Bacterial Physiology Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Glycan chains are crossed-linked by:
peptides
Peptidoglycan is made up of:
glycan chains
Glycan consist of:
Alternating residues of NAG and NAM
NAG and NAM are attacked to each other by
Beta 1,4 glycoside bonds
NAM stands for
N-acetylglucosamine
NAM stands for
N-acetylmuramic acid
What type of network does the peptidoglycan structure allow:
a mesh like network
What type of bonds does the cross linking of structure form?
Covalent
Where is the peptidoglycan layer located?
Surrounds the cell membrane
What gives the cell wall its strength?
Covalent bond, the give the cell wall its rigidity and strength
The peptidoglycan is a _____________ molecule
very large
What can destroy the cell wall?
lysosome or antibiotics
What happens when the peptidoglycan wall is destroyed?
It can create weak spots in the cell, swelling can then occur and cause lysis due to internal turgor pressure
Where are the bonds on NAG and NAM?
C1 bond of NAM and C4
_______ is a modified structure of __________
NAM is a modified version of NAG
How is NAM modified?
Lactyl group attached to the C3 carbon
_______ is attached to each NAM
tetrapeptide
Tetrapeptide is:
L-alanyl-D-Glutamyl-gamma-L-R3-D-alanine
What can change on the tetrapeptide within different bacterial species:
The position of the 3 carbon, it can be L or R
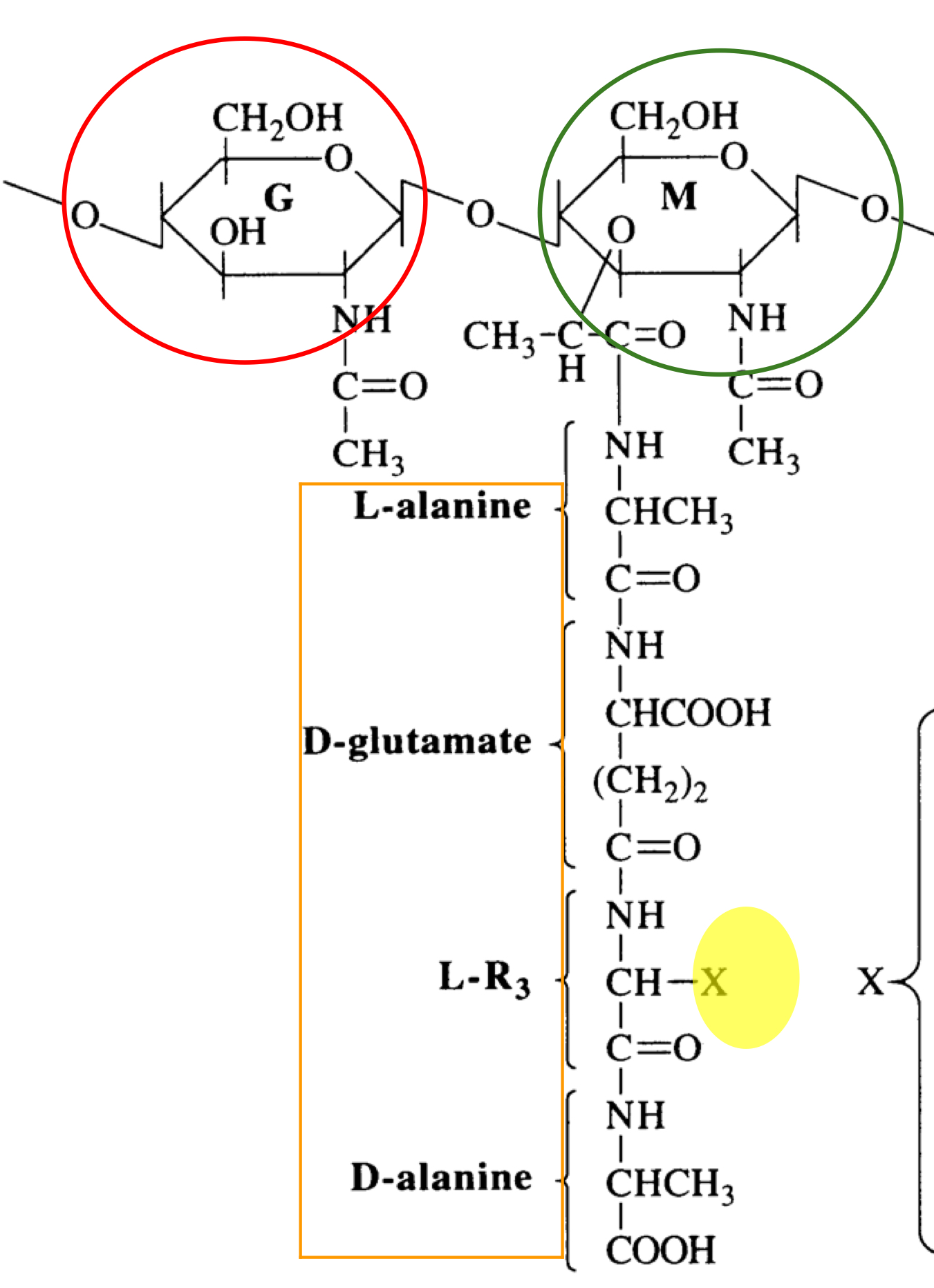
What is this structure of?
Structure of peptidoglycan
