Optics 2A: PUPILS, STOPS, AND RAYS
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
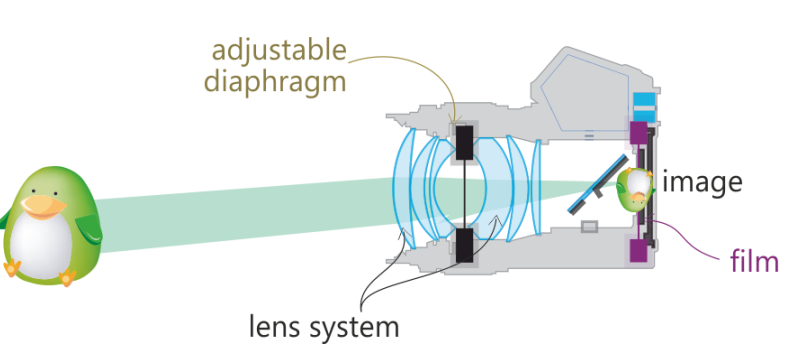
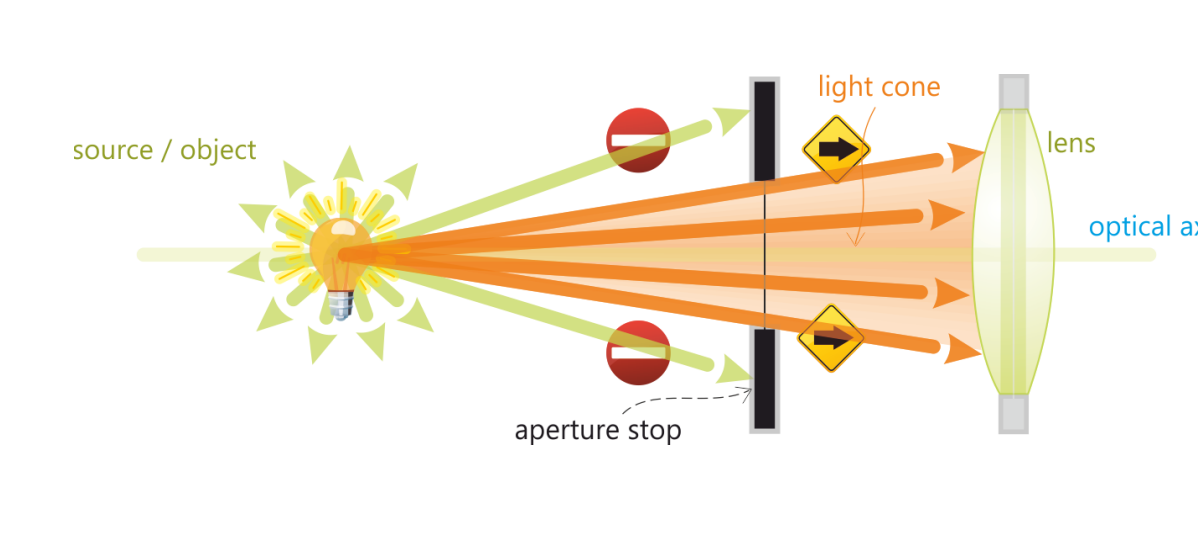
Aperture stop in camera
Adjustable diaphragm placed after first lens element
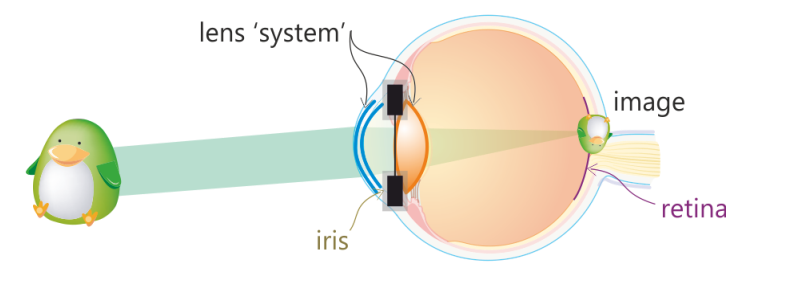
Aperture stop in the eye
Clear opening formed by the iris
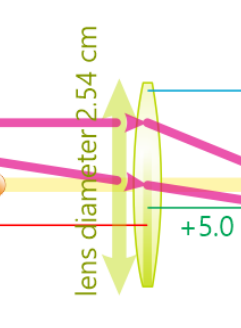
Properties affected/not affected by lens diameter
Affected
