Lecture 4: Brain anatomy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what are the functions of CSF (cerebral spinal fluid)
waste removal
transportation of nutrients and hormones
protection → shock absorption
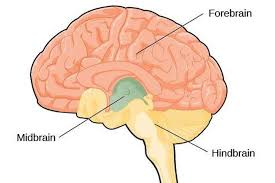
where is the forebrain and what parts or sections is it divided into?
diencephalon
telencephalon
what are the main parts of the diencephalon?
includes the:
thalamus
pineal gland
hypothalamus
posterior pituitary gland
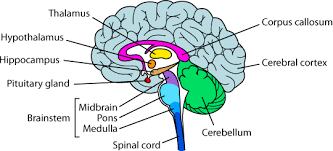
function of the thalamus
receives sensory input and motor input from most of the body regions
filters and integrates the sensory info like a router (except olfactory)
contains the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and other nuclei for processing sensory input
plays a role in regulating sleep.wake states
describe the hypothalamus functions
maintains homeostasis by regulating water balance, blood pressure, appetite, metabolism, and body temp.
associated with behaviours like eating, drinking, sexual behaviour, and other motivated behaviours
regulated the endocrine system by controlling the release of hormones from the pituitary gland
ventral to the thalamus
what are some main nuclei the hypothalamus contains?
mammillary nuclei
spatial memory
lateral hypothalamus (LH)
produces rexins which is part of appetite for food and drugs
also promotes wakefulness
Suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN)
related to the eyes for light and darkness so you can measure time
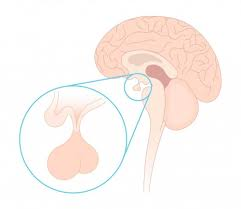
what are the two parts of the pituitary gland and label them
posterior pituitary gland
anterior pituitary gland
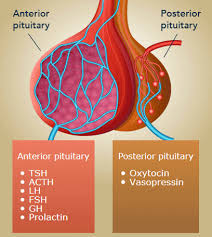
what does the posterior pituitary gland do?
composed of axons (the cell body of the neuron is in the hypothalamus)
releases vasopressin (antidieuretic hormone - affects bp) and oxytocin hormones
what does the anterior pituitary gland do?
composed of endocrine cells
produces hormones that regulate the production of other glands
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinzing hormone (LH)
the hormone production is regulated by the hypothalamus via neurons that secrete a releasing hormone into the hypophyseal portal system
what does the pineal gland do?
produces melatonin
helps induce sleep
what are the major structures of the telencephalon?
cerebral cortex
hippocampus
basal ganglia
amygdala
olfactory bulbs
what are the olfactory bulbs?
smell (sensory info) is processed in the bulbs
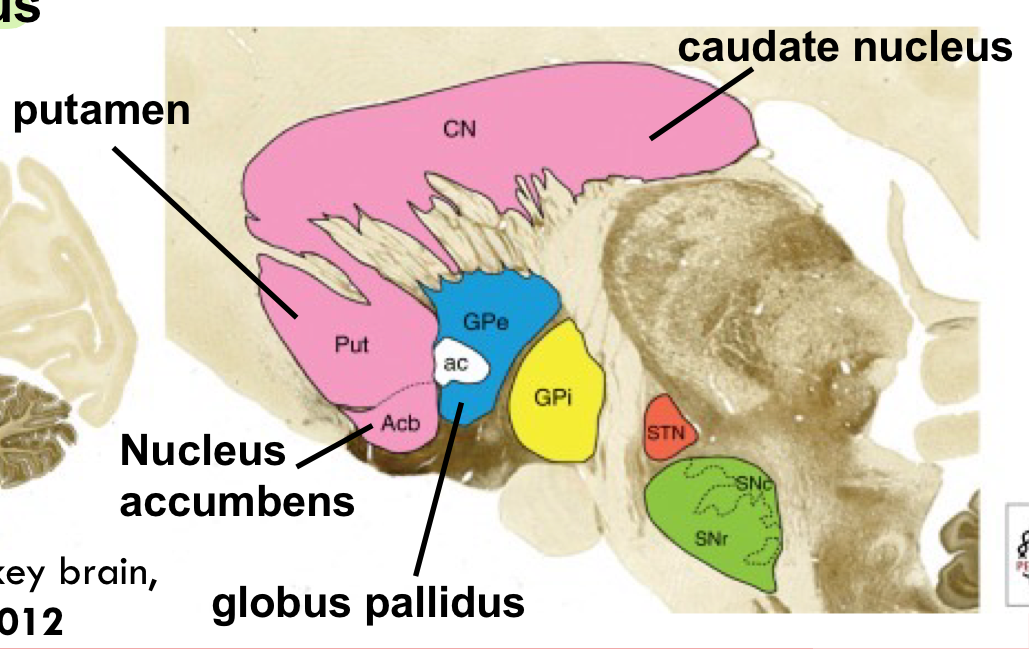
what is the basal ganglia?
a group of large nuclei (a more accurate name would be the “basal nuclei”) located near the thalamus:
The dorsal striatum includes the caudate nucleus and the
putamen
The ventral striatum includes the nucleus accumbens
The globus pallidus
functions of the basal ganglia?
regulation of planning and execution of voluntary motor movement
motivation and reward processing
aspects of memory and learning like procedural learning
Function of the caudate nucleus?
planning voluntary movement
like the movement of eyes
motivation and goal direction behaviour
procedural learning
slide 19