coordination and reponse
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
by responding to changes in their external environment
e.g avoiding places that are too hot or too cold
how to animals increases their chance of survival?
to makes sure that the conditions are always rights for their metabolism
why do animals respond to changes in their internal environment ?
by responding to changes in their environment
how do plants increase their chance of survival?
any change in the internal or external environment
what is a stimulus ?
detect stimuli
receptors in the sense organs are groups of cells that detect external stimuli
e.g rod and cones cells in the eye detect changes in light
what do receptors do?
bring about a response to stimuli.
include muscle cells and found in glands e.g pancreas
respond in different ways- muscle cells contract, whereas glands secrete hormone
what do effectors do?
communicate with effectors via the nervous system, the hormonal system or both.
how do receptors communicate?
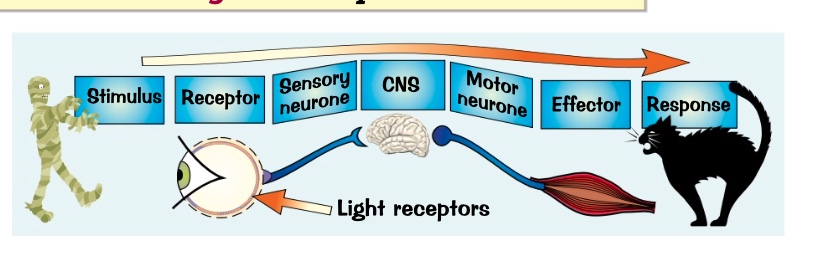
CNS- coordinates info. cooardinated response always needs a stimulus, receptor and effector
made up of all the neurones (nerve cells_ in the body.
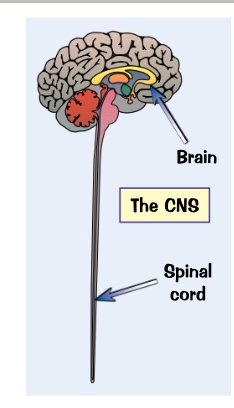
consists of the brain and spinal cord only.
what is the central nervous system and what does it do?
sensory
relay
motor
what are the 3 types of neurones?
send electrical impulses along the sensory neurone to the CNS
CNS then send the electrical impulses to an effector along motor neurone.
effector then responds
what happens when receptors in a sense organ detect a stimulus?
as neurone transmit information using high speed electrical impulses
how come the nervous system brings very rapid responses?
the connection between 2 neutrons
what is a synapse?
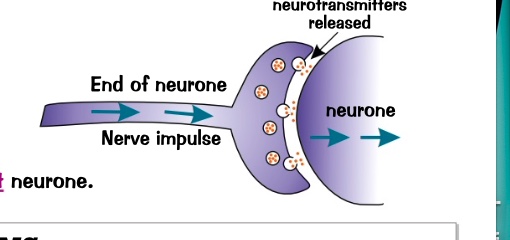
transferred by chemicals called neurotransmitters which diffuse across the gap.
chemicals then set off a new electrical signal in the next neurone.
how is the nerve signal transferred?
reflexes are automatic responses to certain stimuli- reduce the chances of being injured help prevent injury.
what are reflexes?
the route taken by the information in a reflex from receptor to effector
what is the reflex arc?
the CNS.
where does the reflect arc go through?
go through the spinal cord or through an unconscious part of the brain
where do the neutrons in reflex arc go?
stimulus is detected by receptor an impulse is sent along a sensory neurone to the CNS
what detects the stimulus then what happens?
passes the message to another type of neuron- relay
in the CNS what does the sensory neurone do?
relay the impulse to a motor neurone
impulse then travels along motor neurone to effect
