C11 - Nervous System & Nervous Tissue Pt.1
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Define Nervous System
The master controlling and communicating system of body
How do cells communicate?
Via electrical and chemical signals
Rapid and specific
Usually cause almost immediate responses
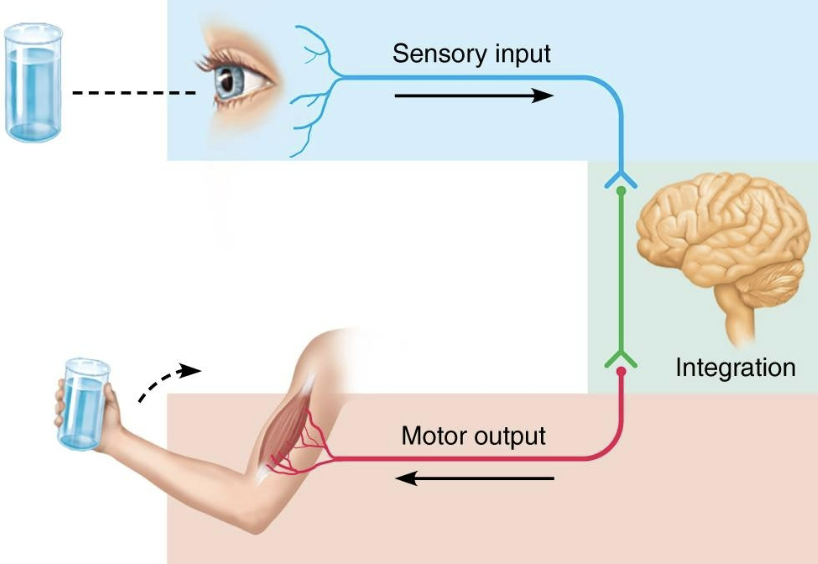
List and explain the basic functions of the nervous system
Sensory input
information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes
Integration
Processing and interpretation of sensory input
Motor output
Activation of effector organs (muscles and glands) produces a response
Explain the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system
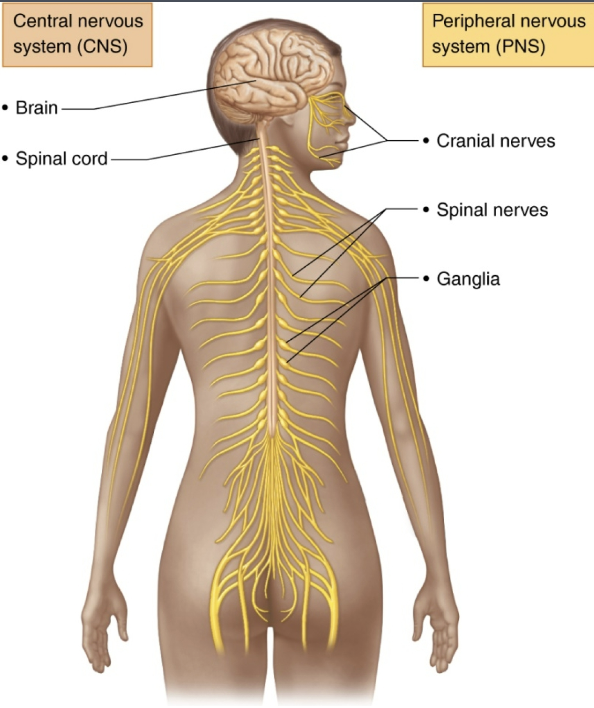
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord of dorsal body cavity
Integration and control center
Interprets sensory input and dictates motor output
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The portion of nervous system outside CNS
Consists mainly of nerves that extend from brain and spinal cord
Spinal nerves to and from spinal cord
Cranial nerves to and from brain
Explain the functional sub-divisions of the PNS
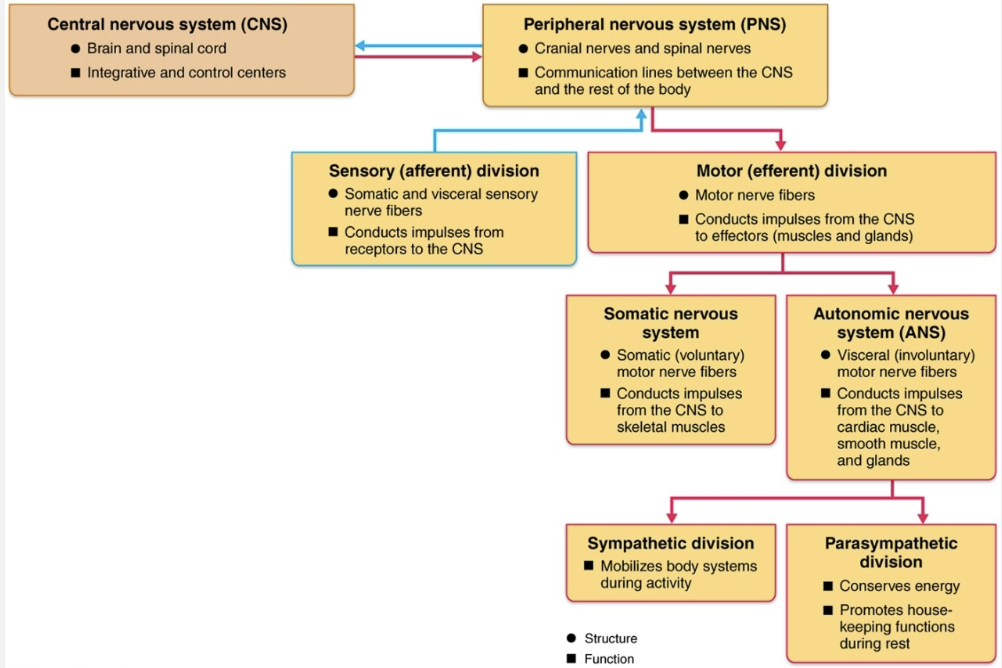
Sensory (afferent) division
Somatic sensory fibers → convey impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to CNS
Visceral sensory fibers → convey impulses from visceral organs to CNS
Motor (efferent) division
Transmits impulses from CNS to effector organs
Muscles
Glands
Two divisions
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Explain the functional sub-sub-divisions of the Motor (Efferent) Division
Somatic Nervous System
Somatic motor nerve fibers conduct impulses from CNS to skeletal muscle
Voluntary nervous system → conscious control of skeletal muscles
Autonomic Nervous System
Consists of visceral motor nerve fibers
Regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
Involuntary nervous system
Two functional subdivisions
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Explain the functional sub-sub-sub-divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic
Puts tour body’s systems on alert
Parasympathetic
Carries signals that relax those systems
Overview of Structural and Functional Divisions of the Nervous System
List and define the two principal cell types in Nervous Tissue
Neuroglia (glial cells)
Small cells that surround and wrap delicate neurons
Neurons (nerve cells)
Excitable cells that transmit electrical signal
List the types of neuroglia and their functions of CNS
Astrocytes
Microglial cells
Ependymal cells
Oligodendrocytes
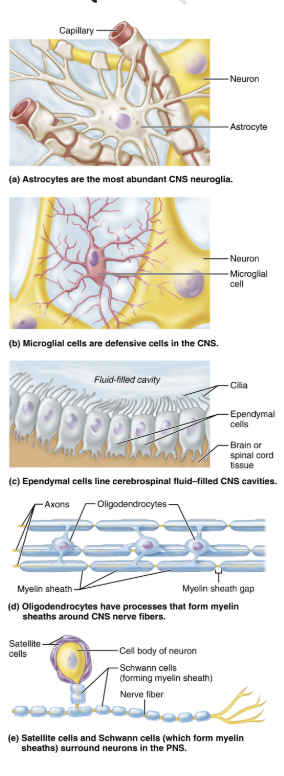
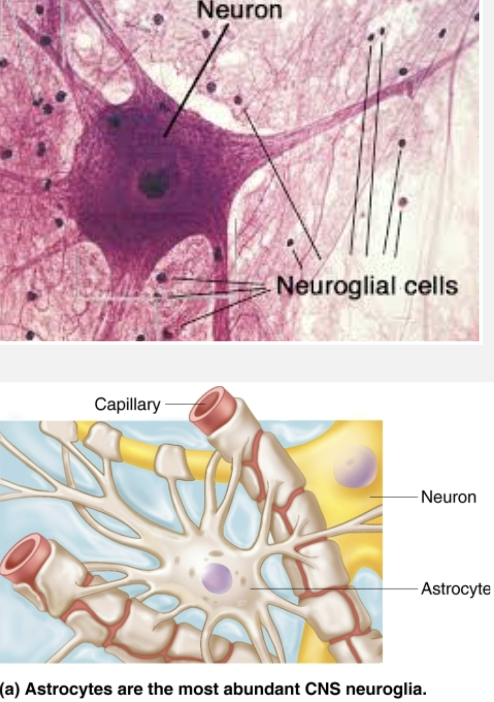
Explain the function of Astrocytes
Neuroglia (glial cells)
STRUCTURE
Most abundant, versatile, and highly branched of glial cells
Cling to neurons, synaptic endings, and capillaries
FUNCTION
Support and brace neurons
Play role in exchanges between capillaries and neurons
Participate in information processing in brain
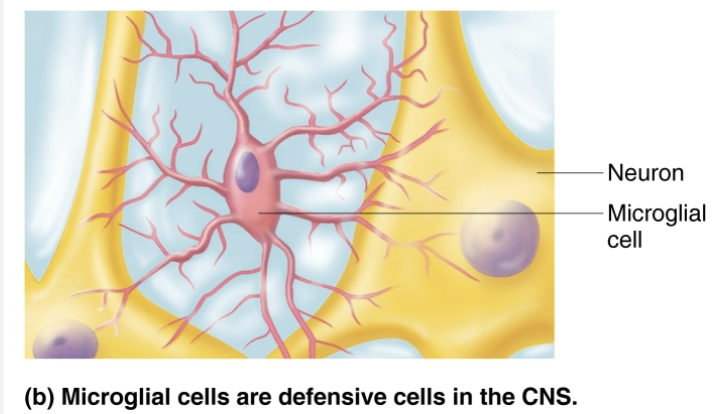