Sharper image
Brighter image
Depth of field
Not affected
Size
Type
Location
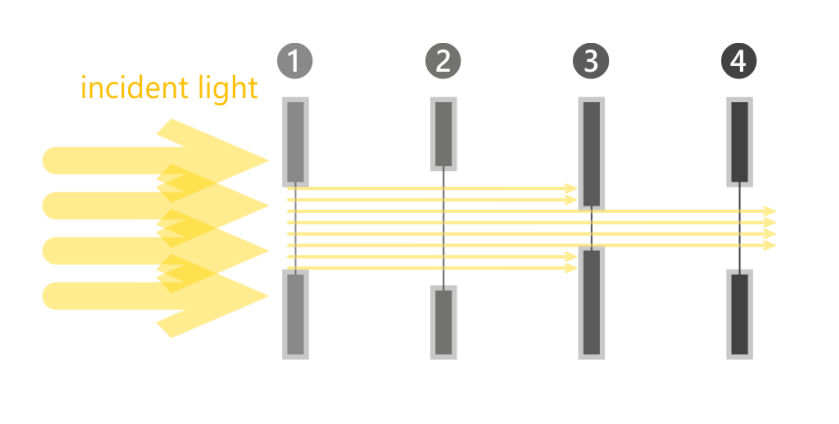
In collimated illumination, the aperature stop is…
The smallest diameter opening
#3
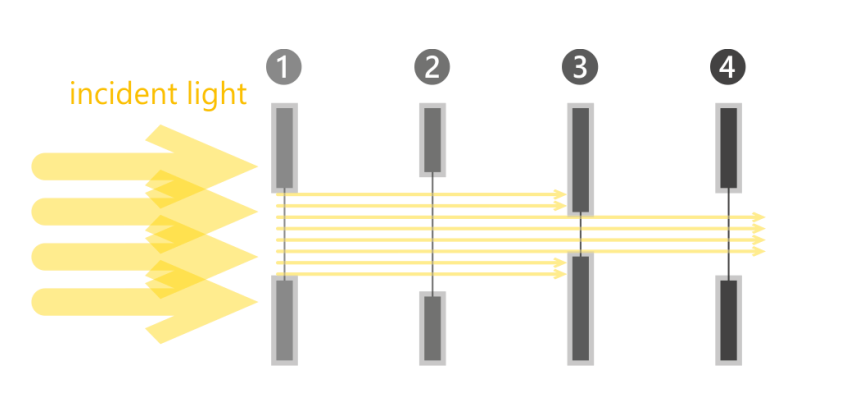
Properties of aperature stop
Determines light gathering capacity of a system
Its edges form the smallest possible angle
Of an on-axis object point
Dependent on object locatoin
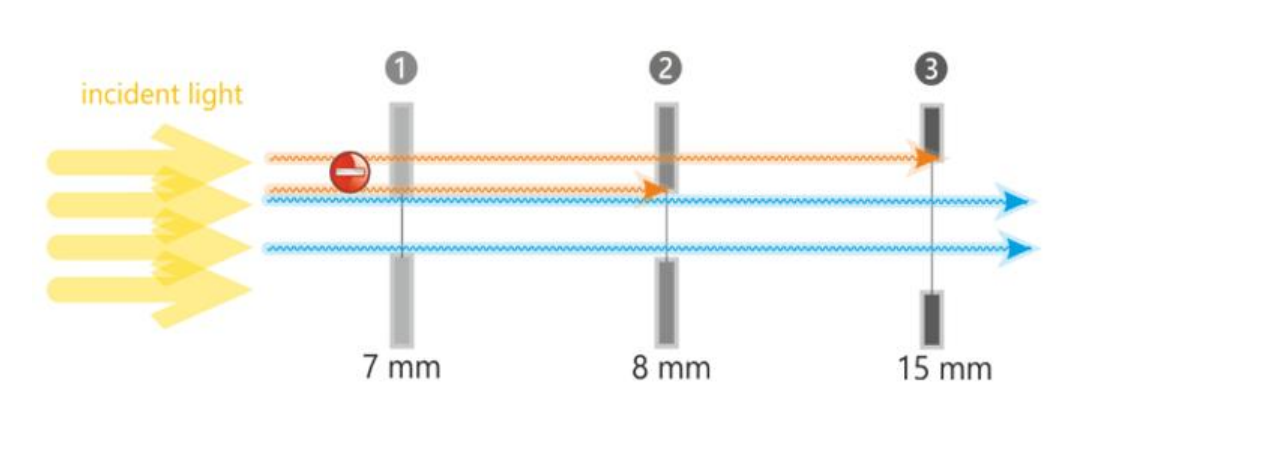
