LESSON 3. Part 2. Sexuality, Sexual Orientation and Sexual Behavior
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Sexuality
a person’s capacity for sexual feelings
Sexual Orientation
refers to a person’s capacity to arouse the sexual interest of another, or, conversely, the sexual interest one feels towards another.
an enduring pattern of romantic or sexual attraction
Gender Identity
individuals concepts of themselves.
Sexual Identity
refers to how one thinks oneself in terms of whom one is sexually & romantically attracted to as defined by his or her biological sex & gender.
Sex
determined by virtue of one’s physical anatomy
GENDER
socially determined likes being masculine or feminine.
Sexual Orientation
enduring pattern of attraction to persons of the opposite sex, same sex, or to both sexes.
HETEROSEXUAL
Individual who are “straight”
HOMOSEXUAL
Considered as lesbians or gays
BISEXUAL
Hermaphroditic
Attracted to BOTH SEXES
GENDER DYSPHORIA
People who have gender identity that DIFFERS from their assigned sex
Considered as transgender
ROBERT WEISS’
description HS variables by?
Erogenous Zones
areas in the body that results in sexual pleasure when manipulated
Clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Mouth and Lips
Neck
. Breasts and Nipples
Ears
FEMALE Erogenous Zones
Penis
Mouth and Lips
Scrotum
Neck
Nipples
Perineum
Ears
MALE Erogenous Zones
Gender Fluid
A person whose gender identity is not fixed & shifts over time depending on the situation
Sexual Preference
a degree of voluntary choice regarding sexual partners
may be influenced by social systems like religion, language, and ethnic traditions.
Sexual Identity
Individuals may or may not consider their sexual orientation to define their identity, as they may experience various degrees of fluidity with sexuality, or simply identify more strongly as other aspects of their identity such as a family role.
Sexual Behavior
the act of engagement in sexual activity, typically involving the stimulation of erogenous zone to derive sexual pleasure between partners or with oneself.
Sexual fantasies
masturbation
coital sex
oral sex
anal sex
Common Types of Sexual Behavior
Sexual Fantasies
any mental imagery that is sexually arousing
Masturbation
tactile stimulation of the body for sexual pleasure
Coital sex
the term for vaginal-penile intercourse
Oral sex
oral stimulation of male or female sexual organ
Anal sex
defined as penetration by the anus of an object (stimulates the sensory nerve of the anus)
Society and Sexual Behavior
Sexual behavior considered normal depends on culture.
Sexually restrictive cultures
Sexually permissive cultures
2 Cultural Attitudes towards Sexual Behavior
Sexually restrictive cultures
possess a more rigid outlook on sexuality along with a dominantly negative attitude towards any form of sexual expression and/or activity.
Sex may be seen as taboo, and related behaviors may be strictly regulated or prohibited altogether.
Sexually permissive cultures
often hold more progressive views and attitudes towards sexuality and exhibit more leniency in evaluation and regulation of sex-related behavior.
Sophia Xepoleas (retrieved, 2015)
Societies generally have norms that reinforce their accepted social system of sexuality.
Non-Western societies – India and China
_____ valued Chastity in a potential mate,
western European countries - Sweden and Norway
_______ place little value on prior sexual experiences
Roman Catholic Church
believes that “Human life and human sexuality are inseparable. Since God created man in His own image, the human body and sex must likewise be good.”
Same-sex marriage:
The Catholic Church considers sexual activity between members of the _______ as a sin; marriage is defined as “a covenant by which a man and woman establish between themselves a partnership of the whole of life…..
Premarital Sex:
The Catholic Church disapproves of fornication (sexual intercourse between two people not married to each other),
12 years old
Age of Sexual Consent
Homosexuality
The Catholic Church welcomes celibate gay and lesbian people but condemns _____ acts.
_______ persons are called to chastity. Such person must be accepted with respect and sensitivity.”
Masturbation and Birth Control
The Catholic Church sees masturbation as sinful and disapproves of “Artificial” means of birth control.
Incest
The Catholic Church disapproves of and does not recognize any form of incestuous relationships
DSM V
the official manual for diagnosis of mental health disorders. Mental Health Disorders Associated with Gender Identity and Sexual Orientation
Gender Dysphoria
the DISTRESS a person feels due to a mismatch between gender identity and their sex assigned at birth.
Transsexualism
desire to live and be accepted as a member of the opposite sex, usually accompanied by the desire for surgery and hormonal treatment.
Gender Identity Disorder of Childhood
persistence and intense distress about one’s assigned gender, manifested prior to puberty.
