Matter & Energy
Matter:
- Anything that has mass and takes up space.
Pure Matter
- substance
- definite
- elements/atom type
- cannot be broken down
- compounds (2+ atoms)
- can be broken down
Impure Matter
- mixtures
- indefinite
- Homogenous
- uniform
- Heterogeneous
- not uniform
Models
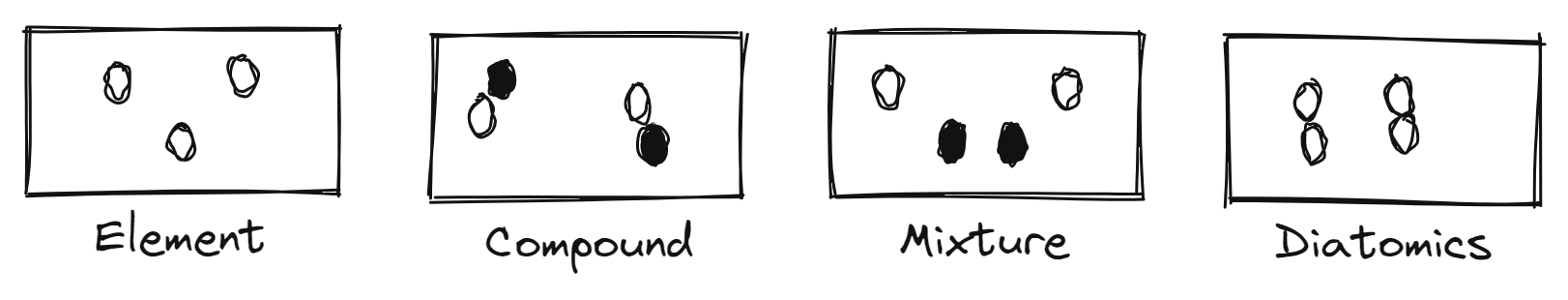 Properties
Properties
- Physical
- 5 senses
- mass
- solubility
- density
- volume
- odor
- phase
- Chemical
- behavior
- flammability
- acidity
- radioactivity
Separating Mixture
Filtration
- heterogenous
- different particle size

Distillation
- homogenous
- different boiling point
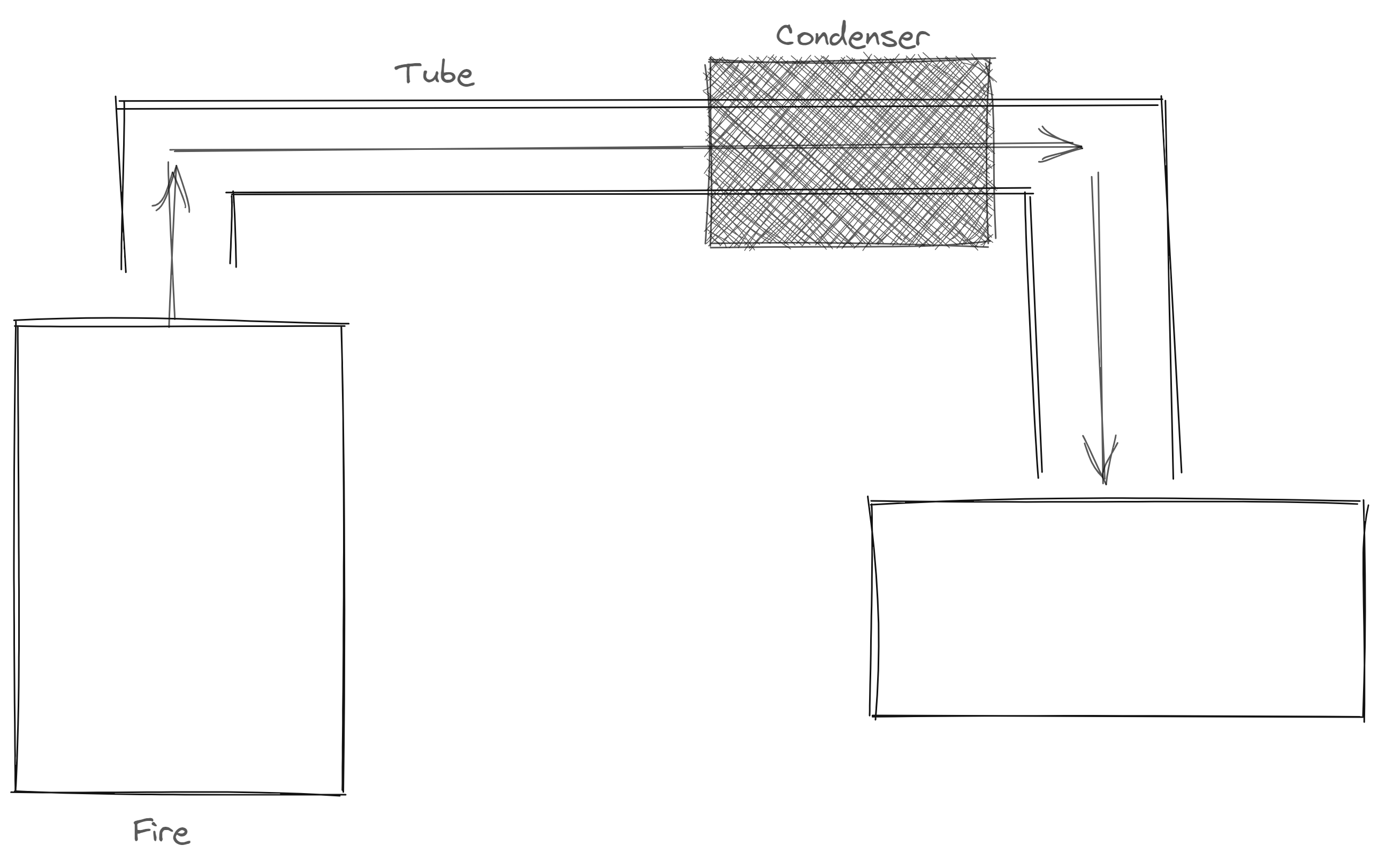
Chromatography
different molecules in a mixture
solubility

Phases of Matter
- Solid
- definite volume & shape
- crystal & lattice structure
- Liquid
- definite volume
- no definite shape
- Gas
- chaotic
- no definite shape & volume
Energy
- ability to do work
- The Law of Conservation of Energy: energy cannot be created nor destroyed.
