Mid-Year Ninth Grade History Exam 2024
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
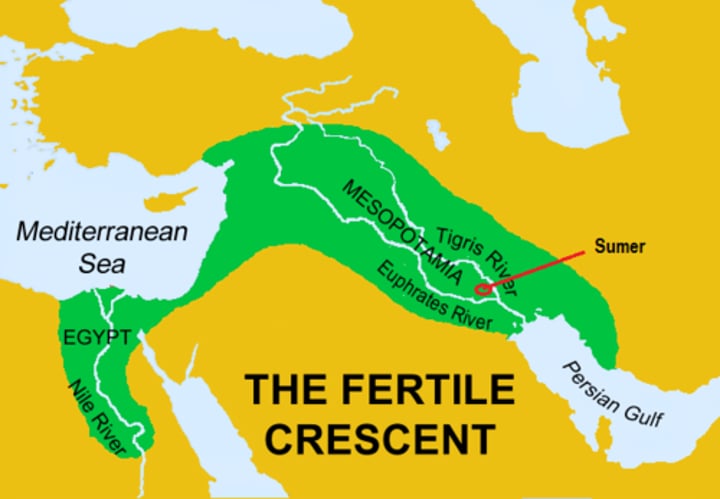
Tigris and Euphrates
Rivers surrounding Mesopotamia, known for flooding and fertile silt
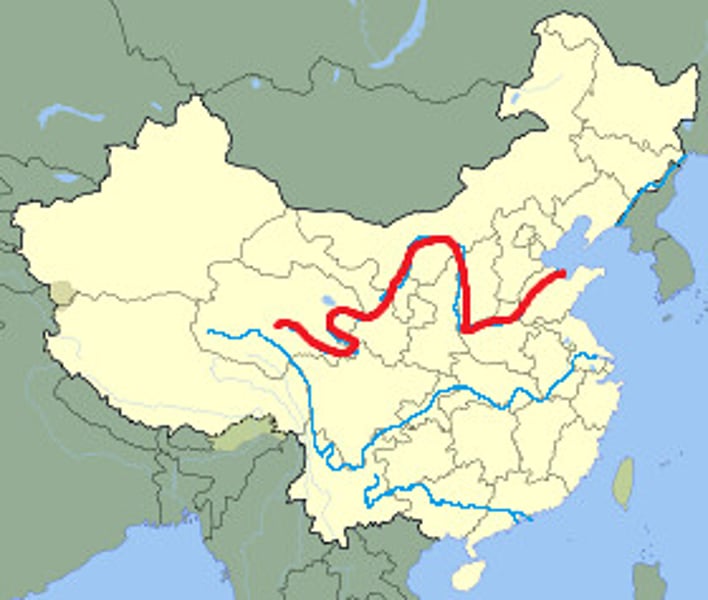
Yellow and Yangtze
China's major river systems known for fertile silt.
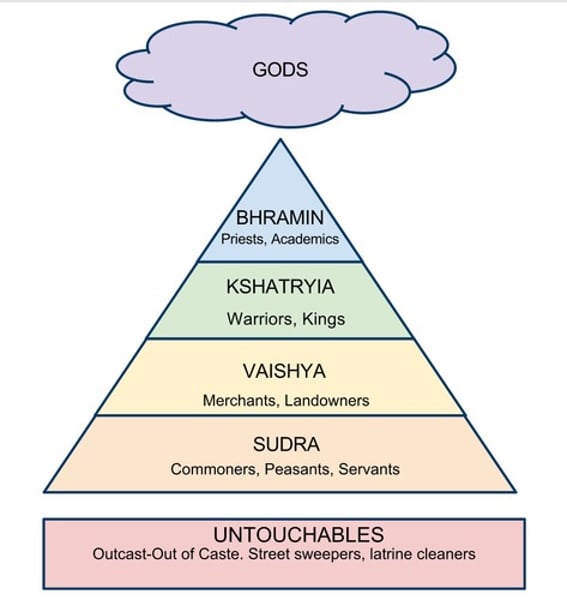
Caste System
Social system with four classes of people
Nile
Longest river in the world, important to Egypt
Indus and Ganges
Important rivers in India for farming
Mandate of Heaven
the belief that the Chinese king's right to rule came from the gods

