Lecture 25 Tripartite synapse
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
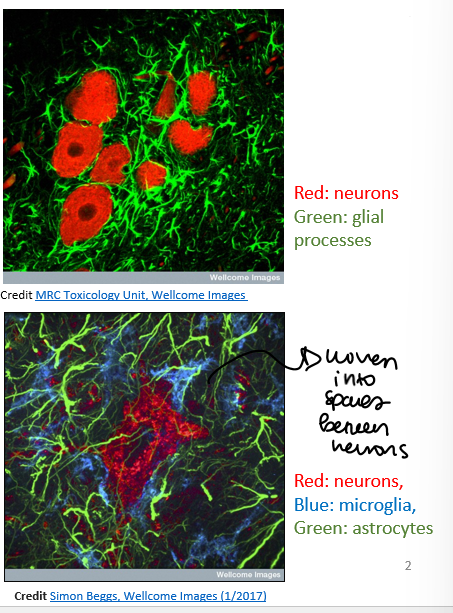
Glial Cells
There are 10-50 times as many glial cells than neurons
PNS:
glial cells are called schwann cells
make myelin for peripheral neurons
CNS:
microglia
oligodendrocytes
astrocytes
Ion channel expression:
potassium channels (so can maintain a resting membrane potential close to EK)
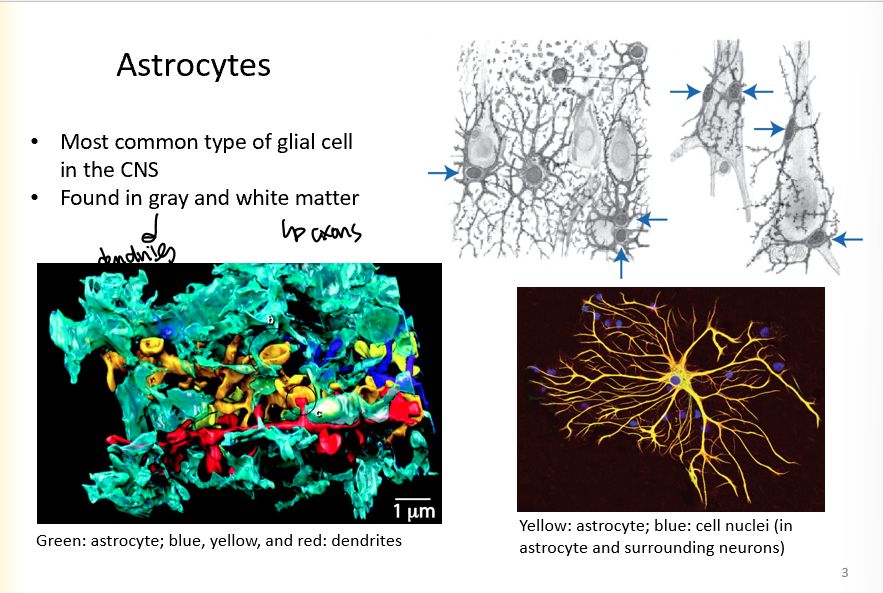
Astrocytes
most common type of glial cell in the CNS
found in gray and white matter
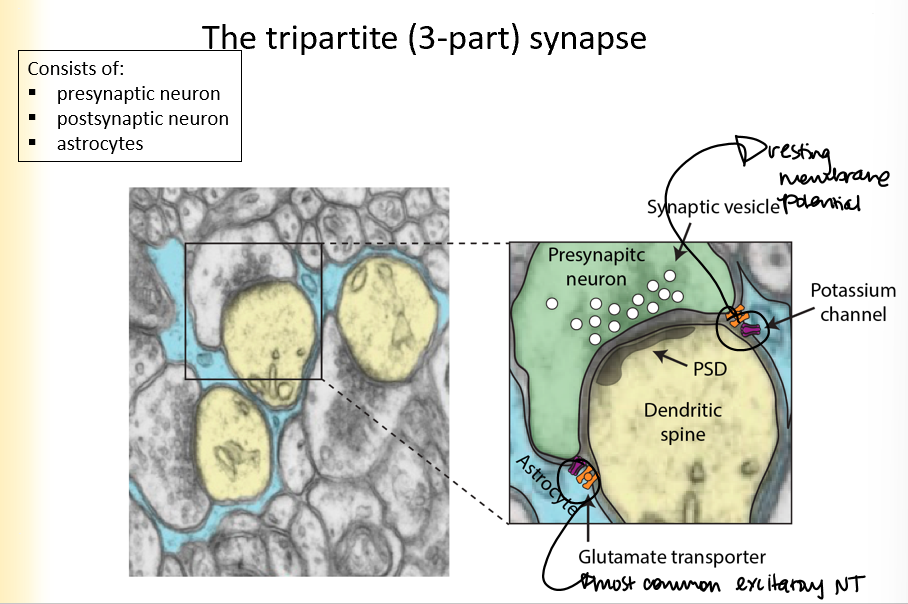
The tripartite (3-part) synapse
consists of:
presynaptic neuron
postsynaptic neuron
astrocytes
Astrocytic processes affect synaptic transmission and shaoe
astrocytes affect diffusion and uptake of neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft
Shape/proximity if astrocytes is not stable
can change over the course of minutes
change across the sleep-wake cycle
