Medical Terminology Chapter 8 Cardiovascular System
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
aneurysm/o
aneurysmorrhaphy: suture of an aneurysm
aneurysm (widened blood vessel)
angi/o
angioplasty: surgical repair of a blood vessel; reopens narrowed blood vessels and restores blood flow using a balloon-tipped catheter
vessel (usually blood or lymph)
vascul/o
vessel (usually blood or lymph)
aort/o
aortostenosis: narrowing of the aorta
aorta
arteri/o
artery
arteriol/o
arteriole
atri/o
atrium
ather/o
atheromas: tumor of fatty plaque; formed when fatty plaque builds up on the inner lining of arterial walls
fatty plaque
cardi/o
heart
coron/o
coronary: pertaining to the heart; coronary artery disease is most common heart disease and leading cause of death in US
heart
electr/o
electrocardiogram: helps detect many heart problems; recording of the hearts electricity
electricity
embol/o
embolectomy: excision, removal of a plug; performed in emergency situations to open blood vessels and reestablish the blood flow
embolus (plug)
hemangi/o
hemangioma: benign tumor cells that line blood vessels and usually disappear over time
blood vessel
my/o
muscle
phleb/o
vein
ven/o
venostasis: abnormally slow blood flow in the veins and is a major risk factor for clot formation
vein
scler/o
arteriosclerosis: abnormal condition of the hardening of an artery; most common cause is atheroma in vessel
hardening; sclera (white of eye)
sept/o
septostomy: temporary procedure performed to increase systemic oxygenation in infants w congenital heart defects until corrective surgery can be performed
septum
sphygm/o
pulse
sten/o
narrowing, stricture
thromb/o
thrombolysis: enzymes that destroy blood clots are infused into the occluded vessel
blood clot
valv/o
valvostomy: use of balloon catheter passed through a blood vessel in the groin to gain access to a stenosed valve
valve
valvul/o
valve
ventricul/o
ventricle (of the heart or brain)
-cardia
heart condition
-stenosis
narrowing, stricture
Brady-
slow
endo-
endovascular procedures are those that occur within the lumen of a vessel
in, within
extra-
outside
peri-
pericardial: refers to membrane that surrounds the heart
around
trans-
across
aneurysm
localized abnormality dilation of a vessel, usually an artery
angina
chest pain caused by obstructions or spasm of the coronary arteries that decrease blood flow to the myocardium; also called angina pectoris