Himalayan Mountains
Tallest mountains in the world, protecting the Indus Valley. Located between India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China
Hammurabi's Code
Code of laws with punishments based on social class

Hieroglyphics
System of writing using pictures and symbols

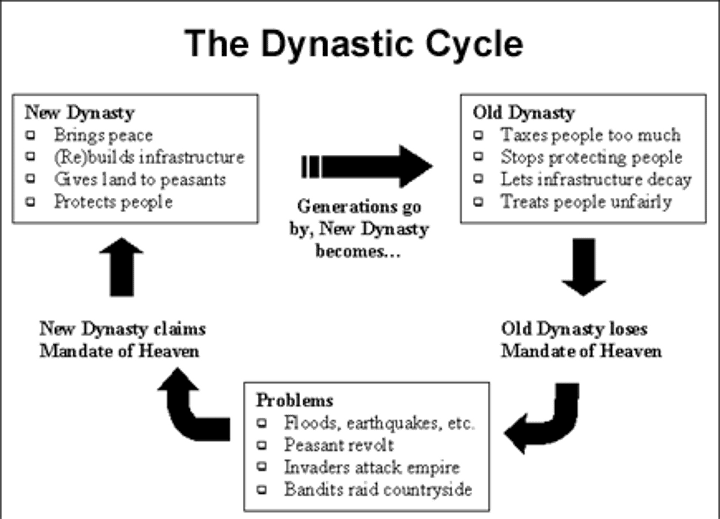
Dynastic Cycle
Pattern of rise, decline, and replacement of dynasties in China
Four Noble Truths
Teachings of Buddhism: Life is suffering, suffering is caused by desire, to end suffering, one must stop desiring, and the way to stop desiring is to follow the Eightfold Path

Buddhism
Religion founded by Buddha in ancient India. Buddhist teachings on how to end suffering and achieve enlightenment was the eightfold path.

Hinduism
Major religion of ancient India, one of the world's oldest religions

Reincarnation
Hindu belief in the rebirth of the soul
Nirvana
State of perfect happiness and peace in Buddhism

Siddhartha Gautama
Founder of Buddhism, known as the Buddha

Ashoka
Unofficial king of northern and central India, promoted Buddhism and improved the lives of the people

