Material Science
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:38 AM on 2/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
Atomic Mass
\
The mass of an individual atom
The mass of an individual atom
2
New cards
Atomic Weight
Average of the atomic masses of an atom’s isotope
3
New cards
amu
average of proton rest mass and the neutron rest mass used for expressing masses of atoms, molecules or nuclear particles.
4
New cards
Force of attraction
FA =( 1/ 4πε0 \* r2) (q1e)(q2e)
5
New cards
At the equilibrium separation-distance the sum of attractive and repulsive forces
zero
6
New cards
net potential energy between 2 adjacent ions
EN = ( - A / r ) + ( B / r^n)
7
New cards
curve of EN versus r is a ………. at E0
minimum
8
New cards
E0 is
bonding energy
9
New cards
Ionic bonding
electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
10
New cards
Covalent bonding
electron sharing between two adjacent atoms such that each atom assumes a stable electron configuration.
11
New cards
metallic bonding
positively charged ion cores are shielded from one another, and also "glued" together by the sea of valence electrons.
12
New cards
Pauli exclusion principle
each electron state can hold no more than two electrons, which must have opposite spins. \n
13
New cards
equilibrium spacing between two atoms occurs when
bond energy (FN) is minimum , so FN = 0
14
New cards
As the atomic \n bonds are stretched the atoms
attract each other
15
New cards
when the atomic bonds are compressed the atoms
repel each other
16
New cards
sp3 hybridization
the mixing character of one 2s-orbital and three 2p-orbitals to create four sp3 \n hybrid orbitals with similar characteristics.
17
New cards
draw a px orbital
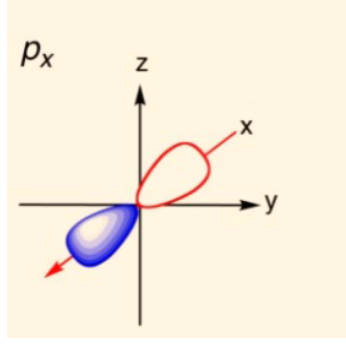
18
New cards
draw a py orbital
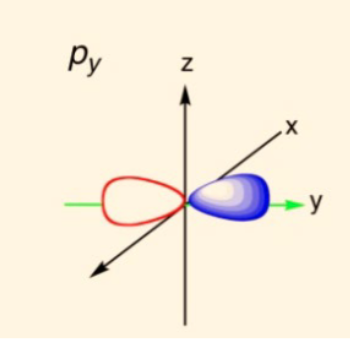
19
New cards
draw a pz orbital
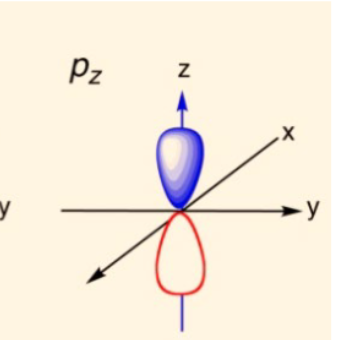
20
New cards
P orbitals have a ……. shape
dumbell
21
New cards
Van der Waals bonding
relatively weak attractive force between atoms or nonpolar molecules caused by a temporary change in dipole moment arising from a brief shift of orbital electrons to one side of one atom or molecule, creating a similar shift in adjacent atoms or molecules.
22
New cards
Hydrogen bond
primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to N / O / F
23
New cards
% Ionic character =
1 - e^\[-(0.25)(electronegative value for more electronegative element - Xb) \] x 100
24
New cards
If %IC = 0 and the elements are metal it is ……. bonding
metallic
25
New cards
atomic structure
relates to the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom and the number and \n probability of distributed electrons.
26
New cards
crystal structure
pertains to the arrangement of atoms in a crystalline s
27
New cards
FCC a =
2Rroot2
28
New cards
BCC a =
4R / root3
29
New cards
V =
a ^3
30
New cards
FCC amount of atoms in unit cell is
4
31
New cards
Number of atoms per unit cell
Ni + (Nf / 2 ) + (Nc / 8)
32
New cards
\# of atoms for FCC
4
33
New cards
FCC coordination number
12
34
New cards
APF =
volume of atoms in a unit cell / unit cell volume
35
New cards
number of atoms in BCC cell
2
36
New cards
Vc for FCC
16R^3\*root2
37
New cards
Vs for BCC
(4/3)*pi*R^3*
38
New cards
FCC APF
0\.74
39
New cards
Vs for FCC
(16/3)*pi*\*R^3
40
New cards
Vc for BCC
64\*R^3 / 3root3
41
New cards
BCC APF
0\.68
42
New cards
HCP number of atoms
6
43
New cards
Vc for HCP
6*R^2*height*\*root3
44
New cards
HCP Area
3a^2\*root3 / 2
45
New cards
HCP APF
0\.74
46
New cards
Vs for HCP
8piR^3
47
New cards
theoretical density for metals =
nA / VcNa
48
New cards
polymorphism
The ability of a solid material to exist in more than one form or crystal structure.
49
New cards
Allotropy
The possibility of the existence of two or more different crystal structures for a substance
50
New cards
angle of diffracted beam equation
nλ = 2d(hkl)sin θ
51
New cards
Linear Density
number of atoms centered on direction vector / length of direction vector
52
New cards
Plane Density
number of atoms centered on plane / area of plane
53
New cards
area of (100) plane
root2 \* a^2
54
New cards
Number average molecular weight
Mn
55
New cards
Mn =
Sum Xi \*Mi
56
New cards
Dp =
Mn / m (repeat unit weight)
57
New cards
DP is
number of repeat units along an average chain
58
New cards
Thermoset
material that strengthens when heated but cannot be remolded or heated after the initial forming
59
New cards
thermoplastics
can be reheated, remolded and cooled as necessary without causing any chemical changes. \n
60
New cards
thermoplastic is synthesized by
addition polymerization
61
New cards
thermosets are synthesized by
condensation polymerization
62
New cards
thermoplastics have ….. between molecular chains
secondary
63
New cards
Have ……. bonds between molecular chains and are \n held together by strong ……..
primar bonds / cross-links
64
New cards
thermoplastics have …… molecular weight compared to thermosets
65
New cards
number of vacancies =
Ne^(-Qv/kT)
66
New cards
Fraction of lattice sites =
Nv / N
67
New cards
Ns =
N*e*^(-deltaH / R (1/T2 - 1/T1)
68
New cards
for BBB h + k + l is
even
69
New cards
for FCC h , k , l are
either all odd or all even
70
New cards
\
\