arrhythmia
irregularly in the rate or rhythm of the heart; also called dysrhythmia
bradycardia
abnormally slow heart rate, usually fewer than 60 beats per minute in a resting adult
fibrillation
abnormally rapid, uncoordinated quivering of the myocardium the can affect the atria or the ventricles
heart block
interference with the normal transmission of electrical impulses from the SA node to Purkinje fibers
tachycardia
abnormally fast but regular rhythm, with the heart possible beating up to 200 beats/minute
bruit
soft, blowing sound heard on auscultation and associated valvular action, the movement of blood as it passes an obstruction, or both; also called murmur
cardiomyopathy
disease of weakening of heart muscle that diminishes cardiac function
coarctation
narrowing of a vessel, especially the aorta
embolism
intravascular mass that dislodges from one part of the body and causes a blockage in another area, commonly leading to life-threatening situations; pulmonary embolism blocks blood flow to the lungs
heart failure (HF)
disorder the occurs when the heart is unable to effectively pump the quantity of blood required by the body
hyperlipidemia
excessive amounts of lipids (cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides) in the blood; associated w a risk of atherosclerosis
hypertension (HTN)
elevated blood pressure persistently higher than 140/90 mm Hg
hypotension
low blood pressure persistently lower than 90/60 mm Hg
mitral valve prolapse (MVP)
structural defect in which the mitral (bicuspid) valve leaflets prolapse into the left atrium during ventricular contraction (systole), resulting in incomplete closure and back flow of blood; creates murmor
palpitation
sensation of irregular heartbeat, commonly described as pounding, racing, skipping a beat, or flutter
peripheral artery disease (PAD)
common circulatory disorder characterized by a reduced flow of blood to the extremities, especially the legs, resulting in muscle cramping and pain, and commonly the result of atherosclerosis
phlebitis
phleb: vein
inflammation of a deep or superficial vein of the arms of legs (more commonly the legs)
rheumatic heart disease (RHD)
serious pathological condition resulting from rheumatic fever, commonly causing permanent scarring of the heart valves, especially the mitral valve
syncope