Explain the function of Microglial cells
Neuroglia (glial cells)
STRUCTURE
Small, ovoid cells with thorny processes that touch and monitor neurons
Migrate toward injured neurons
FUNCTION
Can transform to phagocytize microorganism and neuronal debris
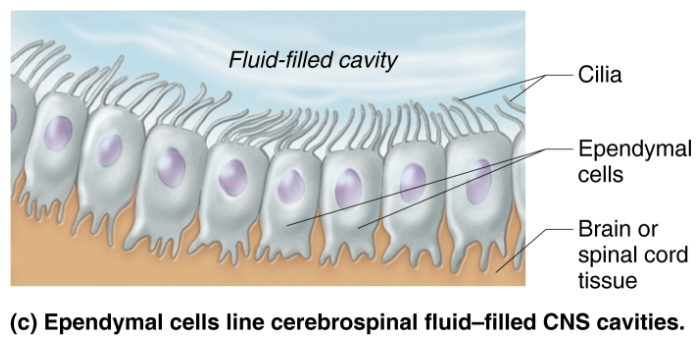
Explain the function of Ependymal cells
Neuroglia (glial cells)
STRUCTURE
Range in shape from squamous to columnar
Line the central cavities of the brain and spinal column
May be ciliated → cilia beat to circulate CSF
FUNCTION
Produce cerebrospinal fluids (CSF)
Form permeable barrier between CSF in cavities and tissue fluid bathing CNS cells
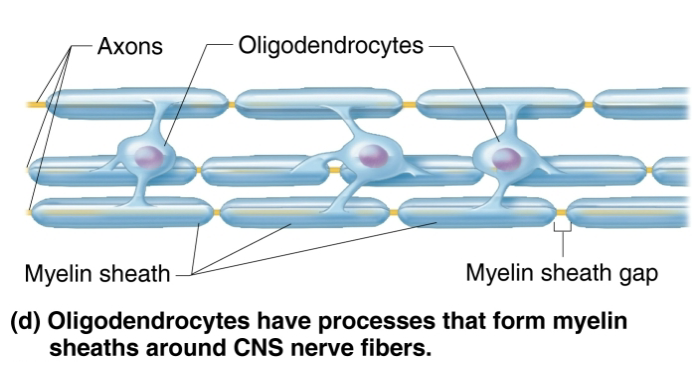
Explain the function of Oligodendrocytes
Neuroglia (glial cells)
STRUCTURE
Branched cells
FUNCTION
Processes wrap CNS nerve fibers, forming insulating myelin sheaths in thicker nerve fibers
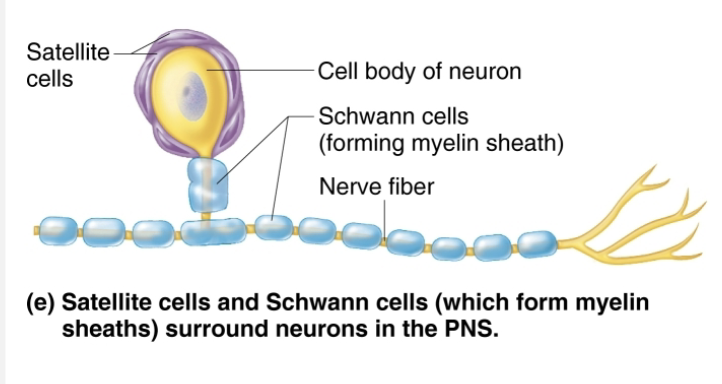
Name and describe two major neuroglia seen in PNS
Surround neurons in PNS
Satellite cells
STRUCTURE
Surround neuron cell bodes in PNS
FUNCTION
Similar to astrocytes of CNS
Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
STRUCTURE
Surround all peripheral nerve fibers and form myelin sheaths in thicker nerve fibers
FUNCTION
Similar functions as oligodendrocytes
Vital to regeneration of damaged peripheral nerve fibers
Define Neuron
aka Nerve cell→ Structural units of nervous system
Large, highly specialized cells that conducts impulses
All have cell body and one or more processes
List the special characteristics of Neurons
Extreme longevity (lasts a person’s lifetime)
Amitotic, with few exceptions
High metabolic rate → requires continuous supply of oxygen and glucose
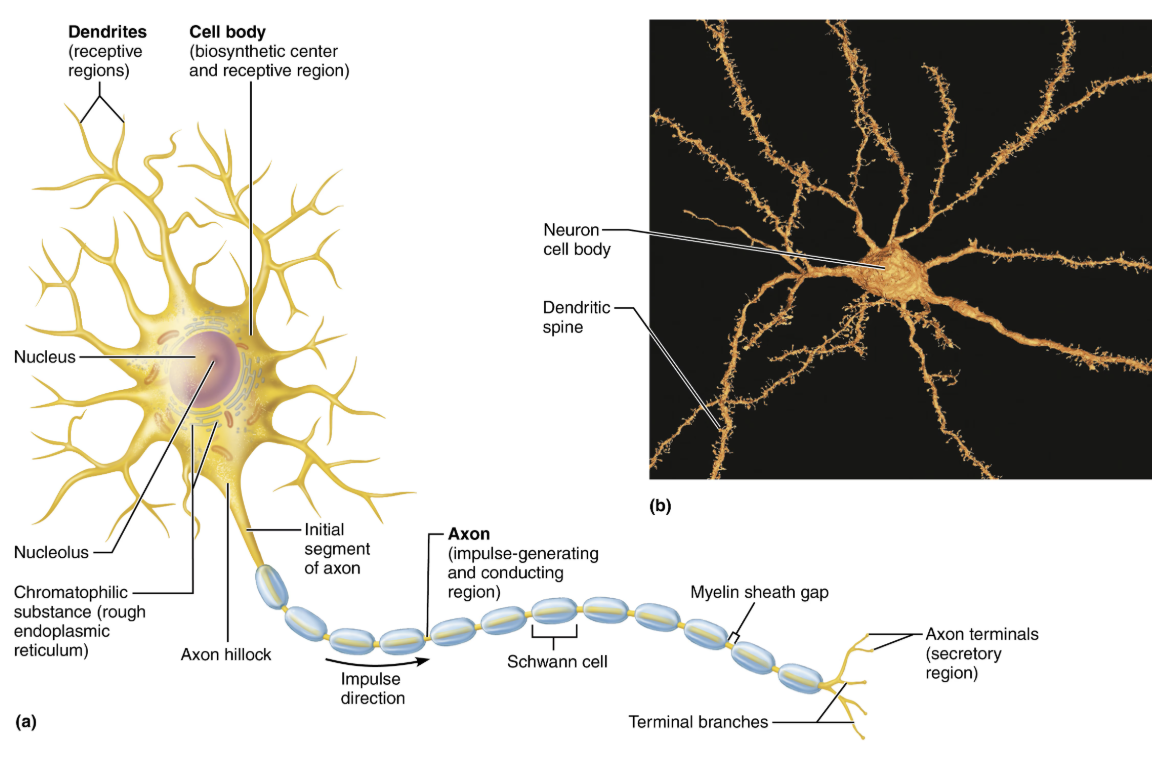
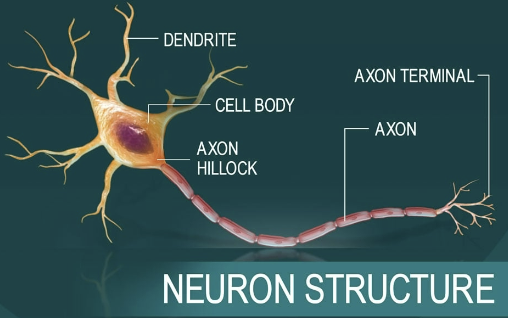
Describe Neurons important structural components, and relate each to a functional role
Cell body (soma)
Biosynthetic center of a neuron
Dendrites (Neuron process)
Branching neuron process that serves as a receptive, or input region
Transmits an electrical signal TOWARD the cell body
Axon (Neuron process)
Carries action potentials AWAY from the neuron cell body
Efferent process
The conduction portion of a neuron
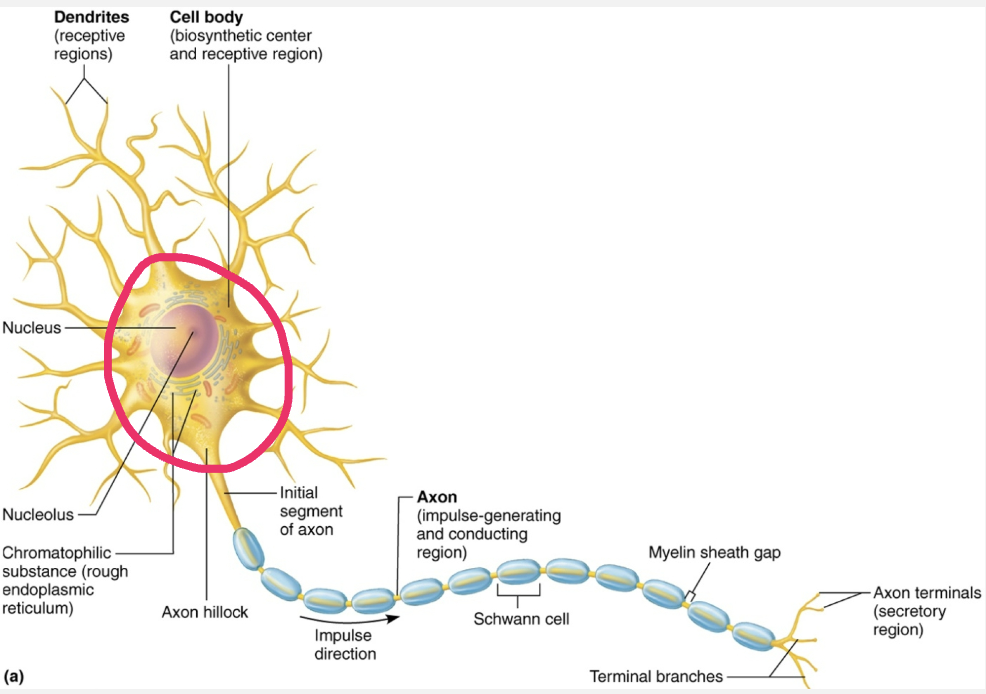
Explain the structure and function of Neuron Cell Body
aka Perikaryon or Soma
STRUCTURE
Contains spherical nucleus with nucleolus
Some contain pigments
In most, plasma membrane is part of receptive region that receives input into from other neurons
FUNCTION
Biosynthetic center of neuron
Synthesizes proteins, membranes, chemicals
Rough ER (chromatophliic substances, or Nissi bodies)
Differentiate between a Nucleus and Ganglion
Most neuron cell bodies are located in CNS
Nuclei → clusters of neuron cell bodies in CNS
Ganglia → clusters of neuron cell bodies in PNS
Explain the structure and function of Neuron Processes
STRUCTURE
Armlike processes that extend from cell body
LOCATION
CNS contains both neuron cell bodies and their processes
PNS contains chiefly neuron processes
FUNCTION
Dendrites
Axon
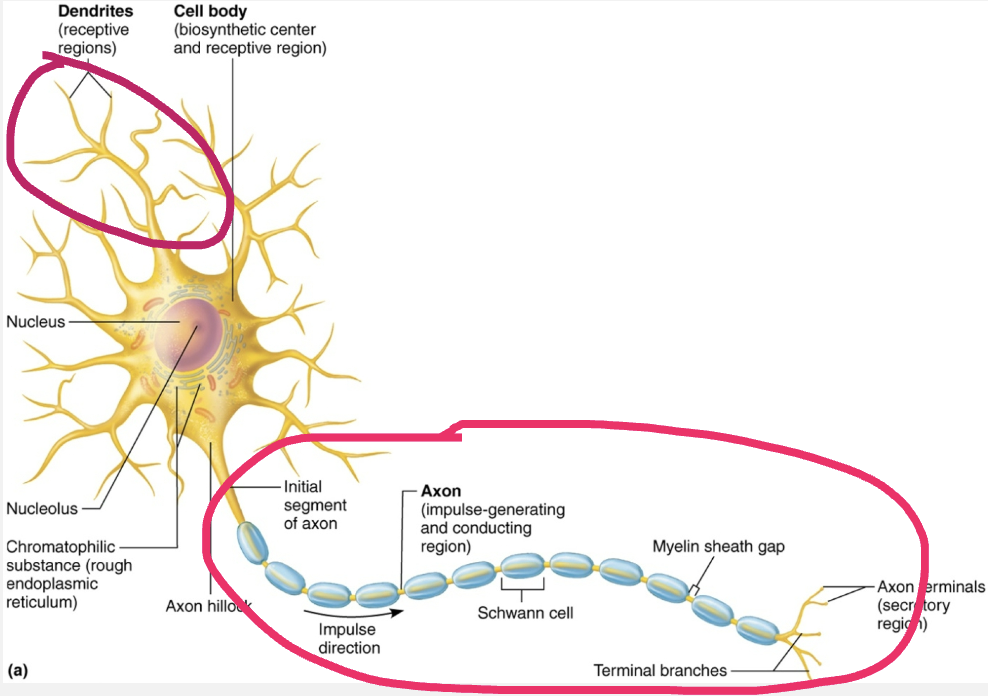