Mauryan government
Well-run government under Chandra Gupta Maurya, with achievements like an efficient postal service
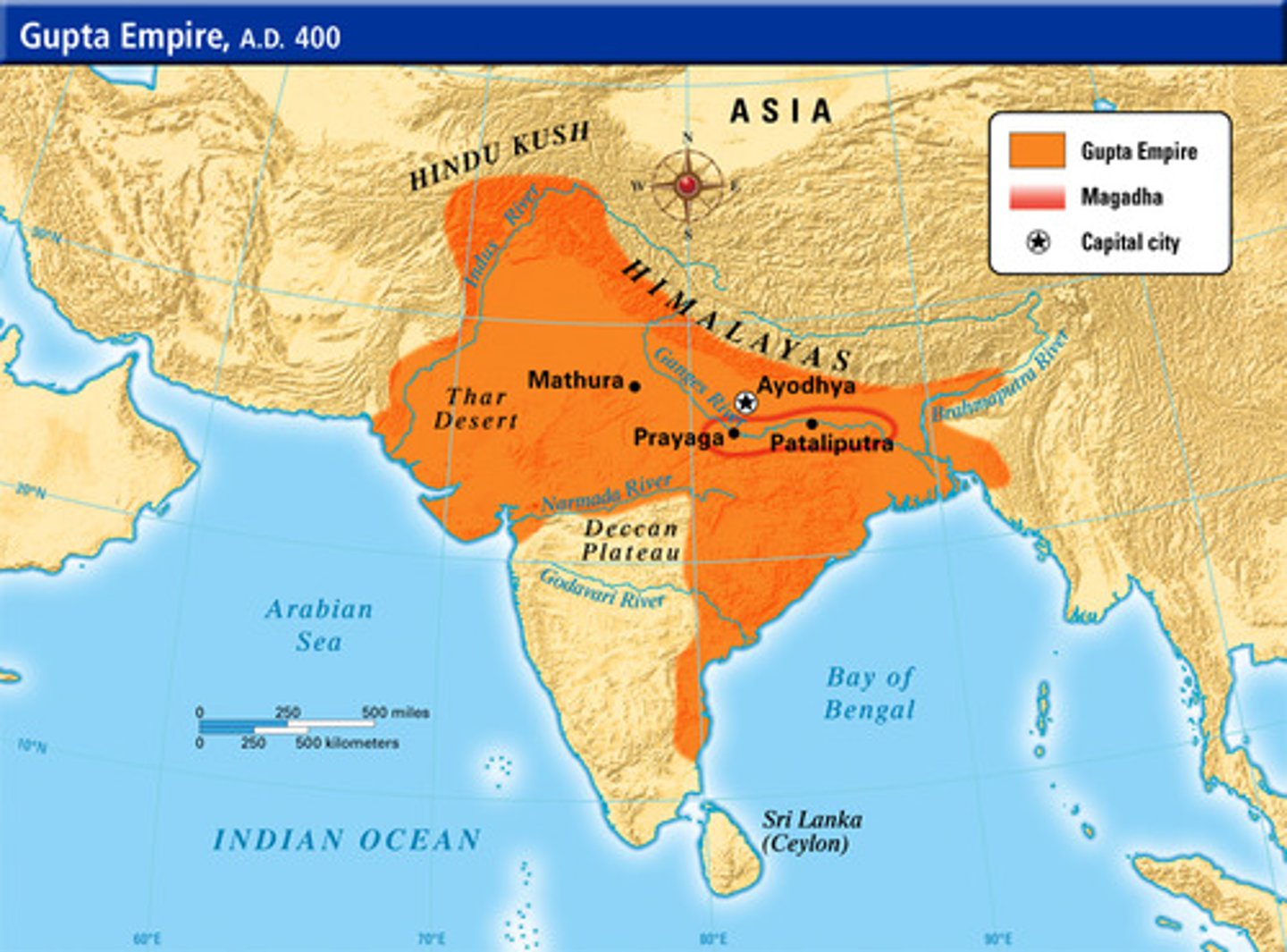
Gupta Empire economy
Thrived through trade, especially in salt, cloth, and iron

Gupta Empire
Golden Age of India; ruled through central government but allowed village power; restored Hinduism
Dharma
A person's personal duty based on their place in society
moksha
The goal of the Hindu religion. It is when a person's Atman is reunited with Brahman. Moksha is achieved by living a perfect life

patricians
The Upper class of Rome. Were given political power through the senate

plebeians
The lower class of Rome. At first given no representation in government but later got representation through tribunes

Twelve Tablets
The written laws of the Romans. The creations of this was considered a great political victory for the plebeians

Julius Caesar
A successful military commander. Responsible for conquering Gaul. Was named consul for life. Creating the Empire. Was assassinated by the senate

Augustus
The adopted grandson of Julius Caesar. Born Octavian and told over control of Rome after Caesar's death. Augustus means "Exalted one"

legion
Roman military unit of 6,000 soldiers

Pax Romana
500 year period of Peace and prosperity in Rome. Means "Roman Peace

Germanic Tribes
Nomadic groups that invaded the Roman Empire from the North and East. The groups of raiding warriors they caused the fall of Rome.

