comp sci Paper 2
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3.1 to 3.4.5 Everything for paper 2 INCLUDING 3.1 from Paper 1 (algorithms, fundamentals, decomposition, merge/binary/bubble/linear) 3.1 is flashcards 1-14. Just until 3.4.5, rest of paper 2 is on knowt part 2 because was getting laggy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Define an algorithm
A sequence of steps that can be followed to complete a task
Define decomposition
Breaking a problem into subproblems, so that each subproblem accomplishes an identifiable task
Define abstraction
The process of removing unnecessary detail from a problem
State why programmers should we use meaningful identifier names?
Easier to understand and debug
How do you compare the efficiency of algorithms?
Look at how many calculations are needed for the algorithm to be completed.
The more calculations it needs, or the more instructions are executed, the more time it takes and the less efficient it is.
(only refer to time efficiency)
What is pseudocode?
A language designed to express algorithms in an easy-to-follow form
State 2 advantages and 2 disadvantages of pseudocode
Advantages
Similar to everyday english so easier to understand
Easily modified
Disadvantages
No accepted standard, varies widely
Informal and not an actual programming language
State the purpose of a search algorithm
An algorithm used to find a value in a list of data
Describe the process of a linear search
Identify a search term
Look at 1st item in the list/array
Compare item with search term
If current item is equal to search term- item is found
If not, look at next item in the list/array
Repeat until last item has been reached
If search term not found AND end of list is reached, search item is not in list, algorithm can stop
Describe the process of a binary search
With each loop that is run, half of the data is removed from the search.
The algorithm determines the next item to be checked by identifying the midpoint of the array, using the index of the items in the list.
The counter is set to the middle position in the list
If the value held there is a match, the search ends.
If the value at the midpoint is less than the value to be found, the list is divided in half, with the lower half of the list ignored.
If the value at the midpoint is greater than the value to be found, the list is divided in half, with the upper half of the list ignored.
The counter moves to the midpoint of the remaining items. Repeat the steps until a match is made or there are no more items in the list.
Compare a linear search algorithm to a binary search algorithm
Linear search is easy to implement, the list does not need to be in order. But it is slow and inefficient on larger lists as it takes longer to run.
Binary search is more complex than linear search and requires items to be in order, but is more efficient on larger lists.
For larger lists, it is more efficient to calculate the indexes of the list/array and use a binary search.
For smaller lists, linear search is more efficient.
Describe the process of a bubble sort
Each run through the list from start to finish is a pass. The bubble sort continues until a pass is made where no values have been swapped.
Look at 1st number in the list
Compare current number with the next number
If next number is smaller than current number, swap them around.
If not, do not swap.
Look at the next number in the list.
Repeat until the last number in the list has been reached.
If any numbers were swapped, make another pass through the list
If end of list is reached without any swaps, algorithm stops, the list is ordered.
Describe the process of a merge sort
The list is divided into half until the elements are individually seperated
The algorithm combines the elements into pairs, with the elements in the pairs in order
The pairs are compared, starting with the 1st number in each pair. If the number from the left pair is smaller than the number from the right pair, it is placed in order.
Else the number from the right pair is placed in order.
The comparison repeats until the list is recompiled.
Compare a bubble sort to a merge sort
Bubble sorts are slow and inefficient for small lists, but it is easier to implement.
Merge sorts are more efficient for longer lists, but it requires more memory to store the sublists, and it is a more complex algorithm to implement.
**MORE COMPLEX ALGORITHMS ARE USUALLY MORE EFFICIENT (**merge sort and binary search are more complex but more efficient than bubble sort and linear search which are less complex but less efficient)
What number base is denary decimal?
base 10
What number base is binary?
base 2
What number base is hexadecimal?
base 16
Explain why hex is base 16, denary is base 10, and binary is base 2
Binary is base 2 → characters 0 and 1
Denary is base 10 → characters 0 to 9
Hex is base 16 → characters 0 to F
What is a bit/byte/nibble
A bit is a binary digit, the smallest unit of data, 1 or 0.
8 bits is 1 byte.
4 bits is half a byte, 1 nibble.
2 nibbles make 1 byte.
b is a bit
B is a byte
Why do computers use binary to represent data and instructions?
Binary is easier to process and takes up less space than denary. Computers have switches with 1s and 0s and cannot process hexadecimal numbers- they only process data in 1s and 0s
What are the decimal prefixes Kilo, Mega, Giga, Tera
1B is 8 bits
1 kB is 1000 bytes
1 MB is 1000 kilobytes
1 GB is 1000 megabytes
1 TB is 1000 terabytes
/1000 each time you go down KMGT
x1000 going up TGMK
kB /1000 = MB
MB x1000 = kB
What is the largest number 1 byte (8 bits) can represent?
