Lecture 25 Buffers
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Recognize buffer pairs: acids & bases and their conjugate bases & conjugate acids. Recognize that ionization, pH, and buffers impact biologic, physical and chemical properties. Understand the ionization of weak acids and bases at varying pH. Understand the predicted pH of active or inactive ingredients in water. Identify buffer pairs in formulations. Recognize that temperature and ionic strength, among others, influence pH and other equilibria constants. Select, recommend, and prepare buffer pair for a selected pH. Interpret buffering capacity of a buffer pair (combined) at a pH. Recognize rationale for combined and universal buffers. Recognize some uses for buffers in pharmaceutical systems.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
True or false: The ionization of weak acids and bases cannot be predicted.
False! They can be predicted
True or false: The pH of active or inactive ingredients in sterile water can be predicted.
True!!!
______ and ______ (+ others) influence pH and pKw
Temperature, ionic strength
How can the pH of a buffer pair be predicted?
It is predicted based on the amount of each substance
Buffering capacity is influenced by the _____ of the buffer pair combined and the __
concentration, pH
Which of the following is not an important pharmaceutical process affected by ionization?
a. distribution
b. solubility
c. potency
d. interaction with proteins
e. transport across lipid membranes
c. potency
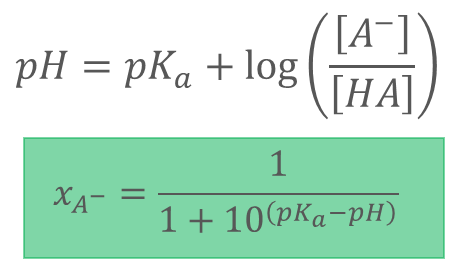
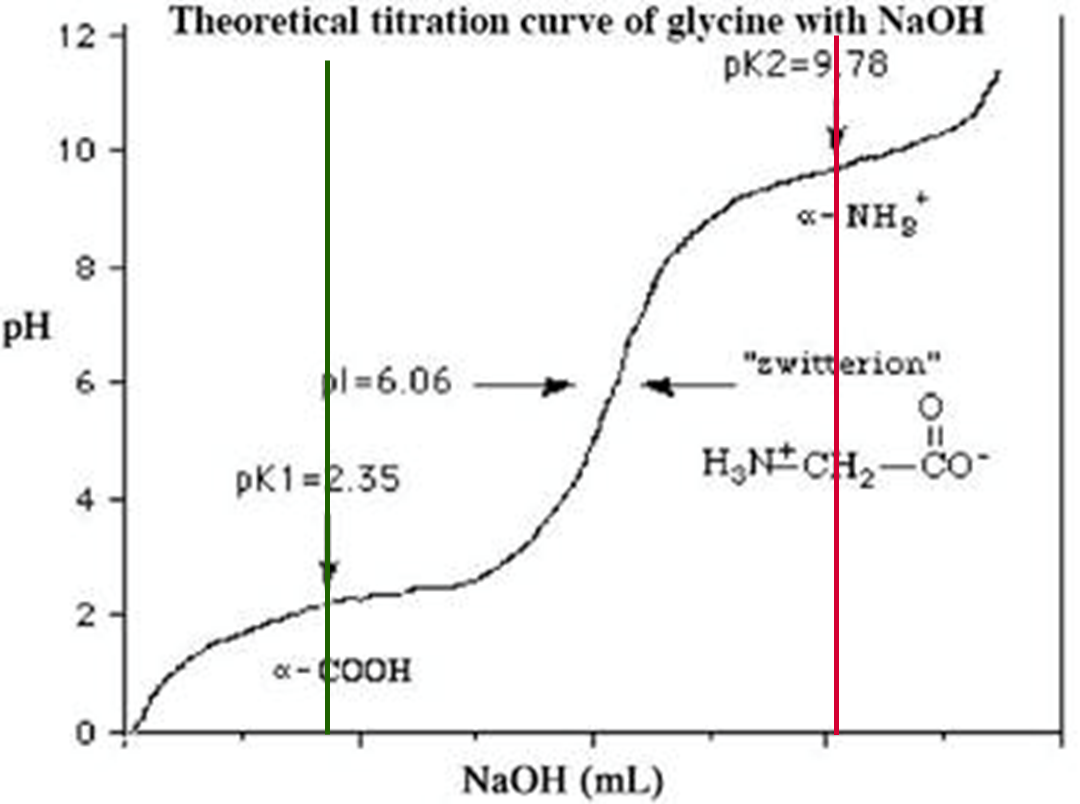
What does the green equation represent?
