Immune, rhum, allergic disorders
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Leukopoiesis
Formation of leukocytes from hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow
First line of defense
Skin and mucous membrane barriers
Second line of defense
Innate immune response with leukocytes, NK cells, inflammation, and fever
Third line of defense
Adaptive immunity with memory and specific pathogen defense
Innate immunity
Rapid response without memory, non specific, fast
Adaptive immunity
Slower response with immunologic memory, specific, fast
Natural killer cells (NK cells)
Innate lymphocytes that attack and destroy without specificity
what do NK cell do
Release cytokines to enhance immune signaling
B cells
Adaptive lymphocytes (plasa cells) that mature in bone marrow and produce antibodies
T cells
Mature in Thymus, include cytotoxic, helper, regulatory, and memory subtypes
Neutrophils
Short-lived WBCs that fight bacteria via phagocytosis and degranulation
What does high neutrophil count suggst?
Bacterial infection
Absolute neutrophil count (ANC)
Measures circulating neutrophils to assess infection risk
Moderate neutropenia
ANC 1000-500
Severe neutropenia
ANC <500
Eosinophils
worms, wheezes, weird diseases
Basophils
Release histamine, heparin, and leukotrienes in allergic responses
Mast cells
Tissue-resident cells releasing histamine, cytokines, and heparin to recruit leukocytes (B/T cells)
Macrophages
Detect and destroy damged tissues.
Complement system
30+ liver-produced proteins aiding innate and adaptive immunity
How do B cells work?
Recognize, react, and remember pathogens via antibody production
How do T cell work
They kill things, and remeber incase it happens again (they hold a grudge)
Primary immune response
First exposure
IgM then IgG
Secondary immune response
Memory B cells rapidly produce IgG
Artificial active immunity
Vaccine-induced antibody formation
Natural passive immunity
Antibodies transferred from mother to infant
Artificial passive immunity
Injection of antibodies (e.g., IVIG)
Cytotoxic T cell actions
Release perforin, interferons, and TNF to kill target cells
Memory T cells
Long-living. Remeber how to kill certain foerign invaders
Type I hypersensitivity
IgE-mediated, immediate reaction (allergy, asthma, anaphylaxis)
Type II hypersensitivity
IgG/IgM attack host cells (cytotoxic autoimmune), blood transusion reaction
Type III hypersensitivity
Immune complex deposition (SLE, PSGN, serum sickness)
Type IV hypersensitivity
Delayed T-cell-mediated (poison ivy, TB test, Hashimoto
s)
Anaphylaxis mechanism
IgE-dependent reaction from mast cells and basophils
Anaphylaxis onset
Within 30 minutes of exposure
Anaphylaxis symptoms
Urticaria, hypotension, bronchospasm, GI upset
Anaphylaxis labs
Elevated tryptase and histamine
Anaphylaxis treatment
Epinephrine 0.5 mg IM q5 min
3, airway, fluids, steroids, antihistamines
Angioedema causes
Allergic vs bradykinin-mediated (ACE inhibitors)
Bradykinin-mediated angioedema
EPI—>Poor response to epi; treat with TXA or bradykinin blockers
Urticaria patho/ treatment
Vascular skin reaction from allergy or infection; treat with antihistamines
Drug-induced cytopenia reaction type and cause
Type II; IgG + complement; caused by penicillin, sulfa, etc.
Drug-induced interstitial nephritis reaction type and leukocyte evolved, how to dianose?