Definition of ray height
Seperation of rays from optical axis
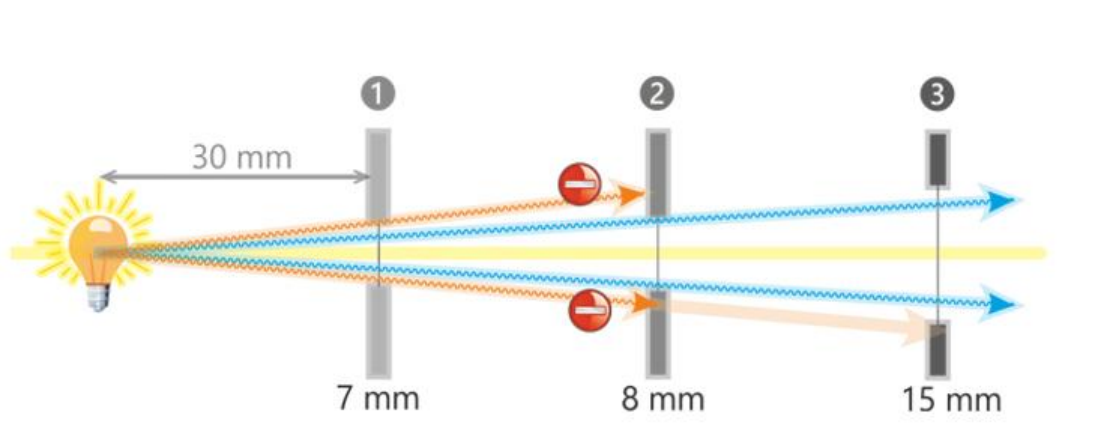
Ray height of 8mm
Maximum ray height is 4mm
4mm above optical axis
4mm below optical axis
Equal to the semi-diameter of the aperature
Semi-diamter of an aperture
Half of the diameter of the aperature opening
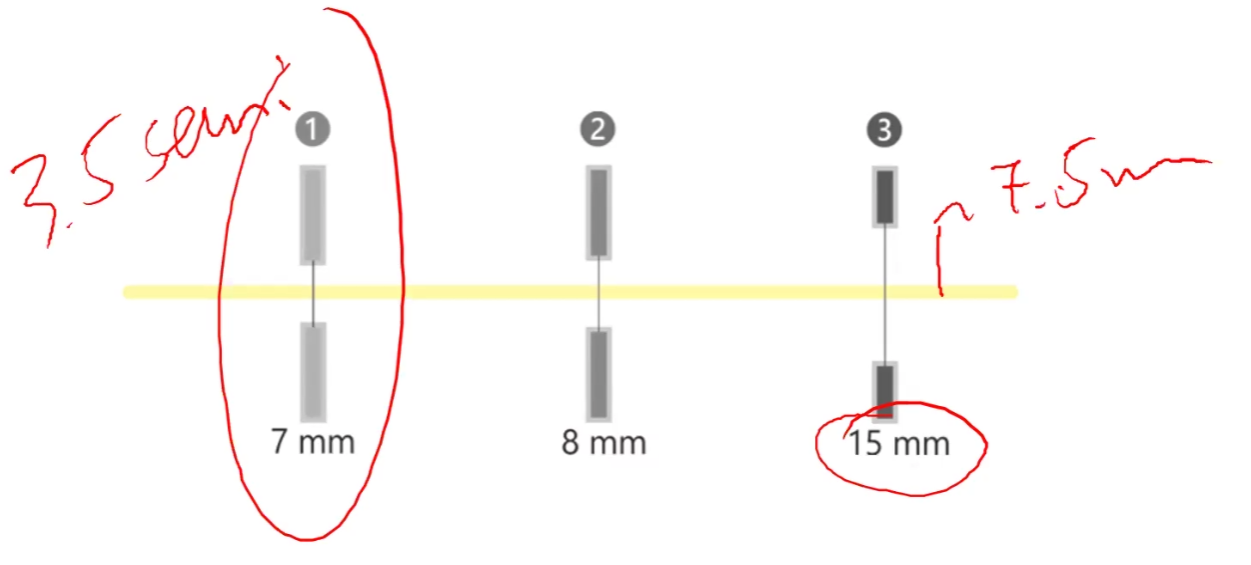
Calculating angular subtense w/ optical axis
Tan^{-1}\left(\frac{Semi-diamter_{.}of.stop}{Distance.from.object}\right)
