Econ 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
what is supply
how much producers produce
what happens to price when supply increases/decrease.
It is a direct relationship. So when price goes up so does supply. And when supply goes down so does price.
what is demand
demand is the different quanities of goods that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices.
what happens when demand increases/decreases
It is an inverse realtionship. So when Price goes up quantity demanded goes down.
5 shifters of supply
prices/avalibilty of resources (input), # of producers, Technology, Taxes and subsidies, and future expectations.
prices/avalibilty of resources (input)
higher price= lower supply. low price = high price. (less profit)
# of producers
increase producers = increase of supply
Technology
High tech = increase in supply
taxes and subsudies
More pay = more product. More taxes = less product
future expectations
more profit in future = decrease
5 shifters of demand
taste/prefernces, # of consumers, price of related goods, Income, future expectations.
taste/prefernces
if someone wants it or not
# of consumers
population (only changes with death or immigaration)
price of related goods
subsitutes: something to use instead. Complements: something to buy with it.
Income
normal and inferioir goods.
normal goods
goods that consumers buy when they have more income (apple ipad)
inferior goods
alternate goods that people buy when they have less income ( samsung ipad )
future expecations
what consumers think will happen in future.
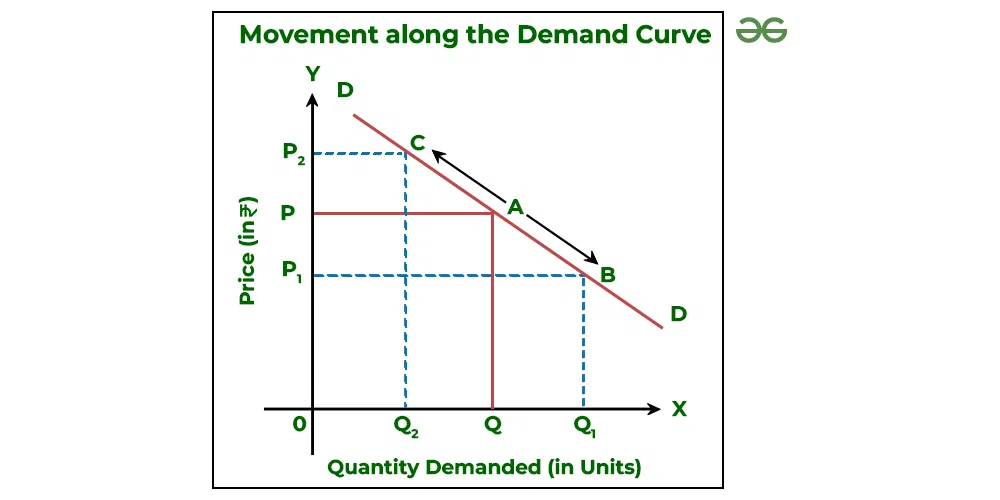
chnage in quanitity demanded
movement of curve
change in demand
a shift
price does not affect
demand curve
equillibrium
when quaiity demanded equqald quantity supplied.
how does equillibrium change with demand shifts
A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall; quantity supplied will decrease.
how does equillibrium change with supply shifts
A decrease in supply will cause the equilibrium price to rise; quantity demanded will decrease.
demand curve
supply curve
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/supplycurve2-102d446740e14584bc355228d72bfd44.png)
elastic demand
when price changes quanitity demanded chnages. increase when price decreases. (coke)
inelastic demand
quantity demand deosnt change based on price. (consumers will buy item no matter what the cost). (glasses)
price ceiling
maximum legal price a place can charge. (keep affordable) (shortage)

price floor
Minimum legal price a seller can sell a product. (surplus)

4 market structure
perfect competition, monoploly, monopolitic competion, and oligopoly.
perfect competion
A simple market where many sellers compete wile sellung identical products. A lot of producers, identical products (fruit), almost no barriers to entry, no control over prices.
monopoly
a market where one single seller dominated the market. 1 producer, unique products, almost impossible to enter, control over prices. (google)
monopolistic competion
A market in which any companies sell products that are similar but not identical mant producers, similar but not identical products, low barriers of entry, limited control over proces.