Differentiate Nerve and a tract
Tracts
Bundles of neuron processes in CNS
Nerves
Bundles of neuron processes in PNS
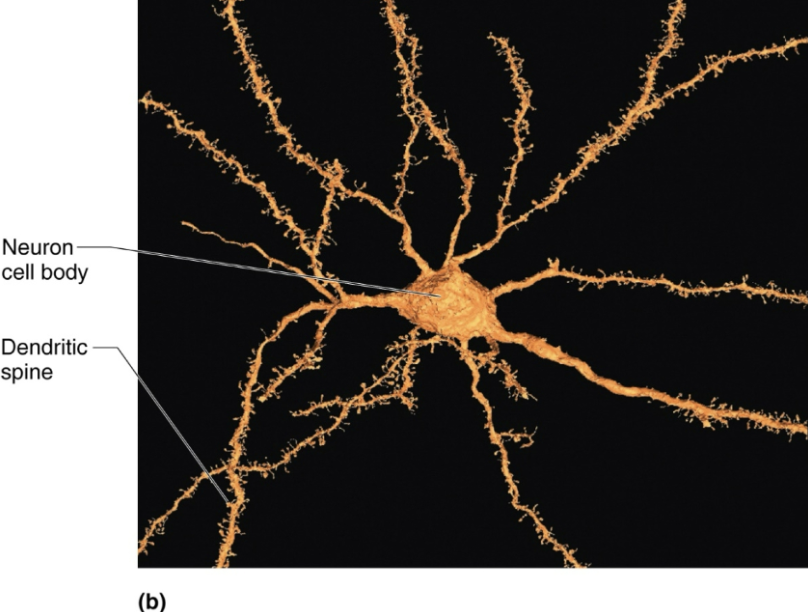
Explain the structure and function of Dendrites
STRUCTURE
Motor neuron can contain 100s of these short, tapering, diffusely branched processes
Contain same organelles as in cell body
In many brain areas, finer dendrites are highly specialized to collect information
Contain dendritic spines, appendages with bulbous or spiky ends
FUNCTION
Receptive (input) region of neuron
Convey incoming messages TOWARD cell body as graded potentials (short distance signals)
Explain the structure and function of Axon
STRUCTURE
Each neuron has one axon that starts at cone-shaped area are called axon hillock
In some neuron axons are short or absent; in others, axon comprises almost entire length of cell
Some axons can be over 1 meter long
Nerve fibers → Long axons
Axon collaterals → Occasional branches
Can number as many as 10,000 terminal branches
Axon terminals (or terminal boutons) → Distal endings
FUNCTION
Axon is the conducting region of neuron
Generates nerve impulses and transmits them AWAY from axolemma (neuron cell membrane) to axon terminal
Terminal → region that secretes neurotransmitters, which are released into extracellular space
Can excite or inhibit neurons it contracts
Carries conversations with different neurons at same time
Axons rely on cell bodies to renew proteins and membranes
Quickly decay if cut or damaged
Axon Transport
Axons have efficient internal transport mechanisms
Molecules and organelles are moved along axons by motor proteins and cytoskeletal elements
Movement occurs in both directions
Anterograde → AWAY from the cell body
EX: mitochondria, cytoskeletal elements, membrane components (vesicles) used to renew the axon plasma membrane, and enzymes needed to synthesize certain neurotransmitters
Retrograde → TOWARD cell body
EX: organelles to be degraded, signal molecules, viruses, and bacterial toxins
Axonal Transport - Clinical Homeostatic Imbalance
Certain viruses and bacterial toxins damage neural tissues by using retrograde axonal transport
EX: polio, rabies, and herpes simplex viruses, and tentanus toxin
Define Myelin sheath
STUCTURE
Composed of myelin, a whitish, protein-lipid substance
FUNCTION
Protect and electrically insulate axon
Increase speed of nerve impulse transmission
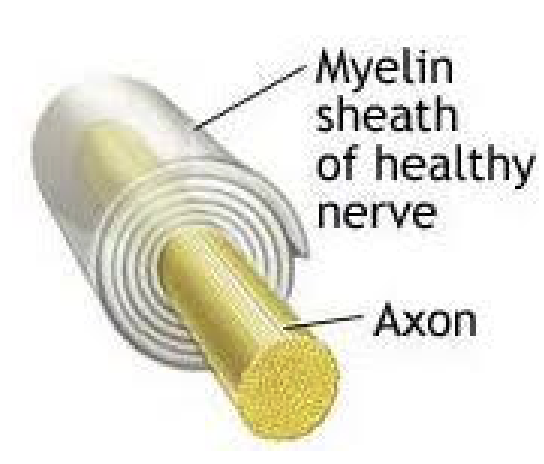
Myelinated vs Non-myelinated fibers
Myelinated fibers
Segmented sheath surrounds most long or large-diameter axons
Non-myelinated fibers
Do not contain sheath
Conduct impulses more slowly
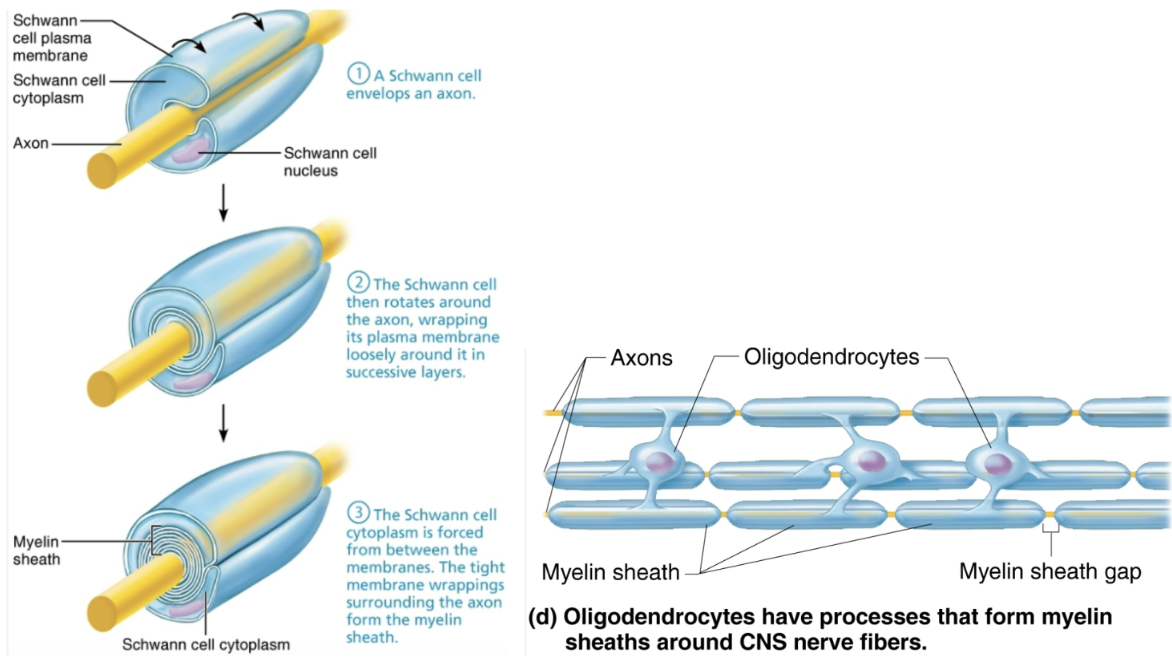
Explain the importance of the myelin sheath and describe how it is formed in the peripheral and central nervous systems
Myelination in PNS
Formed by Schwann cells
Wraps around axon in jelly roll fashion
One cell forms one segment of myelin sheath
Plasma membranes have less protein
No channels or carriers, so good electrical insulators
Myelin sheath gaps
Gaps between adjacent Schwann cells
