Eye, Nose, & Nasal senses
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
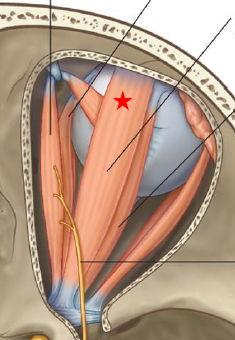
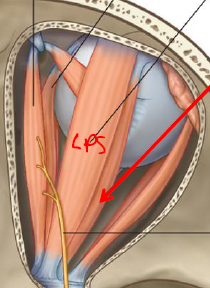
ID/Describe this muscle
Levator Palpebrae Superioris
Origin - Greater wing of sphenoid in orbit
Insertion - Components of upper eyelid
Innervation - Oculomotor N (dmg = drooping eyelid)
Fxn - Elevate upper eyelid
What are the movements of the eye
Elevation - Superiorly
Depression - Inferiorly
Adduction - Medially
Abduction - Laterally
External/Internal rotation
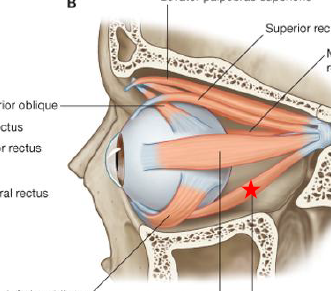
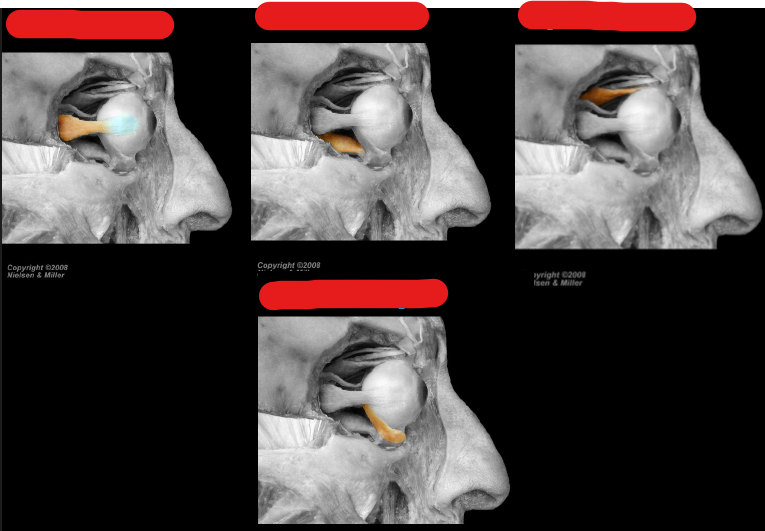
ID/Describe this muscle
Superior Rectus (deep to levator palpebrae superioris)
Origin - Sup part common tendinous ring
Insertion - Sclera of eye / Ant .5 superiorly
Innervation - Oculomotor N
Fxn - Elevation* / Adduction / Medial rotate eyeball
ID/Describe this muscle
Inferior Rectus
Origin - Inferior part common tendinous ring
Insertion - Sclera of eye / Ant .5 inferiorly
Innervation - Oculomotor N
Fxn - Depress* / Adduct / Lat rotate eyeball

ID/Describe the muscle
Medial Rectus
Origin - Medial part common tendinous ring
Insertion - Sclera of eye / Ant .5 medially
Innervation - Oculomotor N
Fxn - Adduct eyeball
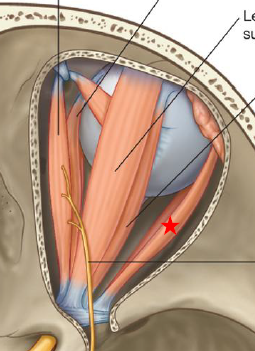
ID/Describe this muscle
Lateral Rectus
Origin - Lateral part common tendinous ring
Insertion - Sclera of eye / Ant .5 laterally
Innervation - Abducens N
Fxn - Abduct eyeball
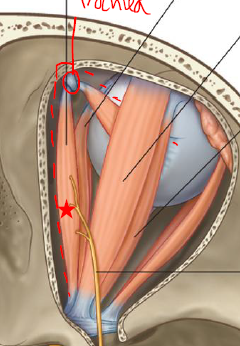
ID/Describe this muscle
Superior Oblique (goes through tendinous loop - trochlea + 90 degree bend in muscle)
Origin - Sphenoid bone
Insertion - Superior surface eye, posteriorly
Innervation - Trochlear N
Fxn - Depress / Abduct / Medially rotate eyeball
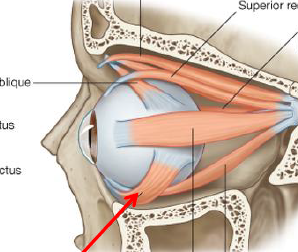
ID/Describe this muscle
Inferior Oblique (“Cradles” eyeball)
Origin - Medial floor bony orbit
Insertion - Sclera of eye, laterally
Innervation - Oculomotor N
Fxn - Elevate / Abduct / Laterally rotate eyeball
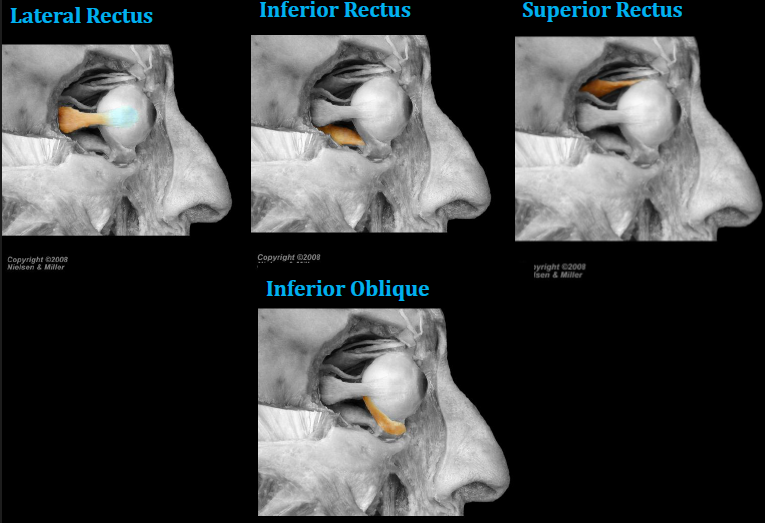
How to clinically test the muscles of the eyeball
Superior + Inferior Rectus
1: “look laterally”, reset or prep muscle so that second movement allows for testing of a specific muscle
Aligns axis of eyeball to long axes of muscles