AKA aspect ratio
Element forming smallest angular subtense→ aperature stop
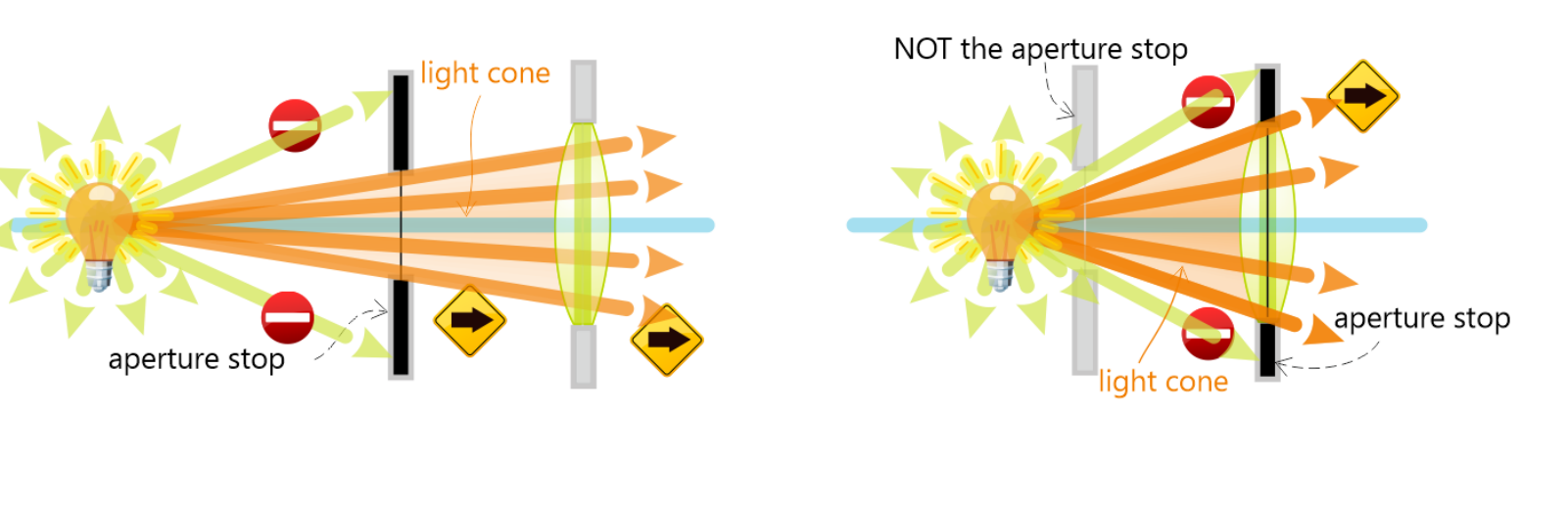
The aperature stop depends on…
Location of object
Semi-diamter of the stop or lens
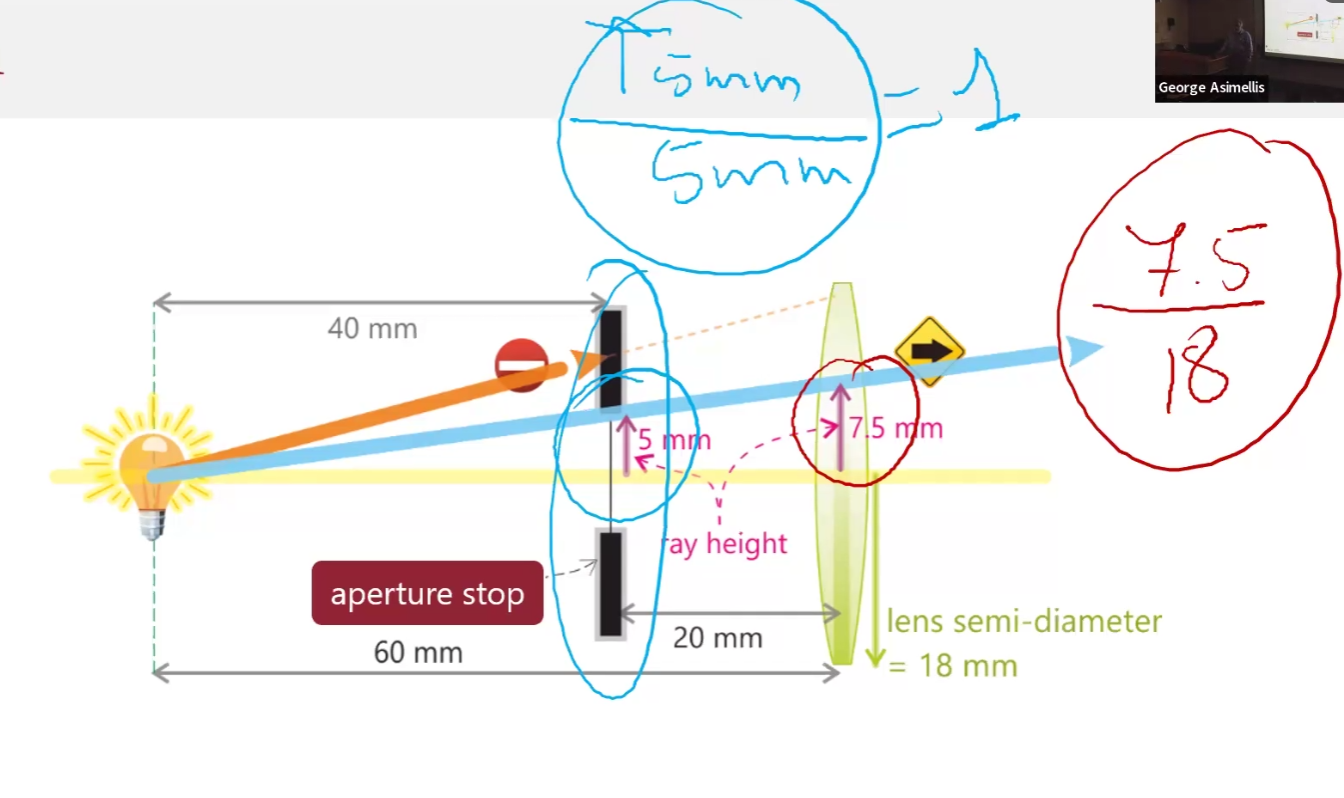
Determining apterature stop using marginal ray
Draw ray from on-axis object that passes through all elements
Mark height at which it intersects the elements
Largest height / semi-diamter ratio