Sites where axon can emerge
Non-myelinated fibers
Thin fibers not wrapped in myelin; surrounded by Schwann cells but no coiling; one cell may surround 15 different fibers
Myelination in CNS
Formed by processes of oligodendrocytes, not whole cells
Each cell can wrap up to 60 axons at once
Myelin sheath gap present
Thinnest fibers are unmyelinateud
But covered by long extensions of adjacent neuroglia
White matter vs Gray matter
White matter
Regions of brain and spinal cord with dense collections of myelinated fibers
Usually fiber tracts
Gray matter
Mostly neuron cell bodies and non-myelinated fibers
Classify neurons by structure and by function
Multipolar
STRUCTURE
1 axon, other dendrites
Three or more processes
FUNCTION
Most common and major neuron type in CNS
Bipolar
STRUCTURE
1 axon, one dendrites
Two processes
FUNCTION
Rare
EX: retina and olfactory mucosa
Unipolar (pseudo-unipolar)
STRUCTURE
Two axons
One T-like processes
FUNCTION
Peripheral (distal) process: associated with sensory receptor
Proximal (central) process: enters CNS
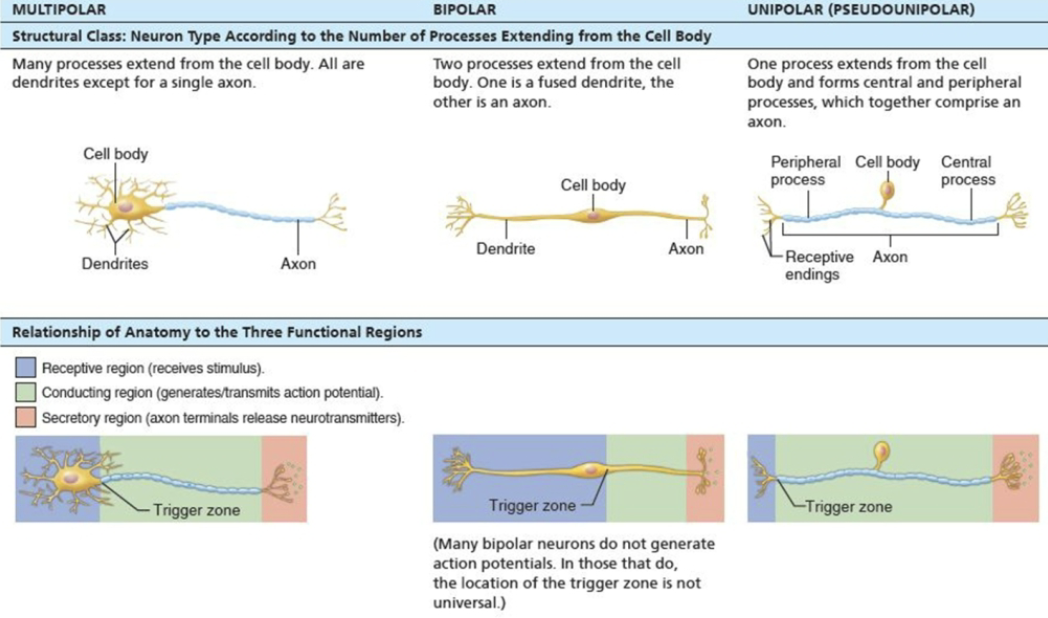
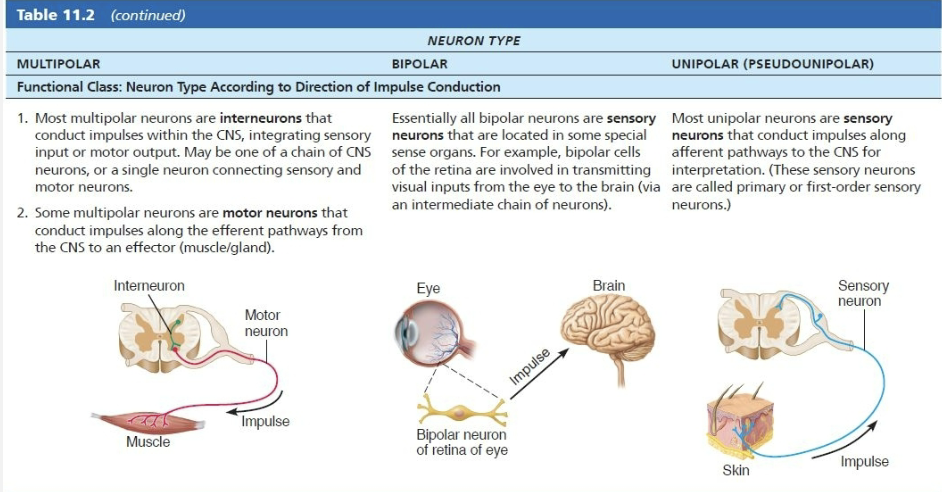
List the types of neurons grouped by direction in which nerve impulse travels relative to CNS
Sensory
Transmit impulses from sensory receptors TOWARD CNS
Almost all are unipolar
Cell bodies are located in ganglia in PNS
Motor
Carry impulses FROM CNS to effectors
Multipolar
Most cell bodies are located in CNS (except some autonomic neurons
Interneurons
Shuttle signals THROUGH CNS pathways
Most are entirely within CNS
Lie between motor and sensory neurons
99% of body’s neurons are interneurons
T/F: Neurons can change their resting membrane potential
True
Like all cells, neurons have a resting membrane
Unlike most other cells, neurons can rapidly change resting membrane potential
Neurons are highly excitable
Explain the Basic Principles of Electricity
Opposite charges are attracted to each other
Energy is required to keep opposite charges separated across a membrane
Energy is liberated when the charges move toward one another
When opposite charges are separated, the system has potential energy
Define Voltage
A measure of potential energy generated by separated charge
Measured between two points in volts (V) or millivolts (mV)
Define Current
Flow of electrical charge (ions) between two points
Role of membrane ion channels
Large proteins serve as selective membrane ion channels
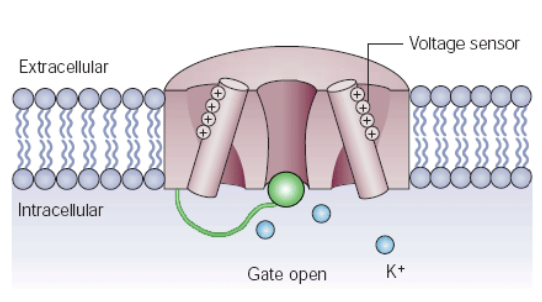
Identify different types of membrane ion channels
Leakage (non-gated) channels
Always open
Gated channels
Part of the protein changes shape to open/close the channel
Chemically gated
Voltage-gated
Mechanically gated
List and describe the three main Gated Channels
Chemically gated
Open in response to binding of the appropriate neurotransmitter
Voltage-gated
Open in response to changes in membrane potential
Mechanically gated
Open and close in response to physical deformation of receptors, as in sensory receptors
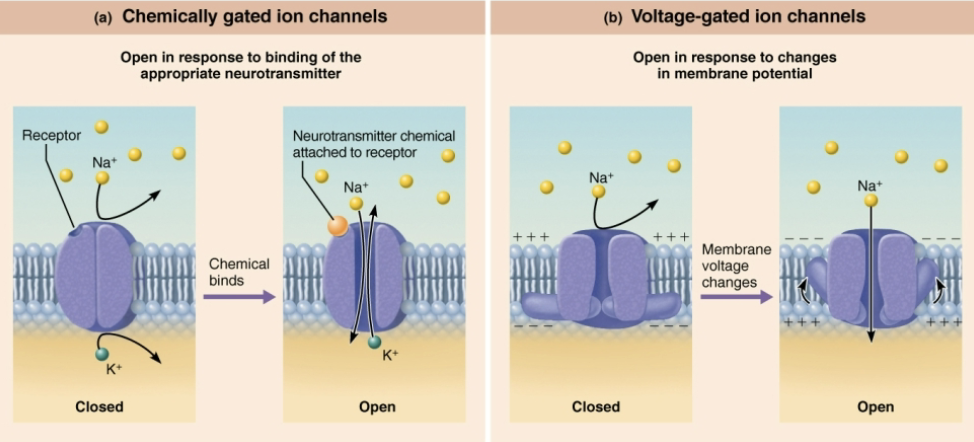
Explain what happens when gated channels are open.