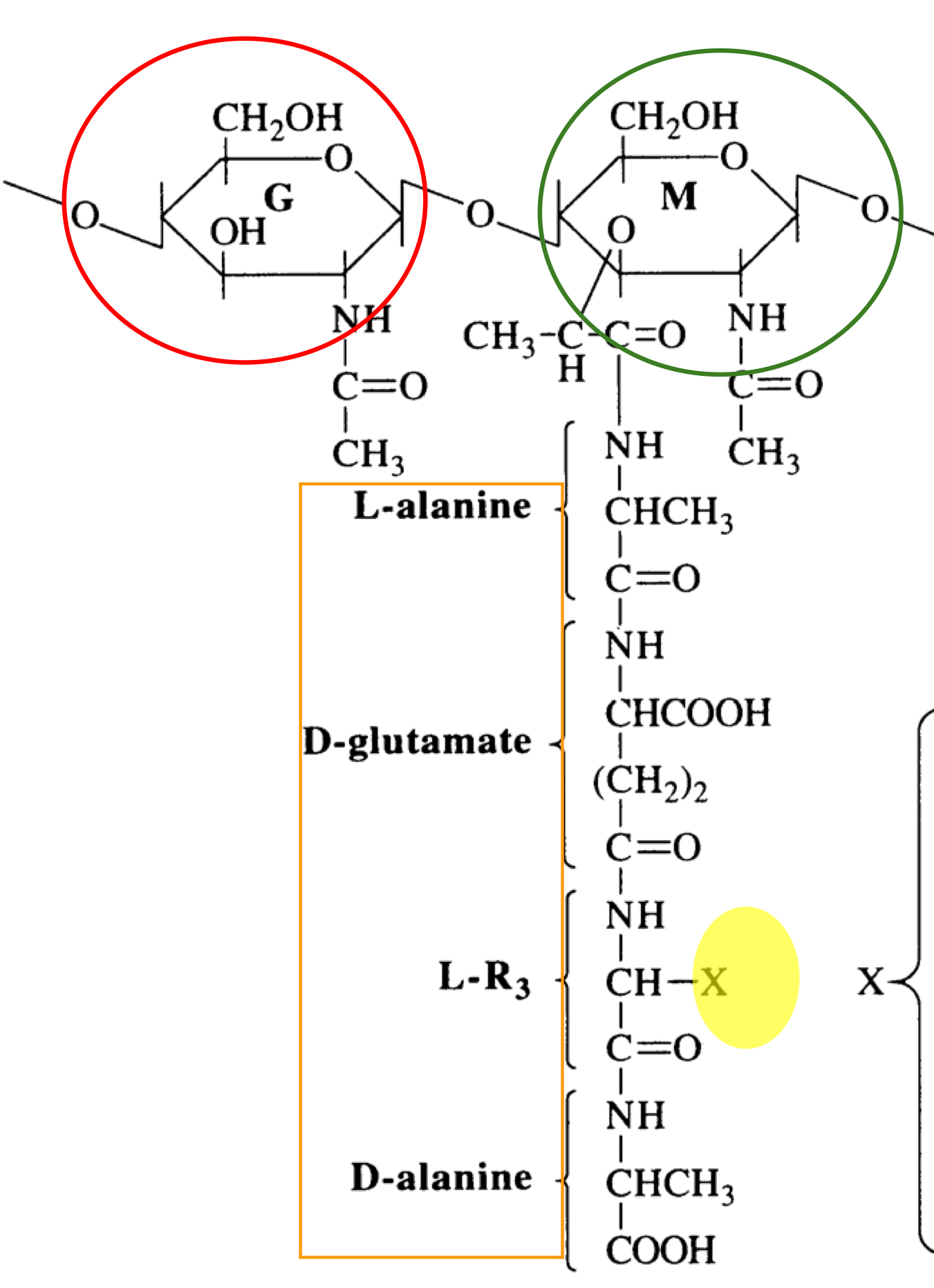
What is the red structure of?
NAG
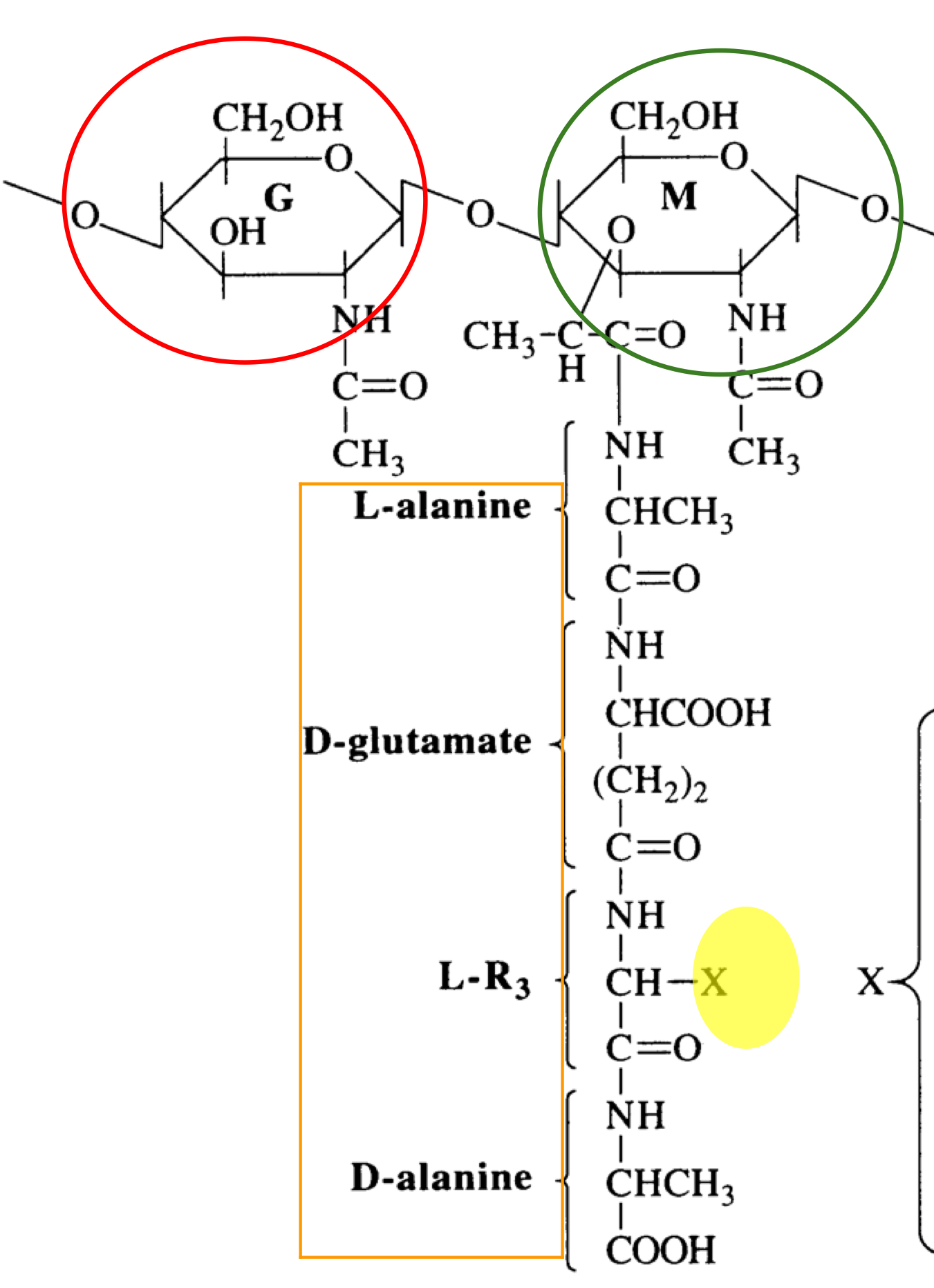
What is the green structure of?
NAM
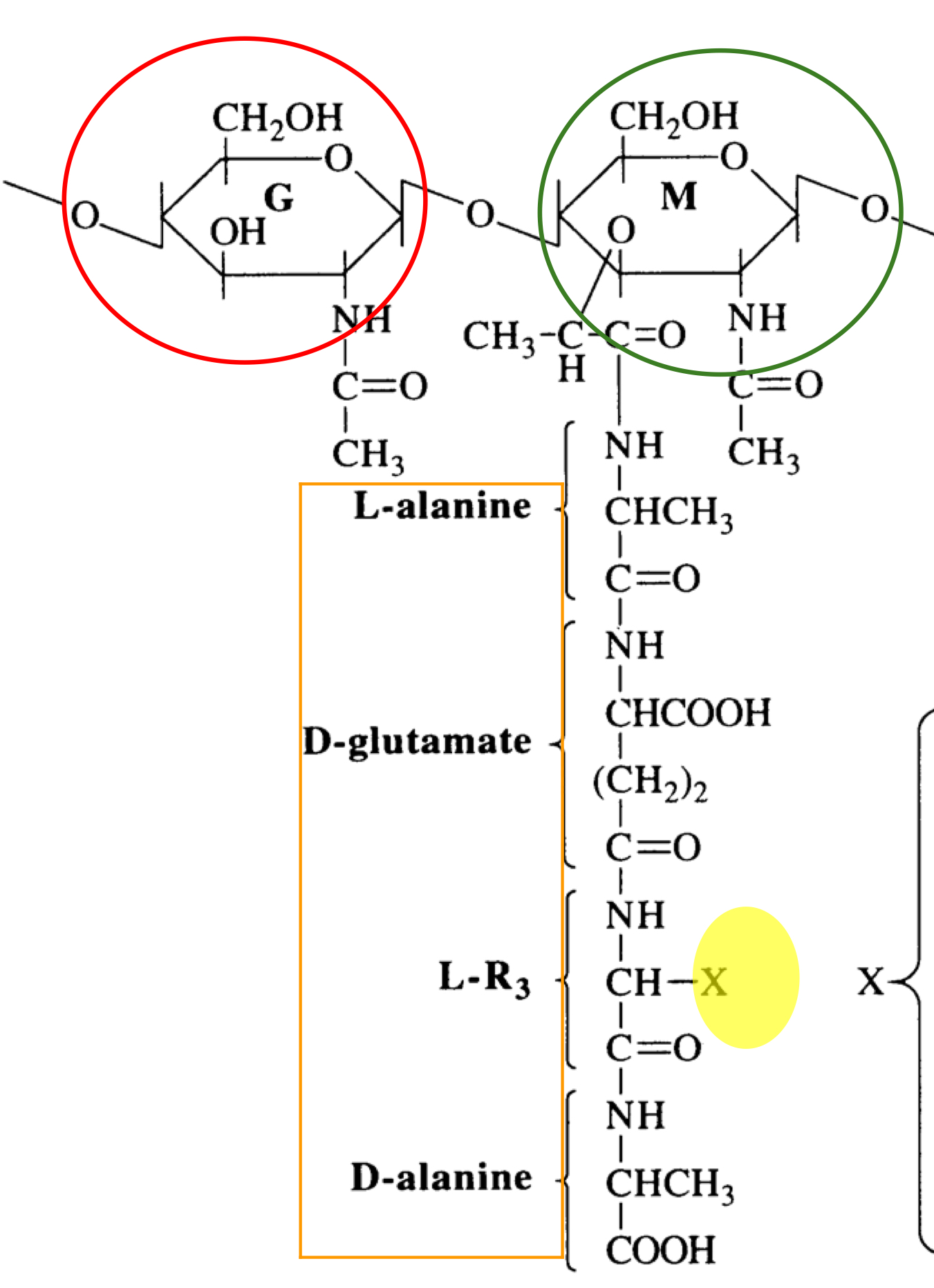
What is the orange structure of?
The tetrapeptide
Tetrapeptide are cross linked by
peptide bonds
Peptide bridge in peptidoglycan:
The D-alanine in one tetrapeptide to a amino acid in the L-R3 position in another tetrapeptide
Gram negatives have a _______ cross-linking
Direct
Why do gram negatives have a more direct cross link?
Because their peptidoglycan is thinner
What is the linkage between in gram negative
D-alanine and diaminopimelic acid
What other species is a direct cross-linking seen in?
Bacillus species
Crosslinking in gram positive
