Urinary System
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
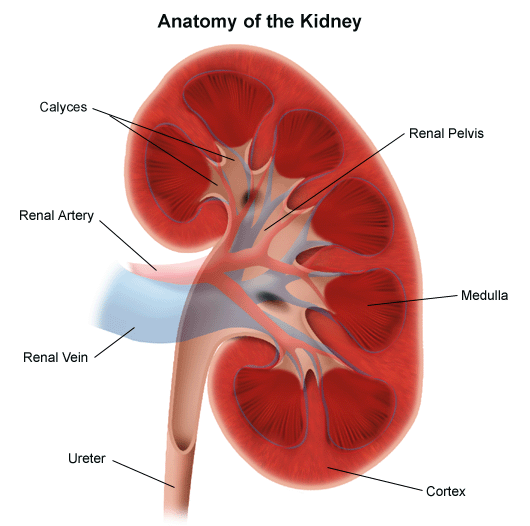
Kidney
located against the dorsal body wall, the kidneys are responsible for filtering blood, removing waste, and regulating fluid balance in the body.
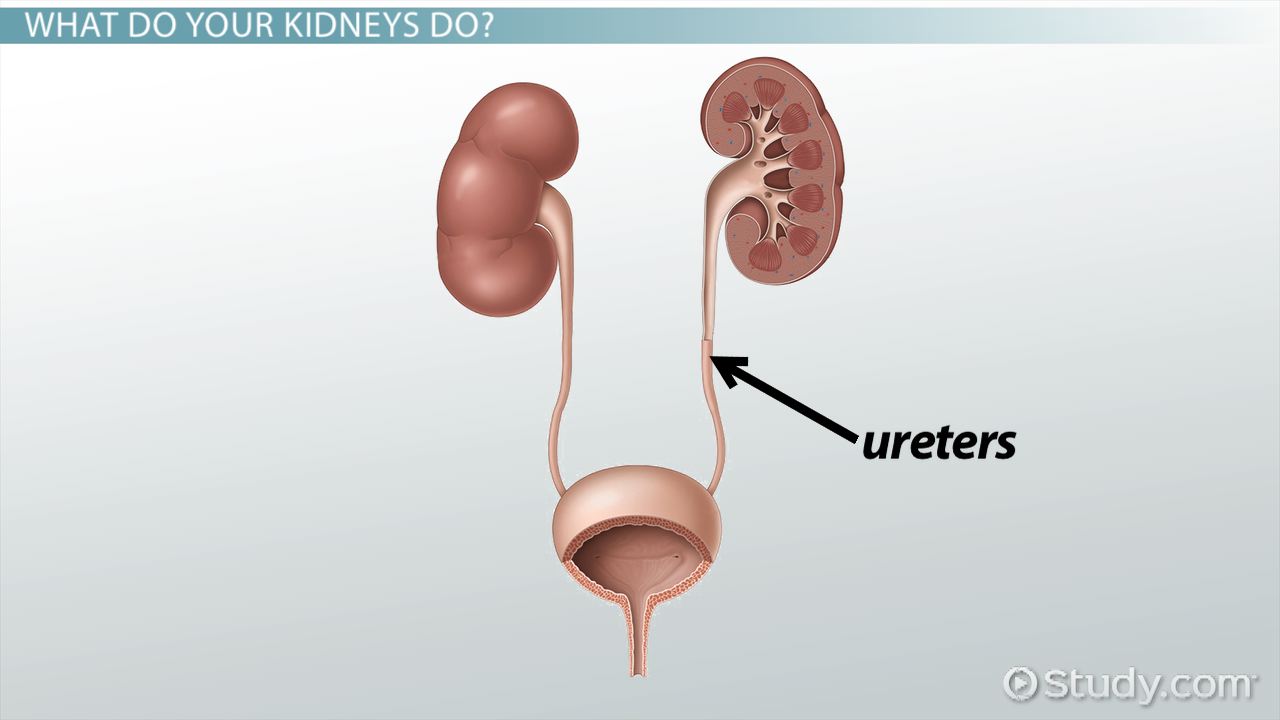
Ureter
a tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
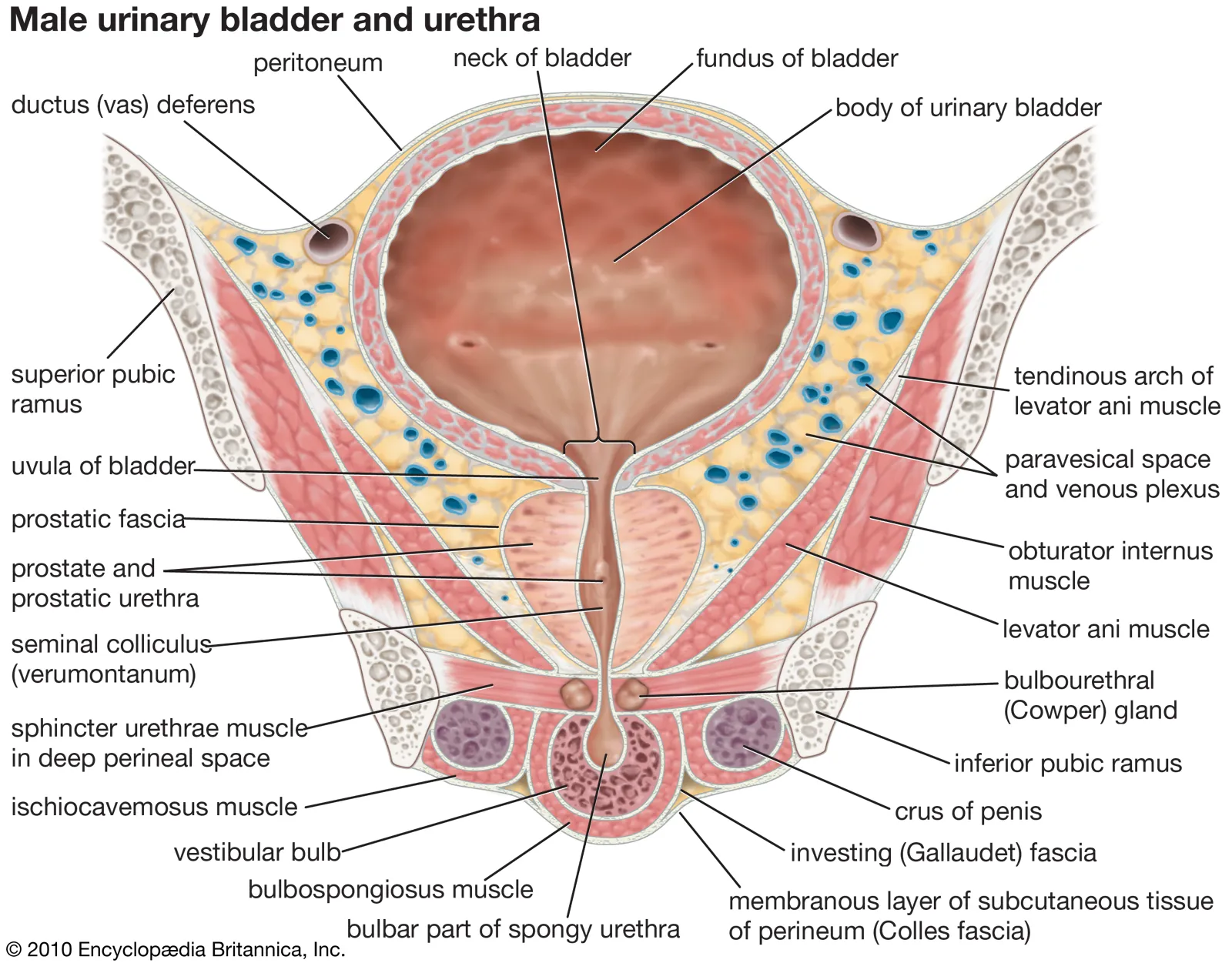
Urethra
the duct through which urine is discharged from the bladder to the outside of the body.
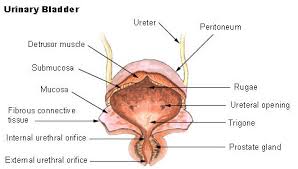
Urinary bladder
a hollow organ that stores urine before it is excreted from the body.
Renal artery
the blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the kidneys.
Renal vein
the blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidneys.