1 byte (8 bits) can represent 256 numbers (0 to 255)
The maximum number 1 byte can represent is 255
How many bits are in 1 hexadecimal digit?
1 hex digit = 4 bits (1 nibble)
Why is hex useful?
Large numbers can be represented using fewer digits, e.g. colour values. It is also easier to understand than binary, so less errors are made.
What is the effect of a LEFT binary shift?
multiply by 2 for each left shift
(fill empty binary positions with 0s)
e.g. 00001111
becomes 00011110
What is the effect of a RIGHT binary shift?
divide by 2 for each right shift
(fill empty positions with 0s)
e.g. 00001111
becomes 1000011
What is a character set and why is it needed? What are the two standard character encoding methods?
Computers work in binary, so characters are stored as binary numbers. The binary digits are converted to chraracters. A character set is all of the characters a computer can use.
The two standard character sets are 7-bit ASCII and Unicode
How many characters is in ASCII
ASCII uses 7 bits, with 128 characters in the character set.
How are character codes grouped?
Character codes are grouped so they run in sequence. In ASCII, A is 65, B is 66. Lowercase letters start from 97, with a is 97.
Therefore, the codes for other letters can be calculated once ‘A’ or ‘a’ is known.
What is extended ASCII?
Basic ASCII codes are 7 bits for each character, so 128 possible characters. (2^7)
The extended ASCII character set uses 8 bits, which gives an additional 128 characters, the extra bit doubled the characters that can be encoded, so 256 characters.
The extended characters represent characters from foreign languages such as accents.
How many bits does unicode use? What is the purpose of unicode? What are the advantages of unicode over ASCII?
Unicode uses 16 bits, so it has a range of over 65,000 characters. It uses the same codes as ASCII up to 127.
Unicode has the advantage that it can represent many more different alphabets and unique symbols than ASCII because of the larger number of bits available to store character codes.
Why do images need to be converted to binary?
Computers work in binary. All data must be converted to binary in order for a computer to process it.
What is a pixel?
Pixel is short for Picture Element.
A pixel is a single point in an image. The smallest identifiable area of an image.
Each pixel is a single colour and is given a binary value which represents that colour. A pixel’s colour can be changed by changing this binary value.
Bitmap images are made from pixels.
What is colour depth/bit depth?
Colour depth is the number of bits used to represent each pixel. It is the amount of bits available for colours in a pixel.
The number of bits determines the range of colours.
How do bits determine the range of colours? How do you calculate the number of bits needed for colours?
Each extra bit doubles the range of colours in a pixel
convert the number of colours to a power of 2 for determining the bits needed
2 colours → one bit per pixel
4 colours → two bits per pixel
8 colours → three bits per pixel
16 colours →four bits per pixel
2^bits per pixel = number of colours
What is image size and how do you calculate image size?
Image size of a bitmap image is the number of pixels an image contains.
image size = width of image (in pixels) x height of image (in pixels)
the image size notation is width x height
e.g. 200 x 400
What two factors affect bitmap image file size?
Number of pixels (image size), colour depth
increased colour depth, increased file size
increased image size, increased file size
How does image size/number of pixels affect file size?
If size is increased, more pixels need to be stored, increasing file size
How does colour depth affect file size?
The more colour an image requires, the more bits per pixel are needed. The more bits needed, the higher the file size.
What is quality and how does it affect file size?
Quality is the combination of image size and colour depth. As you increase the quality, you increase the file size.
Why does zooming in or enlarging an image damage the quality of a bitmap image? Why does resolution affect this?
The picels are stretched and made into larger blocks, so fewer are needed to fill the space, so the image appears as poor quality or pixelated when enlarged too much
An image with a higher resolution has a higher concentration of pixels, and so looks better when enlarged or stretched.
The higher the resolution, the more pixels in the image.
Therefore, the higher the resolution, the larger the file size.
What two factors are needed to calculate a bitmap image file size? How do you calculate it?
Colour depth and file size.
file size = width x height x colour depth (in bits)
size in bits= width x height x colour depth
size in bytes= (width x height x colour depth)/8
What do you do to the file size to get the answer in bytes instead of bits?
Divide by 8 for file size in bytes
If a question states that an image has 16 colours, what is the colour depth in bits?
4 bits (2^4 is 16)
If a question states that an image uses 16 different colours, with a 10x10 resolution, what is the file size in bytes?
16 colours → 4 bits
4 x 10 x 10 = 400 bits
400/8 = 50 bytes
file size = 50 bytes
Why do we need to do analogue to digital conversion of sound?
Sound is analogue and must be converted to a digital form for storage and processing in a computer.
Digital is a series of binary numbers. For a computer to input sound, the sound must be converted to a digital signal.
How does an analogue to digital converter work? What is a sample?