Type IV; AKI with eosinophilia; biopsy diagnostic
what is this patho/treatment
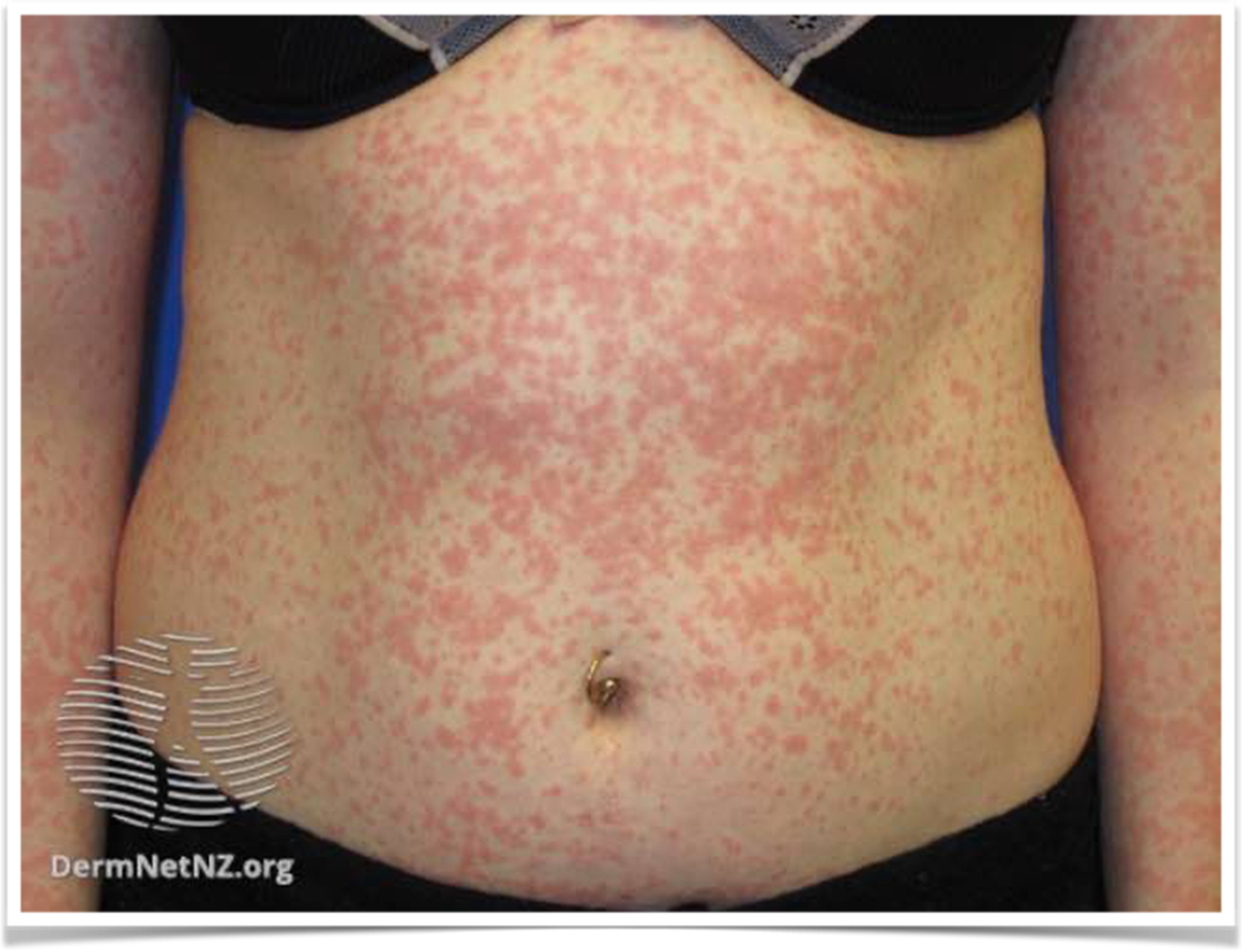
Maculopathic rash -Benign T-cell drug reaction, antihistamine/ topical steroids
Drug Reaction Eosinophilia and Systemic Syndrome Symptoms(DRESS)
Fever, rash, eosinophilia, organ involvement; needs steroids
DRESS cause/ treatment
