Geography 5 Midterm 1
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
Absolute
Objective/real; does not vary from person to person.
Relative
Subjective/perceptual; varies from person to person or between groups.
Space
Areal extent; how much area does something take up.
Absolute Space
Objective, real measurable space.
Relative Space
Perceptual, variable, dependent on relationships and activities.
Place
Attributes and values we associate with a particular location, unique to each person.
Placelessness
Opposite of a place; no emotions or associations with a location.
Economic Approach to Place
The spatial distribution of social and economic activities.
Social and Humanistic Approach to Place
Locale, or the settings for everyday routine social interaction provided in a place.
Cultural Approach to Place
The sense of place or identification with a place endangered by living in it.
Absolute Location
Mathematical location; unique and independent, usually defined by coordinated systems.
Relative Location
Dependent on the relationship of other things; expresses interdependence.
Site
Absolute location concept; actual location of a place/settlement including physical characteristics.
Situation
Relative location concept; information about a location relative to other locations.
Absolute Direction
Uniform and valid everywhere on Earth; North-South-East-West.
Relative Direction
Refers to general reference; left, right, up, down, back, forward.
Absolute Distance
Spatial separation between two points on Earth using standardized metric.
Relative Distance
Transformed distance into some other measure more contextually relevant, like travel time or cost.
Isochrones
Lines of equal travel time.
Psychological Distance
Which feels closer; subjective perception of distance.
Cultural Distance
Differences in cultural perceptions between locations.
Dimensionality
Many features are spatially 3-D but can be modeled at a lower dimension.
Density
Number of something in a defined area.
Distribution
Pattern of events over a space; dispersed vs. concentrated.
Spatial Associations
Two distributions of features spatially corresponding with each other.
Tobler's Law
Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related to distant things.
Distance Decay
Level or likelihood of interaction decreases with distance.
Accessibility
Relative ease with which you can reach a destination.
Connectivity
A measure of the degree of connections or relationships between people across the barrier of space.
Network
The areal pattern of connections between places.
Spatial Diffusion
Dispersion of an idea or items from a center of origin.
Regions
An area distinguished by a unique combination of trends or features as compared to surrounding areas.
Administrative Regions
Politically determined, hierarchical organization, uniform membership.
Statistical Regions
Used for the purpose of collecting and aggregating data.
Thematic Regions
One or more variable or theme; imprecise or vague boundaries.
Functional Regions
Areas defined by connections; usually has a core surrounded by a margin.
Cognitive/Perceptual Regions
How people informally organize places in their mind; usually shaped by culturally shared beliefs.
Maps
A pictorial model of reality; Earth's surface and distribution of features.
Why Maps?
Navigation, visualization, and measurement.
Scale
The relationship between the size of an object on a map and the actual size of the feature.
Small Scale vs. Large Scale
Small scale has a large amount of area with less detail; large scale has a smaller amount of area with more detail.
Cartographic Scale Elements
Representative fraction, graphic scale, verbal scale.
Reference Maps
Maps that show features without representation.
Political Maps
A type of reference map that shows political boundaries.
Topographic Maps
Maps that usually show contour lines to represent height.
Thematic Maps
Maps that present a graphic theme illustrating a fact.
Graduated Circle Maps
Maps where the area of a circle is proportional to the number of entities.
Isopleth Map
A map of lines that connect points of equal value of the mapped entity.
Choropleth Map
Maps where areas are designated by a color or fill pattern proportional to the number of entities.
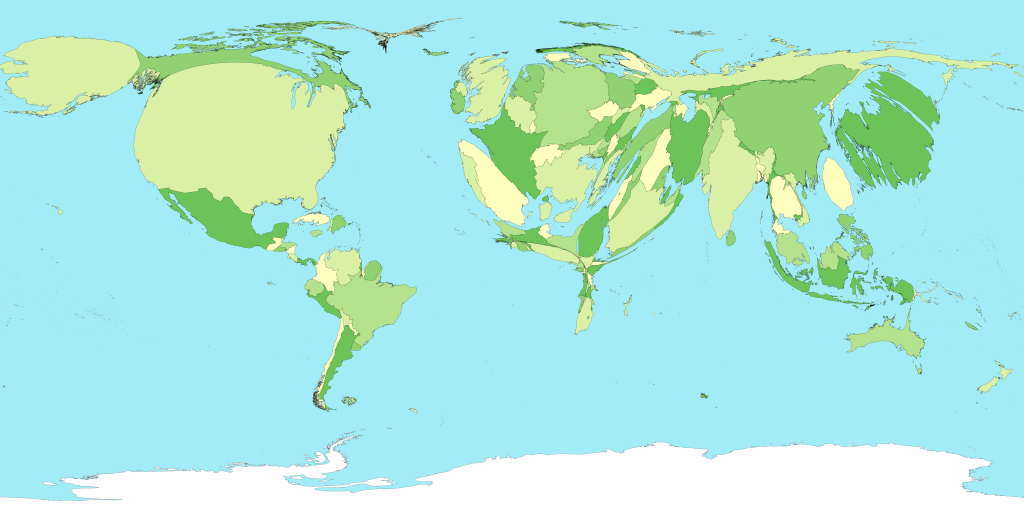
Cartograms
Maps that use statistical data to transform space to appear in proportion to the values.