Diocletian
The Roman Emperor who divided the empire into an Eastern and Western Empire

Torah
First five books of the Hebrew Bible

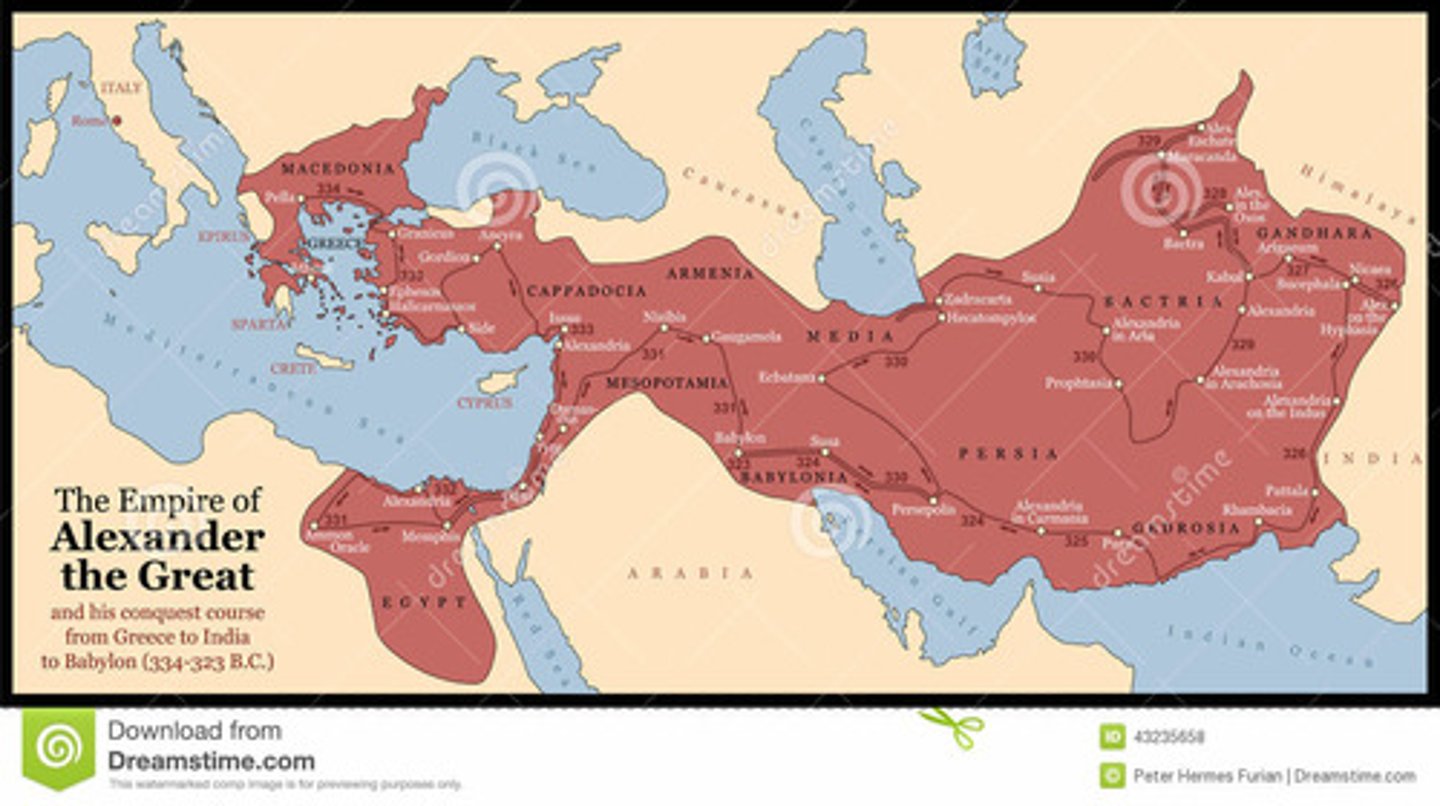
Alexander the Great
Alexander the Great conquered the Persian Empire. As he conquers he spreads Greek ideas to the places he has conquered. However, he also allows these areas to continue to practice their religions and local governments. Alexander improves infrastructure like roads allowing for ideas, learning, and culture to spread quickly. Last he establishes many cities which will become centers of learning like Alexandria in Egypt.

Judaism
one God, the torah and other books of the Hebrew Bible, follow the ten commandments, a moral life through obedience to God's law. Leaders are priests, judges, kings, prophets.