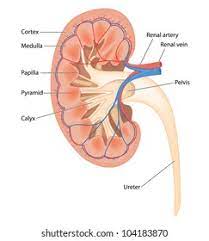
Renal pyramids
triangular structures in the kidneys that contain nephrons and collect urine.
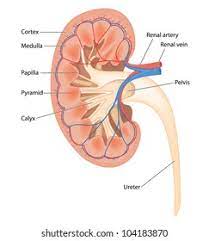
Renal cortex
the outer layer of the kidney that contains renal corpuscles and the proximal convoluted tubules.
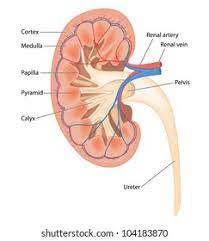
Renal pelvis
the funnel-shaped structure that collects urine from the renal calyces and channels it into the ureter.
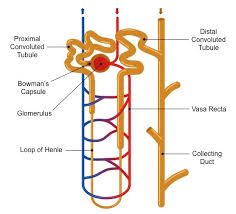
Nephron
The functional unit of the kidney.
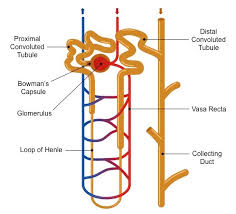
Bowman’s capsule
a cup-shaped structure that encases the glomerulus and is involved in the filtration of blood in the nephron.
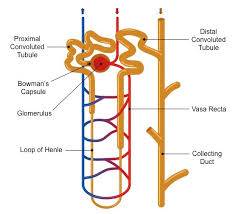
Proximal convoluted tubule
the segment of the nephron that reabsorbs the majority of water, ions, and nutrients from the filtrate back into the bloodstream.
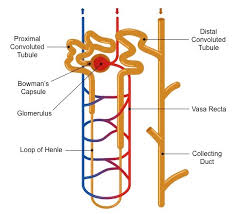
Distal convoluted tubule
the segment of the nephron that follows the loop of Henle and is involved in the reabsorption of sodium, chloride, and water.
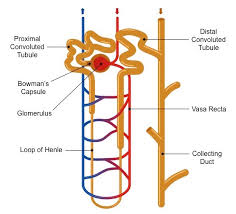
Collecting duct
a tubular structure in the nephron that collects urine from the distal convoluted tubule and transports it to the renal pelvis, playing a key role in water reabsorption and urine concentration.
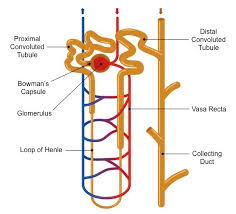
Glomerulus
a network of capillaries in the nephron where blood filtration occurs, forming the initial filtrate that enters the renal tubule.
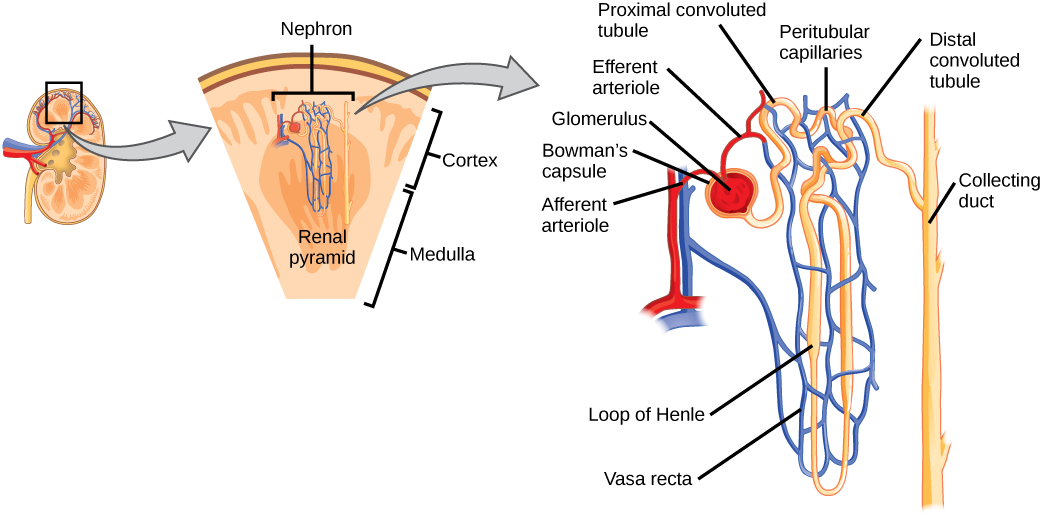
Peritubular capillary network
a network of tiny blood vessels surrounding the nephron's tubules, facilitating the exchange of substances between the blood and the renal tubule.
