Progress Check #2: Unit 4
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Structure of the chloroplast
Site of light dependent reactions →Thylakoid
Site of Calvin Cycle → Stroma
Lots of membrane (Surface area to absorb light energy)
Green pigments [chlorophyll a and b] to absorb specific wavelengths of light.
![<p>Site of light dependent reactions →Thylakoid</p><p>Site of Calvin Cycle → Stroma</p><p>Lots of membrane (Surface area to absorb light energy)</p><p>Green pigments [chlorophyll a and b] to absorb specific wavelengths of light.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/163be8b9-f32a-4e23-a9da-d6546dde43a3.png)
How does the thylakoid membranes facilitate photosynthesis?
Photosystem II takes in sunlight which is absorbed by the chlorophyll which causes the electrons to energize, but then they lose their energy because the energy is used to move hydrogen from a high to low concentration. Then Photosystem I re-energizes the electrons with light energy, and then NADP+ takes a H+ and two electrons which becomes NADPH which is key (input) to the Calvin cycle. Inside the thylakoid water is split into 2 hydrogen and ½ oxygen gas. This hydrogen and the hydrogen from the electron transport chain (low to high to inside of thylakoid) to power ATP synthesis, as hydrogen powers ATP synthase to convert ADP + P into ATP.
How does the fluid-filled stroma facilitate photosynthesis?
Stage 1: Carbon fixation: RuBisCO (enzyme) which is abundant in the stroma takes inorganic carbons and attaches them to already existing organic molecules.
What is the importance of light in photosynthesis?
Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules, and excites the electrons kickstarting an electron transport chain that transfers electrons and hydrogen ions (H+) from water to NADP+, forming NADPH. Some of the energy is also stored in ATP. Both ATP and NADPH are crucial to the Calvin cycle, and thus photosynthesis. It also causes the water to lose electrons (excited) and thus become oxygen (through oxidation).
Light energizes the electrons

What are the two stages of photosynthesis? (INCLUDE DIAGRAM)
Light dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle (light independent reactions)
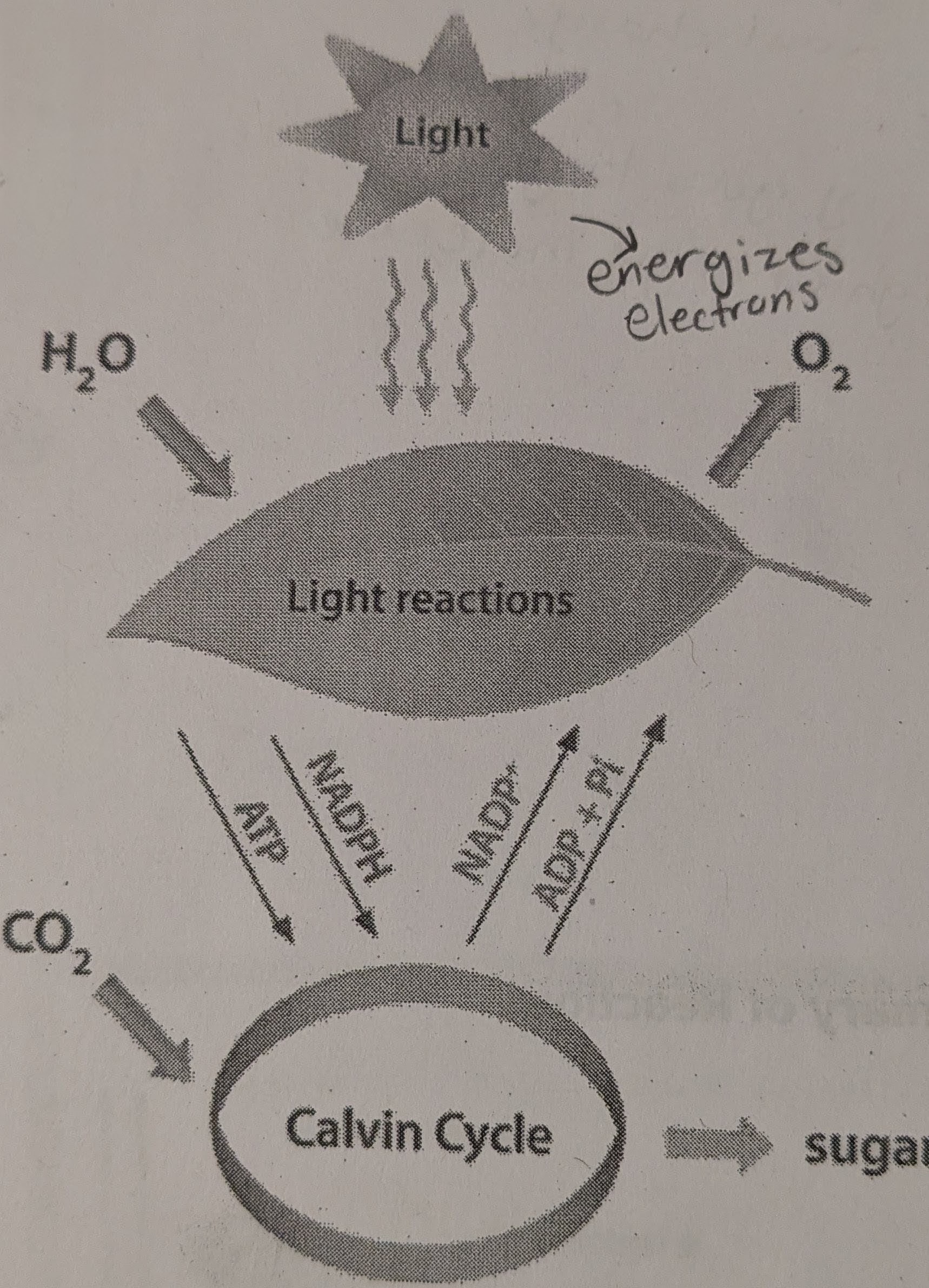
Light-dependent reactions (Inputs and outputs, location)
Inputs: H2O, Light, NADP+, and ADP+P
Outputs: ATP, NADPH, and O2
Location: Thylakoids
Calvin cycle [Light independent reactions] (inputs and outputs, location)
Inputs: ATP, NADPH, and CO2
Outputs: G3P (a precursor to glucose) NADP+ and ADP + P
Location: Stroma of the chloroplast
Role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis
Chlorophyll molecules absorb light energy, and transfer it to the electrons, exciting them and are built into the thylakoid membranes.
Role of ATP in photosynthesis
ATP stores light energy, and acts as the universal energy currency, and powers (with NADPH) the Calvin cycle, by providing the energy for the chemical reactions that build sugar molecules (G3P) NEEDS 2 G3Ps for glucose.
Role of NADPH in photosynthesis
A mobile electron carrier, or a full dump truck for electrons and hydrogen (H+) taking them to the calvin cycle. NADP+ is the empty dump truck that picks up the electrons and hydrogen. NADPH recycles, coming back as NADP+.
Oxidation (definition) and how it applies to photosynthesis
Oxidation is when a molecule loses electrons, and it applies to photosynthesis since water is oxidized, contributing to it becoming oxygen. You can tell since it looses hydrogen molecules.
Reduction (definition) and how it applies to photosynthesis
Reduction is when a molecule gains electrons, and it applies to photosynthesis since carbon dioxide is reduced, contributing to it becoming sugars/glucose. You can tell since it gains hydrogen molecules.