Lecture 7 - Electric Circuits
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Loop Rule = conservation of energy
net potential changes = 0 (in closed loop)
OR
net voltage gains = net voltage losses
Junction Rule = conservation of charge
net currents entering = net currents leaving (at any junction)
Resistors in a series
Req = R1 + R2
Resistors in parallel
I/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2
globes connected in parallel give…
more light
what is brightness based on?
Amount of power
When calculating the multiple resistors, treat the parallel circuits…
as one entity, calculate the resistance of the parallel part and then add with the series
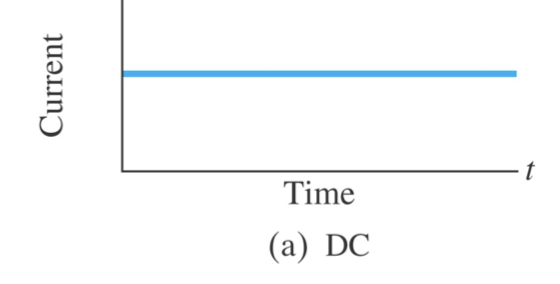
Current from a battery flows steading in one direction…
direct current (DC)
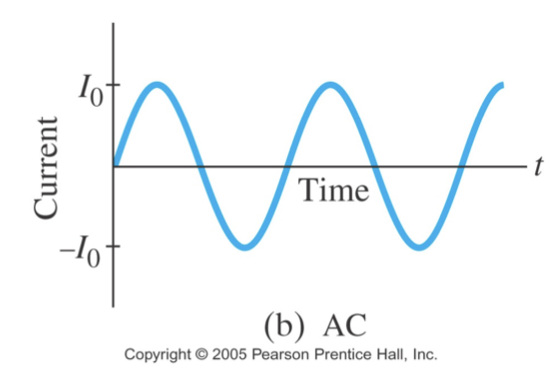
current from a power plant varies sinusoidally…
alternating current (AC)
the electrons in a wire first move in one direction and then in the other, thus polarity changes every half a cycle
Average power in AC circuit
Average power = VI/2
max power in AC circuit
Max power = VI
electric hazard
faulty wiring and improper grounding can be hazardous
make sure electrical work is done by a professional
appliance connected to a wall socket via a 3 prong plug
3rd prong connects the metal casing directly to the ground wire, in this case the current will go directly into the ground instead of flowing into the person’s body
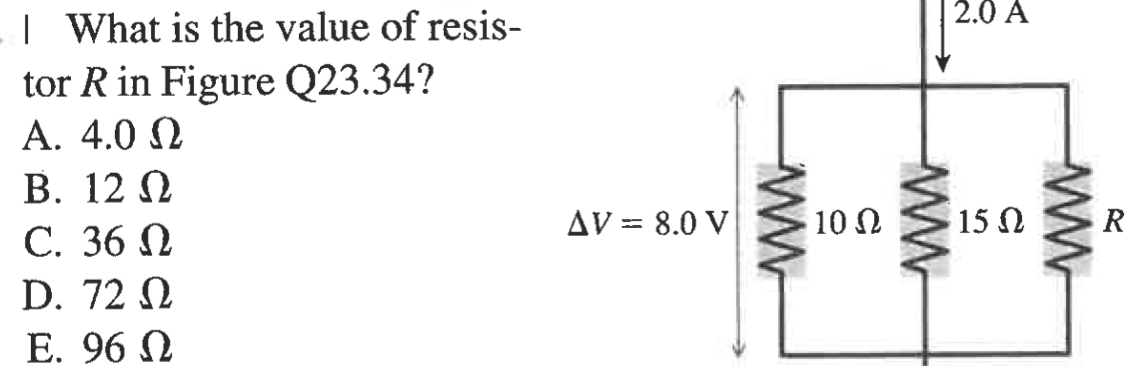
How to find the value of one parallel resistor
I = VR
I = 8/10 + 8/15 + 8/R
2 = 8/10 + 8/15 + 8/R
R = 12 ohms
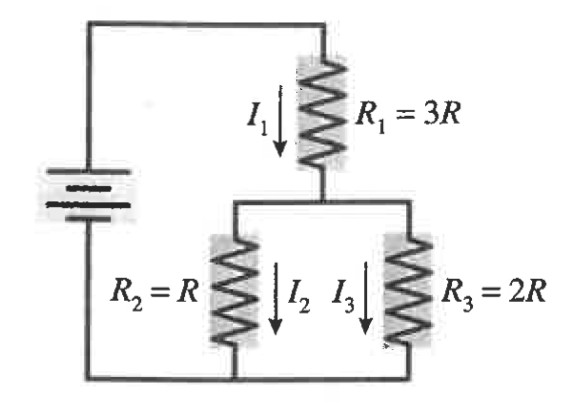
Rank the largest to smallest currents
I1 = I2 + I3
I2/I3 = R3/R2 = 2R/R → I2 = 2I3
I1 = 2I3 + I3 = 3I3
I1 > I2 > I3
In a series circuit current is the…
and voltage is….
same everywhere
shared
In a parallel circuit, voltage is…
the same for all branches
In a parallel circuit, the current in the two branches must be equal to…
the overall charge