muscles then contracts and move hand away from the object
what do the relay neurons do?
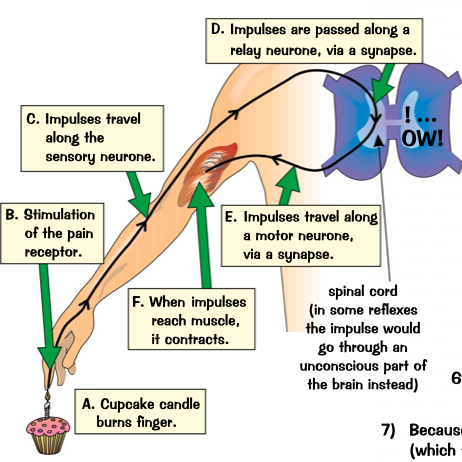
touching hot object diagram?
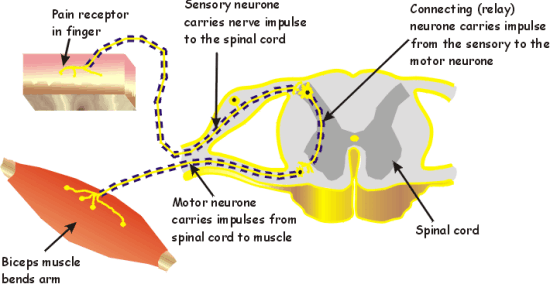
reflex arc labeled
block diagram used to represent reflex arc?
eye labelled
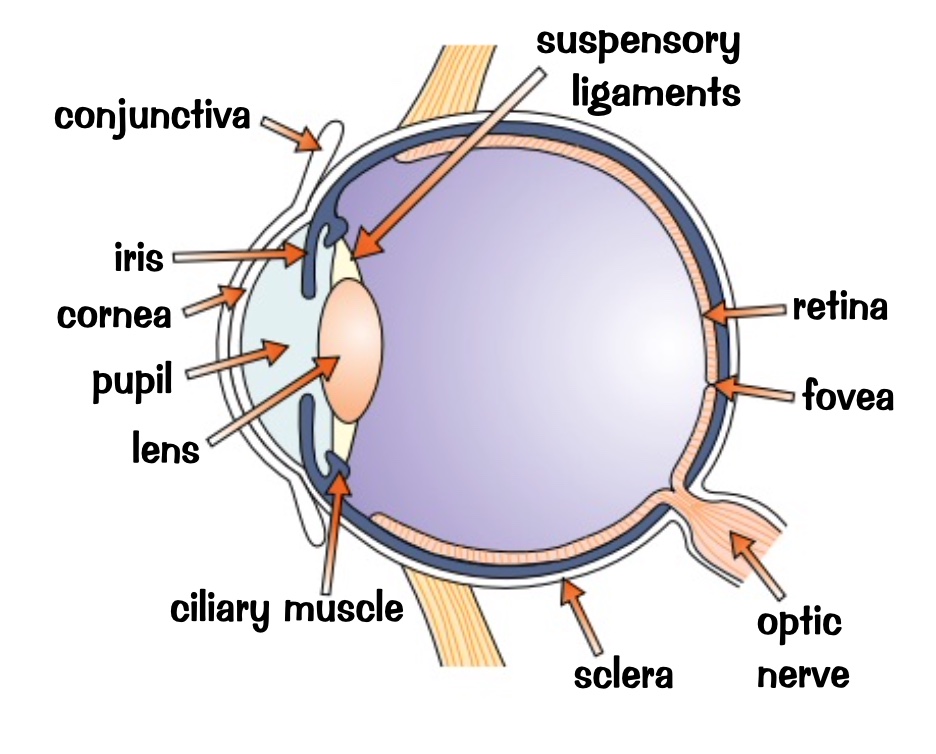
lubricates and protects the surface of the eye
what does the conjunctiva do?
tough outer layer protects the eye
what does the sclera do?
refracts light. transparent and has no blood vessels to supply it with o2 o2 diffuses in from outer surface
what does the cornea do?
controls the diameter of the pupil and therefore how much light can enter
what does the iris do?
focuses the light onto the retina covered in lights receptors called rods and cones
what does the lens do?
more sensitive in dim light and cannot sense colour.
what do rods do?
sensitive to colours and are not so good in dim light
found all over retina but there are lots at the fovea
what do cones do?
carries impulses from receptors to brain
what does the optic nerve do?
adjusting for bright light as can damage retina- reflect to protect
what does the iris reflex do?
triggers a reflex that makes the pupil smaller allowing less light.
light receptors detect the bright light and send a message along a sensory neurone to the brain. message then travels along a relay neurone to a motor neurone will tells the circular muscles in the iris to contract, making pupil smaller
what does the very bright light trigger?
brain tells the radial muscles to contract which makes the pupil bigger
what happens in the dim light?
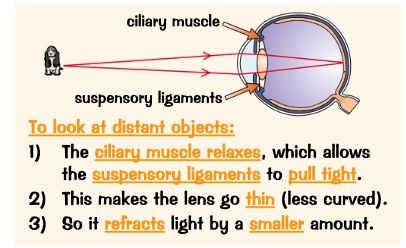
ciliary muscles relax which allow the suspensory ligaments to pull tights
makes the legs go thin less curved
so it refracts light by a smaller amount
what happens to the eye to look at distant objects?
ciliary muscles contract which slackens the suspensory ligaments.
lens become more fat and curved
increases amount by which it will refract light
what happens to the eye to look at near objects?
when the cornea or lends bends the light too much or the eyeball is too long. image of distant objects are brought in front of retina.
why can’t people focus on distant objects?
unable to focus on near objects. when cornea or lens does not bend enough. image is bought behind retina.
what are long sighted people unable to focus on?
chemicals released directly into blood.
carried in the blood plasma to other parts of the body, but only affect particular cells- target cells
controls things in organs and cells that need constant adjustment
produced in the gland. travel quite slowly and tend to have long lasting effects .
acts as chemical messenger
what are hormones?

