Test on Endocrine System
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What is the function of the endocrine system?
Group of ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
What are hormones also referred to as?
Chemical messengers.
How are hormones carried throughout the body?
Through the blood stream.
What is the function of hormones?
Stimulate exocrine glands, stimulate other endocrine glands, regulate growth & development , regulate metabolism, control various sex processes.
What are exocrine glands?
Release chemical substances through ducts to outside the body or another surface within the body.
Examples of substances transported by exocrine glands?
Sweat and saliva.
The pituitary gland is also known as?
Master gland.
What does the pituitary gland do?
Produces hormones to regulate other glands.
How is the pituitary gland divided?
Anterior and posterior lobe.
How is the pituitary glands anterior lobe controlled?
From the hypothalamus.
How many hormones does the anterior lobe in the pituitary gland produce?
Seven.
Growth Hormone (GH)
Responsible for growth and development.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Stimulates the growth and secretion of the thyroid gland.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Stimulates the growth and secretion of the adrenal cortex
Prolactin hormone (PRL)
Develops breast tissue and produces milk in females after childbirth. The function of this hormone for males is not known.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Stimulates the growth of the ovarian follicle and estrogen production in females. It stimulates the production of sperm in males.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Stimulates ovulation and the formation of corpus luteum to secrete progesterone in females.
Interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH)
Stimulates the secretion of testosterone in males.
What hormones does the anterior lobe in the pituitary gland produce?
GH, TSH, ACTH, PRL, FSH, LH, ICSH.
How many hormones does the posterior lobe in the pituitary gland produce?
Two.
What hormones does the posterior lobe in the pituitary gland produce?
ADH, Oxytocin.
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Maintains water balance by increasing the absorption of water by the kidneys. It is also called vasopressin.
Oxytocin
Stimulates contractions of the uterus in females during childbirth. It also stimulates milk flow during breastfeeding.
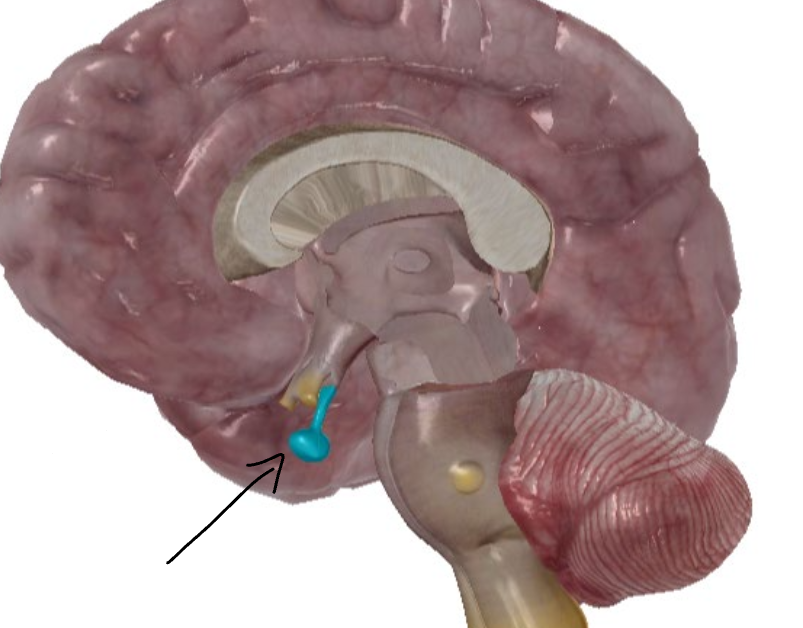
What is this gland?
Pituitary gland.
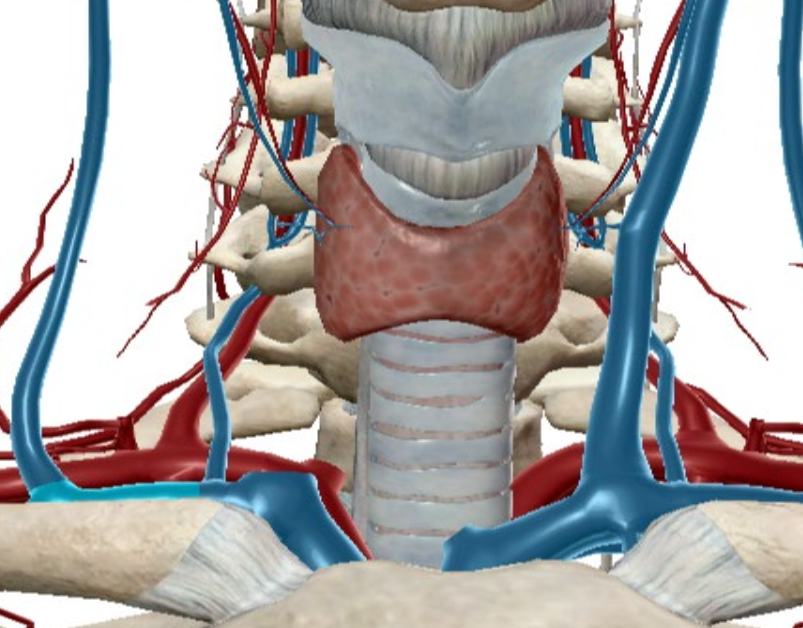
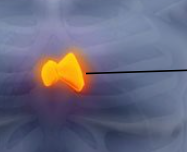
What is this gland?