Mental Maps
Internal models or representations of an area developed by an individual.
The Globe Grid
The geographic coordinate system consisting of longitudes and latitudes.
Map Projection
The method of representing the curved surface of the Earth on a flat surface.
Conformal Projection
Projections that preserve angles and shapes but distort area.
Equivalent Projection
Projections that preserve proportions of areas but distort shape.
Equidistant Projections
Projections that preserve distance in one direction or along lines.
Remote Sensing
Collection of information about Earth's surface through aerial photography or satellite imagery.
Primary Data
Data collected through field or lab measurements, interviews, and observations.
Secondary Data
Data collected by someone else, such as archives and national surveys.
GISystem
A tool that allows users to create interactive queries and analyze spatial information.
GIScience
The science underlying geographic ideas, concepts, applications, and systems.
Spatial Interaction
Contact between places and how activity in one place influences another.
Friction of Distance
Factors that can hinder spatial interaction, such as travel mode and cost.
Facilitators of Spatial Interaction
Elements that make spatial interactions easier, such as networks.
Networks
Nodes and connecting links along which spatial interaction is facilitated.
Technology
Facilitator of interaction that changes patterns and reduces friction.
Telecommuting
Alters shopping and errand patterns.
Amazon
Affects daily travel patterns.
Social Media
Affects interpersonal interaction over time.
Space-Time Compression
The phenomenon of reducing the time it takes for spatial interactions.
Globalization
Trends towards greater connectivity among places around the globe.
Physical Barriers
Impediments to interaction such as mountains, rivers, country borders, and distance.
Socio-Cultural Barriers
Barriers related to language, culture, race/ethnicity, and cultural practices.
Psychological Barriers
Personal barriers such as fear, risk, age, and distaste.
Behavioral Geography
Attempts to understand human activity in space, place, and environment.
Individual Activity Space
Where people go on a typical day or week, shaped by various factors.
Space Time Path
Diagram describing where we are at any given time and how fast we move.
Descriptive Models
Models that describe spatial and temporal trends and their causes.
Normative Models
Models that determine the best approach to solve a technical problem.
Predictive Models
Models that forecast future events.
Parsimony
The principle of keeping models simple.
Gravity Model
Consumer behavior reflects that more people in a place increases potential customers.
Retail Gravity Model
Predicts the distance from city to market boundary based on population.
Huff Model
Measures attraction based on population and distances between locations.
Demography
Study of human populations, including size, composition, and distribution.
Pillars of Demography
Fertility, mortality, and migration.
Population Geography
Application of demography to study human beings in relation to earth conditions.
Crude Birth Rate
Annual number of live births per 1,000 people.
Total Fertility Rate
Average number of births a woman would have during her childbearing years.
Age-Specific Fertility Rate
Number of births per 1,000 women in an age group per year.
Replacement Fertility Rate
Number of births per woman needed to keep the population stable.
Crude Death Rate
Annual number of deaths per 1,000 people.
Infant Mortality Rate
Number of deaths to children under 1 year old per 1,000 live births.
Life Expectancy at Birth
Average number of years a person is expected to live based on current death rates.
Population Pyramids
Illustrates age and sex distribution in a region or country.
Dependency Ratio
Ratio of dependants younger than 15 and older than 64 to the working-age population.
The J Curve
Describes exponential growth at an increasing rate.
Biotic potential
Ability of a population to increase under ideal environmental conditions.
Logistic Growth (restricted)
Increase until population size reaches carrying capacity.
Carrying Capacity
Number of people an environment can support without environmental degradation.