partial or complete loss of consciousness usually caused by a decreased supply of blood to the brain; also called fainting
thrombosis
abnormal condition in which a blood clot develops in a vessel and obstructs it at the site of its formation
deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
blood clot that forms in the deep veins of the body, especially those in the legs or thighs; also called deep venous thrombosis; clots may break away from vein wall and travel in the body
electrocardiography (ECG, EKG)
procedure that graphically records the spread of electrical excitation to different parts of the heart using small metal electrodes applied to the chest, arms, and legs; helps diagnose abnormal heart rhythms and myocardial damage
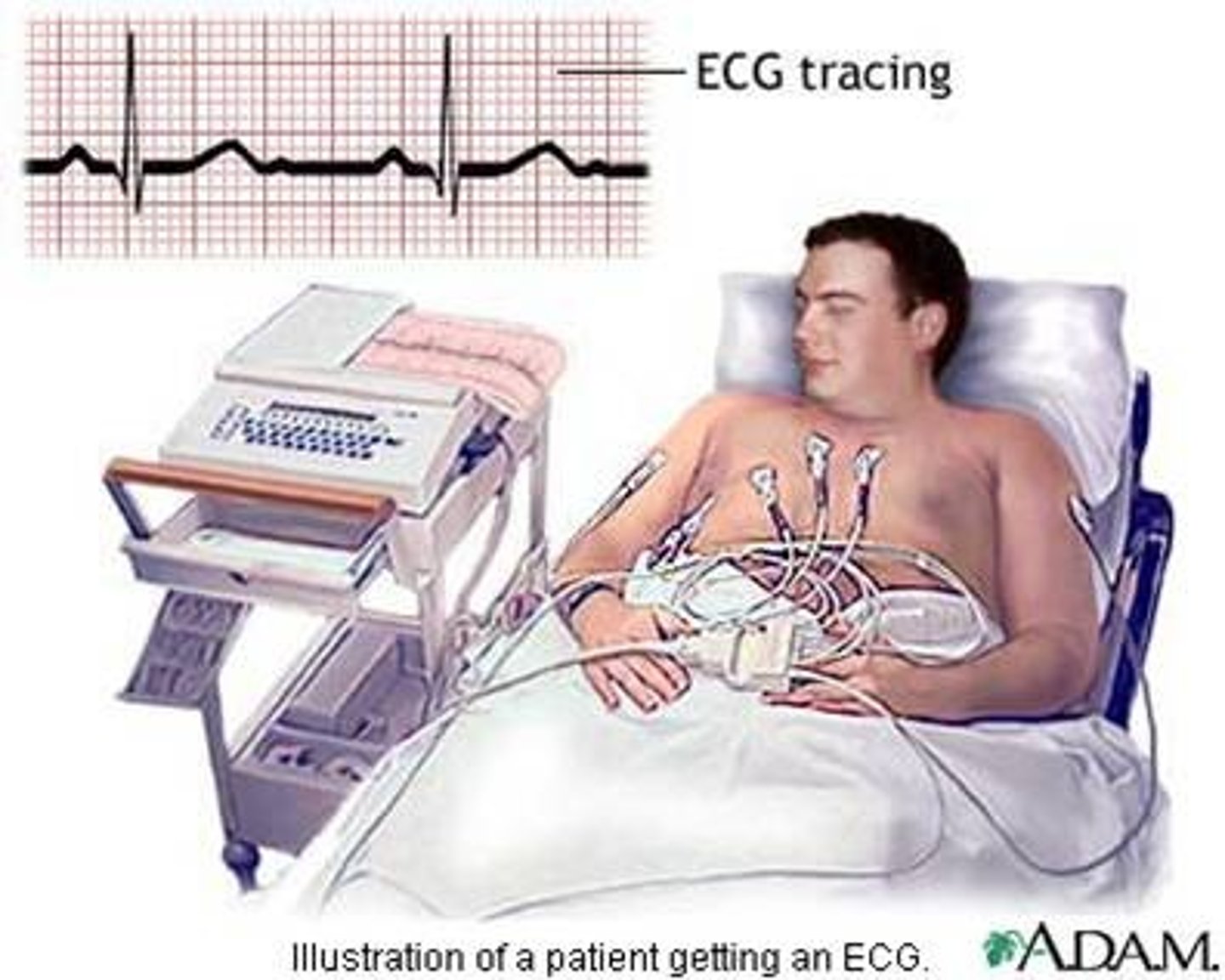
Holter monitor test
procedure that uses a small, portable system to record and store the electrical activity of the heart over a 24- to 48-hour period; also called event monitor test; helpful in diagnosing a cardiac arrhythmia
stress test
ECG taken under controlled exercise stress conditions (bicycle or treadmill)
cardiac biomarkers
blood test that measures the presence and amount of several substances released by the heart when it is damaged or under stress; also called cardiac enzyme test