Thyroid gland.
What are the lobes in the thyroid gland and what are they connected by?
Larynx or voice box (one on both sides); isthmus.
What does the thyroid gland require to function properly?
Iodine
Where can be iodine be obtained from?
Salty foods or iodized salt.
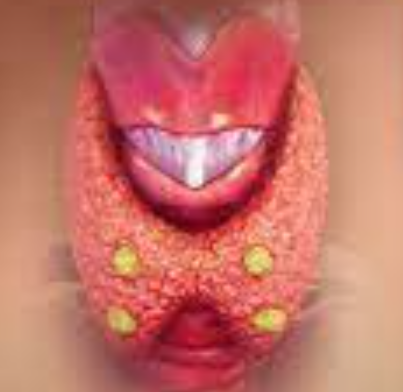
What are the glands which are the yellow dots?
Parathyroid.
Which hormone does the parathyroid produce?
Parathormone
What is the function of the parathormone hormone?
Maintains the balance of calcium and phosphorus in the blood.
Why does the parathormone break down bone tissue?
To release calcium and phosphates into the blood
What does parathormone cause the kidneys to do?
To conserve calcium and remove excess phosphorous from the blood.
Parts of the endocrine system?
Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, testes, ovaries.
Where are the adrenal glands?
Pair of glands, with one located above each kidney.
The sections of the adrenal glands.
Cortex and Medulla.
What is the cortex?
The outer part of the adrenal glands.
What is the medulla?
The inner part of the adrenal glands.
How many hormones does the adrenal cortex produce?
Thirty.
What are the three groups of adrenal cortex hormones?
Glucocorticoids, Mineralocorticoids, Gonadocorticoids.
Gonadocorticoids function?
(Estrogens & Androgens) help to develop sexual characteristics in males & females.
Mineralocorticoids function?
Control the body’s fluid level and electrolyte balance. They influence the rate at which the kidneys excrete mineral salts, such as sodium and potassium.
Glucocorticoids function?
Reduce inflammation, metabolize food, and make new cells.
What two hormones does the adrenal medulla produce?
Epinephrine and norepinephrine.
The hormones of what gland work with the sympathetic nervous system and cause the “fight or flight” response?
Adrenal medulla.
Where is the pancreas?
Located behind the stomach.
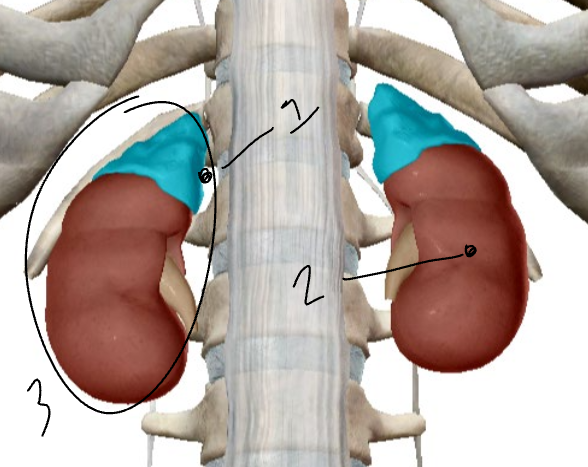
What is #1?
The adrenal cortex.
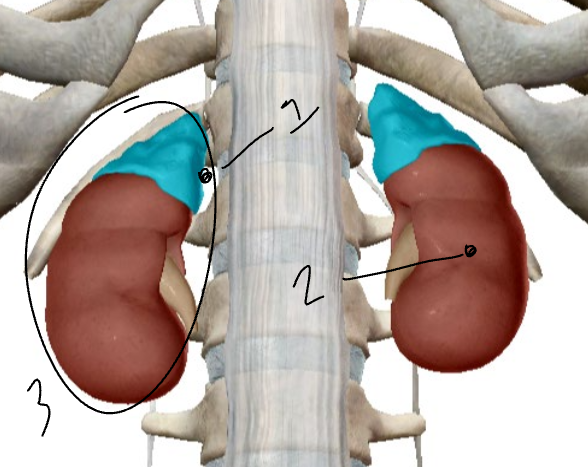
What is #2?
The adrenal medulla.