2: movement in BOLD is what you are looking for the pt to do
Superior + Inferior oblique
Same but “look medially”
Follow finger to follow for all movement

What is the lacrimal apparatus responsible for
Production, Movement, Drainage of fluid from surface of eyeball (tears)
What composes the Lacrimal Apparatus
Lacrimal gland, Lacrimal ducts, Puncta, Lacrimal canalciculi, Lacrimal sac, Nasolacrimal duct
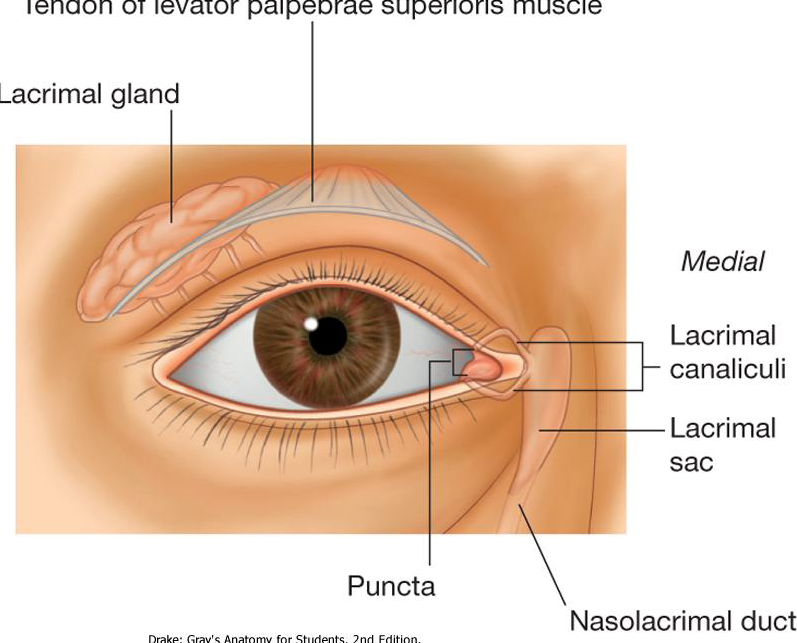
Describe the Lacrimal Gland
Located in superolateral region of orbit
Produces tears/fluids
Fluid moves from gland to eye via ducts
Fluid continually secreted/moved across eye when blink
What is most medial on the eye
fluid moves over eye towards medial side of orbit to Lacrimal Puncta
Medial side of orbit + Opening fluid enters to reach lacrimal canaliculi
What are the small tubs associated with upper/lower eyelid
Lacrimal canaliculi (carry fluid to lacrimal sac)
Where is the Lacrimal Sac located
Medial to orbit + Lateral to nose
Where does the lacrimal sac drain
It drains into the Nasolacrimal Duct
Duct runs along maxilla and dumps tears into nasal cavity (why your nose runs when u cry)
Describe the Optic N
CN 2, Large N, Post wall of eyeball, Runs through Optic Canal
Describe the Oculomotor N
Enters orbit via Superior Orbital Fissure
Divides into a sup/inf division
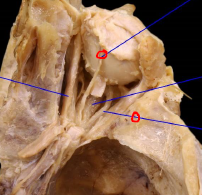
Describe Trochlear N
Innervates: Superior Oblique
Enters orbit via Superior Orbital Fissure
Describe the Abducens N
Innervates: Lateral Rectus
Enters orbit via Superior Orbital Fissure
Describe the walls of the eyeball
3 layers:
Outer Fibrous Layer → Sclera + Cornea
Middle Vascular Layer → Choroid + Cilliary Body + Iris
Inner Layer → Optic part of retina + Nonvisual part of retina
Describe the Sclera of the Eye (outer)
“Whites” of your eye
Fibrous CT
Post placed
Protects and shapes eye
Describe the Cornea of the Eye (outer)
Transparent ant portion
Allows light to enter eye
Describe the Choroid of the Eye (middle)
Supplies blood to all layers
Brown pigment to absorb light, prevent scatter, & visual confusion
Firmly attached to retina / Loosely attached to sclera
Describe the Cillary Body of the Eye (middle)
Thickened ring of tissue surrounding lens
Contains: Ciliary Muscles + Processes
Suspensory ligament
Describe the Iris of the Eye (middle)
