Bio Unit 4: Cell Membrane & Transport
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Homeostasis
Balancing act that can be thrown out of place by environmental changes

Positive feedback
Moving away from homeostasis; when a change in a system is amplified(snowball effect)
What are examples of positive feedback?
Childbirth, lactation, blood clotting, fruit ripening
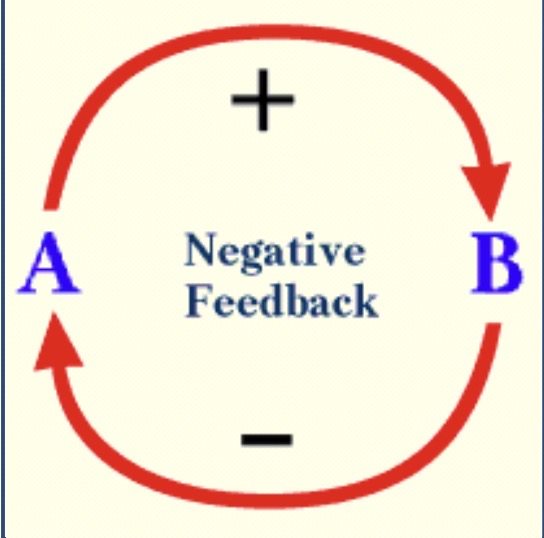
Negative feedback
Returning to homeostasis; when a system responds to change y returning to its original state or by decreasing the rate at which the change is occurring
Examples of negative feedback?
Body temperature, blood pressure, blood sugar levels
What types of cells are surrounded by the cell (plasma) membrane?
All cells
What are the characteristics of the cell membrane?
It’s thin and flexible
Why is the cell membrane thin?
To easily allow for movement of materials into and out of the cell
Why is the cell membrane flexible?
To allow for ease of movement and confirming to different spaces
Plasma membrane functions
Regulates what enters and exits the cell and provides protection and support for the cell
How is the cells membranes structure described?
A fluid mosaic model
Why is the cell membrane described as a fluid mosaic model?
There are many diverse protein molecules suspended in a fluid phospholipid bilayer
What does the plasma membrane include?
Primary and secondary
Primary
Protein and phospholipids
Secondary
Carbohydrates and cholesterol
What part of the phospholipid bilayer is hydrophilic?
Outer portion of the cell membrane that comes in contact with external liquid environment and internal cytoplasm
What part of the phospholipid bilayer is hydrophobic?
The inner part of the membrane that doesn’t come in contact with interior or exterior environments
What part of the bilayer play a role in selective permeability?
Hydrophilic tails
Selective permeability
Only certain molecules can cross the membrane
What molecules can pass the membrane with ease?
Oxygen and water
What cant cross the membrane with ease?
Polar molecules and many ions, they need assistance from transport proteins
What polar molecule can pass the membrane no problem?
Water
Why are proteins embedded in the membrane?
Carry out some of the cells chemicals reactions (enzyme), aid in the transport of specific molecules or ions across, send and receive chemical signal, recognize neighboring cells
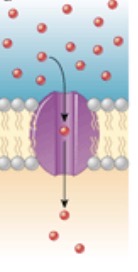
What is this?
Transport of materials
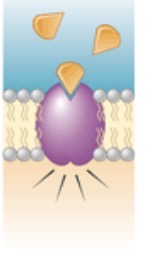
What is this?
Cell signaling
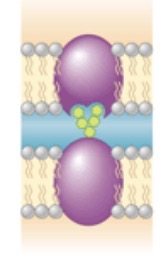
What is this?
Cell to cell recognition
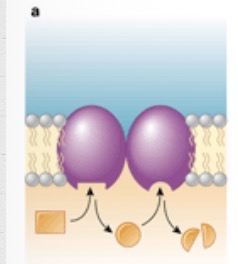
What is this?
Enzyme activity
What do membranes regulate?
The movement of particles from the liquid on one side of the cell membrane to the liquid on the other side
Concentration gradient
The different in the concentration of a substance between two area
What is the natural flow of concentration gradient?
High concentration to low concentration
Diffusion
Movement of particles down a concentration gradient from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Equilibrium
Occurs when the volute has become evenly distributed throughout the solution(equal)
Does diffusion require energy?
No it is passive transport
Passive transport
Does not require energy
How do particles move in diffusion?
Randomly
What does diffusion allow cells to gain?
Useful substances they require to obtain energy and grow
What does diffusion allow cells to get rid of?
Waste products
What are substances required by the cell?
Glucose, oxygen, amino acids
What are cells waste products?
Carbon dioxide, urea
Wha is urea?