- endothermic - absorbed
- exothermic - released
Temperature
- Q=MCΔT
- Q - Heat (Joules)
- M - Mass
- C - Specific Heat
- Water: 4.18 J/g*k
- ΔT - Change in Temperature
- final temp minus initial temp (Tf - Ti)
- High Temperature → More Kinetic Energy → More Movement
- Heat travels from High → Low
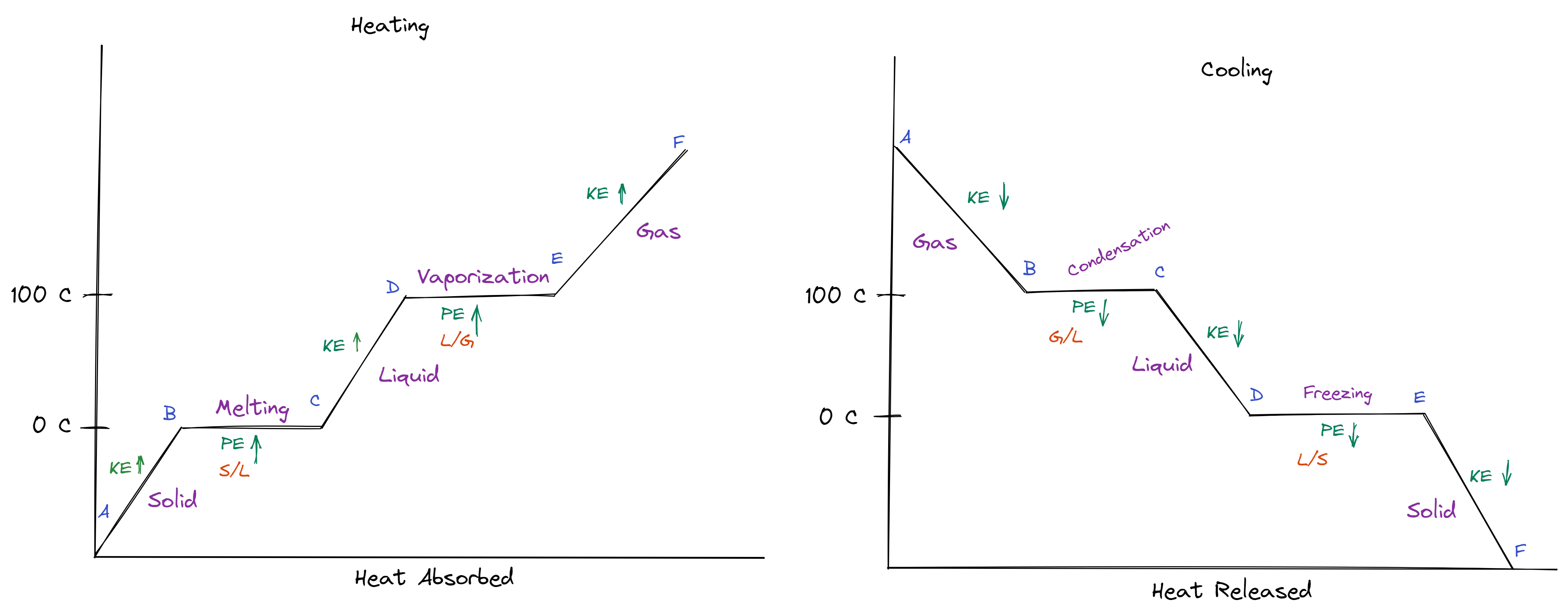
Heating & Cooling Curve
Heating: endothermic
- Heat of Fusion: Melting
- Q=MhF
- hF = 334 J/g
- Heat of Vaporization: Vaporization
- Q=MhV
- hV = 2260 J/g
Cooling: exothermic
Diagrams:
Changes
- Physical
- change in appearance
- does not change in identity
- phase changed (solid → liquid → gas)
- Chemical
- identify