Biopsychology exam 2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are the four steps of pharmacokinetics?
Absorption - affected by route of administration
distribution- via circulation(sometimes across BBB)
Metabolism- liver, stomach, or GI tract
Excretion- kidneys filter blood
What are agonists and antagonists?
Agonists mimic neurotransmitters by binding to receptor and activating it
Antagonist- blocks receptor by binding to it but not activating it
What is drug action, drug effect, and drug potency?
Drug action- what it does at receptor
Drug effect- what happens after
Drug potency- dose response curve - give different doses to see threshold and maximum response(ED 100) and 50% response(ED50)
What is classical vs operant conditioning and how does it relate to addiction?
Classical conditioning associates a stimulus with an involuntary response while operant conditioning associates a behavior with a certain outcome using positive or negative reinforcement.
addiction uses operant conditioning and positive reinforcement for reward and neg. reinforcement for withdrawal
what area is activated by drug use? How are pathways strengthened?
addiction effects the ventral tegmental area which is made up of groups of cell bodies(nuclei) with axons being the nucleus accumbens, the pleasure and reward center of the brain. addiction occurs due to releasing of dopamine by the nucleus accumbens which leads to want of that release again. going through the addiction spiral(preocupation, binge intoxication, withdrawal, persistant want), neural connections strengthen.
What is the incentive salience theory of motivation?
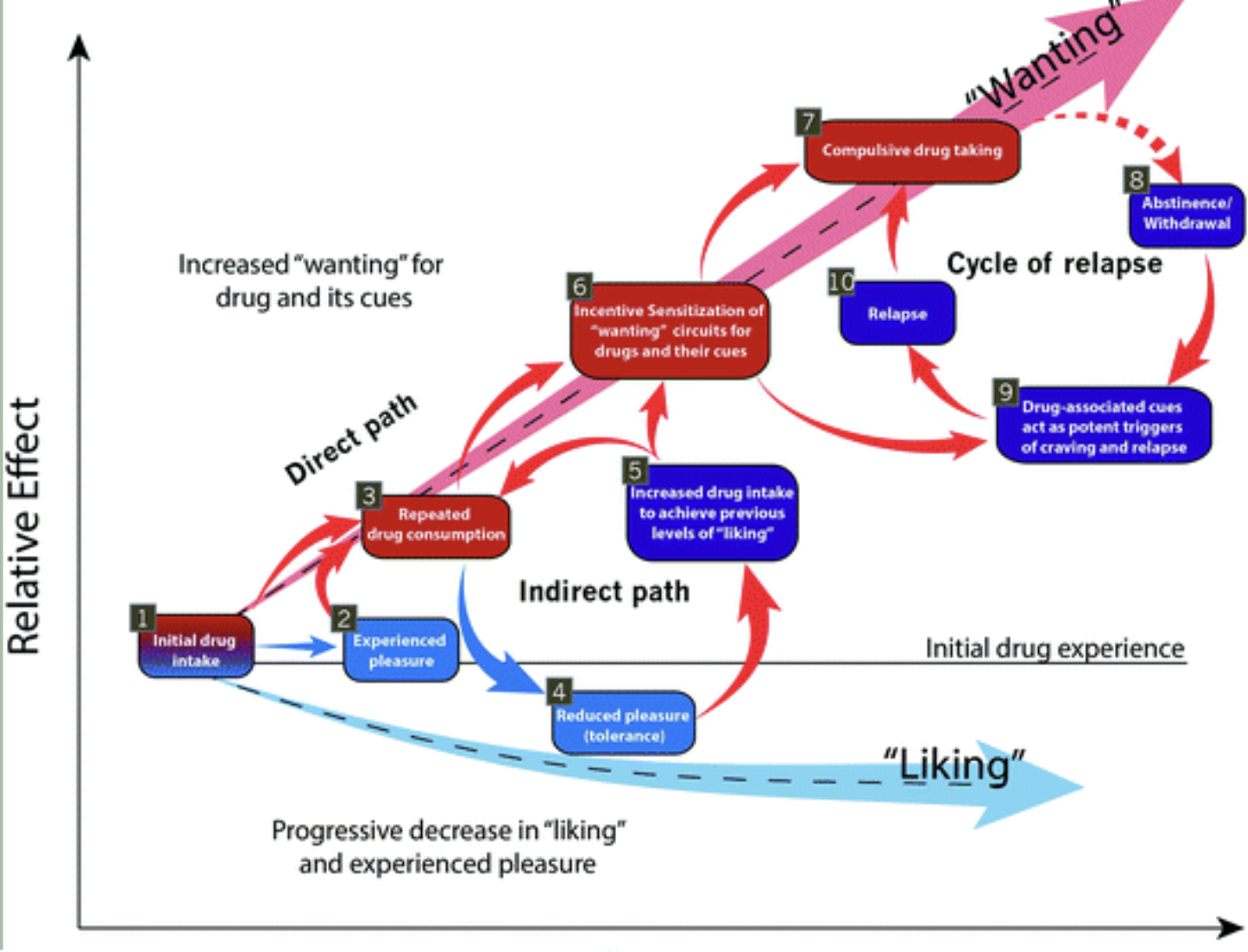
relative drug effect over time; liking goes down and wanting goes up
What are the mechanisms of cocaine and LSD?
cocaine blocks dopamine, seratonin, and norepinephrine reuptake by blocking the transporter proteins which overstimulates the nucleus accumbens
LSD is synthetic psychidellic that typically a seratonin agonist that binds to the 5HT-2a receptor and activates hallucinogenic effects by increasing blood flow to the primary visual cortex.