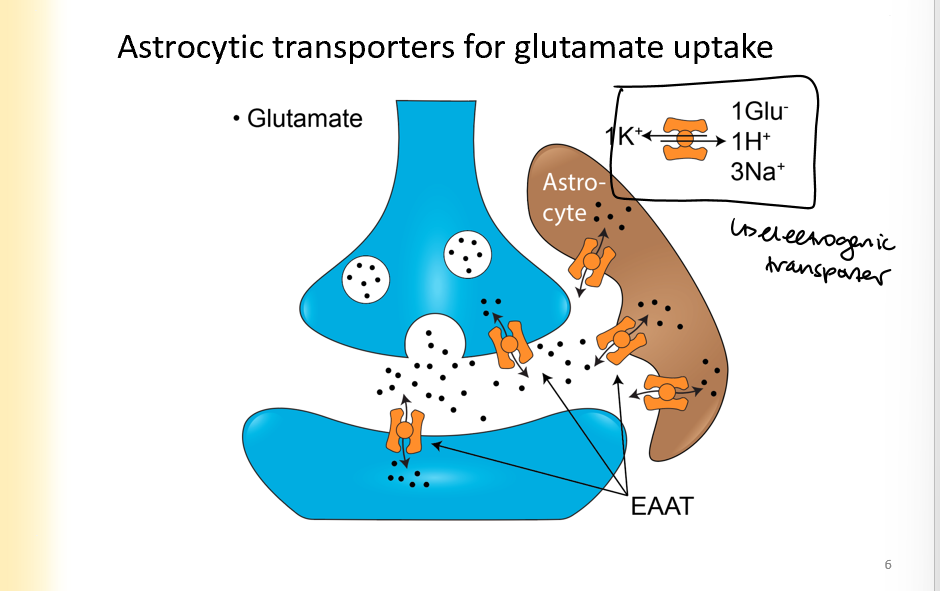
Astrocytes contributing to glutamate reuptake
glutamate goes from synaptic cleft to surrounding astrocytes to be taken out of the cytoplasm sooner
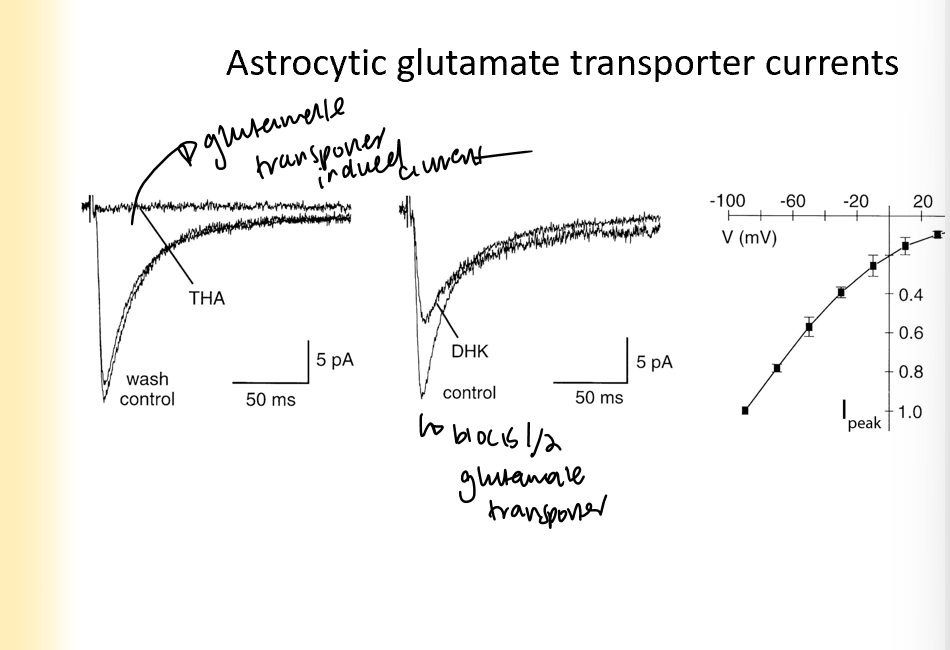
Astrocytic glutamate transporter currents
when you block glutamate transporters, the current going into the astrocyte decreases
current also changes based on the resting membrane potential
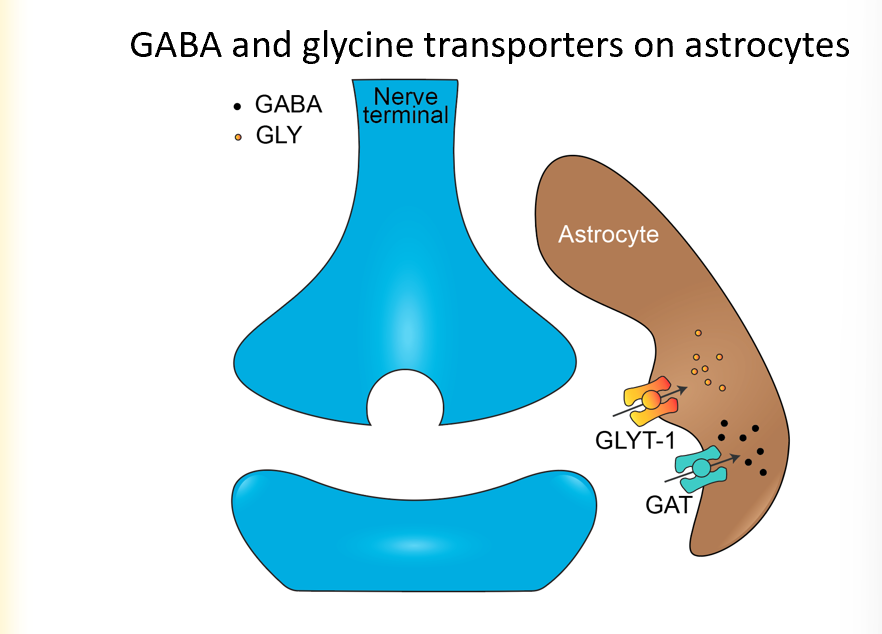
GABA and glycine transporters on astrocytes
do same thing as glutamate
Ion channels in astrocytes
Potassium channels:
maintain normal levels of K+
drive Vm of astrocytes (80 mv)
Voltage-gated ion channels
NA+
Cl-
Ca2+
Other cA2+ channels:
intracellular
mechano-sensitive
cannot produce AP’s but can respond to depolarization
Electrically-coupled groups of astrocytes
astrocytes are connected to other astrocytes via gap junctions
groups of 50-100 electrically coupled astrocytes can be regulated together