Colored portion of eye, surrounds the pupil
Projects outward from ciliary body
Contains 2 muscles that control size of pupil: Sphincter pupillae + Dilator pupillae
Describe the Optic part of the retina of the Eye (inner)
Delicate 2-layered membrane
Outer pigmented layer → No photoreceptors
Inner neural layer → Photoreceptors / Sensitive to light
Describe the Pigmented Layer of Retina (optic part)
One cell thick, firmly attached to choroid
No photoreceptors
Absorbs light and prevents scattering
Stores Vit A
Describe the Neural Layer of Retina (optic part)
Contains: Photoreceptors, Rods/Cones, Other neurons involved in transmitting impulses to optic N
Only attached to pigmented layer around optic N and Ora Serrata (what detaches in detached retina)
Describe Rods and Cones (optic part)
Photoreceptor Cells
Rods → Responsible for detecting Black and White
Cones → Responsible for detecting Colors
Describe the Optic N and Optic Disc (optic part)
Optic N: Exits eyeball at back of eyeball
Optic Disc: Where Optic N extis retina, No photoreceptor cells, “Blind Spot”
Describe the Macula Lutea (optic part)
Lat to Optic Disc, Small area, Yellowish color
Central depression → Fovea Centralis
Describe the Fovea Centralis (optic part)
Depression in back of eye → Thinnest portion of Retina
HIGH visual sensitivity
High concentration of cones, color and bright light
Describe the Nonvisual part of retina
Covers internal surface of ciliary body and iris
No light sensitivecells
Junction B/T nonvisual and optic part (Ora serrata)
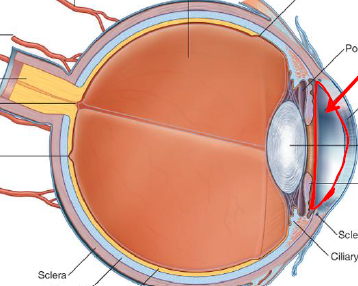
Describe this chamber
Anterior Chamber
Space directly behind cornea
Ant to iris
Filled with liquid → Aqueous humor
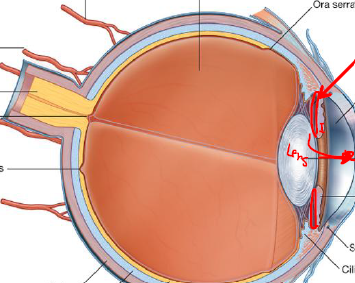
Describe this chamber
Posterior Chamber, post to iris / ant to lens
SMALL
Filled with liquid → Aqueous humor / Secreted here
Continuous w/ anterior chamber via pupil (Aqueous humor exits posterior chamber to enter anterior chamber)
What is Aqueous Humor
Found in Ant/Post chambers of eye
Supplies nutrients to cornea and lens
Maintains intra-ocular pressure
Absorbed via Scleral Venous Sinus in ant chamber
Problems w/ production or absorption of aqueous humor can cause intraocular pressure to increase → Glaucoma