How are drugs classified in the US?
Schedules; schedule 1 drugs, like heroin, are the most illegal and have no medicinal effects.
How do opioids work?
opioids increase neuropeptides, such as endophins, to relieve pain
works on many receptors including mu receptors which are metabotropic and coupled to K+ channels, which hyperpolarizes the post-synaptic cell and reduces the inhibitor GABA so dopamine neurons can fire more and send more dopamine to the nucleus accumbens
what is the pathway for pain reception?
nociceptors are free nerve endings in skin that release chemicals at the site of damage to send pain info up the spinal cord and to the thalamus and somatosensory cortex
what is the difference between rats that were raised in impoverished environments or enriched environments?
rats raised in an impoverished environment where no sensory needs were met had less synaptic connections between neurons than rats that grew up in an enriched environment with friends and toys.
What’s the difference between bottom-up and top-down processing?
Bottom-up processing refers to sensation and does not include much ambiguity or thought and culminates in sensory perception. Top-down processing refers to perception and uses prior knowledge to process the same sensory information.
Explain the difference between the across-fiber and labeled line model.
The labeled line model refers to a sensory system that has an identifiable location of a sensory receptor cell for a specific stimulus, as seen in the auditory system. The across-fiber model refers to a sensory system that activates multiple fibers when exposed to a stimulus and one sensory receptor cell may be activated by multiple stimuli, as seen in the olfactory system.
How do taste buds work to send gustatory messages to the brain?
Taste buds are under papillae on the tongue and have receptors on the sides that food chemicals bind to and activate a certain signal pathway that generates an action potential from the activated cells to travel down the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves to the thalamus in the brain. These action potentials deliver information about whether food is sweet, sour, umami, salty, or bitter, depending on which receptors are bound to(receptors are specific to certain chemicals).
What is the pathway for odorants to send messages to the brain?
Odorants are trapped in the nose by mucus and they bind to the olfactory epithelium and activate a pattern of receptors that correspond to a smell in the brain. The binding of odorants ionotropically and metabotropically open sodium channels that create action potentials that travel from neuron-to-neuron(down the olfactory nerve) to the amygdala and hippocampus for sensory processing.
What are the differences in roles of rods and cones in vision?
Rods are light sensitive and open ion channels, called opsins, in response to different levels light stimulus to convey information to the brain, and they are more active in dim lights and are motion sensitive. Cones convey information about different colors because they have receptors that respond to different wavelengths of light and transmits that information to create detailed color vision in bright light
What is the difference between photopic and scotopic systems?
Scotopic systems are when rods are active(cones are silenced), require less light to generate an action potential(very sensitive), form black and white vision, and have larger receptive fields . Photopic systems are when cones are active(rods are silenced), form color vision, and require and have smaller receptive fields.
how does neuroplasticity relate to afferent stimulation and learning? What is rerouting and sprouting in synaptic pruning?
Neuroplasticity refers to the brains ability to form, prune, and reorganize synpatic pathways for more efficient processing. Rerouting is when new connections are made between active neurons to create alternate neural pathways and sprouting is when neurons form new dendrite and axon extensions to form new pathways.
what’s the pacinian corpuscle and what sense does it control?
the pacinian corpuscle is a sensory nerve that responds to touch and vibration. Touch pulls open channels for Na+ to enter and depolarize cell to send a graded potential to next cell. stronger touch=higher graded potential
what is retronasal olfaction vs orthonasal olfaction?
orthonasal olfaction is what is smelled through nostrils whereas retronasal olfaction is when odorants travel from the mouth through the throat and to the nasal cavity, and helps develop flavor.
what are pheromones?
pheromones can be sensed by animals of the same species using pheromone receptors in the vomeronasal organ
what are the five layers of the retina?
Pigmented epithelium, rods and cones layer, ganglion layer, bipolar layer, optic nerve layer
light goes through other layers to the rods and cones layer and signals are transmitted upwards.
what are bipolar cells?
reduction of glutamate(hyperpolarization) excites bipolar cell because glutamate is inhibitory to bipolar cell. bipolar cell depolarizes and releases glutamate to make more ganglion action potentials
is the cell hyperpolarized or depolarized in response to light?
the cell hyperpolarizes with light causing a reduction in glutamate release and depolarizes in the dark
what is off-center vs on-center bipolar cells?
off center bipolar cells are excited by glutamate and on-center bipolar cells are inhibited by glutamate. on center cells refer to all the photoreceptors that talk to the bipolar cell, creating the receptive field of the bipolar cell(on-center= center of receptive field).
what are horizontal cells?
horizontal cells connect cone cell and bipolar cell and make and release GABA onto off-center bipolar cell to inhibit it bipolar cell and ganglion cell.
What is the pathway for vision?
eye - optic nerve - optic chiasm - optic tract - lateral geniculate nucleus(thalamus) - primary visual cortex - non-primary visual cortex - association cortex.
what are simple and complex cortical cells and where are they located?
located in V1 of the primary visual cortex, simple cortical cells percieve bars of light in a specific orientation while complex cortical cells perceive light in a specific orientation moving in a direction.