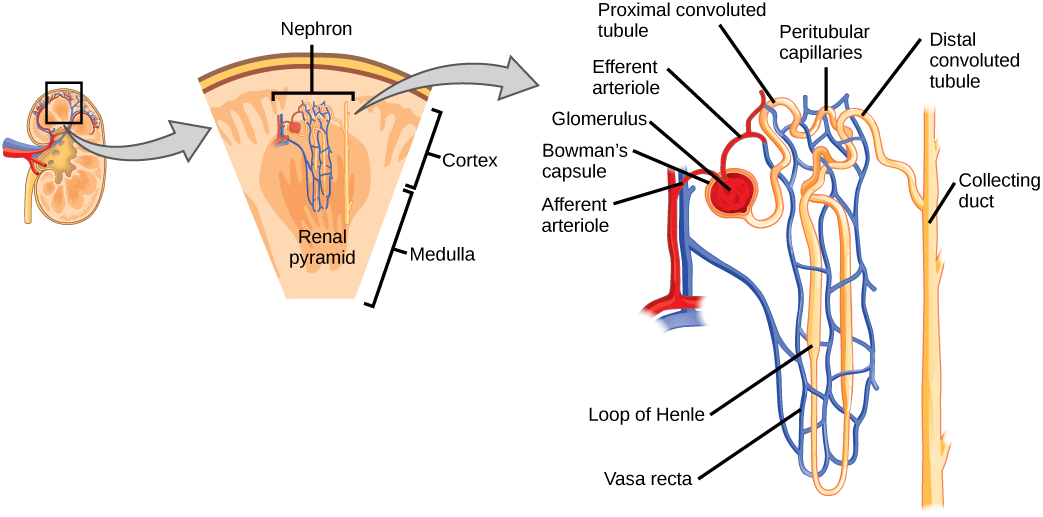
Loop of Henle
a U-shaped portion of the nephron that plays a critical role in concentrating urine and reabsorbing water and sodium.
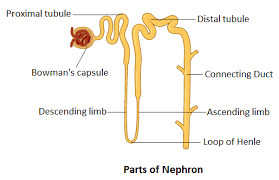
Descending loop of Henle
the portion of the Loop of Henle that allows for the reabsorption of water while being impermeable to salts.
Ascending loop of Henle
the part of the Loop of Henle that reabsorbs sodium and chloride ions while being impermeable to water, contributing to urine concentration.
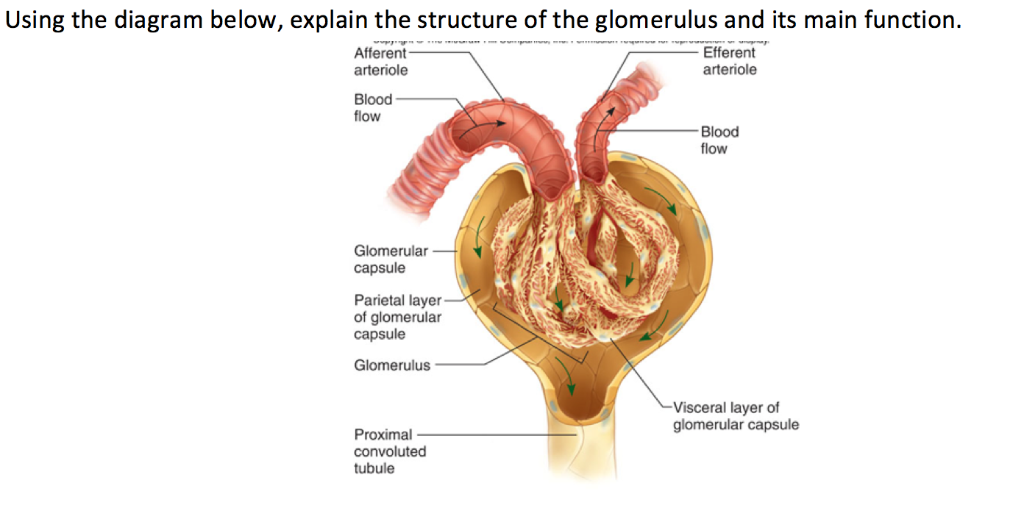
Afferent arteriole
a small blood vessel that carries blood to the glomerulus in the kidney, playing a key role in regulating blood flow and filtration.