Pericles
Athenian statesman who promoted democracy
Delian League - an alliance that was formed to help Athens gain power in Greece and fight the Persians

Hellenism
Spread and influence of Greek culture, language, and civilization in the ancient world, particularly in the centuries following the conquests of Alexander the Great.
senate
Represented the patricians in the Roman Republic

tribunes
Represented the plebeians in the Roman Republic

consuls
Highest government office in Roman Republic. Traditionally served for 2 years. Julius Caesar was elected to this position than used his army to for the senate to vote him into this position for life.

Jesus
The Messiah in the Christian faith. Traveling, spreading his beliefs. Crucified by the Romans

Socrates
Greek Philosopher famous for developing the socratic method. was sentenced to death for corrupting the youth of Athens

Plato
Greek Philosopher, who was the most famous student of Socrates, wrote the Republic and created the Academy in Athens.

Aristotle
Greek Philosopher famous for being the teacher of Alexander the Great and opening the school called the Lyceum

Daoism
a Chinese philosophy which taught that one must go with the natural flow of nature or The Dao. Believed the best government is one which governs the least

Confucius
Chinese Philosopher. Believed that there were 5 key relationships which needed to be preserved for there to be harmony in the world. Believed that the most educated person was the best qualified to serve the government.

Legalism
The Chinese philosophy which believes in harsh rules and strict laws. It was only through a powerful and strict government could peace and harmony be achieved.

Golden Age
A time of peace, prosperity, and happiness in a civilization
Epic Hero Cycle
1. Call to adventure. 2. Threshold (beginning of transformation) 3. Revelation (abyss: death and rebirth) 4. transformation 5. atonement 6. return (gift of the Goddess)
Empire
A political unit in which a number of people or countries are controlled by a single ruler
polytheism
Belief in many Gods

Monotheism
Belief in a single God

Covenant
A mutual promise or agreement, especially an agreement between God and the Hebrew people as recorded in the bible.

Republic
A form of government in which power is in the hands of representatives and leaders are elected by citizens who have the right to vote.

Punic Wars
A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage. Resulted in the destruction of Carthage and Rome's dominance over the western Mediterranean.
Characteristics of a civiliation
specialized workers, complex institutions, record keeping, advanced technology
cultural diffusion
the spreading of ideas and products from one culture to another

Sumerians
The creators of the first Mesopotamian civilization.

Athens
A democratic Greek polis who accomplished many cultural achievements, and who were constantly at war with Sparta. Athenians avoided major political upheaval by moving toward democracy, which was rule by the people.

Sparta
Greek city-state that was ruled by an oligarchy, focused on military, used slaves for agriculture, discouraged the arts

Trojan Wars
A series of wars between Athens and Sparta that are said to be about Sparta kidnapping Helen of Athens and Athens fighting to reclaim Helen. A more logical reason is that Athens and Sparta were major trading rivals and they were fighting over the hellespont. The greeks won the war.

Persian Wars
A series of wars between the Greeks (mainly Athens) and the Persians in which the Greeks were usually victorious.

Peloponnesian Wars
a war fought between Athens and Sparta in the 400s BC, ending in a victory for Sparta

Marcus Aurelius
Last of the "Good Emperors", Wrote "Meditations" personal reflections of his beliefs, End of the Pax Romana

Constantine
Emperor of Rome who adopted the Christian faith and stopped the persecution of Christians (280-337)

Attilia the Hun
King of the Huns who invaded Europe and was defeated by Romans and Visigoths

Carthage
The greatest Phoenician colony was at Carthage in North Africa. Phoenicians traded goods they got from other lands: wine, weapons, metals, ivory, slaves. Superb craftspeople who worked in wood, metal, glass, and ivory. Developed alphabet.
Christianity
A religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus. Spread slowly, but steadily, through the Roman Empire.