Analogue signals are sampled to create the digital version of sound. An analogue to digital converter captures sound waves at regular time intervals. Each recording is a sample.
What is a digital to analogue conerter?
Converts digital signal to analogue sound, in order for the computer to output sound.
What is the sample rate?
Sampling rate is the number of samples taken in one second.
1 Hz (hertz) = 1 sample per second
How does sample rate affect the quality?
The higher the sample rate, the closer the recorded signal is to the original.
How does sample rate affect file size?
The higher the sample rate, the larger the file size.
What is sample resolution (bit depth)?
The number of bits per sample. The higher the sample resolution, the more accurately a sound can be recorded, the larger the file size.
What two factors affect sound file size?
Sample rate and sample resolution (bit depth)
How do you calculate the sound file size?
File size (bits) = sample rate x sample resolution x seconds
sample resolution aka bit depth
What are the 2 ways to improve recording quality?
More frequently sound is sampled
increasing sample rate→more data points recorded
More accurately wave height is recorded
increasing sample resolution (bit depth) → improves accuracy of each data point
What is data compression?
Data compression is the process of reducing file size, in video, image and sound files.
Why might it be necessary or desirable to compress data?
More files can be stored on a memory device
Files are transmitted in less time, with less bandwidth needed to send and recieve those files
What are the two types of data compression?
Lossy and Lossless
What is lossy compression?
Reducing digital file size by removing data
What is lossless compression?
Encodes digital files without losing detail.
Files can be restored to their uncompressed quality.
How does lossy compression work for sound files?
Audio is compressed by reducing bit depth of the samples
How does lossy compression work for image files?
Images are compressed by reducing colour depth.
It reduces the range of colours an image contains.
Images can be stored using fewer colours so fewer bits per pixel, reducing file size, degrading the original quality.
What are the disadvantages of lossy compression?
removed data is discarded permanently
reduces image quality
poorer audio quality
What is a disadvantage of lossless compression?
Does not usually achieve the same file size reduction as lossy compression
What are advantages of lossless compression over lossycompression?
when data is uncompressed it is restored exactly to original- no original data is lost
image or audio quality remains the same
Is RLE lossless or lossy?
When is Run length encoding (RLE) useful?
When is it not useful?
RLE is a form of lossless compression.
RLE is useful for images that contain many pixels of the same colour.
RLE is not useful with files that don’t have many consectuive runs of data, in that case RLE can increase the file size.
How does huffman coding work?
LEFT BRANCH IS ALWAYS 0
Huffman coding is a compression method that reduces the number of bits to represent each letter.
The more frequently a letter appears in the text, the fewer bits are used to represent it in a text file.
What is the boolean expression operator for AND
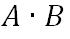
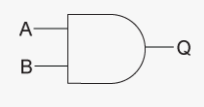
What is the logic gate for AND
What is the boolean expression operator for NOT
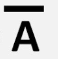
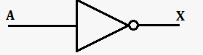
What is the logic gate for NOT
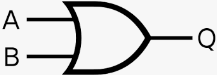
What is the boolean expression operator for OR
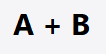
What is the logic gate for OR
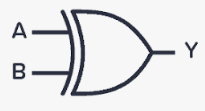
What is the boolean expression operator for XOR

What is the logic gate for XOR
Define the terms hardware and software and 3 examples of each
Hardware is the physical components of a computer (CPU, keyboard)
Software is the programs that run on a computer (system software and application software)
What is system software? Give 2 examples
System software is programs needed to enable the computer to function, a platform to run application software
e.g. operating systems, security software
What is application software? Give 2 examples
Application software performs end-user tasks, e.g. spreadsheets and web browsers
What is utility software? Give 3 examples
Utility software performs specific tasks to help manage and optimize computer resources. Examples of utility software include antivirus programs, disk cleanup tools, and backup software
What is the difference between System software, Application software and Utility software?
System software is the basic software that your computer needs to run including the operating system, utility software helps maintain and optimize the computer, and application software is software designed for specific end user tasks and applications.
What is an operating system?
A collection of programs that manages and controls the computer
Give 5 functions of an operating system
processor management
memory management
input/output devices management
applications management
security management
Explain the role of processor management
A processor executes the processes needed to open a program. Processor management allows operating systems to multitask- which means they can run more than one program simultaneously.
Processor cores
A computer with a single processor core can only carry out one process at a time, with the OS swapping tasks in and out of the processor to make it appear to the user that they are being carried out at the same time.
Modern computers have more than one processor core, making them more efficient at multi-tasking, and the OS system can allocate individual tasks to each core.
Explain the role of memory management
The OS system needs to manage computer memory to ensure programs can be run. When a program is running, the OS system allocates a memory space for each program and where the data it needs will go.
