Nervous System 1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
function of sensory components
detect the environmental changes
feel the pain
function of integrative components
process the sensory data coupled with the information stored in memory
function of motor components
provide for a response to the processed information
the output, moving away from pain
nervous system function
a communication network that enables an animal to adjust itself or its parts to changes in the external and internal environments
CNS
brain
spinal cord
myelin is formed by oligodendrocytes
nodes are broadly exposed to the extracellular space
PNS
peripheral nervous system
cranial nerves, spinal nerves
somatic (voluntary) vs autonomic (involuntary) nervous systems
outer cytoplasmic processes of adjacent neurolemmocytes overlap to restrict exposure to the extracellular space
communicate with Schwann cells at nodes to activate impulse
autonomic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
involuntary control
sympathetic
fight/flight
parasympathetic
rest/digest
enteric
gut activity
neurons fuction
transmit nerve impulses and join with others via synapses
100 billion neurons
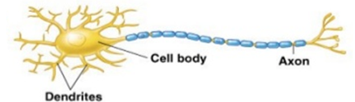
neurons consist of (7)
cell body
dendrites
axon
neurilemma
axolemma
nodes of ranvier
telodendritic zone
dendrites
conducts impulses towards cell body
provide sites for receiving information from other neurons
highly branches, large surface area for communication with axons
many dendrites per neuron
axon
conducts impulse away from cell body 1 per neuron
axon + myelin covering = nerve fiber
arrows indicate direction of impulse conduction
neurilemma
sheath of schwann
myelinated axon
axolemma
plasma membrane of axon
covers the axon
nodes of ranvier
regularly spaced intervals by myelin free gaps
interruptions of the sheath
junctions of adjacent wrappings
the nerve fiber plasma membrane is directly exposed to fluid
exchanges electrolytes and nutrients
causes depolarization
saltatory conduction
depolarization action potential jumps from node to node, traveling along myelinated segments
faster than unmyelinated
telodendritic zone
terminal branches/bulbs
glial cells basics
neuroglia and glia
provide services to neurons and their environment
support, nourishment
10x the amount of neurons
glial cells consist of (5)
oligodendrocytes
Schwann cells
astrocytes
ependymal cells
microglia
oligodendrocytes
myelin sheath formation in the CNS
cytoplasm is different from Schwann
several extensions exist
each form wraps around a nerve fiber
one cell provides a sheath at several axon locations
axon bulges at the node and is exposed to extracellular space
wrap around a cell fiber
Schwann cells
myelin sheath formation in the PNS
the cytoplasm is wrapped around a nerve fiber many times
nucleus lied within the cell beneath the neurilemma
one Schwann cell per axon
astrocytes
the most numerous
start shaped
acts like CT
provides support and nourishment
release excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate in response to stimulation
ependymal cells
line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord
unite with the capillaries to form the choroid plexus
where cerebrospinal fluid is produced
microglia
phagocytic function
enter the CNS from blood vessels and increases in numbers during inflammatory process or where neuron injury has occurred
polarity of a neuron
refers to the number of poles or processes that stem from its cell body
bipolar
one axon and one dendrite extending from the cell body
found in the retina and olfactory region

multipolar
many branching dendrites and one axon extending from the cell body
most neurons in the CNS
nucleus
a group of nerve cell bodies within the brain for spinal cord
CNS
ganglion
a group of nerve cell bodies outside the brain or spinal cord
PNS
tract or a fasciculus
a bundle of parallel neuron fibers within the brain or spinal cord
CNS
nerve
bundle of neuron fibers outside the brain or spinal cord
PNS
synapse function
provides continuity from one neuron to the next
important characteristics
one way conduction
facilitation
repeated impulse provides for easier subsequent transmission
greater fatigability than the neuron
allows for repetitive impulses to fade
sypase areas (4)
synaptic gap
terminal bulb
synaptic vesicles
presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron
synaptic gap
between terminal bulb and dendrite
no physical contact of neurons at the synapse
a space exists between the neurons
impulses are transmitted by chemical means
chemical synaptic transmission
conductor that facilities information movement
terminal bulb
swelling at axon end
fits into the indentation of the postsynaptic cell membrane
come in close contact with each other but never touch
synaptic vesicles
inside the terminal bulb
contain neurotransmitters
myelin
a white lipid substance that forms a sheath around nerve fibers and serves as an electrical insulator
helps propagate the nerve impulse, insulator
myelinated? faster conduction
formed by oligodendrocytes in CNS and by Schwann cells
unmyelinated fibers
uninsulated because they maintain a direct association with extracellular fluid