historian
an expert who studies and records the past

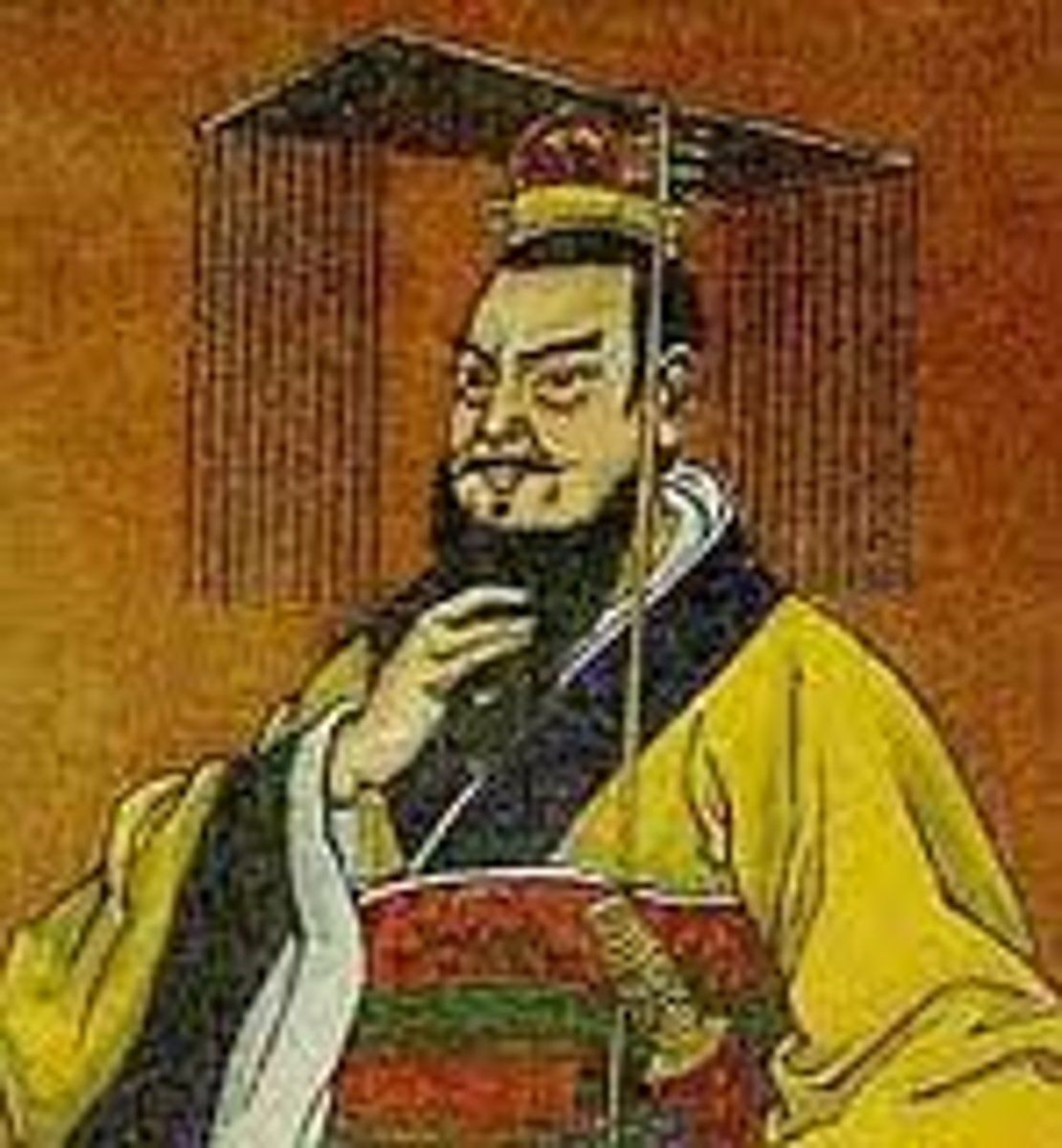
Shi Huangdi
founder of the Qin dynasty and China's first emperor