xA-: mole fraction ionized acid
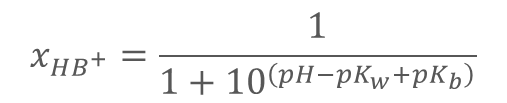
What does this equation represent?
xXB+: mole fraction ionized base
How does a Weak Acid influence pH of solution?
assume no other substances are added
assume dissociation is small but still present
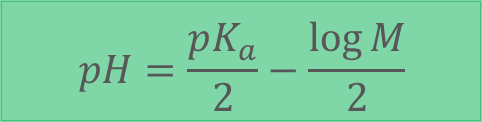
units: mol/L
Which of the following is NOT a way buffers are used in Pharmaceuticals?
a. Maintain chemical and physical stability of molecules in solution.
b. Mimic biologic environments.
c. Optimize release from a device.
d. Avoid irritation and toxicity in vivo.
e. Avoid physical instability after administration.
f. All of the above are correct
f. All of the above are correct
What is a buffer?
It is the resistance to change in pH with the addition of an acid or base.
Select the correct ways on making a buffer?
a. Basic form + Acid form
b. Basic form + Acid salt form
c. Acid form + Basic salt form
d. Acid salt form + Basic salt form
b. Basic form + Acid salt form
c. Acid form + Basic salt form
What are the steps to solve acid and base problems?
Determine which is the acid and which is the base.
Calculate the number of moles for the acid and base.
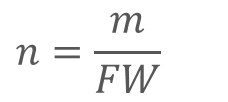
Calculate the pH
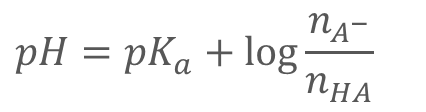
Changing the number of __ (ionic strength: µ) can influence pH
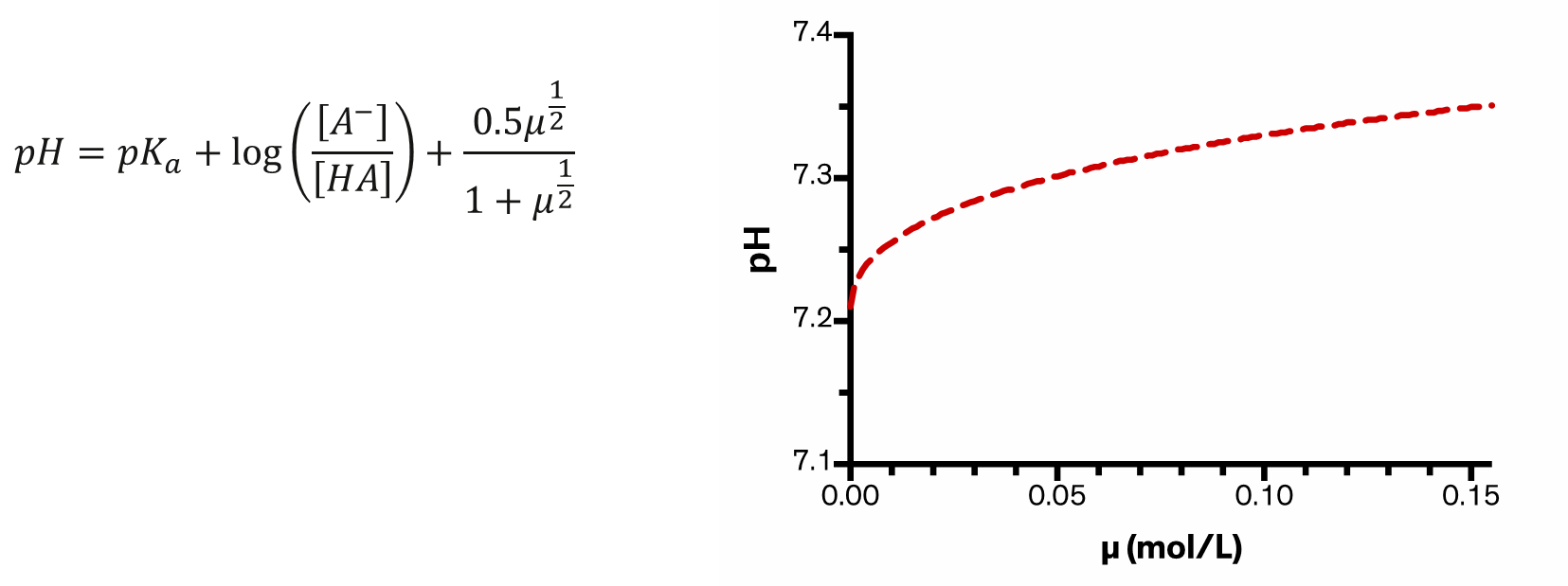
ions
What is buffer capacity and what does it depend on?