Ions diffuse quickly:
Along chemically concentration gradients from HIGHER concentration to LOWER concentration
Along electrical gradients toward OPPOSITE electrical charge
Define Electrochemical Gradient
Electrical and chemical gradients combined
Ion flow creates an electrical current, and voltage changes across membrane
Describe the relationship between current, voltage and resistance
Current: flow of electrical charge (ions) between two points
Voltage: a measure of potential energy generated by separated charge
Called potential difference or potential
Charge difference across plasma membrane results in potential
Greater charge difference between points = higher voltage
Electrochemical gradient: electrical and chemical gradients combined
Ion flow creates an electrical current, and voltage changes across membrane
Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis
Resting membrane potential of a resting neuron is approximately -70mV
The cytoplasmic side of membrane is negatively charged relative to the outside
The actual voltage difference varies form -40mV to -90mV
The membrane is said to be polarized → one side having postive charge and other having negative
Define Voltmeter
Can measure potential (charge) difference across membrane of resting cell
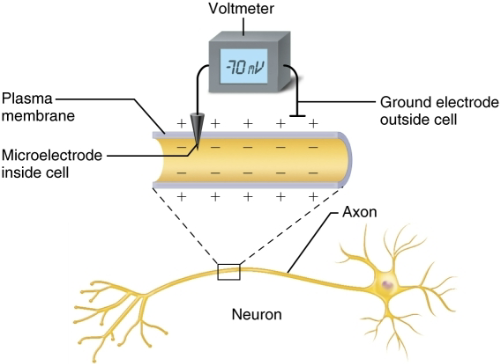
How is Potential generated?
Differences in ionic composition of intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF)
Differences in plasma membrane permeability
Explain Differences in Ionic Composition
Generating the resting membrane potential
ECF has HIGHER concentration of Na+ than ICF
Balanced chiefly by chloride ions (Cl-)
ICF has HIGHER concentration of K+ than ECF
Balanced by negatively charged proteins
K+ plays most important role in membrane potential
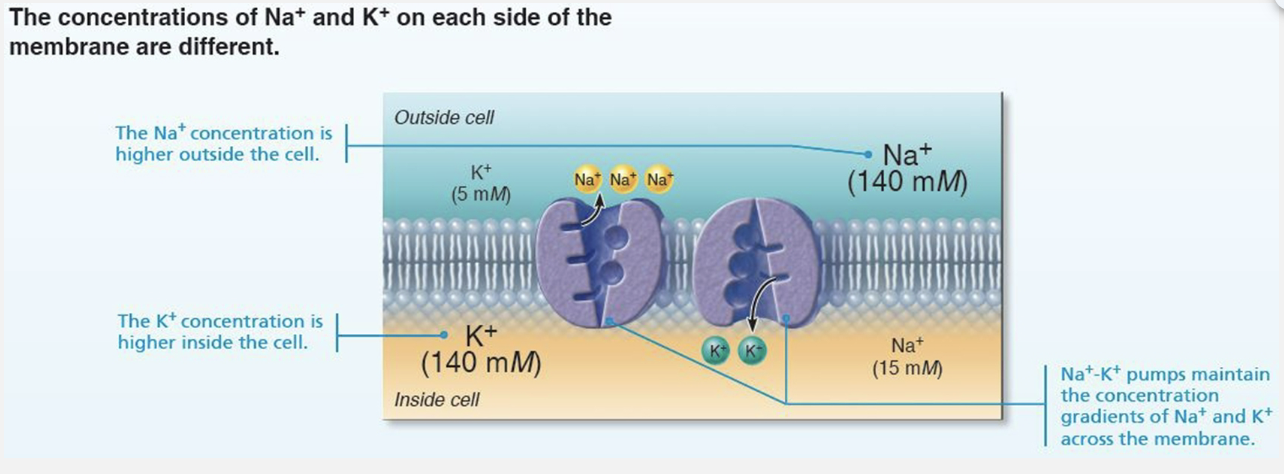
Explain Differences in Plasma Membrane Permeability
Generating the resting membrane potential
Impermeable to large anionic proteins
Slightly permeable to Na+ (through leakage channels)
Na+ diffuses into cell down concentration gradient
25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+ (more leakage channels)
K diffuses out of cell down concentration gradient
Quite permeable to Cl-
More potassium diffuses out than sodium diffuses in
RESULT INSIDE OF THE CELL MORE NEGATIVE
Negative membrane potenital
Role of Sodium-Potassium Pump (Na+/K+ ATPase)
Stabilizes resting membrane potential
Maintains concentration gradients for Na+ and K+
Three Na+ are pumped out of cell while two K+ are pumped back in
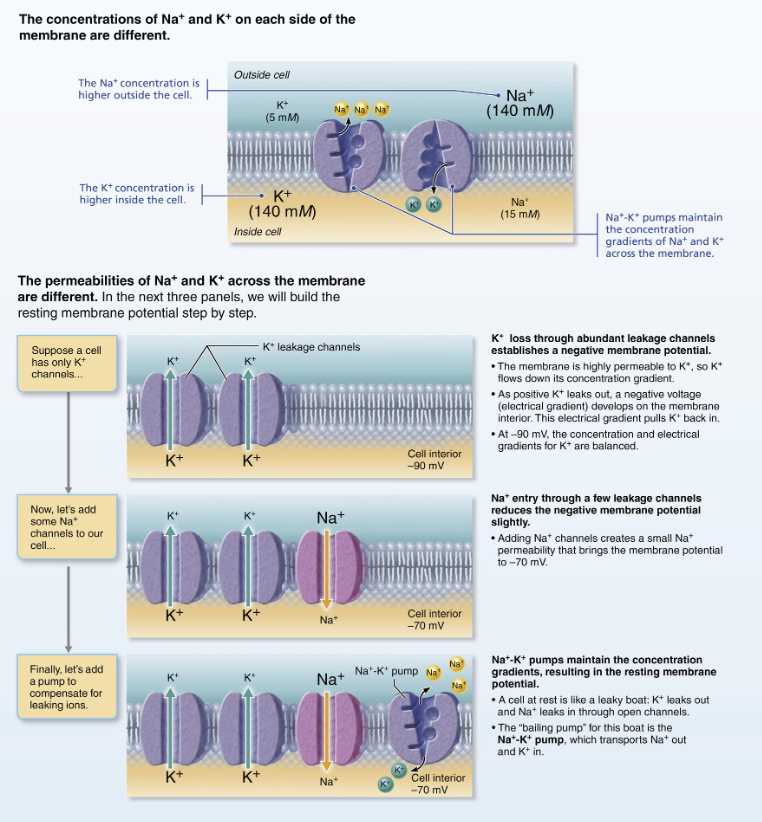
How is the Resting Membrane Potential Changed?
Concentrations of ions across membrane change
Membrane permeability to ions changes
Changing the Resting Membrane Potential produces what two types of signals?
Changes in membrane potential are used as signals to receive, integrate, and send information
Graded potential
Incoming signals operating over short distances
Action potentials
Long-distance signals of axons
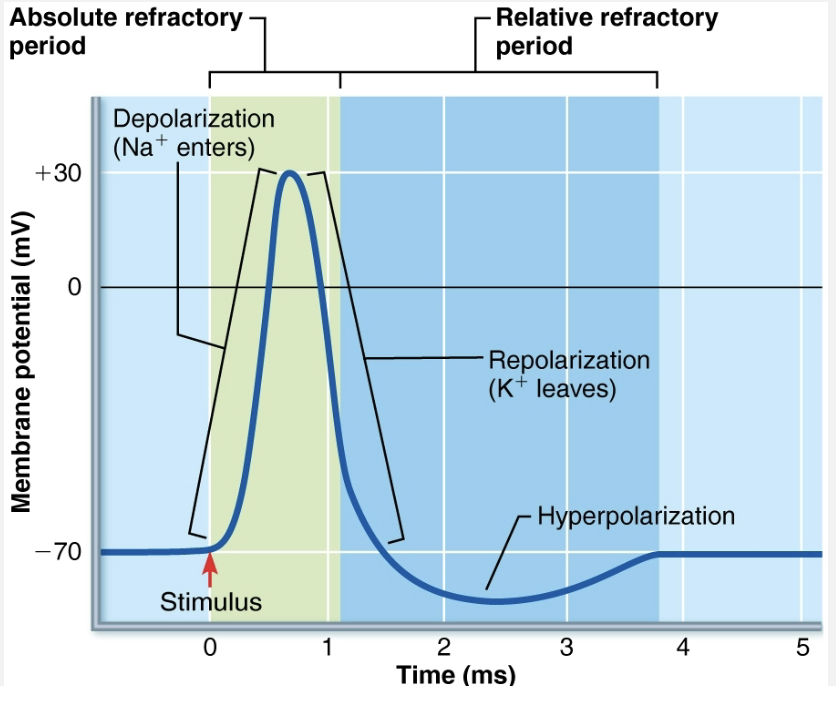
Depolarization vs Hyperpolarization
Depolarization: Decrease in membrane potential (moves toward zero and above)
Inside of membrane becomes LESS NEGATIVE than resting membrane potential
Probability of producing impulse increases
Hyper-polarization: Increases in membrane potential (away from zero)
Increase of membrane becomes MORE NEGATIVE than resting membrane potential
Probability of producing impulse decrease