cause: meds, mostly abx. treatment: steroids, stop drug
AGEP
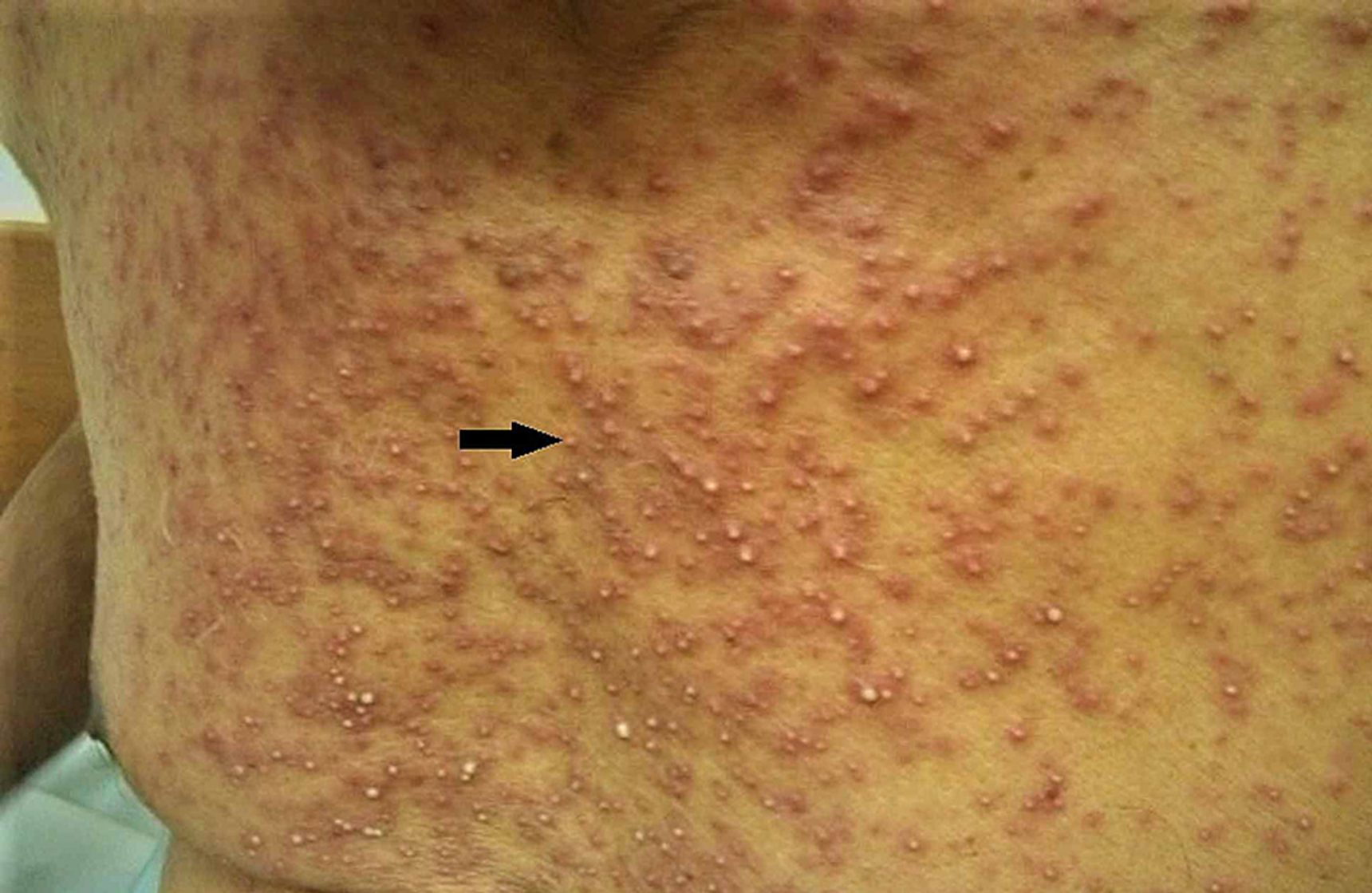
AGEP -Pustules, neutrophilia; stop offending drug
SJS/TEN patho /treat
Mucosal sloughing, epidermal necrosis; supportive (burn unit)
AERD -Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease causes
COX-1 inhibition → leukotrienes ↑ → asthma, nasal polyps → aspirin desensitization.
