
Influences on choice of positioning strategy
Influence will consider that strategic positioning is long-term, perceived benefits and price:
- competitors
- core competencies i.e production, supply chain,innovation, workforce, current market segment appeal
- external environment
- Scale/size of business
- Customer perceptions i.e brand loyalty
- Customer base
- Values of customer base
- Stakeholders perspectives, power and interest
Benefits of having a competitive advantage
Through low cost:
- Gain increased sales taken from competitors through charging low prices
- Or higher profit margin on each product
Through differentiation:
- Be seen as superior to competitors attracting customers from competitors
- Charge higher prices increasing profit margins
How competitive advantage may be achieved
- Investment in new technology and equipment: greater flexibility, reliability, quality, speed, lower unit costs
- Innovation through investment in R&D: Keep up with changes, tackle shorter product life cycles
- Enterprise: Being entrepreneurial and driven
- Effective marketing: Correct marketing mix
- Improving quality: Great customer satisfaction, USP
- Effective HR: Highly skilled, well organised, motivated workforce
- Efficiency operations: Lean production, supply chain management, stock control, quality assurance
- Financial planning and control: Detect issues, set targets ensure efficiency of firm
Difficulties in maintaining competitive advantage
- Investment in new technology and equipment: Expensive, changes rapidly
- Innovation through investment in R&D: Expensive, no guarantee of successful product development
- Enterprise: High risk and difficult to keep finding gaps in the market and coming up with new ideas
- Effective marketing: Unless brand loyalty is created may not be sustainable source as other can copy
- Improving quality: Impact in costs and price, techniques can possible be copied
- Effective HR: Employee can leave and have free will unlike other resources so this can be easily eroded over time
- Efficiency operations: Unless some processes patented or agreements made with suppliers competitors can copy
- Financial planning and control: Unlikely to be a key factor and also need to ensure not too many resource are put into just planning and monitoring rather than implementing