Excess amino acid
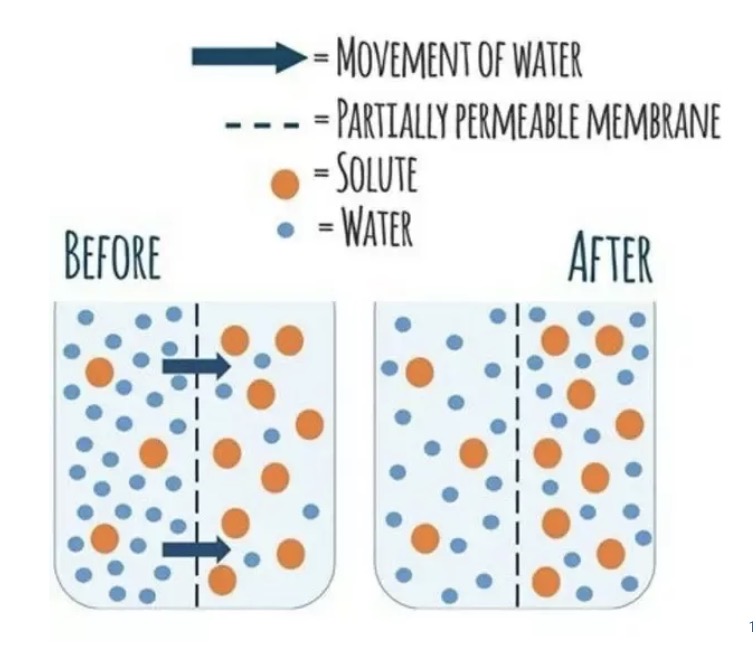
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through selectively permeable membrane
What type of gradient does osmosis follow?
Natural concentration
Natural concentration
High concentration to low concentration
Is osmosis passive?
Yes
Whats the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
Diffusion involves the movement of many types of substances and osmosis refers specifically to the movement of water
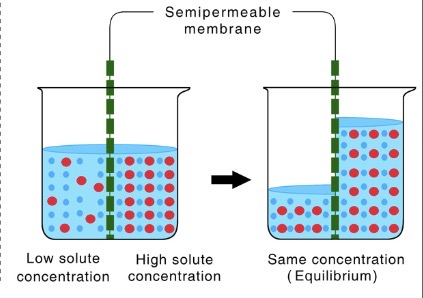
What is this?
Osmosis
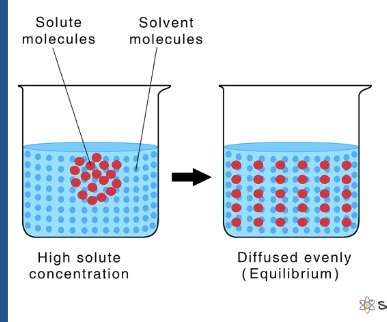
What is this?
Diffusion
Tonicity
Describes the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
What determines how a cell will be affected by osmosis?
The solution the cells in
What depends on the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane?
Tonicity
What are the 3 types of solutions?
Hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic
Hypertonic
The solution is more concentrated compared to the cell; higher concentration of solute and lower concentration of water
Hypotonic
The solution is less concentrated compared to the cell; lower concentration of solute and higher concentration of water
Isotonic
The solution has an equal concentration compared to the cell (on both sides of the membrane); equal concentrations of solute and water
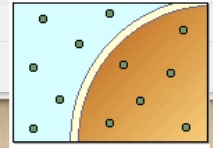
What is this?
Isotonic solution
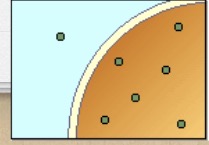
What is this?
Hypotonic solution
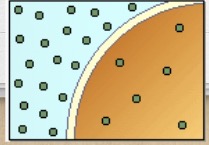
What is this?
Hypertonic solution
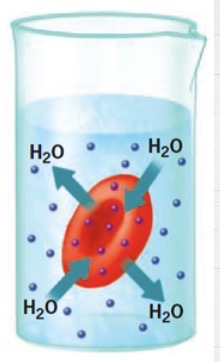
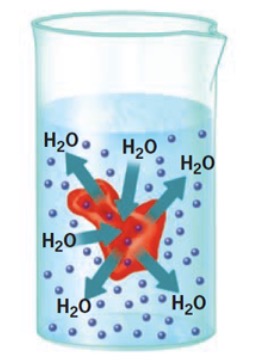
Where does water move for a hypertonic solution and how does the cell change?
Out; shrivel
Crenation
Shrivel
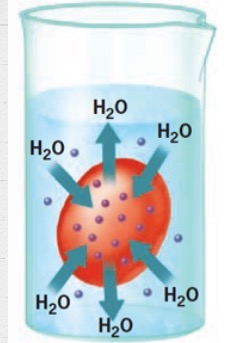
How does water move in a hypotonic solution and how does the cell react?
