AP Bio - Unit 2 biochem
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
covalent bond
when 2 atoms share a pair of electrons - strong bond
hydrogen bond
a weak attraction that H and O
Ionic bond
a strong attraction between a positive and negative charged ion
specific heat
the amount of heat (thermal energy) required to raise the temperature of a specific mass of a substance by one degree Celsius (or one Kelvin)
surface tension
the property of a liquid's surface, like water, to act like a stretched elastic membrane due to strong cohesive forces between its molecules
Adhesion
H bonding between H2O and other substance - water sticking to things (paper towel)
cohesion
H bonding between H2O molecules - surface tension, water is sticky, water bugs floating on water
Heat of vaporization
how much energy it takes to get water to move from a liquid to a gas
Hydrophobic
a molecule or substance that repels water and does not mix with it, often because it is nonpolar
hydrophilic
substances with a strong affinity for water, meaning they are attracted to it and can dissolve or interact easily with it.
pH scale
hydroxyl group
the chemical group or ion OH that consists of one atom of hydrogen and one of oxygen and is neutral or positively charged.
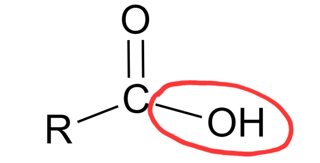
carboxyl group
a functional group made of a carbon atom double-bonded to one oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group
carbonyl group
a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom
amino group
N attracted to 2 H
phosphate group
P bonded to 4 O
sulfhydryl group
S bonded to H
polymer
a large molecule made from smaller molecules which are linked together by chemical bonds
monomer
a small, single molecular unit that can be chemically bonded to other identical ones to form bigger molecules
dehydration reaction
chemical process where two smaller molecules are joined together to form a larger molecule with the loss of a water molecule
hydrolysis reaction
uses water to break down large, complex molecules into smaller, simpler units,
monosaccharide
simplest form of carbohydrate, a single sugar molecule that cannot be broken down into smaller units
glycosidic link
covalent bond formed by dehydration synthesis - when they hold hands
polysaccharide
large polymers like starch
fatty acid
type of lipid
triacylglycerol
glycerol molecule attached to three fatty acid chains
ester linkage
the bond found when a fatty acid joins another molecule via dehydration synthesis reaction - bond is found in lipids
phospholipid
a fat-like molecule that forms the essential structure of cell membranes, creating a barrier with a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and a hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail.
steroid
any group of lipids that have a certain chemical structure
amino acid
organic molecules that are building blocks of proteins
peptide bond
covanlent chemical bond that links two amino acids together
primary structure
order of amino acids determined by DNA - form fits function - protein
secondary structure
folding a long short sections of polypeptide - protein - local folding
tertiary structure
interactions between distant amino acids - whole protein molecule folding - all proteins fold to this level
quaternary structure
arrangement or interaction of two or more polypeptide chains - most proteins fold to this level
denaturation
unfolding of a protein - conditions that disrupts H bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges
disulfide bridges
strong covlanet bonds that form between sulfide atoms
DNA
molecule that carries genetic information and instruction
RNA
carries genetic information from DNA and makes proteins and regulates celluar processes
Nucleotide
building block and DNA and RNA
enzyme
protein that catalyzes (speeds up) a specific chemical reaction within living organisms, acting as a biological catalyst that is not consumed by the reaction
activation energy
minimum energy to start a chemical reaction
catalyst
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, without being consumed or permanently changed in the process.
substrate
a fundamental substance or surface that serves as a base, a point of attachment, or a reactant in a chemical or biological process.
product
an end result of a chemical reaction
active site
a specific region on an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction, ultimately converting them into products.
cofactors
a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's activity.
competitive inhibition
a type of reversible enzyme inhibition where a molecule similar to the substrate binds to the enzyme's active site, directly competing with the substrate for binding
noncompetitive inhibition
a type of enzyme inhibition where an inhibitor binds to an enzyme at an allosteric site (a site other than the active site), causing a conformational change that reduces the enzyme's ability to function, regardless of substrate concentration
allosteric site
a location on a protein
feedback inhibition
a biological process where the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits the activity of an enzyme early in that same pathway.
hydroxyl
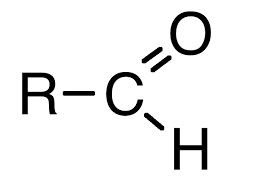
carbonyl
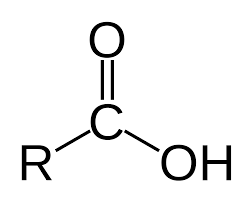
carboxyl
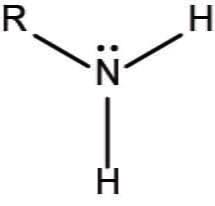
amino group
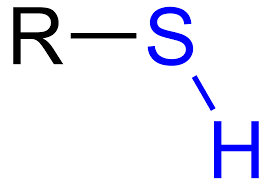
sulfhydral
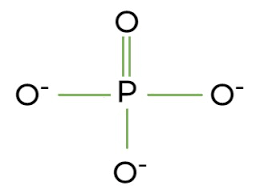
phosphate