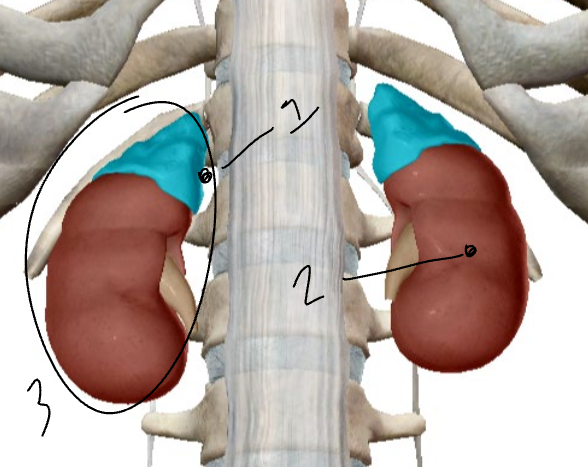
What is #3?
The adrenal gland.
What hormones does the pancreas produce?
Insulin and glucagon.
Insulin function
Causes cells to store glucose to reduce high blood sugar levels.
Glucagon function
Causes stored glucose to be released in response to low blood sugar levels.
What type of gland is the pancreas exocrine or endocrine?
Both.
Where is the pineal body?
Pea-sized gland located deep within the brain
What hormones does the pineal body produce?
Melatonin.
Function of melatonin.
Effects the sleep cycle and delay the onset of puberty.
Where is the thymus?
Butterfly-shaped gland located above the heart, but below the thyroid.
What hormone does the thymus produce?
Thymosin
Function of thymosin?
Stimulates cells in the immune system.
What happens to the thymus after puberty?
Wastes away and becomes a small mass of connective tissue and fat.
Where are the ovaries?
One is located on each side of the uterus in the pelvic cavity.
What do the hormones produced by the ovaries do?
Regulate menstruation and secondary sexual characteristics.
Where are the testes?
They are suspended outside the body in the scrotal sac.
What do the hormones produced by the testes do?
Regulate the sexual characteristics of the male.
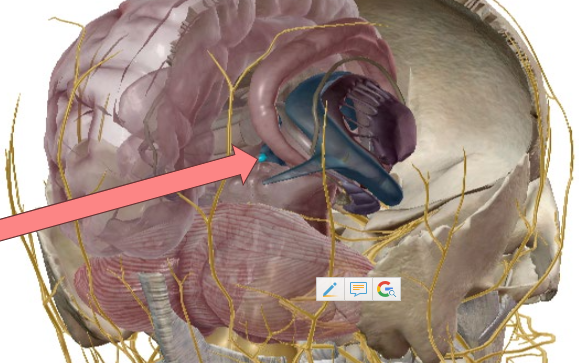
What is this gland?
Pineal body
What is this gland?
Thymus
Diabetes is caused by what?
Results when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin.
Cause of diabetes?
The exact cause is not known.
Symptoms of diabetes?
Excessive urination, thirst, and hunger.
How many types of diabetes?
Two
Results when the pancreas does not produce any insulin. (b)
Diabetes type 1 (b)
This type of diabetes may occur at any age but it is usually diagnosed early in life. (a)
Diabetes type 1 (a)
Treatment involves the injection of insulin on a regular basis. (d)
Diabetes type 1 (d)
Symptoms of diabetes type 1?
Feeling tired and sleepy, confusion, passing out, stomach pain, feeling or being sick, needing to pee more often, high ketones, blurred vision, being very thirsty, sweet smelling breath, high sugar levels.
Results when the pancreas produces insulin, but not enough to meet the needs of the body. (a)
Diabetes type 2 (a)
This type of diabetes is linked with obesity and is most common in adults over the age of 45. (b)
Diabetes type 2 (b)
Treatment may involve oral medication, exercise, weight loss, and insulin injections. (d)
Diabetes type 2 (d)
Symptoms of diabetes type 2?
Frequent urination, feeling very thirsty or hungry, extreme fatigue, blurry vision, bruises or wounds slow to heal, tingling pain or numbness in feet or hands, dry itchy skin.
Long term complications of diabetes?
Neuropathy (nerve pain), kidney failure, poor circulation, and slow wound healing as a result of poor circulation.
Improperly managed diabetes can result in what?
Multi-system complications or organ failure.
Results when the thyroid is overactive, which leads to increased metabolism. (a)
Hyperthyroidism (a)
Symptoms include extreme nervousness, irritability, weight loss, goiter (swollen thyroid gland), bulging eyeballs, and rapid pulse. (b)
Hyperthyroidism (b)
Treatment involves surgery or radiation to remove all or part of the thyroid. (d)
Hyperthyroidism (d)
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
Bulging eyes, goiter, swelling, increased palpations, hand tremors, hunger, enlarged thyroid, breathing problems, mood swings, weight loss, hair loss.
Results when the thyroid is underactive, which leads to decreased metabolism. (a)
Hypothyroidism (a)
Symptoms include fatigue, slow mental function, weight gain, coarse skin, and a slow pulse. (b)
Hypothyroidism (b)
Treatment involves regular doses of oral medication to restore the level of thyroid hormones. (d)
Hypothyroidism (d)
Symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Weight gain, constipation, dry skin, hoarseness, slow heart rate, tingling in hands and feet.