Memory management keeps track of what portions of memory have been allocated, determines how much memory to allocate, and when a portion of memory should be cleared.
Explain the role of input/output devices management
Input devices take data and convert it into a form that can be stored on a computer, e.g. a mouse or sensor. The output could be a speaker or a computer screen.
The OS uses a program called a device driver to operate input and output devices- a small program installed in the OS that acts as in interface between the application and the device. The device drivers need to be specific, e.g. if a gaming console has extra X or Y buttons, a generic device driver for a keyboard mouse won’t perform desired functions, slowing down computer performance.
Interrupts are signals sent to the processor to request immediate action. If an I/O device makes a more critical request than what is being currently executed, the OS can interrupt the current execution and swap to the more important task. This removes delays appearing to the user, e.g. if a user presses a key, the processing is interrupted and the character is displayed immediately.
Explain the role of applications management
Application systems interact with the OS through an Applications Program Interface. The interface allows applications systems to be installed and communicate with the OS. The application needs to communicate through this interface in order for it to save, update and delete data.
The OS allocates memory space and processor time for the application to be run.
Explain the role of security management
Operating systems protect system resources from unauthorised access through specific utility software such as firewalls. Operating system security controls passwords, sets up admin rights for authorised users which enables them to allocate access rights for other users, checks for software updates, creates and deletes users and encrypts files stored on the hard disk.
What is disk defragmentation
Files are stored on a hard disk as a series of segments, known as fragmentation. Overtime, files become more fragmented, taking longer to read from and write to, making a computer run slower.
Defragmentation software takes the fragmented files and rearranges the segments so that they run continuously, decreasing read/write time, speeding up computer performance.
What is the difference between High level languages and Low level languages
High level languages (source code) are user-oriented and closer to everyday languages. They are easy to learn and use.
e.g. C# and Python
Low level languages are machine-oriented and harder to understand. They are designed for a processor to directly use.
e.g. machine code and assembly language
Most programs are written in high level languages
What is machine code? What can we use to represent machine code to make debugging and writing easier?
Machine code is written in binary and is directly executed by processors. Every language needs to be translated into machine code before a processor can execute it.
Machine code is specific to a processor. Each type of processor has its own specific machine code instruction set.
It is hard for humans to debug and write programs in machine code, so HEX is used to represent the binary digits because hexadecimal is easier to understand.
What is assembly language?
Assembly languages uses mnemonics to form instructions. Each mnemonic directly translates to a machine code instruction, e.g. ADD (addition). This means they have a 1:1 correspondence with machine code. Assembly languages are translated by an assembler.
These are easier to understand than machine code, and quicker to write than binary.
Explain the 2 common uses of assembly languages
Embedded systems are computer systems designed to complete a limited number of specific tasks efficiently.
Low-level languages allow a programmer to create optimised programs with efficient use of processing power and memory available.
Device drivers are programs that enable the computer to interact with an input/output device.
Low-level languages allow precise control of hardware components. A device driver written in a low-level language allows the CPU to directly communicate with the I/O device.
Therefore, assembly language is used to
develop software for embedded systems
control specific hardware components in device drivers
Which languages need to be translated to machine code?
All programming code written in high-level/source code or assembly languages need to be translated to machine code.
Give 2 advantages of low-level languages
gives programmer complete control over hardware components
written for a specific processor, so it occupies less memory and executes faster than a compiled high-level language
Give 4 disadvantages of low-level languages
limited number of programming constructs, e.g. cannot do selection/iteration. programmer needs to write every process required and cannot import functions
harder to learn/write/debug
more time consuming to code, one instruction at a time with more likely errors
not portable, specific to a processor, whereas a high-level language program can be compiled or translated for multiple different processors
Give 3 advantages of high-level languages
most software is developed using high-level languages
close to everyday languages makes them easy to learn, debug and faster to program in
portable, can be compiled or translated for multiple different processors
have pre-written functions that can be imported and used, e.g. iteration loops (WHILE, FOR)
Give 3 disadvantages of high-level languages
Slower execution speed compared to low-level languages.
Higher memory usage due to the need for additional libraries
Limited control over hardware resources
What is a program translator and what are the three types
A program translator is a type of system software that translates source code into machine code that can be executed by a processor.
Interpreter, compiler, assembler
Explain how an assembler converts languages
Assemblers convert assembly language into machine code with a 1:1 correspondence. Each line of assembly language directly translates to one line of machine code.
Explain how a compiler converts languages
Compilers translate programs into machine code. A single line of source code can be multiple lines of machine code, The user does not need a compiler to be installed when you want to execute a program, because the executable code does not need to be translated again unless the source doe is changed.
However, any errors are reported at the end of the process. Any changes to source code mean the entire program needs to be recompiled, unlike interpreters which translate line by line.