In; swells
How does water move in an isotonic solution and how does the cell react?
In and out; normally
What is this?
Isotonic solution
What is this?
Hypertonic solution
What is this?
Hypotonic solution
How does plants take up water through their roots?
Osmosis
Turgor pressure
The force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall
Whats the difference between Tonicity between plant cells and animal cells?
The cell wall prevents plant cells from bursting when in a hypotonic solution
What is this?
Hypotonic solution; turgid
What is this?
Isotonic;flaccid
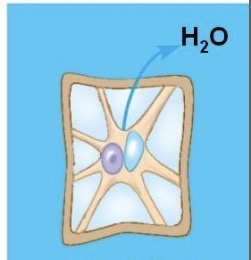
What is that?
Hypertonic; plasmolyzed
Facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific particles (polar or charged substances) across the cell membrane though transport proteins
Does facilitated diffusion require?
No its a form of passive transport
Driving force
Concentration gradient
What concentration does facilitated diffusion use?
Concentration gradient- high to low
What are transport proteins?
Helps specific substances move across the membrane
Types of transport proteins
Channel protein and carrier protein
Channel protein
Creates a hydrophilic channel that some molecules or ions use as a tunnel through the membrane
Carrier protein
Binds its passenger, changes shape, and releases its passenger on the other side
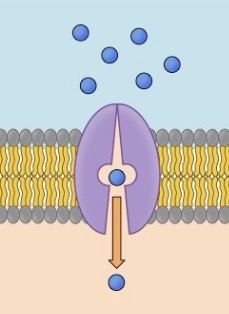
What is this?
Carrier protein
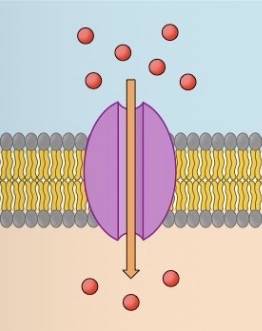
What is this?
Protein channel
Why is osmoses slow?
Because water is a polar molecule
Why can water diffuse rapidly in and out of cells?
A protein channel called aquaporin
What type of transport protein is aquaporin?
Protein channel
Where is aquaporin found?
Plant cells, Disney cells, and red blood cells
Active transport
When a cell must expand energy to move solute against its concentration gradient
What type of protein is involved in active transport?
Transport protein
What source of energy is used for active transport?
ATP
What concentration does active transport use?
Low to high concentration
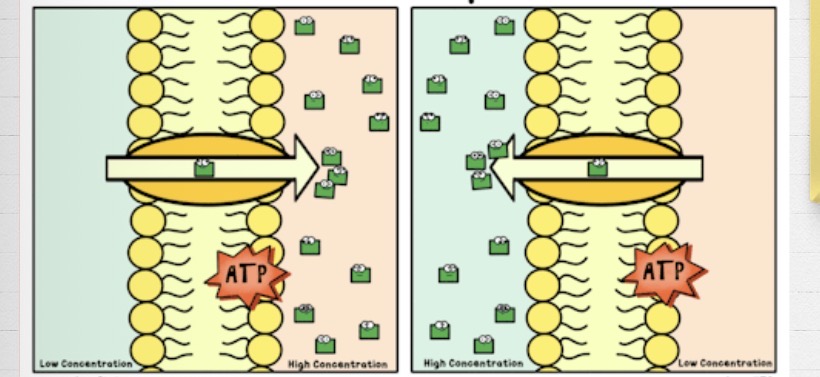
What is this?
Active transport
What does active transport allow?
A cell to maintain internal concentrations of small molecules and ions that are different from concentrations in its surroundings
What does a cell depend on to move a large molecule across the cell membrane?
Exocytosis and endocytosis
Exocytosis
Used by the cell to export bulky material like proteins and polysaccharides
Endocytosis
Used by the cell to take in large
What do both Exocytosis and endocytosis do?
Material to be transported is packaged within a vesicle that fuses with the cell membrane
What does Exocytosis involve?
A vehicle forming around the material to be released
Is Exocytosis what does the vesicle fuse with?
The cell membrane and forces contents out of the cell

What is this?
Exocytosis
What does a cell form in endocytosis?
A pocket of cell membrane around the material being taken in
What does the pocket do it endocytosis?
Breaks loose from the outer portion and forms a vesicle within the cell
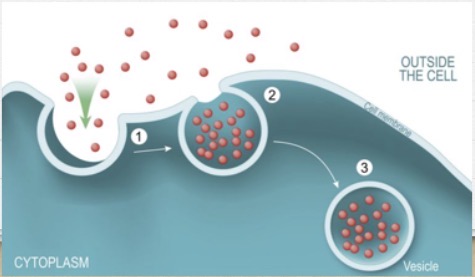
What is this?
Endocytosis