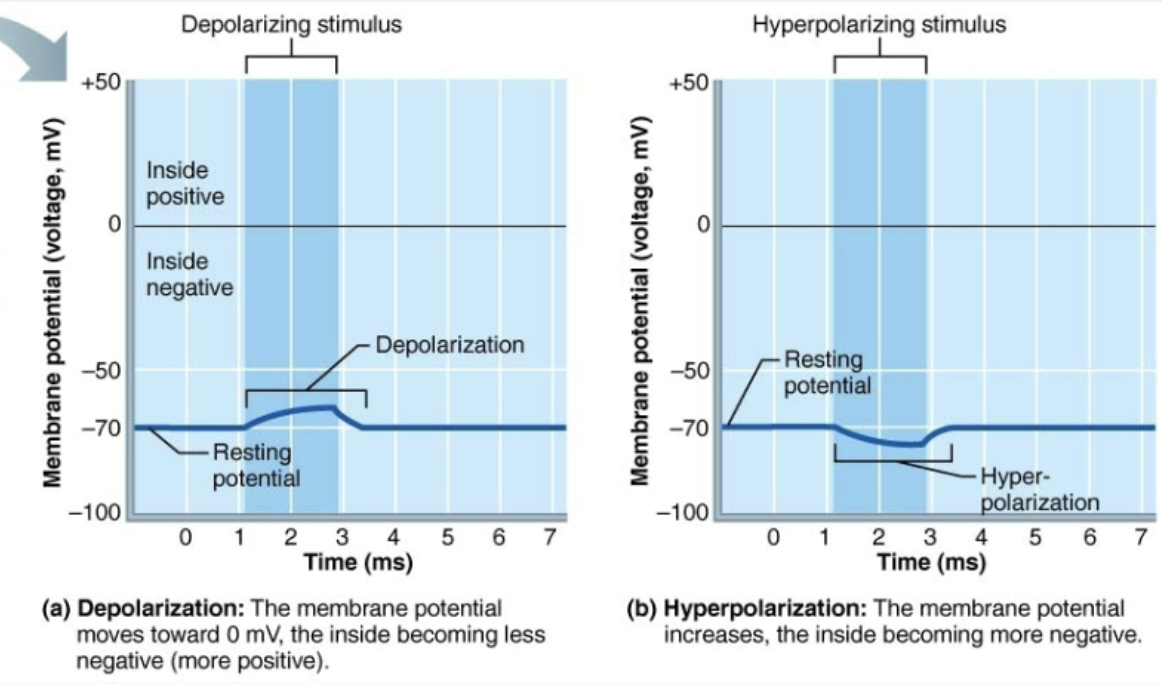
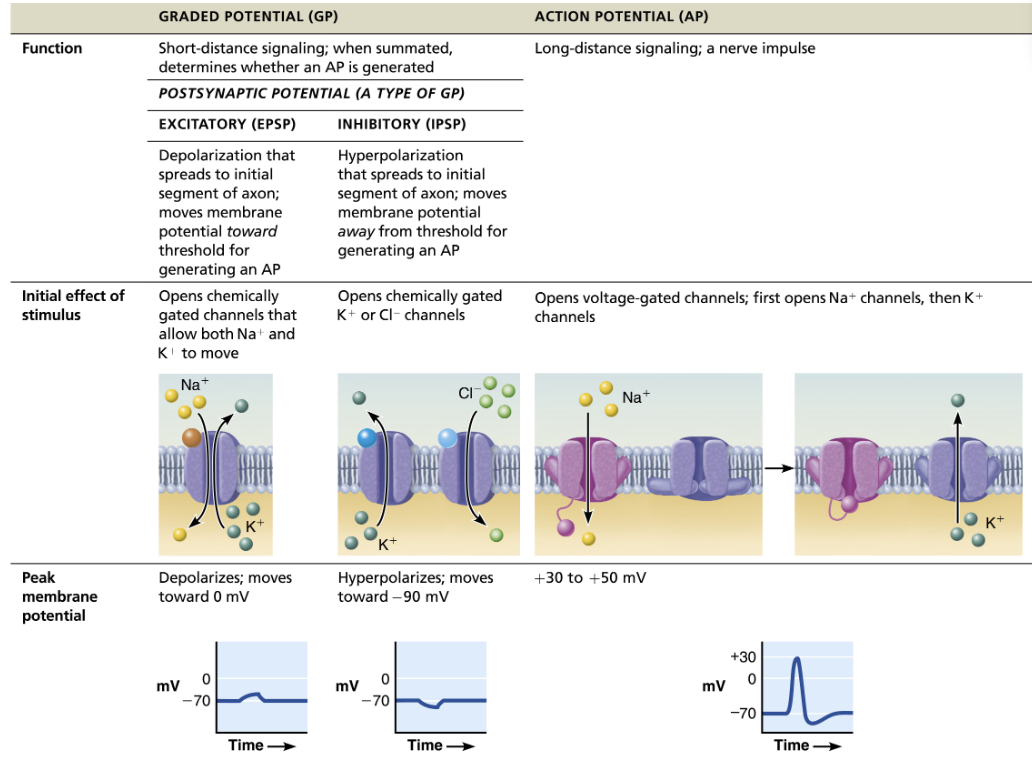
Compare and contrast graded potentials and action potentials
SIMILAR
Brief reversal of membrane potential with a change in voltage of ~100mV
In neurons, also referred to as nerve impulses
Involves opening of specific voltage-gated channels
DIFFERENCE
Action potentials do not decay over distance as graded potentials do
Principle way neurons send signals - means of long distance neural communication
Overview of Voltage channels
Explain how action potential are generated and propagated along neurons
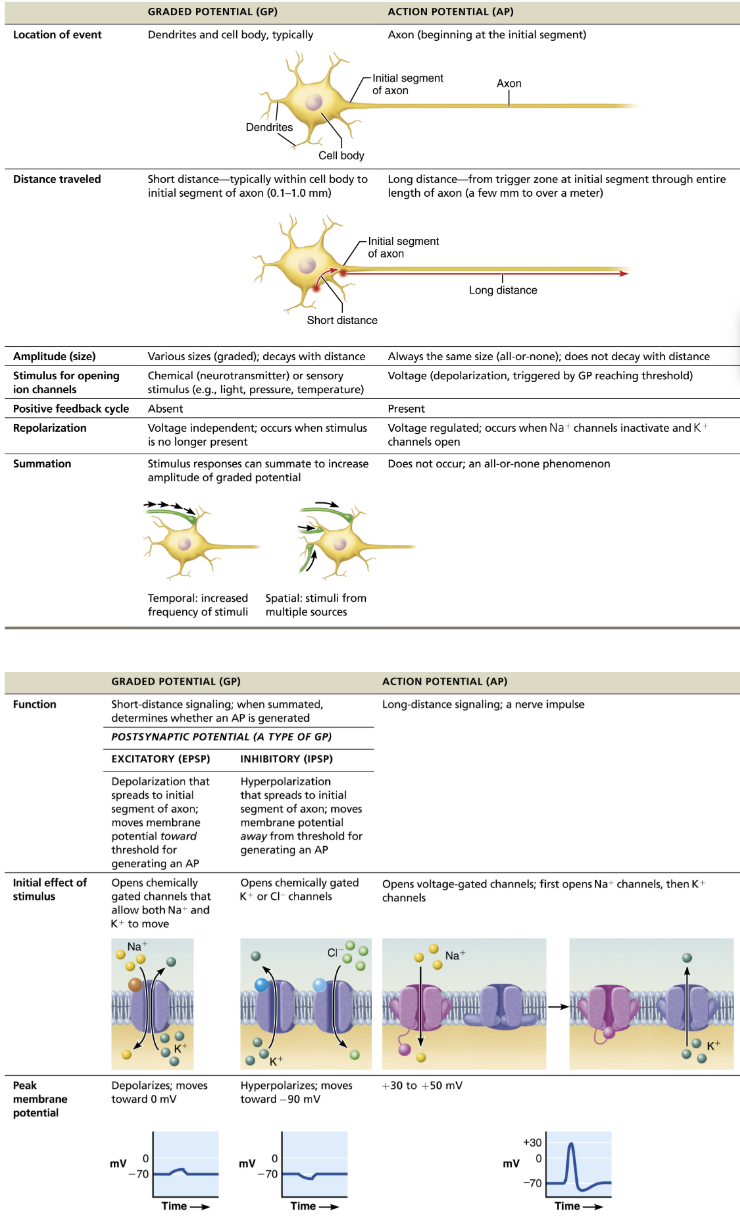
Resting state: all voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are closed
Only leakage channels for Na+ and K+ are open
Maintains the resting membrane potential (-70mV)
Depolarization: Threshold stimulus → Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ entry
Inside less negative
Repolarization: Na+ channels are inactivating and K+ voltage-gated channels open
Na+ channel inactivation gates close
Membrane permeability to Na+ declines to resting state
AP spike stops rising
Voltage-gated K+ channels open
K+ exists cell down its electrochemical gradient
Repolarization → membrane returns to resting membrane
Resets electrical conditions, not ionic conditions
Hyperpolarization: Some K+ channels remain open and Na+ channels reset
Na+/K+ pumps (thousands of them in an axon) restore ionic conditions
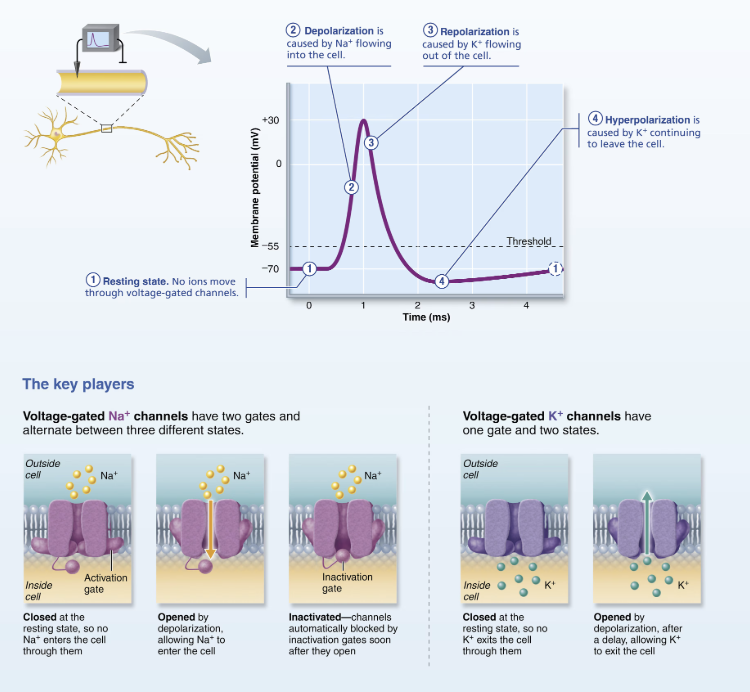
T/F: All depolarization events produce APs
False
Not all depolarization events produce APs
For an axon to “fire,” depolarization must reach threshold voltage to trigger AP
Explain Threshold and the All-Or-Nothing Phenomenon
At threshold:
Membrane is depolarized by 15-20 mV
Na+ permeability increases
Na+ influx exceeds K+ efflux
The positive feedback cycle begins
All-or-None
An AP either happens completely, or does not happen at all
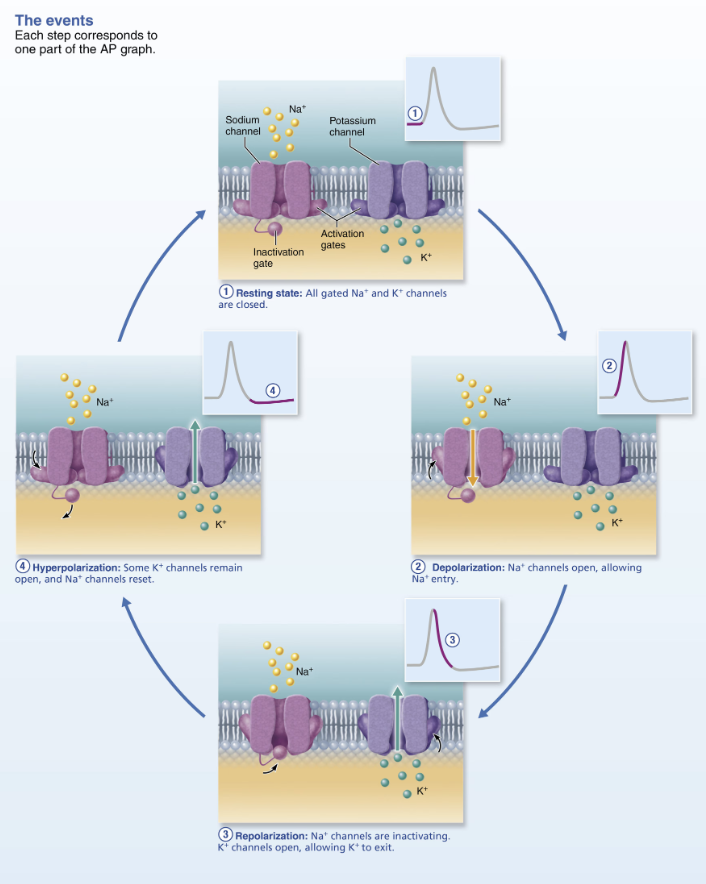
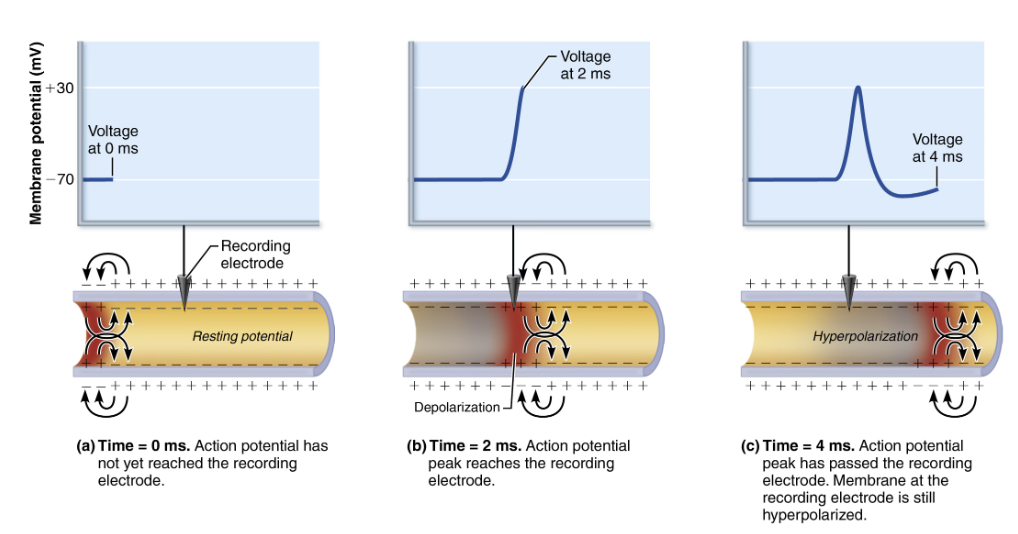
Explain Propagation of an Action Potential
Propagation allows AP to be transmitted from origin down entire axon length toward terminals
Na+ influx through voltage gates in one membrane area local currents that cause opening of Na+ voltage gates in adjacent membrane area
Leads to depolarization of the area → which in turn causes depolarization in the next area
One initiated an AP is self-propagating
Since Na+ channels closer to the AP origin are still inactivated, no new AP is generated there
AP occurs in a FOWARD DIRECTION
Define Refractory period
Time in which neuron cannot trigger another AP
Voltage-gated Na+ channels are open, so neuron respond to another stimulus
Define absolute and relative refractory periods
Absolute refractory period: neuron cannot respond to another stimulus, no matter how strong
Relative refractory period: An exceptionally strong stimulus can reopen the Na+ channels that have already returned to their resting state and generate another AP
Define Continuous Conduction
Slow conduction that occurs in non-myelinated axons
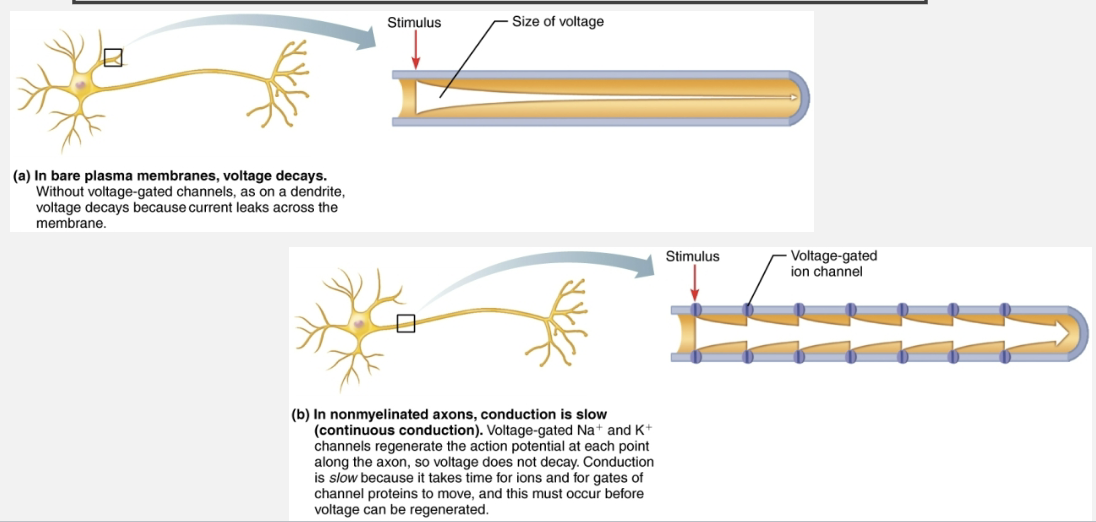
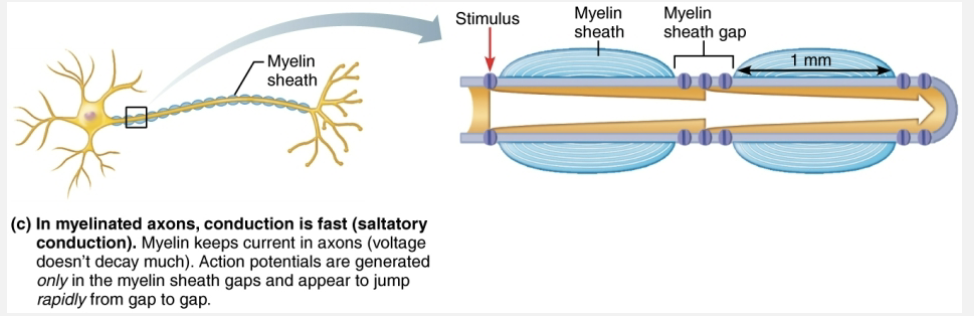
Define saltatory conduction and explain how it differs from continuous conduction
Saltatory conduction: occurs in myelinated axons is about 30x faster
Myelin sheaths insulate and prevent leakage of charge
Voltage-gated Na+ channels are located at myelin sheath gaps
APs generated only at gaps