Rise in pressure - compression of retina and blood supply to retina
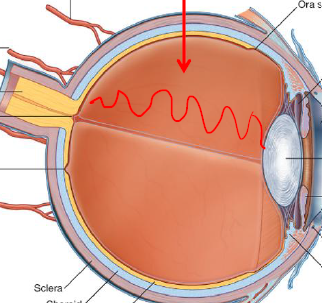
Describe this chamber
Vitreous chamber, post to lens
Filled w/ gelatinous vitreous body (humor) / gives shape to eyeball
What are the general fxns of the interal eye structures
Amount of light entering into the eye
Changes in the shape of lens to focus light onto the retina
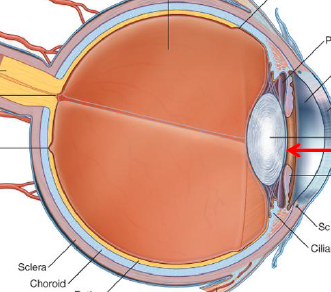
ID/Describe
Pupil - central opening in the iris
Can change shape as muscels in iris contract or relax → Dilate & Constrict
ID/Describe
Sphincter Pupillae
Smooth muscle fibers in circular pattern
PNS control
Contraction constricts pupil

ID/Describe
Dilater Pupillae
Smooth muscle fibers in circular pattern
PNS control
Contraction dilates pupil
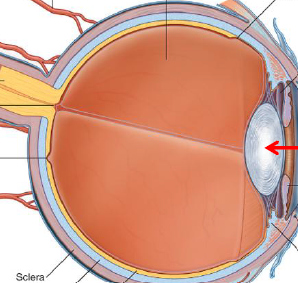
ID/Describe
Lens, attached cirumferentially to muscles associated w/ outer wall of eye
fxn: focus light entering eye
Distance focus - Ovoid shaped lens
Nearby focus - Round shaped lens
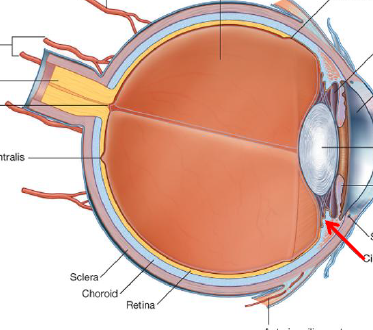
ID/Describe
Ciliary Body, contains ciliary muscle (Triangle shape extension of choroid)
Attach to lens via suspensory lig
Work to change shape of lens
Leads to changes in how light entering eye is focused
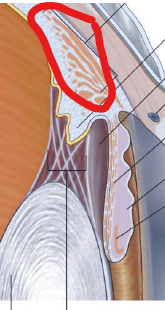
ID/Describe
Ciliary Muscles
Smooth muscle fibers, longitudinally, circular, and radial in orientation
PNS control
When they contract, decrease size of ring formed by ciliary body
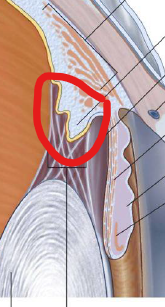
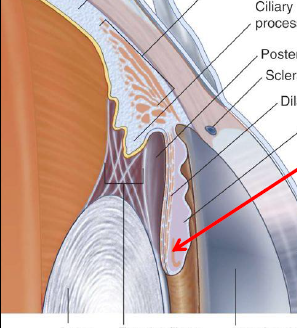
ID/Describe
Ciliary Processes
Ridges that project from inner surface of ciliary body
Zonular fibers extend off processes → Collectively form Suspensory Ligament that attach to lens
What are the fxns of the ciliary body

Describe the Nasal Cavity
Uppermost part of resp tract
House olfactory receptors
Held open by bone & cartilage
Small ant region (External nose)
Large post region (Within skull)
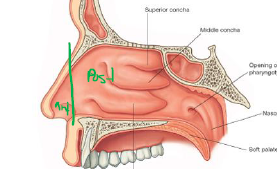
What are the general fxns of the Nasal Cavity
House Olfactory receptors
Adjust temp & humidity of respired air (rich blood supply)
Filter air through hair
Capture foreign materialy in mucus (moved by ciliated epithelial cells
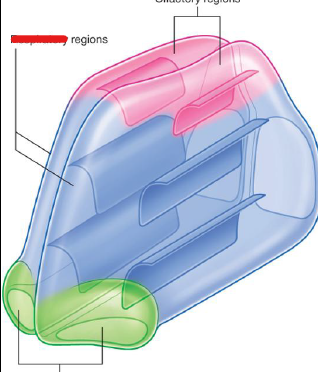
What is the green region
Nasal Vestible