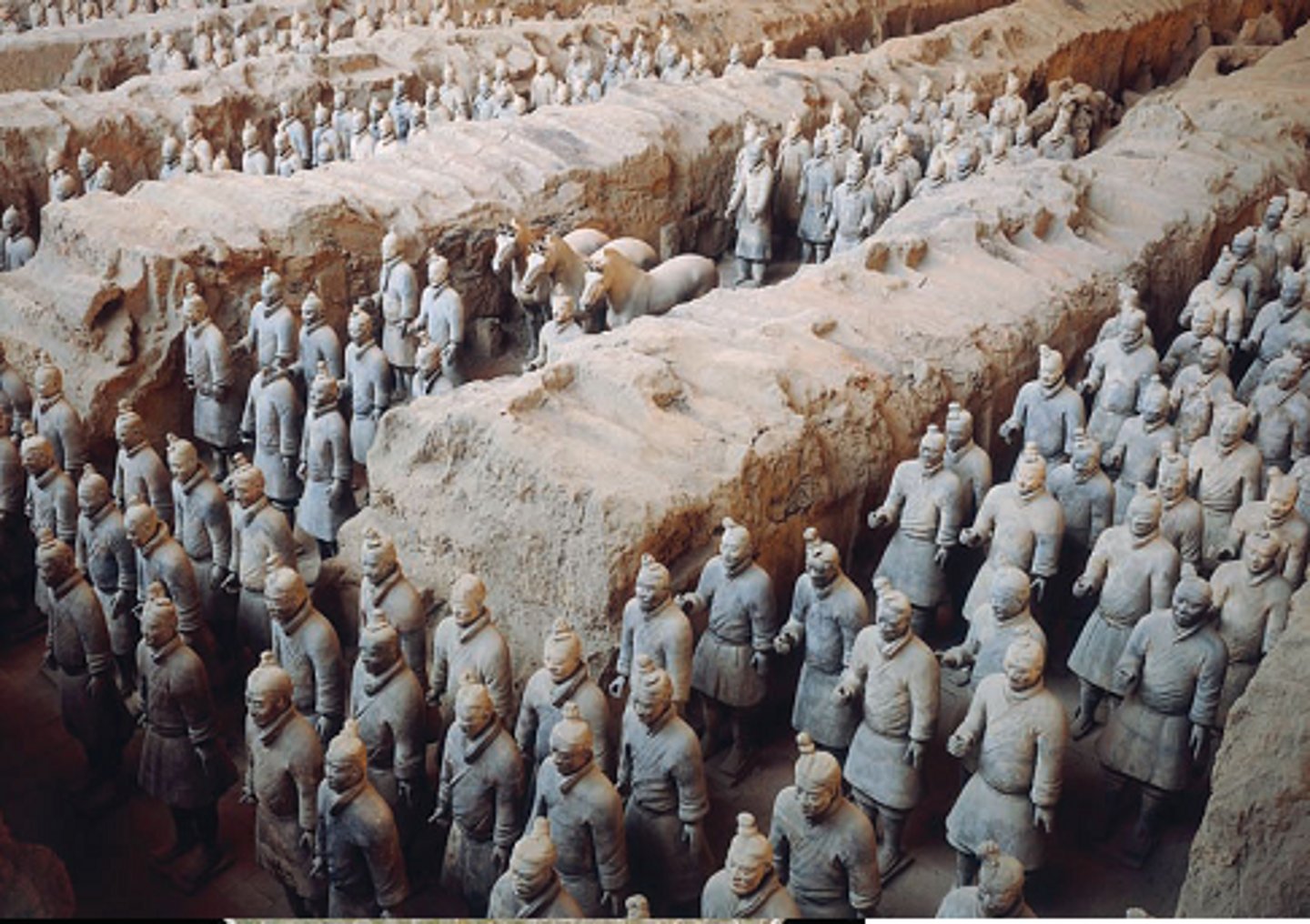
Qin Dynasty
the Chinese dynasty (from 246 BC to 206 BC) that established the first centralized imperial government and built much of the Great Wall. Replaced the Zhou Dynasty. It emerged from the western state of Qin.

Han Dysnasty
Came after the Qin Dynasty. Dynasty that ruled China from 206-220 BCE creating a durable state based on Shihuangdi's state-building achievement.