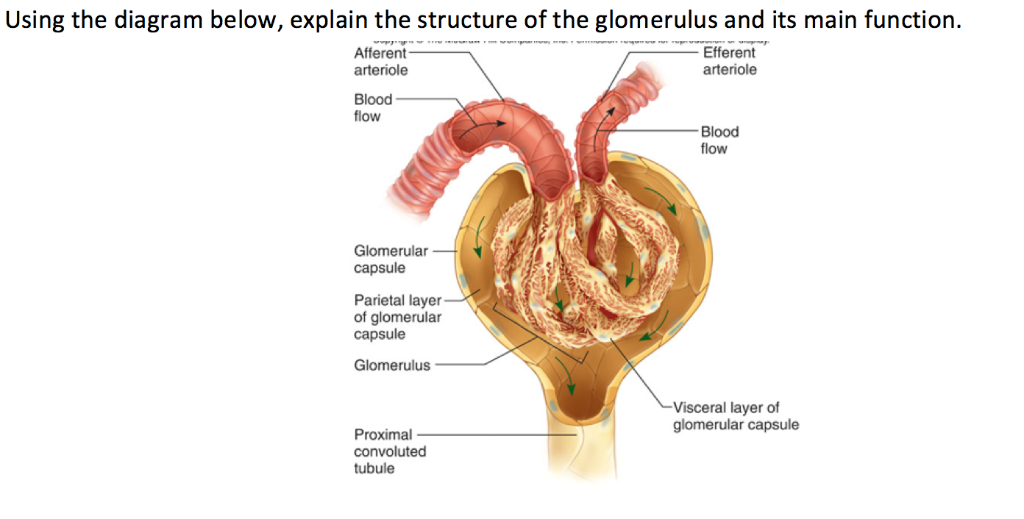
Efferent arteriole
a blood vessel that carries filtered blood from the glomerulus to the rest of the kidney and back into the body's general circulation.
Urinalysis interpretation
the process of analyzing urine samples to diagnose medical conditions, assess kidney function, and monitor health.
Chronic kidney failure
a long-term condition that occurs when the kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood properly.
Glomerulonephritis
inflammation of the glomeruli in the kidneys, which can lead to kidney damage and impaired function.
Nephrotic syndrome
a kidney disorder characterized by high levels of protein in the urine, low levels of protein in the blood, swelling, and high cholesterol.
Nephritic syndrome
A kidney disorder characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli, leading to symptoms such as hematuria, proteinuria, and hypertension.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) / Vasopressin
A hormone produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland that regulates water balance in the body by promoting water reabsorption in the kidneys.
Micturition
The process of urine expulsion from the bladder, commonly known as urination.
Filteration
The process by which the kidneys remove waste and excess substances from the blood to form urine.
Reabsorption
The process by which the kidneys reclaim water and essential solutes from the filtrate back into the bloodstream, helping to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
Secretion
The process by which substances are produced and discharged from cells into the urine. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's fluid and electrolyte balance.
Dialysis
A medical process that removes waste and excess fluid from the blood when the kidneys are not functioning properly.
Cytitis
inflammation of the bladder, often caused by infection, leading to symptoms such as frequent urination and pelvic discomfort.
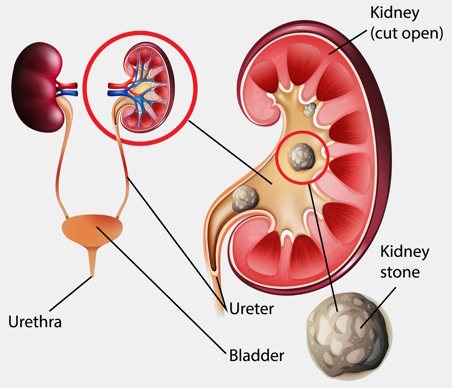
Kidney stones
Solid mineral and salt deposits that form in the kidneys, causing pain and urinary obstruction.