Electrical signals appear to jump rapidly from gap to gap
Clinical Example: know the cause of multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects primarily young adults
Myelin sheaths in CNS are destroyed when immune system attacks myelin
Turns myelin into harden lesions called scleroses
Impulse condition slows and eventually ceases
Demyelinated axons increase Na+ channels, causing cycles of relapse and remission
Symptoms and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis
Symptoms
Visual disturbances
Weakness
Loss of muscular control
Speech disturbances
Incontinence
Treatment
Drugs that modify immune system activity
List examples of impaired AP impulse propagation
Impaired AP impulse propagation can be caused by a number chemical and physical factors
Local anesthetics act by blocking voltage-gated Na+ channels
Cold temperatures or continuous pressure interrupt blood circulation and delivery of oxygen to neurons
Cold fingers get numb, or foot “goes to sleep”
Define synapse
Junctions that mediate information transfer, connects neurons
From one neuron to another neuron
Or from one neuron an effector cell
Nervous system works because information flows from neuron to neuron
Describe the Structure of the Synapse
Most function as both
Presynaptic neuron
Neuron conducting impulses TOWARD synapse (sends information)
Postsynaptic neuron
Neuron transmitting electrical signal AWAY from synapse (receives information)
In PNS may be a neuron, muscle cell, or gland cell
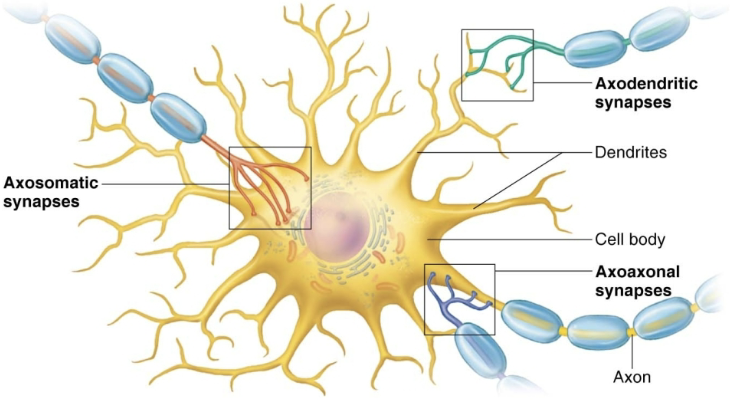
List the Main Types of Synapses
Chemical synapse
Most common type of synapse
Specialized for release and reception of chemical neurotransmitters
Electrical synapse
Distinguish between electrical and chemical synapses by structure and by the way they transmit information
Chemical synapses
STRUCTURE
Axon terminal of presynaptic neuron → contains synaptic vesicles filled of synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitter
Receptor region on postsynaptic neuron’s membrane → receives neurotransmitter
Usually on dendrite or cell body
Two parts separated by fluid filled synaptic cleft
FUNCTION
Electrical impulse changed to chemical across synapse, then back into electrical
Transmission across synaptic cleft
Synaptic cleft prevents nerve impulses from directly passing from one neuron to next
Chemical event (as opposed to an electrical one)
Depends on release, diffusion, and receptor binding of neurotransmitters
Ensures unidirectional communication between neurons
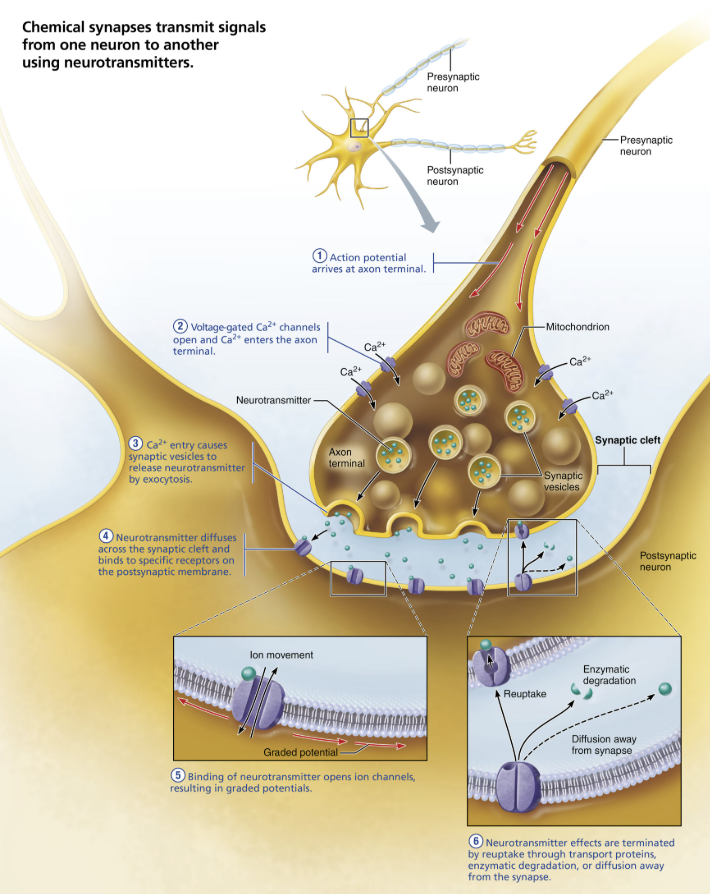
Events at the Chemical Synapse
AP arrives at axon terminal of presynaptic neuron
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open, and Ca2+ enters axon terminal
Ca2+ flows down electrochemical gradient from ECF to inside of axon terminal
Ca2+ entry causes synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitter
Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft
The higher the impulse frequency, the more vesicles exocytose, leading to a greater effect on the postsynaptic cell
Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane
Often chemically gated ion channels
Binding of neurotransmitter opens ion channels, creating graded potentials
Binding causes receptor protein to change shape, which causes ion channels to open
Causes a graded potential in postsynaptic cell
Can be excitatory or inhibitory event
Some receptor proteins are also ion channels