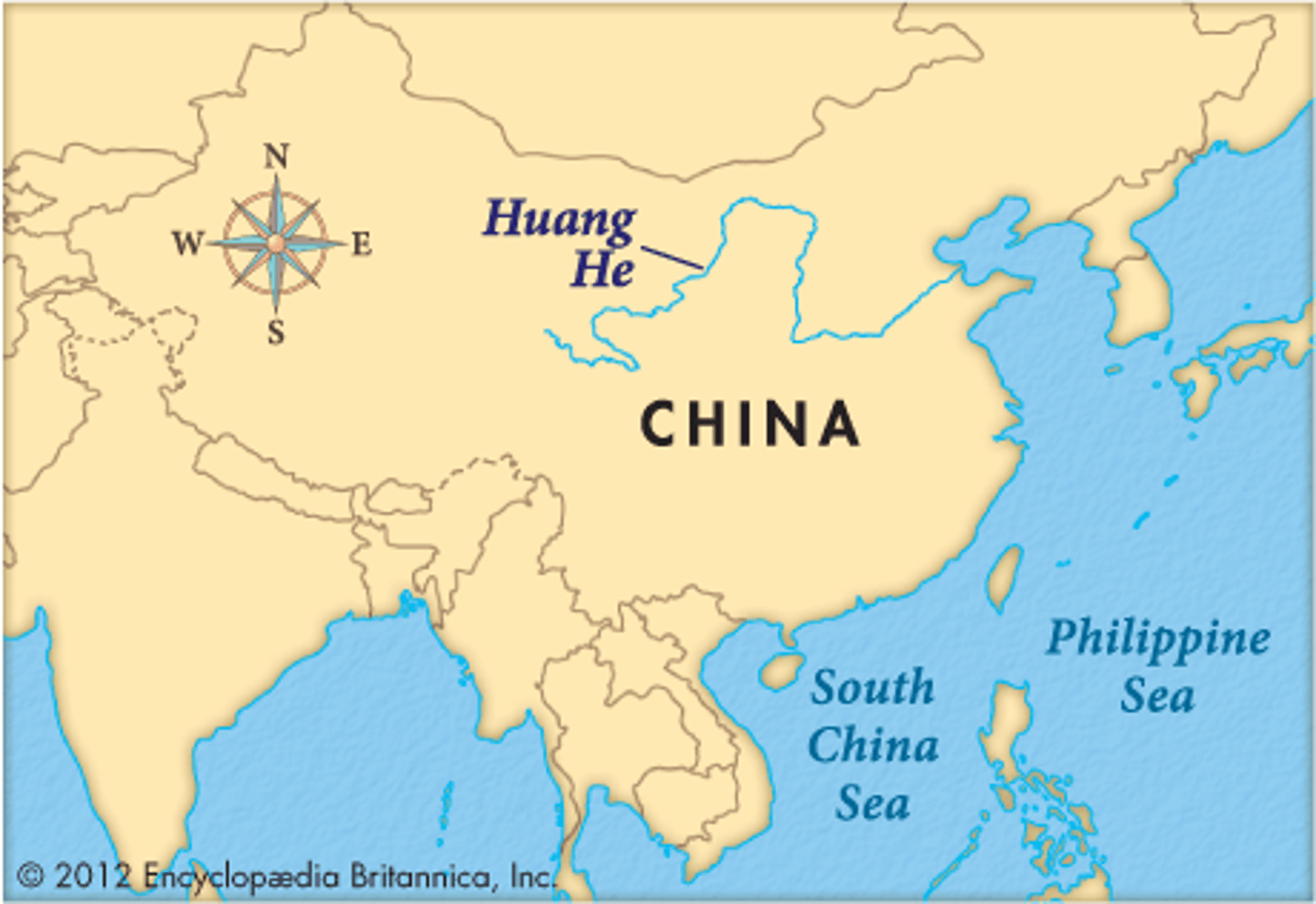
Huang He River
"river of sorrows" floods; located in the north east, very long. Also called the "yellow river".