ECON 248 6.1 The Consumer Price Index
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
The overall measure of the cost of goods and services bought by a typical consumer.
Consumer Price Index
The first step in calculating the consumer price index is to determine the (), the goods with prices that consumers deem most important.
Basket
The 2nd step in finding consumer price index is to find the () of goods within the basket.
Prices
The 3rd step of consumer price index is calculating the basket’s () for each year.
Cost
The 4th step of consumer price index is to choose a () and calculate the consumer price index with the following equation.
Base Year, (Price Of Basket Goods/Services In Current Year/ Price Of Basket In Base Year) * 100
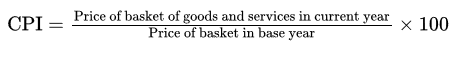
The 5th step of calculating CPI is finding the () rate, which is calculated by the following equation.
Inflation, ((Year 2 CPI - Year 1 CPI)/Year 1 CPI)) * 100
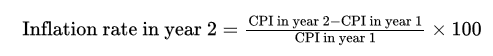
A trend of inflation which accounts for 19% of the CPI basket and excludes fruit, vegetables, fossil fuels, mortgage interest, transportation, and tobacco.
Core Inflation
A problem with the consumer price index where some prices change at a different rate than others.
Commodity Substitution Bias
In the case of commodity substitution bias, consumers have a bias towards goods which have () or () in cost.
Risen Less, Decreased
A problem with the consumer price index is that the () causes greater variety and less dollars to maintain a standard of living.
Introduction Of New Goods
A problem with CPI is (), where the cost of a good may not change when it’s actual value changes.
Unmeasured Quality Change
A difference between GDP deflator and CPI is that GDP deflator measures the costs all goods and services produced (), while CPI only reflects market value of goods and services ().
Domestically, Bought By Consumers
CPI compares the () price of goods and services to the prices of the base year, while GDP deflator compares () to the price of those goods and services in the base year.
Fixed, Currently Produced Goods