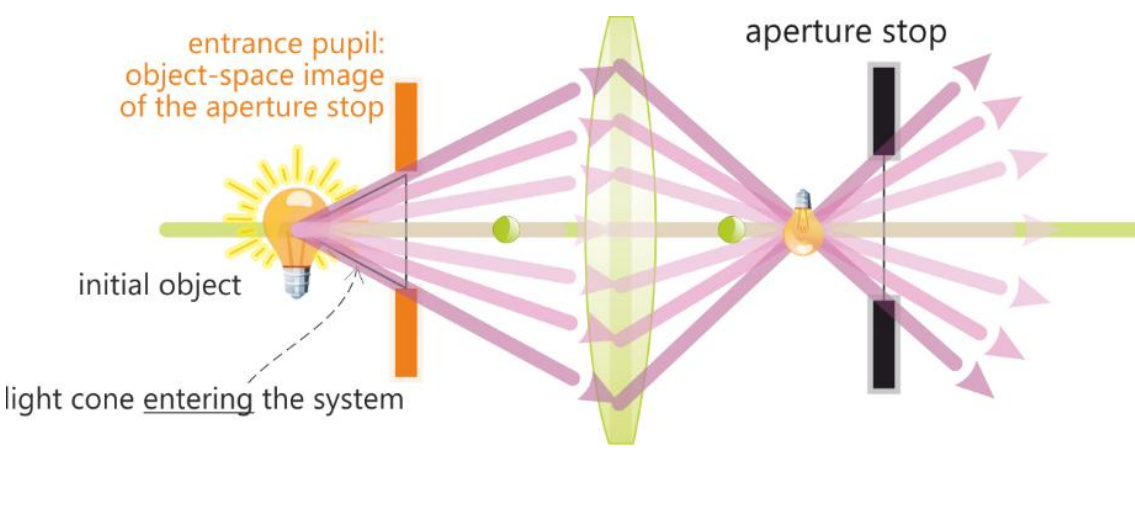
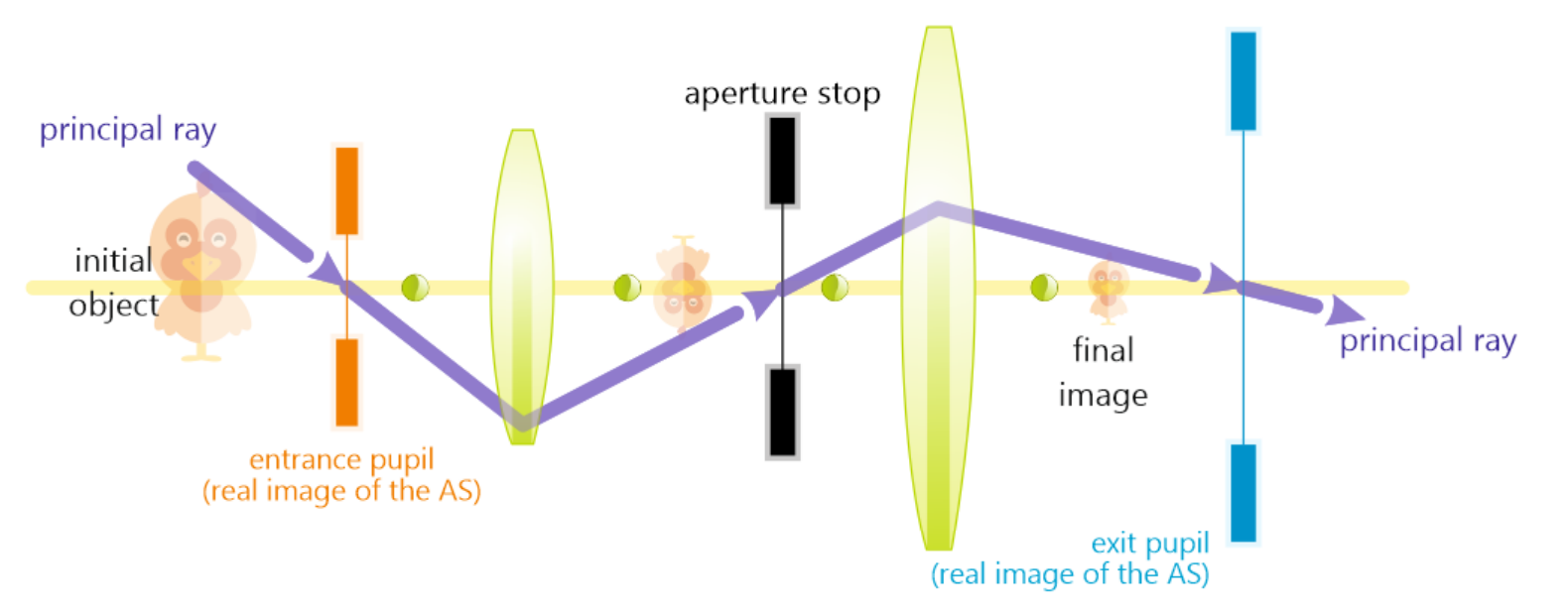
Entrance pupil
Object-space image of the aperture stop
Formed by optical elements preceeding aperture
Aperature stop as seen from an axial point on the object
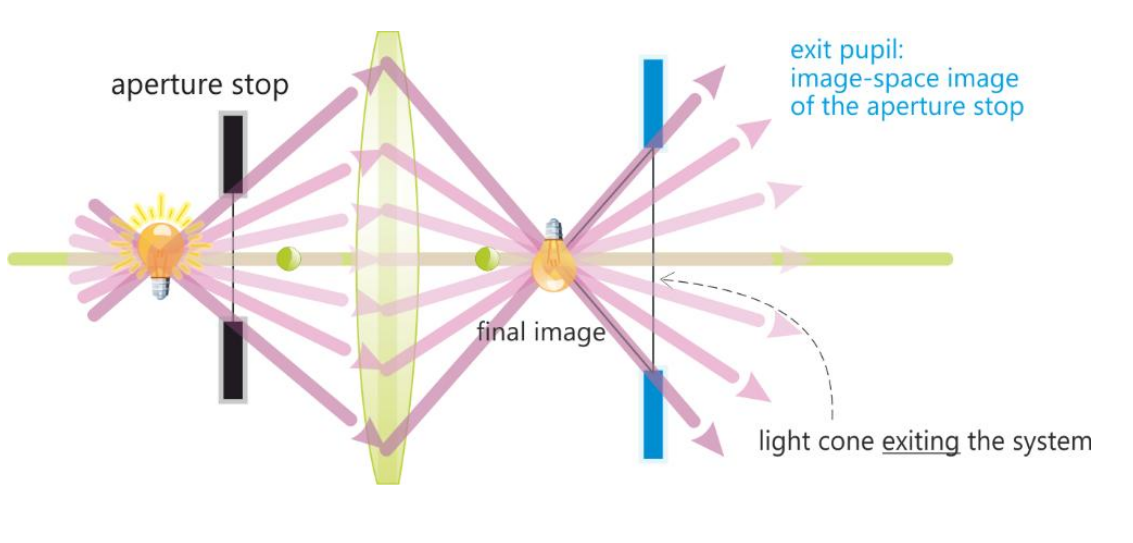
Exit pupil
Image-space image of the aperature stop
Formed by optical elements suceeding it
Aperature stop as seen from an axial point on the image
The aperature stop is the entrance pupil when…