Internal to nares, skin, hair follicles
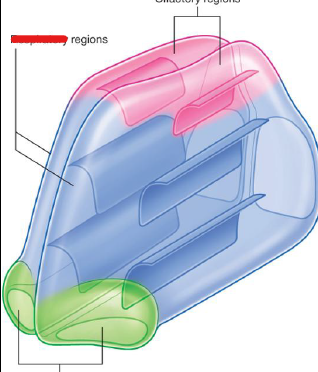
What is the blue region
Respiratory Region
Largest, rich neurovascular supply, respiratory epithelium, ciliated cells, mucous cells
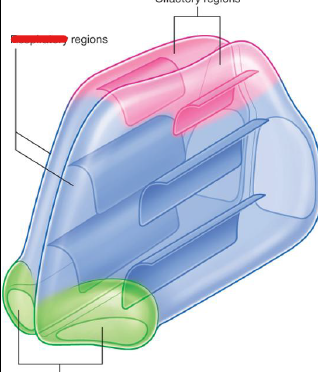
What is the pink region
Olfactory Region
Small, superior most, olfactory epithelium & receptors
What are the Nasal Cavity Boundaries
In half - Nasal Septum
Oral Cavity - Hard palate
Cranial Cavity - Frontal, Ethmoid, Sphenoid bones
Lateral Wall
Conchae - increased SA, Divide nasal cavity into 4 air channels
Skeletal Framework of the Nasal Cavity
Unpaired: Ethmoid, Sphenoid, Frontal, Vomer
Paired: Nasal, Maxillary, Palatine, Lacrimal, Inf nasal concha
What makes up the Lat wall of the Nasal Cavity
Superior, Middle, Inferior nasal concha of ethmoid
What openings are found in the Lat wall of Nasal Cavity
Nasolacrimal Duct + Paranasal Sinuses
Describe a normal + abnormal paranasal sinuses
Norm - Ciliated, respiratory mucus secreting / open into nasal cavities
Infected - Inflammed respiratory mucosa / blockage and fluid / bacteria, fungi, etc grow
PND can happen
Describe the Nasal Septum
Medial wall, bone + cartilage
Posteriorly: Perp plate of ethmoid, vomer, small contributions from nasal/frontal bone
Anterioly: Septal nasal cartilage
What is the floor of the Nasal Cavity
Soft tissue of external nose
Hard palate → Maxilla + Palatine bone

What is the roof of the Nasal Cavity
Superiorly - Ethmoid Bone (cribiform plate)
Anteriorly - Frontal + Nasal bone, Lateral process septal cartilage, Major alar cartilage
Posteriorly - Sphenoid, Medial pterygoid plate, Vomer
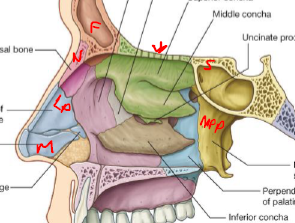
Describe the Ethmoid
Contributes towards → roof, lateral/medial walls, ethmoidal sinuses
Ethmoidal labyrinths → laterally, linked superiorly via cribifrom plate
Perp plate → vert, upper portion of nasal septum

What makes up the external nose
Bone: Nasal, Maxillary, Frontal
Cartilage: Single septal cartilage, Lateral processes of septal cart, Major + Minor alar
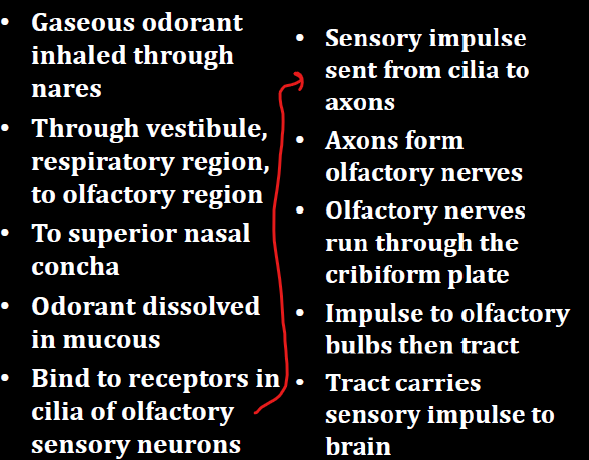
What is the Olfactory N
Formed from axons from olfactory sensory neurons
Through cribifom plate
Synapse w/ neurons in olfactory bulb
Sensory info sent to brain via olfactory tract
What is the pathway for the sense of smell