Teori Personaliti Abraham Maslow dan Hirarki Keperluan
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Abraham Maslow
Founder of humanistic psychology movement.
Humanistic Theory
Focuses on individual potential and personal growth.
Critique of Behaviorism
Challenges behaviorism's neglect of human nature.
Critique of Psychoanalysis
Opposes Freud's focus on abnormal cases.
Optimistic View
Belief in human potential and creativity.
Self-Actualization
Realizing one's full potential and capabilities.
Hierarchy of Needs
Five-tier model of human needs motivation.
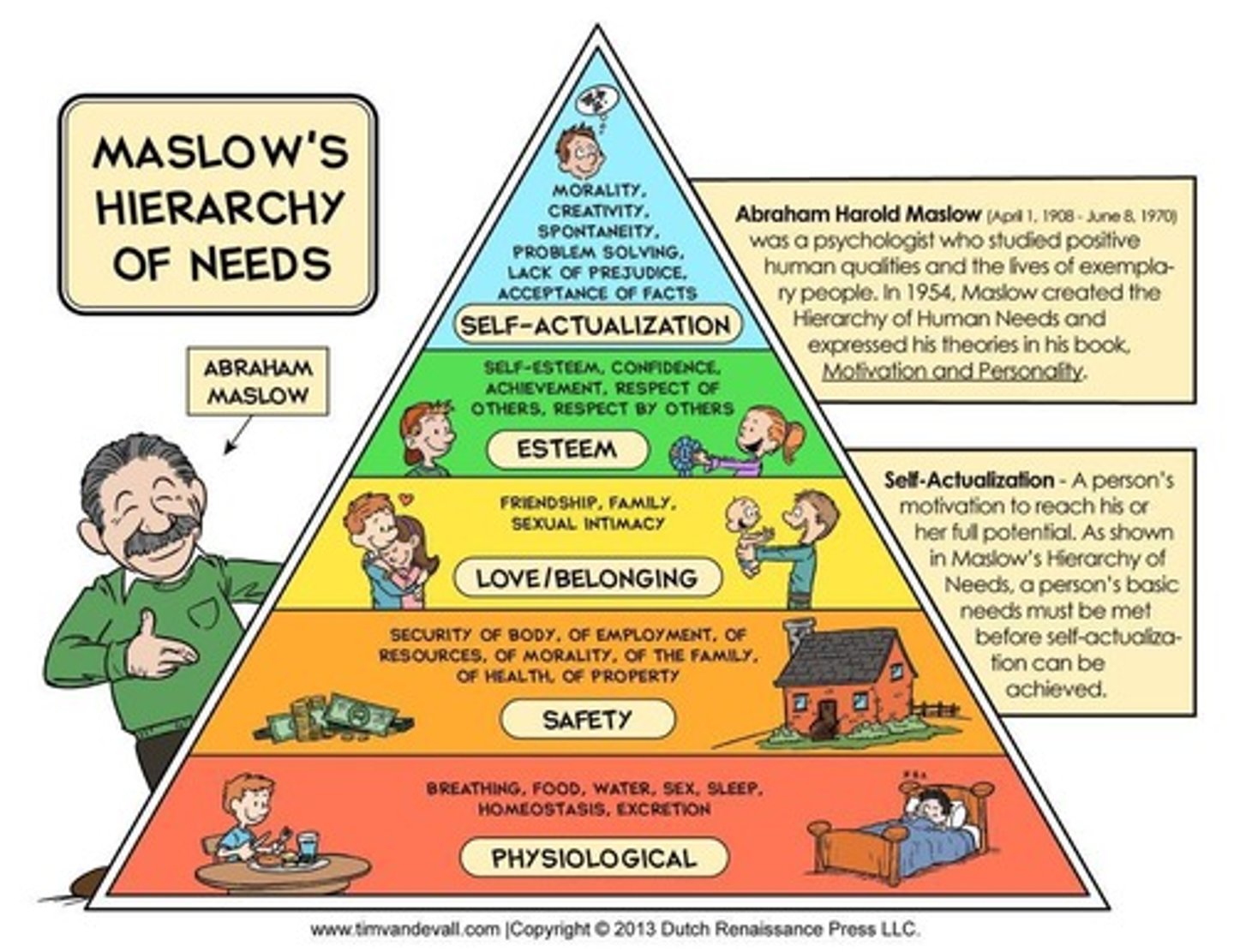
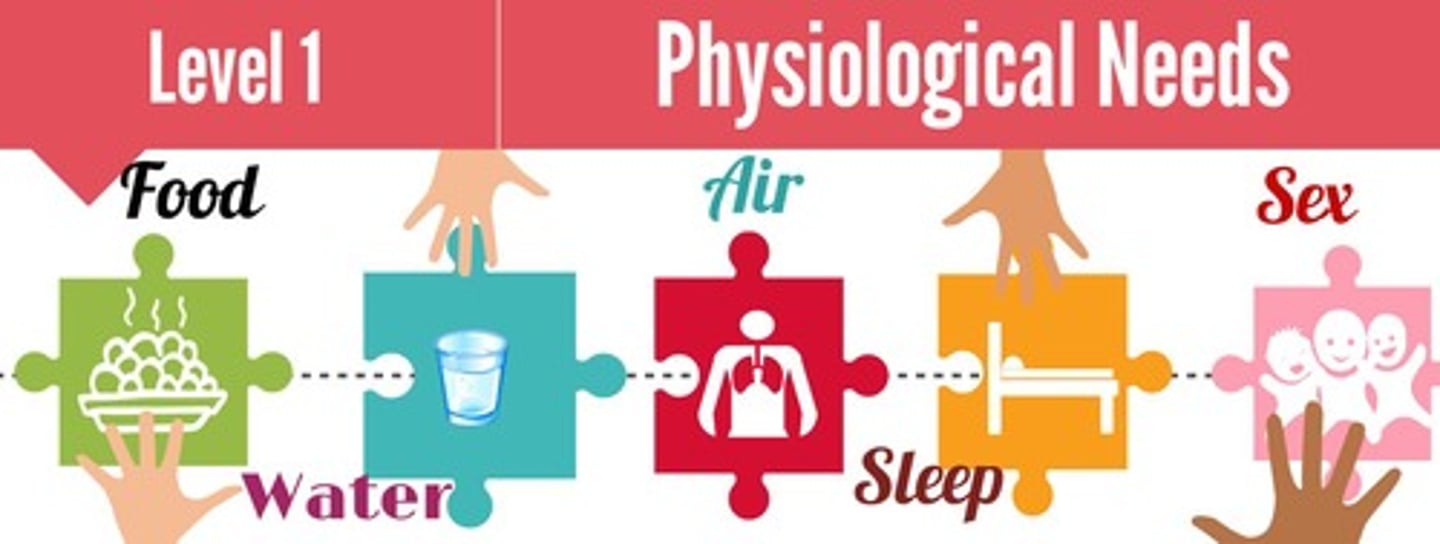
Physiological Needs
Basic biological requirements for survival.
Safety Needs
Desire for security and stability in life.
Love and Belonging Needs
Need for relationships and social connections.
Esteem Needs
Desire for respect, status, and self-esteem.
Self-Actualization Needs
Pursuit of personal growth and fulfillment.
Instinctoid Needs
Innate needs influenced by culture and learning.
Deficiency Needs
Basic needs essential for survival and well-being.
Growth Needs
Higher-level needs that promote personal development.
Childhood Experiences
Early experiences shape future personality development.
Cognitive Needs
Desire to know and understand the world.
Characteristics of Self-Actualized Individuals
Traits include acceptance, spontaneity, and problem focus.
Independent Individuals
Self-sufficient and autonomous in their actions.
Democratic Personality
Tolerance and acceptance of others' differences.
Interpersonal Relationships
Meaningful connections with others are essential.
Motivation Ladder
Hierarchy shows prioritization of human needs.
Crisis from Unmet Needs
Failure to meet basic needs causes distress.
Maslow's View on Humanity
Humans can shape their societal lives.
Potential Development
Individuals can grow and fulfill their potential.
Early Childhood Needs
Structure and routine are crucial for children.
Emotional Health
Satisfaction of needs leads to emotional stability.