These groups of electrically coupled astrocytes tend to be somewhat exclusive, forming “microdomains” of 200-200 micrometerss

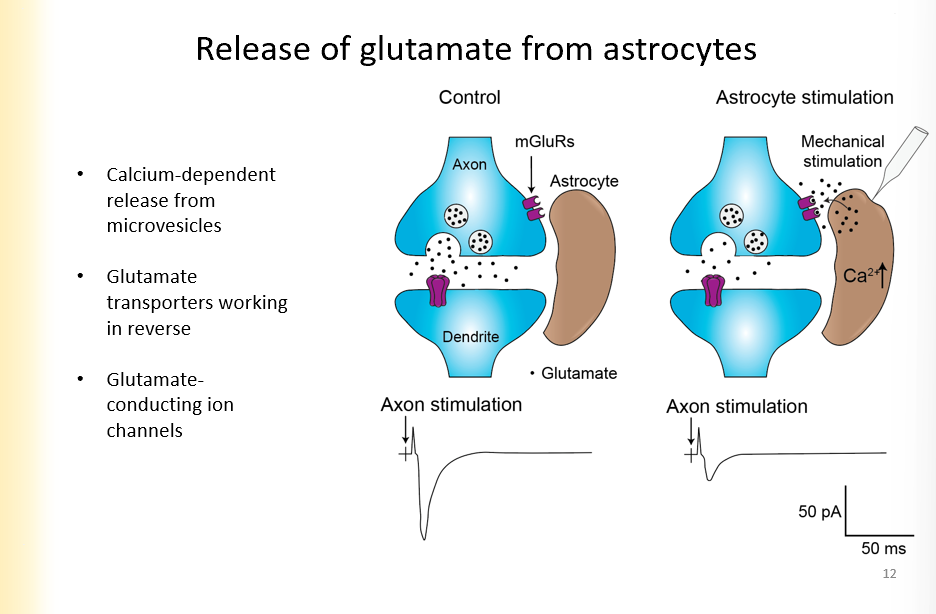
Release of glutamate from astrocytes
calcium dependent release from microvesicles
glutmate transporters working in reverse
glutamate conducting ion channels
There are mGLUR’s on the side of the presynaptic terminal
with mechanical stimulation and calcium entry, glutmate can be released by the astrocytes into the presynaptic terminal
smaller epsp
Are astrocytes involved in “information processing”
1.Astrocytes respond to external signals from other elements of the nervous system, including neurons.
2.Responses to external signals can change cytosolic calcium levels inside astrocytes rapidly and at high temporal precision.
3.Astrocytes release neurotransmitters in a calcium-dependent manner.
4.Release of neurotransmitter by astrocytes can affect neuronal responses.