The have a bridge of one or more amino acids and the thickness varies in each species
How many residues in Staphylococcus
5 glycine residues
How many residues in micrococcus roseus
3 L-alanine and 1 L-threonine
How many residues in staphylococcus epidermidis
3 glycine and 2 L-serine
Functions of peptidoglycan:
Helps maintain the shape of the cell wall and responsible for cellular morphogenesis
Where is lysozyme found and what does it do?
Found in tears, saliva, breast milk, and mucus. It hydrolyzes the glucosidic linkages
What antibiotics target the peptidoglycan:
Penicillin, vancomycin, and bacitracin all infer with the synthesis
Peptidoclyxqn protects cells from lysis in ________ solutions
Hypotonic
First step of peptidoglycan synthesis:
precursors are UDP derivatives of the amino sugars made in the cytosol
Second step of peptidoglycan synthesis:
Amino sugars are transferred to a lipid carrier in the membrane
Third step of peptidoglycan synthesis:
Peptidoglycan is polymerized in the outer surface of the membrane
Fourth step of peptidoglycan synthesis:
Transpeptidation reaction cross-links the peptidoglycan
NAG and NAM are made up of
Fructose-6-phosphate
What are the sugars of peptidoglycan
NAG and NAM
Glutamine donates what during UDP derivatives synthesis?
An amino group
What does the fructose-6-phosphate convert to after reviving an amino group?
Glucosamine-6-phosphate
How is NAG-6-P created?
Transacylase transfers an acetyl group to the amino group on glucosamine-6-phosphate.