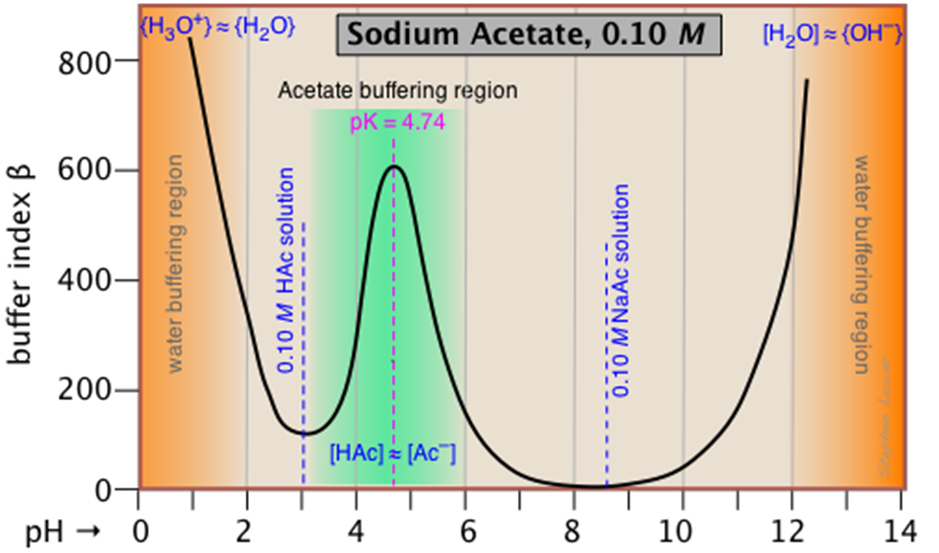
It is the amount of a base or acid necessary to change the pH
depends on the amount of buffer and the pH relative to the pKa
What is a universal buffer?
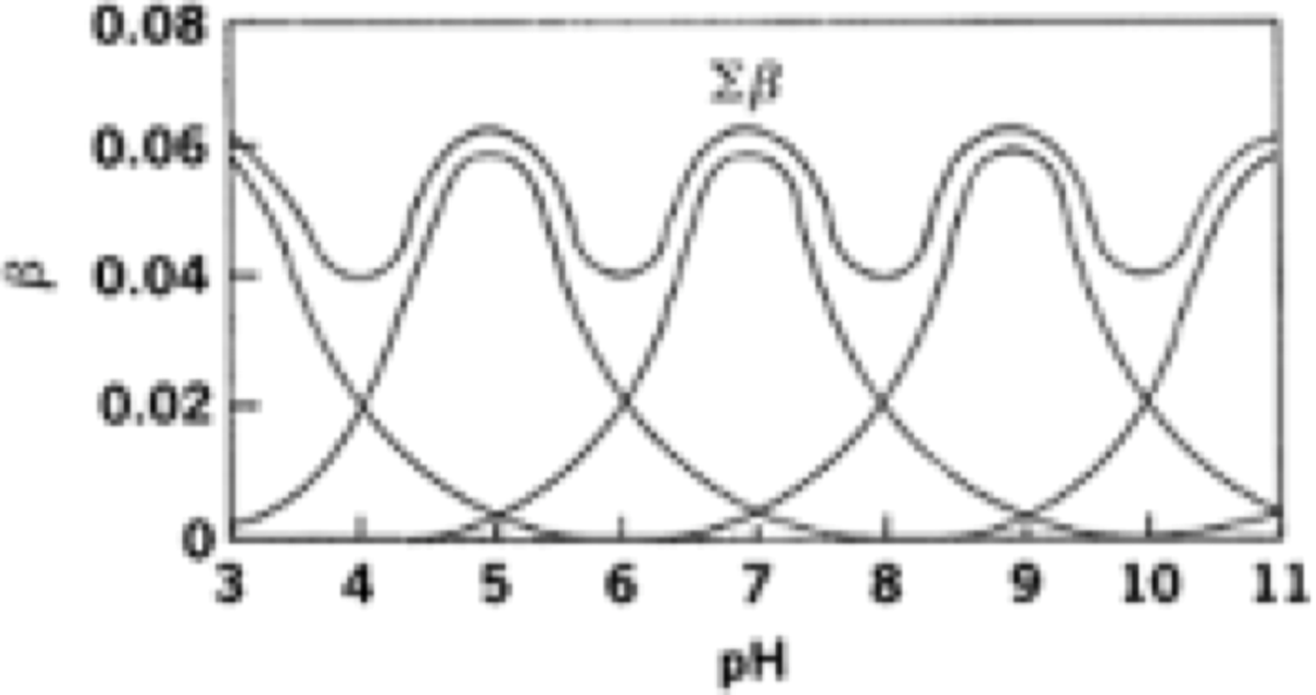
It is when multiple buffers are added where the buffering capacity is high at almost all pH.
Example:
Borate, phosphate, acetate
or
Borate, phosphate, citrate
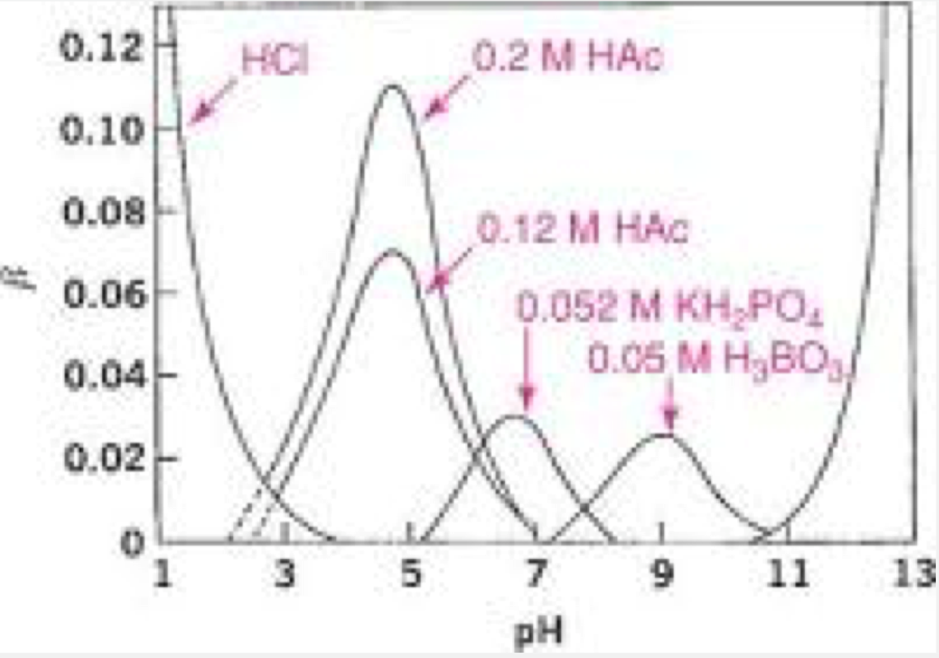
Each buffer will have a specific ___ and a buffer capacity
pKa
True or false: Some excipients can influence pH since they can have residual acid or base.
True! This is one of the issues.
Should you pick buffers with a pKa nearest or furthest from your desired pH?
nearest
For pharmaceutical products, why would you want to lower buffer capacity as possible?
So that natural buffering can take over after administration.