what is the hormone adrenaline
source, role and effects?

what is the hormone insulin
source, role and effects?

what is the hormone testosterone
source, role and effects?

what is the hormone progesterone
source, role and effects?

what is the hormone oestrogen
source, role and effects?

what is the hormone ADH
source, role and effects?

what is the hormone FSH
source, role and effects?

what is the hormone LH
source, role and effects?

what is the main different between nerves and hormones?
the maintenance of a constant internal environment
what is homeostasis?
1- water content- need to keep a balance between the water you gain and the water you lose
2- body temperature- need to get rid of excess body heat when hot, but retain heat when environment is cold
what 2 conditions need to be kept balanced in the body?
by food and drink
how is water taken in the body?
through the skin as sweat
via the lungs in breath
via the kidneys as urine
how Is water lost from the body?
sweat a lot
produce less urine more concentrated
los more water though breather when excercising as you breathe faster
on a hot day if exercising what will you produce?
don’t sweat much
produce more urine which will be pale since the waster carried in the urine is more diluted.
on a cold day what will you produce?
all enzymes work best at optimum temperature- 37
brain acts as thermostats. receives message from temperature receptors in skin that provide information about skin temperature
CNS can activate necessary effectors to make sure body temperature stays the same
what is the temperature that has to be kept the same for body?
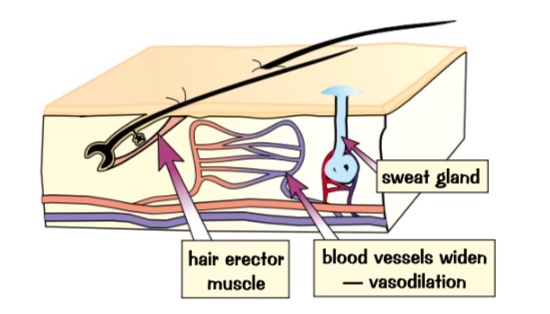
lots of sweat is produced- when it evaporates and transfers energy from skin to environment cooling you down.
blood vessels close to the surface of the skin- widen- vasodilation. allows more blood to flow near the surface so it can transfer more energy into surrounding.
hairs lie flat
what happens when you’re too hot?
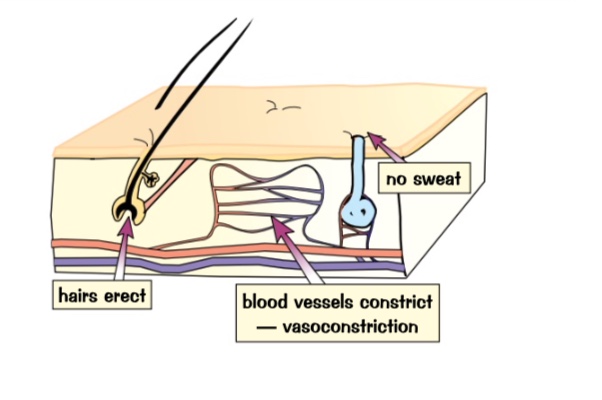
very little sweat produced
blood vessels near the surface of the skin constrict - vasoconstriction. less blood flows near surface and less energy transferred to surrounding
shiver, increases rate of respiration transfers more energy to warm body
hairs stand to tap insulating layer of air keep you warm
what happens when you’re too cold?
smaller organism have bigger surface area to volume ratio
organisms with bigger surface area to volume ratio can gain or lose heat faster because there is more area for heat to transfer across.
which type of organisms can cooly down quicker?
have smaller surface area to volume ratio gain or lose heat more slowly because there is less area for heat to transfer across.
animals living in cold conditions have a compact rounded shape to keep surface area to minimum.
which organisms can lose heat more slowly?
respond to changes in environment
sense the direction of light and grow towards it to maximise light absorption for photosynthesis
can sense gravity so their roots and shoots grow into right direction
climbing plants have sense of touch, so they can find things to climb and reach sunlight
how to plants increase their chance of survival?
plant growth hormones
hormones which control growth at the tips of shoots and roots
move through the plant is solution
what are auxins?
produced in the tips and diffuse backwards to stimulate the cell elongation process which occurs in the cell behind the tips
where is auxin produced?
promote growth in the shoot and actually inhibits growth in the root
involved in the growth response of plants to light (phototropism) and gravity
(geotropism)
what does auxin promote?
change the direction of root and shoot growth
what do auxins change?
positively phototropic (grow towards light)
what do shoots grow towards do?
accumulates more auxin on the side that is in the shade than the side that is in the light
makes the cell grow elongate faster on the shaded side so the root bends towards the light
what happens when a shoot tip is exposed to light?
from gravity
negatively geotropic
when a shoot is growing sideway gravity produces an unequal distribution of auxin in the tip with more auxin on the lower side
causes the lower side to grow faster bending the shoot upwards
what do shoot grow away from?
towards gravity
positively geotropic
root growing sideways will have more auxin on its lower side
but in a root extra auxin insist growth. means the cells on top elongate faster and root bends downwards.
what do roots grow towards?
light
negativity phototrophic
root starts to be exposed to light, more auxin accumulate on the more shaded side
auxin inhibits cells elongation on shaded side so the root bends downwards back into ground.
roots that are underground not exposed to light.
grow downwards due to positive geotropism.
what do roots grow away from?