NAG-6-phosphate is isomerized to:
NAG-1-P
How is NAG-6-P isomerized?
Mono phosphate attacks UTP and displaces the pyrophosphate to form UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc)
What then happens to some the UDP-GpcNAc
Converted to UDP-N-acetylmutamic acid (UDP-MurNA )
How is UDP-GlcNAc converted to UDP-N-acetylmutamic acid (UDP-MurNAc)
Addition of a lactyl group to the sugar
How is enol pyruvate created?
C3 hydroxyl or the sugar displace the phosphate from the alpha carbon of phosphoenolpyruvate
What is is enol pyruvate?
Derivative of UDP-MurNAc
What then happens to enol pyruvate?
Reduced to the lactyl moiety by NADPH
What is UDPMurNAc then converted to:
To UDP-MurNAc pentapeptide
How is UDP-MurNAc pentapeptide created
Sequential addition of amino acids: L-alanine, D-glutamate l, L-R3, dipeptide D-alanyl-D-alanine, ATP
What does the reaction of UDP-MurNAc to UDP-MurNAc pentapeptide require?
ATP
Why does UDP-MurNAc need ATP for its reaction?
To activate the carboxyl group of the amino acid and allows for the displacement of phosphate
What are the products of the conversion of peptidoglycan synthesis?
UDP-MurNAc Pentapeptide, ADP, and inorganic phosphate
What enzymes are used to create D-alanine-D-alanine?
Racemase ans synthetase
Racemase:
Concerts L-alanine to D-Alanine
Synthetase:
Makes D-alanine-D-alanine from 2 D-alanines
What inhibits synthesis of D-alanine-D-alanine
Cycloserine
UDP-MurNAc Pentapeptide is then transferred to the:
Lipid carrier in the membrane
Lipid carrier:
Bactroprenol, or lipid P
Lipid A serves as a:
Carrier for peptidoglycan precursors and other components of the cell wall
Nucleotide sugars defuse the membrane by:
Lipid P attacks UDP-MurNAc pentapeptide displacing UMP and produces lipid-PP-MurNAc (pentapeptide)
GlcNAc is transfered from ___________ to _______________
UDP-GlcNAc to the MurNAc on the lipid carrier
How is the GlcNAc transferred?
C4 hydroxyl in the MurNac attacks the carbon in UDP-GlcNAc displacing the UDP
Disaccharide precursor to peptidoglycan is produced and move to:
Lipid-PP-MurNAc-GlcNAc and moves to the other side of the membrane
What then happens to the lipid disaccharide?
Transferred to the growing end of the acceptor glycan chain
How is the lipid disaccharide transferred to the growing end?
Transglycosylation reaction; the C4 hydroxyl of the incoming GlcNAc attacks the C1 of the murNAc in the glyan and displace lipid-Pp from the growing glycan chain
The growing glycan chain remains anchored to the membrane by:
lipid carrier at the site of transglycosylation
Lipid-PP is released by and produces:
Released by membrane bound pyrophosphatase and produces Lipid-P and Pi
Lipid-PP is important bc:
drives transglycosylation to completion
_________ regenerates Lipid-P
Hydrolysis
Why is hydrolysis of Lipid-P important?
Necessary for continuing the growth of the peptidoglycan
Hydrolysis of Lipid-PP is inhibited by:
bacitracin
Transpeptidation
provides the energy necessary to make the peptides cross-link outside the cell membrane
Transpeptidation is inhibited by:
Penicillin
How does peptide cross-linking work?
NH2 from the diamino acid in position 3 attacks the carbonyl carbon in the peptide bond holding the 2 D-alanine residues and displaces the terminal D-alanine and results in a new bond
PBP:
penicillin binding proteins and they are membrane proteins found in the peptidoglycan of bacteria
What do PBP do?
Catalyze the transglycosylation and transpeptidation steps and some are required for peptidoglycan synthesis in the septum