There is no lenses preceding the the AS
The aperature stop is the exit pupil when…
There is lenses preceeding the aperture stop
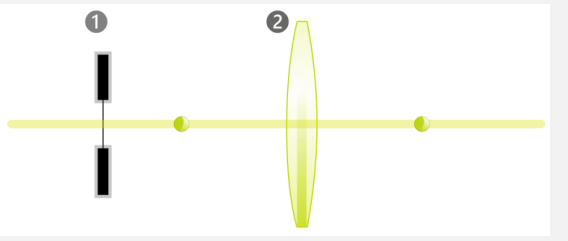
Element one is…
Aperature stop
Entrance pupil
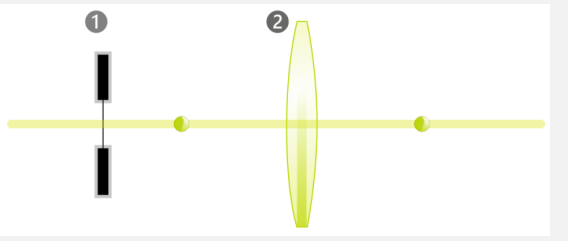
The exit pupil is…
The image of element 1 via element 2
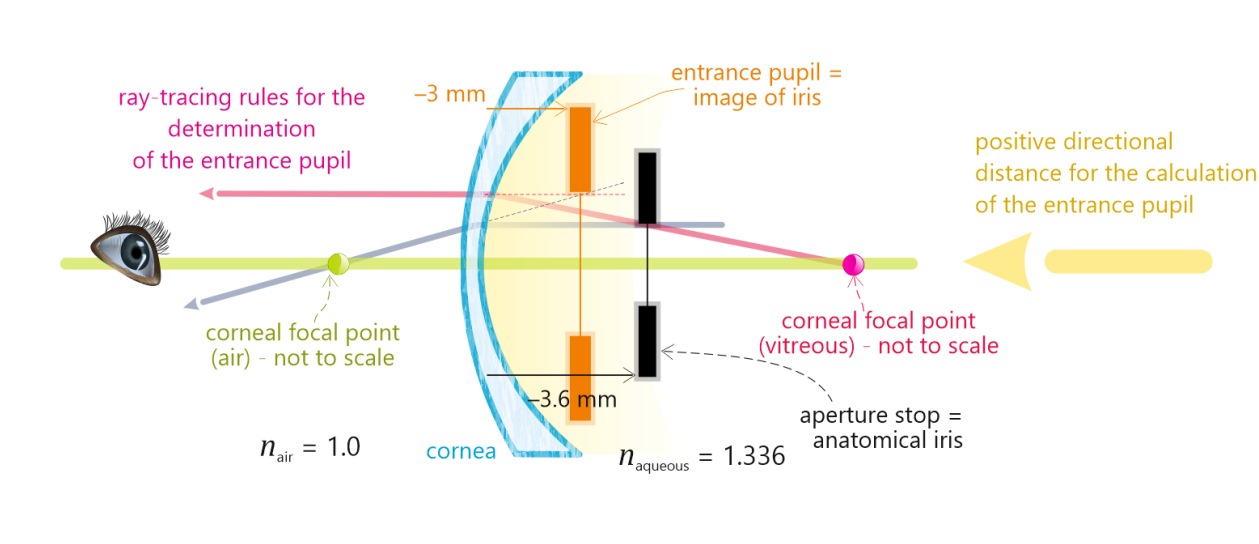
Entrance pupil of the human eye
What we call the pupil (Apparent pupil)