Red man syndrome patho/treat
Non-IgE mast cell activation from vancomycin infusion; avoid trigger, antihistamine
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Degenerative, non-inflammatory arthritis; pain
with activity
OA imaging
Joint-space narrowing
OA treatment
NSAIDs, acetaminophen, steroid injections, arthroplasty
Does the degree of degerneation correlate with symptoms for oesteo arthrits?
No
Gout, definition and most common areas
Urate crystal build up in serum and deposit in joints—>arthritis and nodular joints AKA tophie ; MTP joint
Gout treatment
NSAIDs, allopurinal, colchicine (acute treatment 1.2 mg load and 0.6 mg BID), steroids if refractory, diet
Chronic gout prevention
Allopurinol or febuxostat; avoid thiazides/alcohol
Calcium pyrophosphate Deposition (pseudogout)
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition; chondrocalcinosis on XR.
Gout vs Pseduo gout
Gout is uric crystals, use allopuinol and colchicine, steroids, NSADIS
Pseudo gout it calcium crystals. Colchicine kinda effective, NSAIDS
CPPD / pseudo gout treatment
NSAIDs; colchicine prophylaxis
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies
Catch all group for Rh negative arthritis types like ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis.
Ankylosing spondylitis definition and s/s
Chronic inflammatory disease, High ESR. Rhumatoid factor neg
Young men, chronic back pain, uveitis,bamboo spine on XR
Ankylosing spondylitis treatment
NSAIDs
TNF inhibitors
Psoriatic arthritis def, S/s, Labs
Chronic autoimmune artithirts that comes from skin psorisis.
S/S: psoriasis, finger/joint pain/arthritis, nail pitting, Elevated ESR/CRP, Rhamtoid factor ngative
Psoriatic arthritis treatment
NSAIDs
methotrexate
TNF inhibitors
Reactive arthritis (Reiters) Def / s/s
Arthritis that usually comes after an STI or GI infection
Arthritis + urethritis + conjunctivitis post-GI/STI
Cant see, cant pee, cant walk
Reactive arthritis treatment
NSAIDs; prolonged antibiotics if chlamydia-associated
HLA-B27 gene
a gene associated with an increased risk of autoimmune diseases, including ankylosing spondylitis and reactive arthritis.
Nongonococcal Acute Bacterial Septic arthritis. Def and S/S
Infection of the joint space. Leukocytits, fever chills, inflamed joints,
Septic arthritis risk factors
IV drug use, ENDOCARDIITS, joint replacements,
Septic arthritis organisms
S. aureus, E. coli, Pseudomonas
Septic arthritis treatment
Hospitalize, IV antibiotics
Gonococcal arthritis def s/s
Goncoccal infection that spread to the joints. S/S; 1.Tenosynovitis , Purulent monoarthritis, general infection symptoms and skin lesions around infected joint
Gonococcal arthritis treatment
Ceftriaxone + azithromycin
Osteomyelitis
Bone infection (S. aureus common);
ESR/CRP; MRI sensitive
Osteomyelitis treatment
Long antibiotics
surgical debridement
Sarcoidosis definition s/s and hallmark factoid
Multisystem inflammatory disease with non-caseating granulomas; brownred patches on skin, arthritis
Sarcoidosis organs
Lungs, lymph, skin, eyes, heart
Sarcoidosis CXR
Bilateral hilar adenopathy
Sarcoidosis labs
ACE, hypercalcemia
Sarcoidosis diagnosis
Biopsy
Sarcoidosis treatment
Prednisone
methotrexate/azathioprine if chronic
Lupus pernio
Chronic facial sarcoidosis lesion
Sarcoid hematologic
Lymphopenia, anemia
Sarcoid cardiac
Arrhythmia or heart failure risk