Sexual Maturation Disorder
UNCERTAINTY about one’s gender identity or sexual orientation, causing anxiety or distress.
Unprotected sex-work
Multiple Sexual Partners / Anonymous partners
Elicit drug use
Penile-anal sex
Risky Sexual Behaviors
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
– a condition passed from one person to another through sexual contact
Vaginal Sex
Anal Sex
Oral Sex
Transmission from a mother to baby during childbirth
Skin to skin contact
Sharing Equipment
HOW CAN SOMEONE GET AN STI?
Young people ages 15-24 years old
Long-term travelers
Sex Workers
People who experience Sexual Molestation
WHO GETS STIs?
1. Chlamydia
2. HPV / Human
Papillovirus
3. Syphilis
4. HIV
5. Gonorrhea
6. Pubic Lice
7. Trichomoniasis
Most Common Types of STDs
Chlamydia
Gonorrhea
Syphilis
3 BACTERIAL STIs
Days or Weeks
Days or Weeks
Weeks or Months
Chlamydia
Among the most common bacterial STIs in the world
Passed by having unprotected oral, anal or vaginal sex
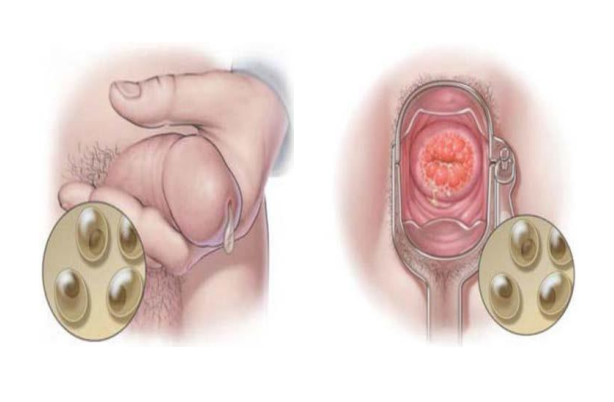
Condoms or Dental dams
can help prevent the spread of chlamydia during vaginal/anal sex
used for protection during oral sex
Gonorrhea
Sexually transmitted bacterial infection
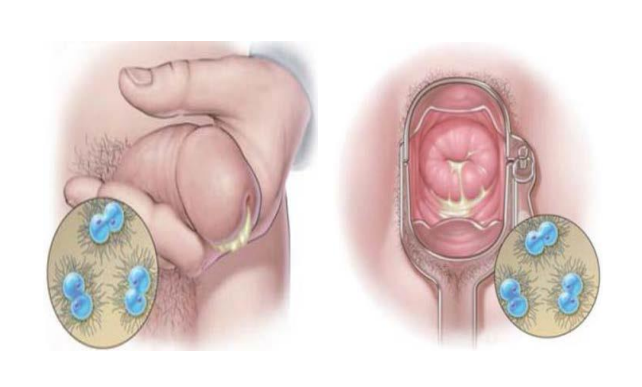
Curable
Remember chlamydia, gonorrhea, & syphilis is ______
Syphilis
Rare sexually transmitted bacterial infection
Can cause serious damage to the body if not cured, including death.
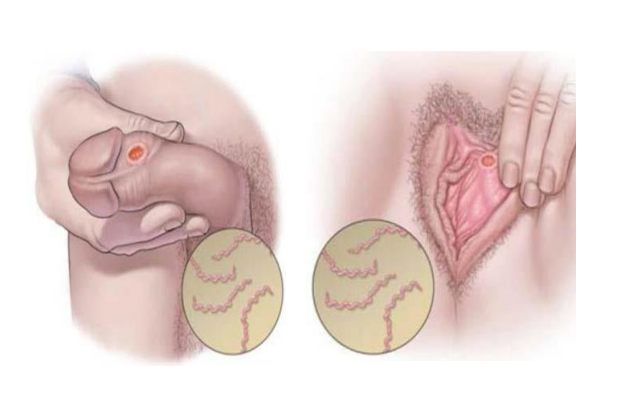
Pubic lice
Scabies
Trichomoniasis
PARASITIC STIs
Pubic Lice
Intense itchiness
Scabies
Reddish Rash
Trichomoniasis
Pain during sex or Urination
Vaginal Discharge
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
Genital Herpes
Hepatitis
HIV/AIDS
VIRAL STIs
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
spread through skin to skin contact, oral, anal and vaginal sex with an infected partner
there is no cure
contagious
Genital Herpes
Caused by the Herpes Simple Virus (HSV)
never develop sores
contagious
NOT CURABLE. It is TREATABLE