Image of the iris via the cornea
Slightly closer to cornea and aobut 12.7% larger than the iris
Principal ray
Ray from off-axis object point → Center of entrance pupi → Lens
Ray = Refracted at lens
Refracted towards center of the exit pupil
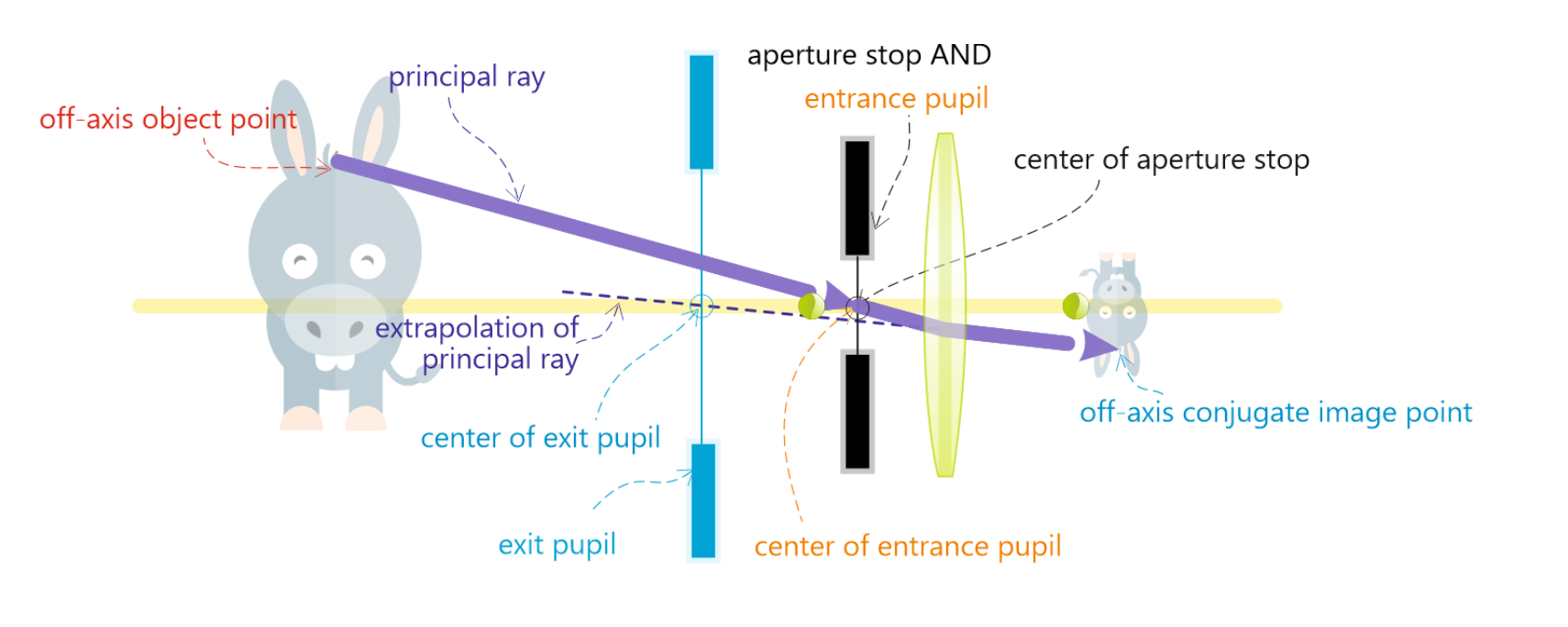
A ray from an off-axis object point crosses the center of the AS… It also crosses the…
Center of exit pupil
Center of entrance pupil
Marginal ray definition