oligoply
few producers, similar products, high start up costs, agreements over proces. (airlines)
gov monopoly
military
natural monopoly
market that runs most efficinetly when one firm supplies all of the products. (power plants)
physical capital
human made objects used to create ither goods and services ( machines/tools)
human capital
knowledge and skills that are used to help make a product. ( eductaion, expiernes)
factors of production
land , labor, capital, entrepreneurship
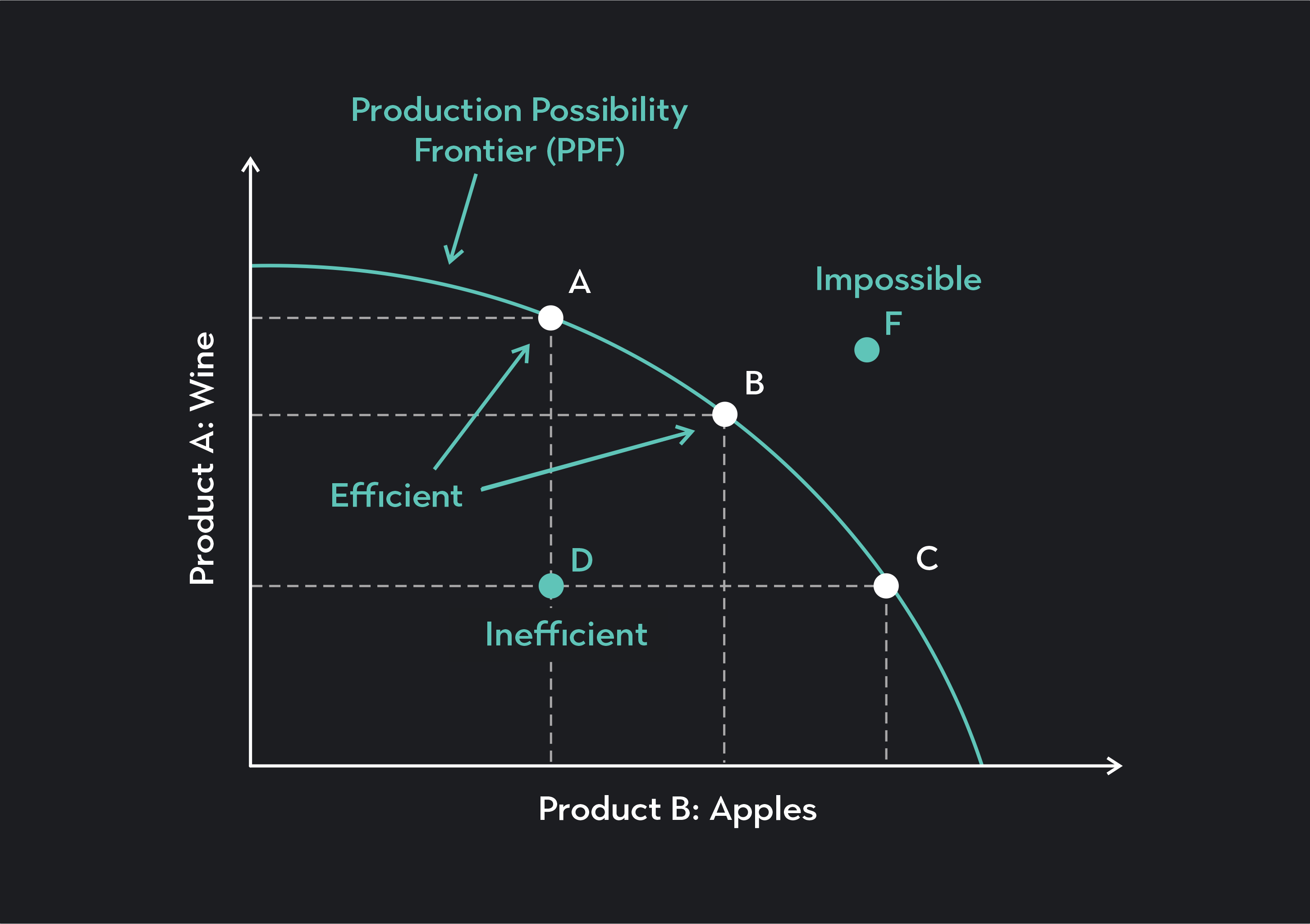
oppurtunity costs
the best decision given up in order to make a better decision. (apple vs samsung)
basic questions of economics
what should be produced, how should it be produced, and for whom should it be prodcued.
PPC
quantity demand
the amount of a good that people are willing and able to buy at a pruce
law of demand
inverse realtionship between price and quanity demand. Price Goes Up and Quantity Demanded Goes Down
dminiishing
decreasing
marginal
additional
utility
satisfaction
substitution effect
chnage in price motivates consumers to buy relativley cheaper goods.
income effect
change in proce affect the purchasing power of consumers income.
law of diminishing marginal utility
as you continue to consume a given product you will eventually get less additional satisfaction from each unit you consume.
ceteris paribus
all other things constant
law of supply
there is a direct relationship between price and quanitity supplied.Price Goes Up and Quantity Supplied Goes Up
total revenue
price x quanitity
elasticity of demand
determines how much more or how much less consumers will buy when prices changes.
SPLAT
substitues, proportion of income, luxury/necessary, additive or not, time of response
demand is ___ when the price change results in a relativley larger change in quanityy demandeed. people ___ need products urgently with this type of demand.
elastic, do not
demand is ___ when the price change results in a relatively smaller change in quanitity demanded. people ___ need prodcuts urgently with this type of demand.
inelastic, do
demand is ___ when the proce chnage results in a proportional change in quanitoty demanded.
unit elastic
market failure
a situation in which the free market system fails to satisfy society wants. (gov steps in)
4 market failures
public goods, externalties, monopolies, unequal distribution of income
public goods
goods that all society can use that are paid by taxes.
subsidies
gov pays bussiness to produce something that benefits society. (vacacines, schools)
trusts
combinations of firms designed to restrict competeion or control prices in a particular industry ( monopoly)
preditory pricing
dropping and raising money to hurt others in a competion.
demand for public goods
marginal social benefits its usefullness to society add is determined by citizens willingness to pay.
supply of public goods
marginal social costs providing eachh additional quanitity.
who determines demand
buyer
who determines supply
sellers
what is required to be placed on a SandD curve
Q, P, Pe, Qe, S, D, and da da das...
the amount of a product that consumers will purchase at dif proces
Demand Schedule
if prices raise on inelastic goods
total revuenue will increase
demand is inelastic if
quanitity demanded does not change
what is the purpose of reglation and dereuglation by the gov
encourgae competion in the market
sherman anti-trust act
break up monopolies to create more competieion.