Neurotransmitter effects are terminated
As long as neurotransmitter is binding to receptor, potentials will continue, so process needs to be regulated
Within a few milliseconds, neurotransmitter effect is terminated in one of three ways
Re-uptake → by astrocytes or axon terminal
Degradation → by enzymes
Diffusion → away from synaptic cleft
Define Synaptic delay
limiting step of neural transmission
Transmission of AP down axon can be very quick, but synapse slows transmission to postsynaptic neuron down significantly
Not noticeable,, because these are still very fast
Time needed for neurotransmitter to be release diffuse across synapse, and bind to receptors
Can take anywhere from 0.3 to 5.0 ms
Clinical - Examples of disorders linked to issues in the synaptic region
ADHD
Autism
Schizophrenia
Define Neutransmitters receptors
Cause graded potentials that vary in strength based on:
Amount of neurotransmitter released
Time neurotransmitter stays in cleft
List the two types of Postsynaptic potentials
EPSP → Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials
IPSP → Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potenitals
Distinguish between excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
Depending on effect of chemical synapse
Excitatory (EPSP)
Depolarization that spreads to initial segment of axon → moves membrane potential TOWARD threshold for generating an AP
Opens chemically gated channels that allow both Na+ and K+ to move
Inhibitory (IPSP)
Hyper-polarization that spreads to initial segment of axon → moves membrane potential AWAY from threshold for generating an AP
Opens chemically gated K+ or Cl- channels
Define Neurotransmitter
A signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse
~50 neurotransmitters have been identified
Most neurons make two or more neurotransmitters
Neurons can exert several influences
Usually released at different stimulation frequencies
Classified by:
Chemical structure
Function
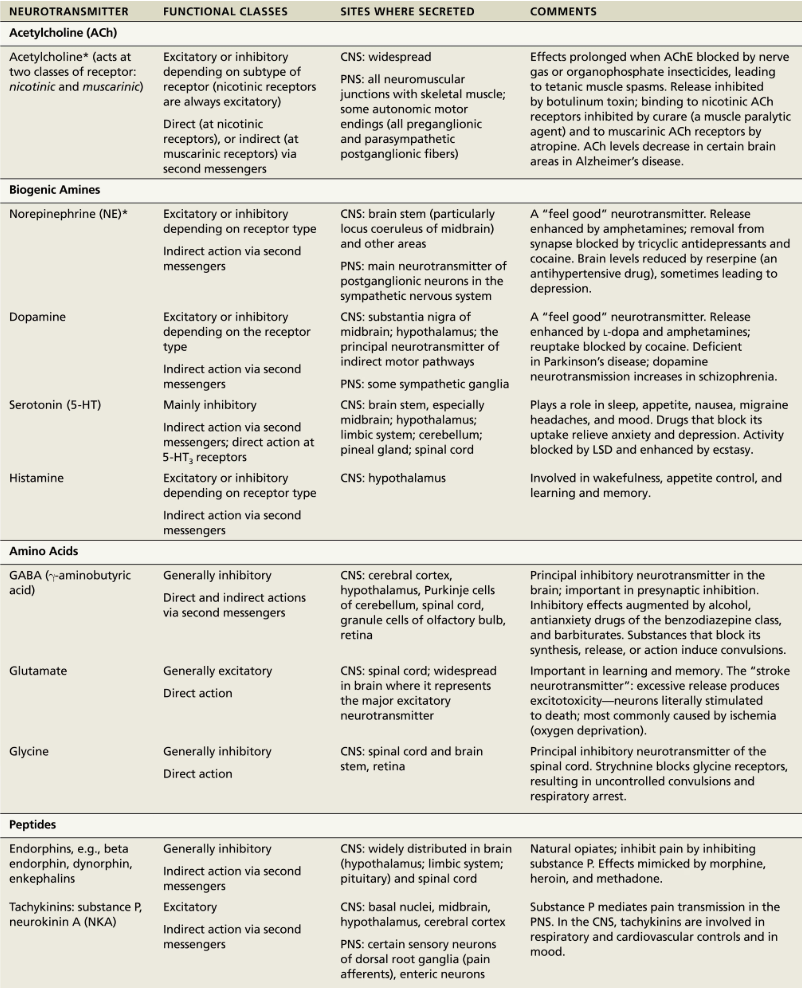
Classify neurotransmitters by Chemical Structure
Acetylcholine (ACh)
First identified and best understood
Released at neuromuscular junctions
Also used by many autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Degraded by enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Biogenic amines
Catecholamines → made of amino acid tyrosine
Dopamine
Norepinephrine (NE)
Epinephrine
Peptides
Neuropeptides → strings of amino acids that have diverse functions
Endorphins: acts as natural opiates; reduce pain perception
Endocannabinoids
Act as same receptors as THC (active ingredient in marijuna)
Lipid soluble
Synthesized on demand
Regulate sleep, mood, appetite, suppress nausea, learning, memory, body temperature, pain immune functions and fertility
Classify neurotransmitters by Function
Effects → determined by receptor to which is binds
Excitatory
Depolarizing → decrease in membrane potential; Inside membrane becomes less negative than resting
Inhibitory
Hyper-polarizing → increase in membrane potential; Inside membrane becomes more negative than resting
EX: Acetylcholine and NE bind to at least two receptors types with opposite effects
ACH is excitatory at neuromuscular junctions in skeletal muscle
ACh is inhibitory in cardiac muscle
Actions
Direct
Fast
EX: ACh and the amino acid neurotransmitters
Indirect
Slow; Broader, longer-lasting effects
EX: biogenic amines, neuropeptides, and dissolved gases are indirect neurotransmitters