Most extreme ray that propagates through the system unobstructed
Confines the cone from an on-axis object point
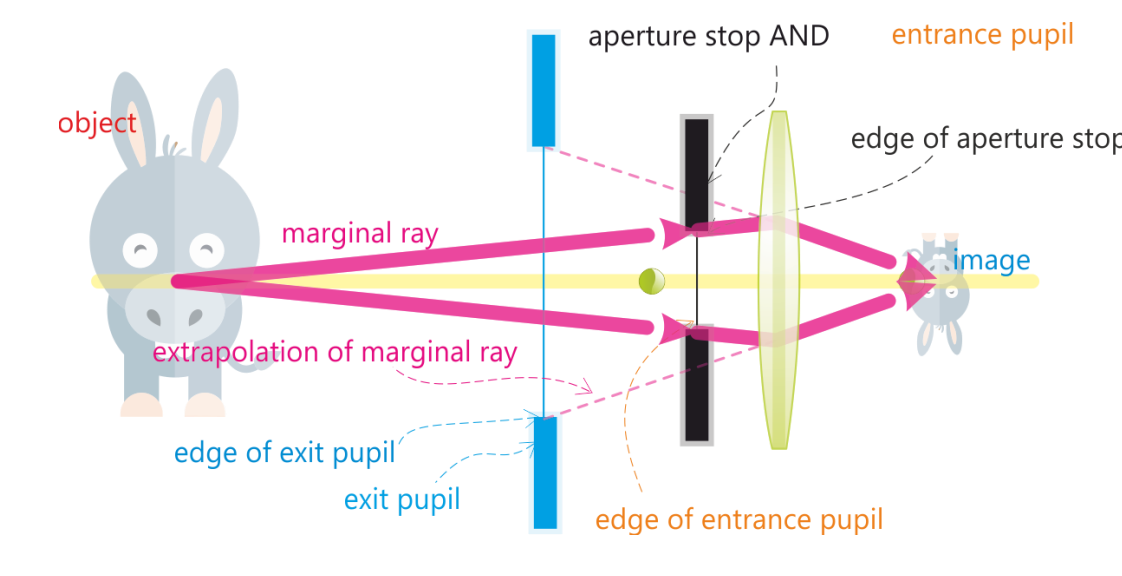
Finding marginal ray
Ray from on-axis object point → Edge of entrance pupil
Lens infront of AS→ Ray bends and passes edge of aperture stop
Lens after AS→ Ray bends and passes through exit pupil
A ray from an on-axis object point crosses the edge of the AS… It also crosses the…
Edge of the entrance pupil
Edge of the exit pupil