lipid panel
series of blood tests (total cholesterol, high-density lipoproteins, low-density lipoproteins, and triglycerides) used to asses risk factors of ischemic heart disease
angiography
procedure that records a radiographic image of the inside of a blood vessel after injection of a contrast medium
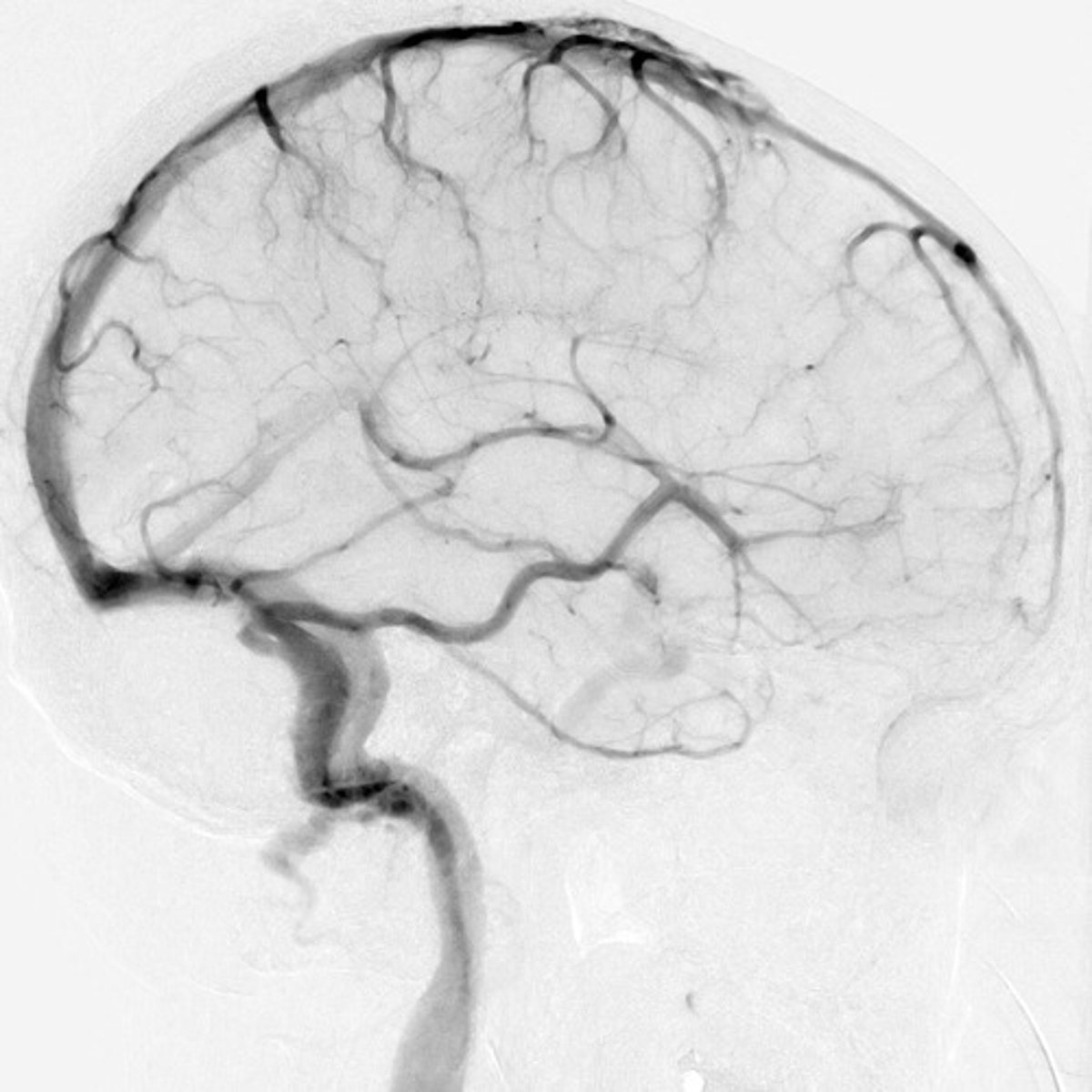
aortography
angiography of the aorta and its branches after injection of a contrast medium
coronary angiography
specialized type of angiography that helps diagnose stenosis or obstruction of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle
Doppler US
Ultrasonography used to asses the direction and speed of blood flow through blood vessels by reflecting sounds waves off red blood cells; also called ultrasonography using sound pitch
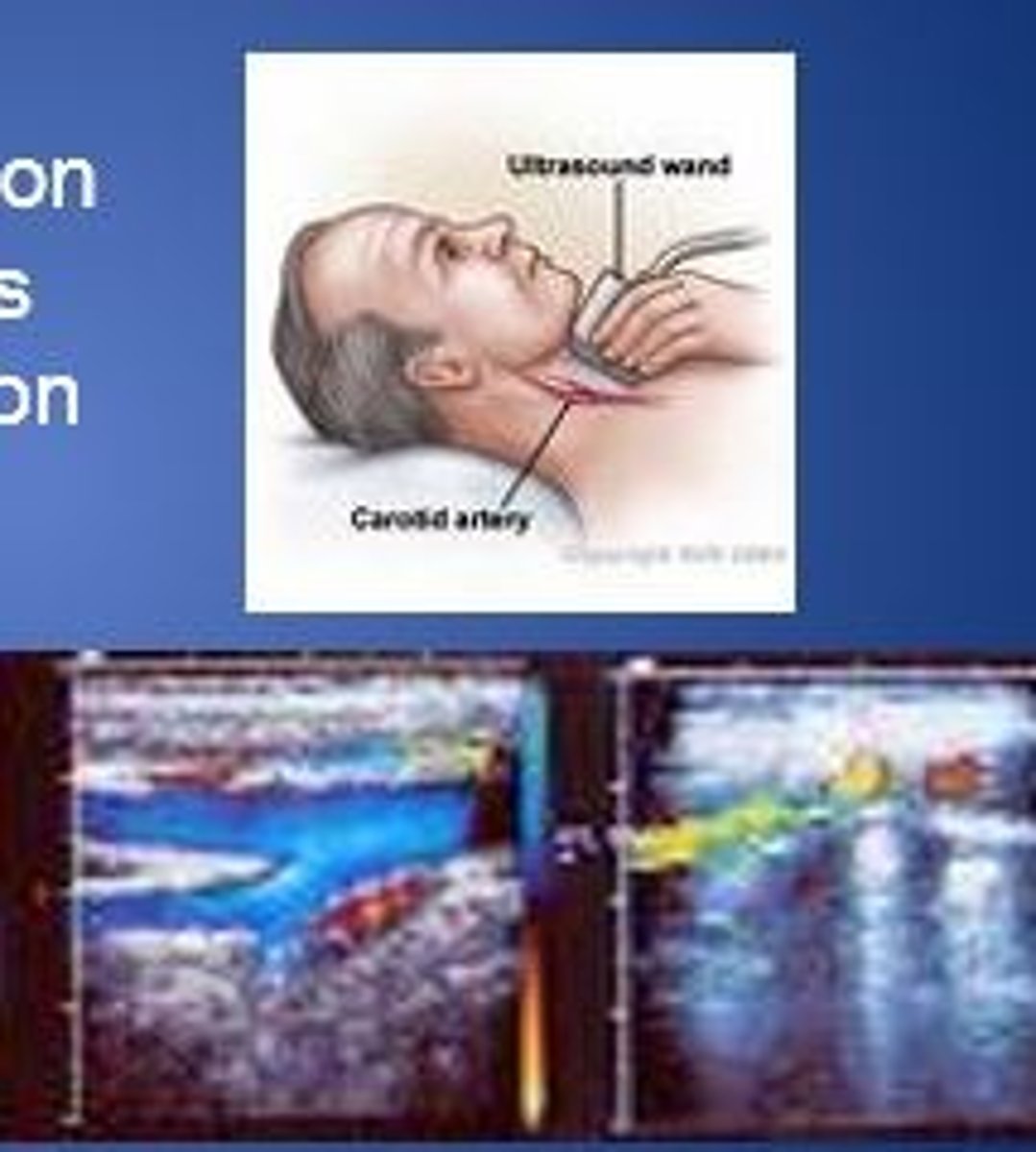
carotid artery US
ultrasound procedure that determines blood flow problems caused by blood clots, plaque, or tears on the walls of the carotid arteries
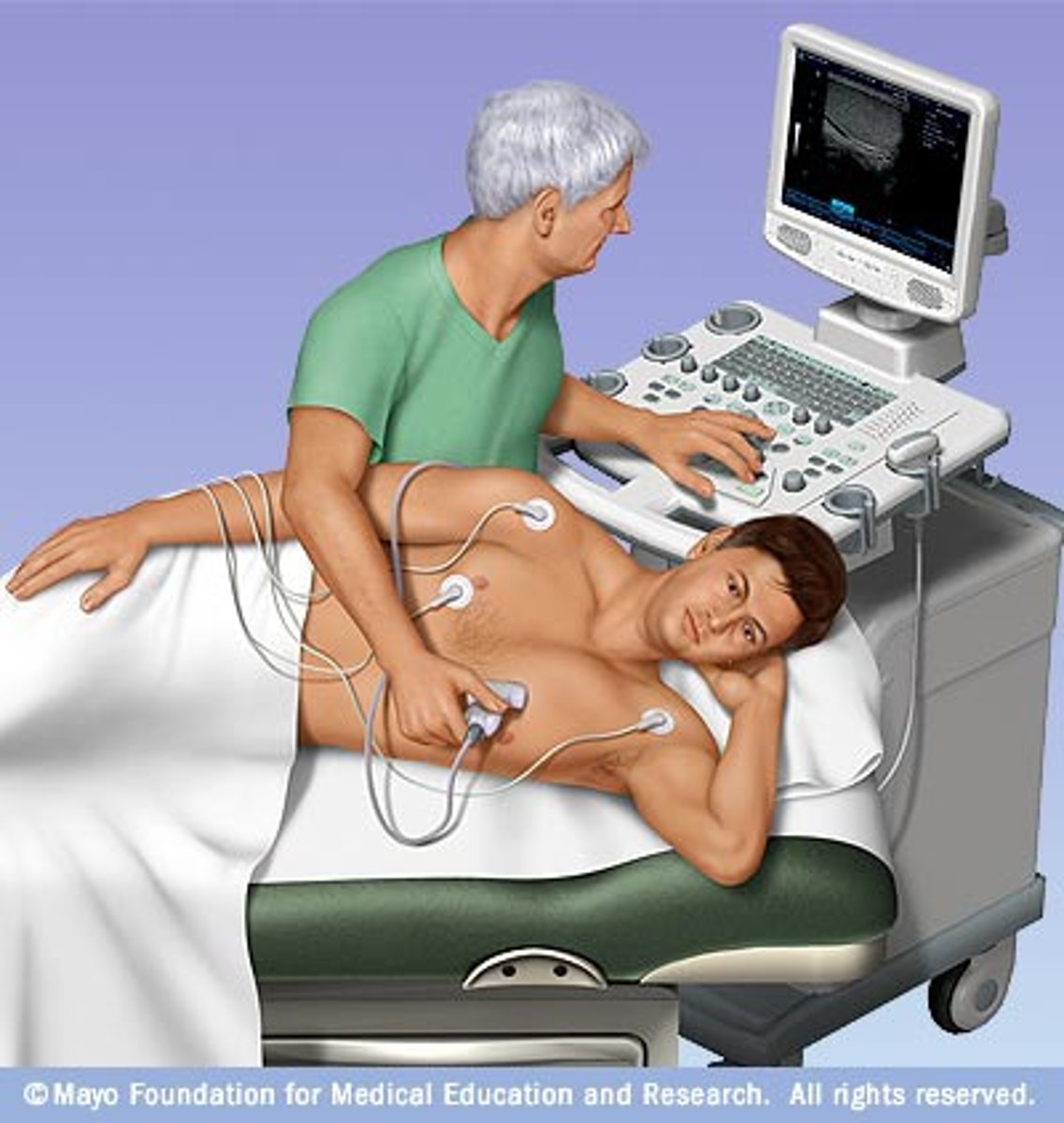
echocardiography (ECHO)
ultrasound test that produces moving images of blood passing through the heart, valves, and chambers, and asses cardiac output; place transducer on chest to direct ultrahigh frequency sound waves towards cardiac structures
myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI)
noninvasive imaging test using a radioactive tracer in conjunction with a stress test to show how well blood flows through (perfuses) the heart muscle at rest and during exercise; also called nuclear stress test
single-photon emission computer tomography (SPECT)
myocardial perfusion test that involves injection of a radioactive tracer into the blood while a gamma camera moves in a circle around the patient to crest individual images as "slices" of the heart (tomography)
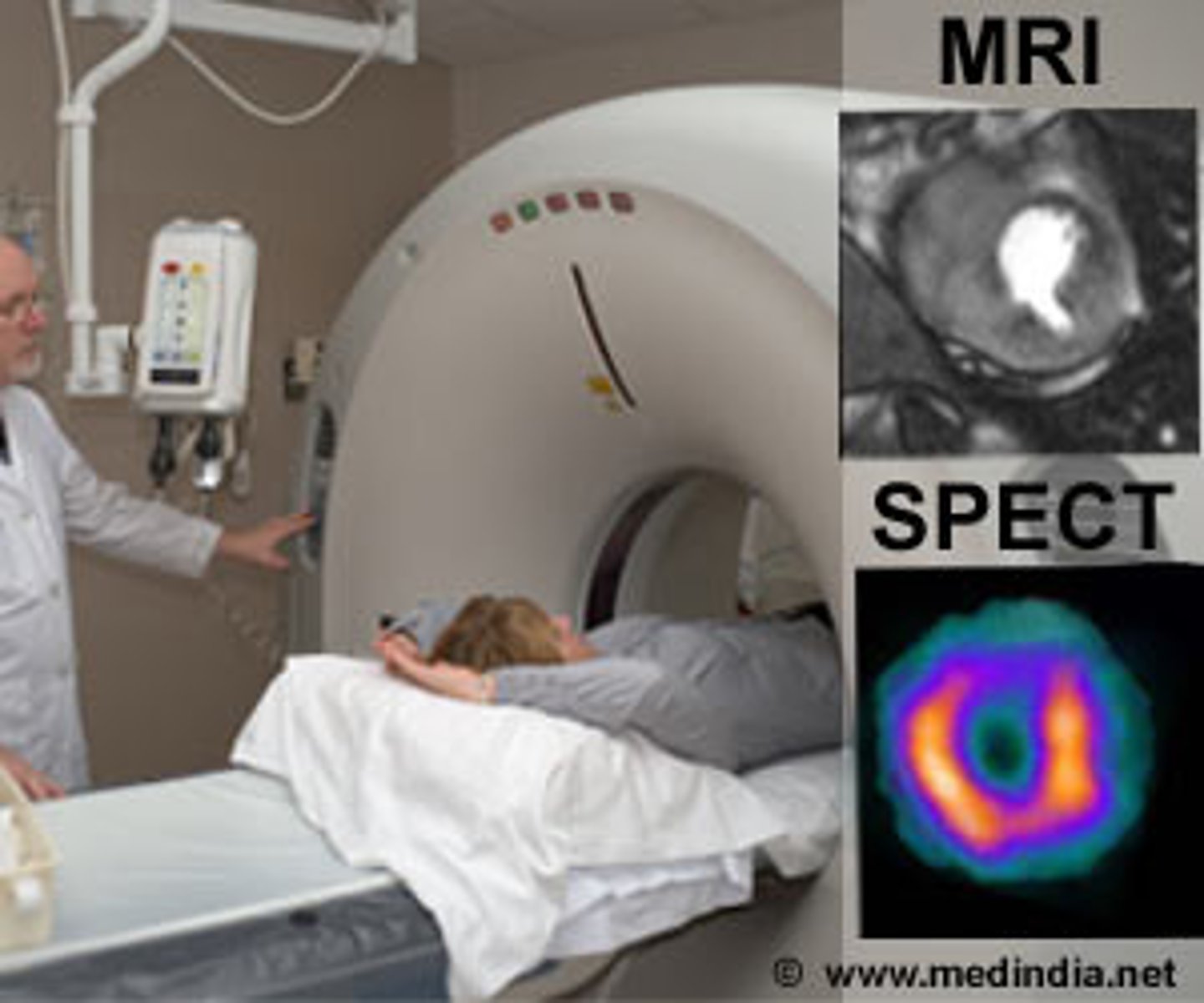
cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
specialized MRI procedure that provides images of the heart chambers, valves, major vessels, and pericardium
magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
type of MRI that provides high detailed images of blood vessels; unlike angiography, MRA detects blood flow, the condition of blood vessel walls, and blockages without a contrast medium
multiple-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan
nuclear procedure that uses radioactive tracers to detect how effectively the heart walls move as they contract and then calculates the ejection fraction rate (amount of blood the ventricle can pump out in one contraction)
cardiac catheterization (CC)
passage of a catheter into the heart through a vein or artery to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the heart
electrophysiology study (EPS)
special catheterization test that involves insertion of electrode catheters into the heart to study and map the conduction system and safely reproduce the abnormal heart rhythm affecting the patient's heart; information determined from EPS helps determine best medication, treatment, or device to control abnormal rhythm
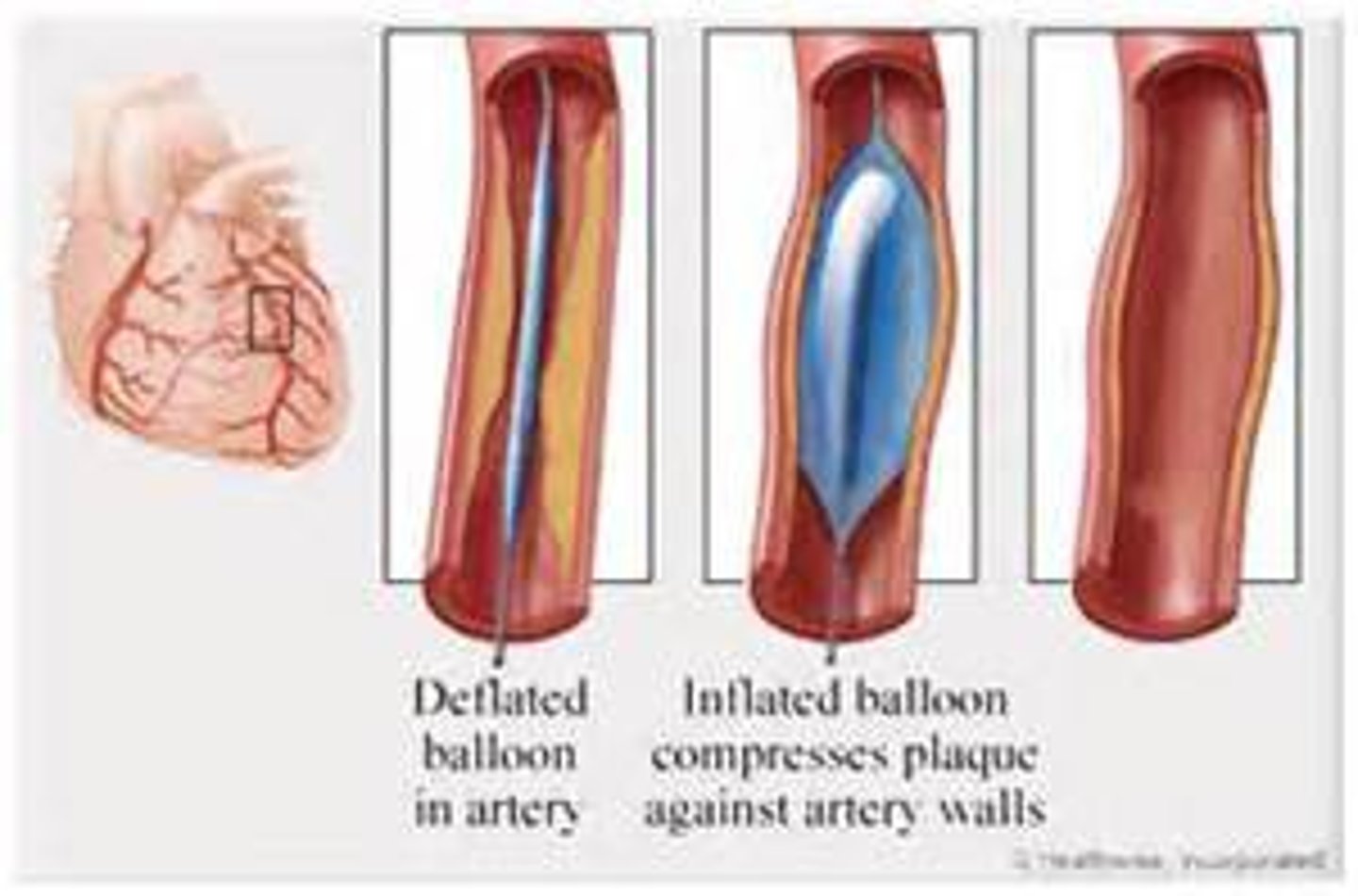
angioplasty
endovascular procedure that reopens narrowed blood vessels to restore forward blood flow; performed are arteries occluded by atherosclerosis
percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)
angioplasty of the coronary arteries that involve insertion of a balloon catheter through the right femoral artery to the site of the stenosis to enlarge the lumen of the artery and restore blood flow; often performed in conjunction with a stint placement
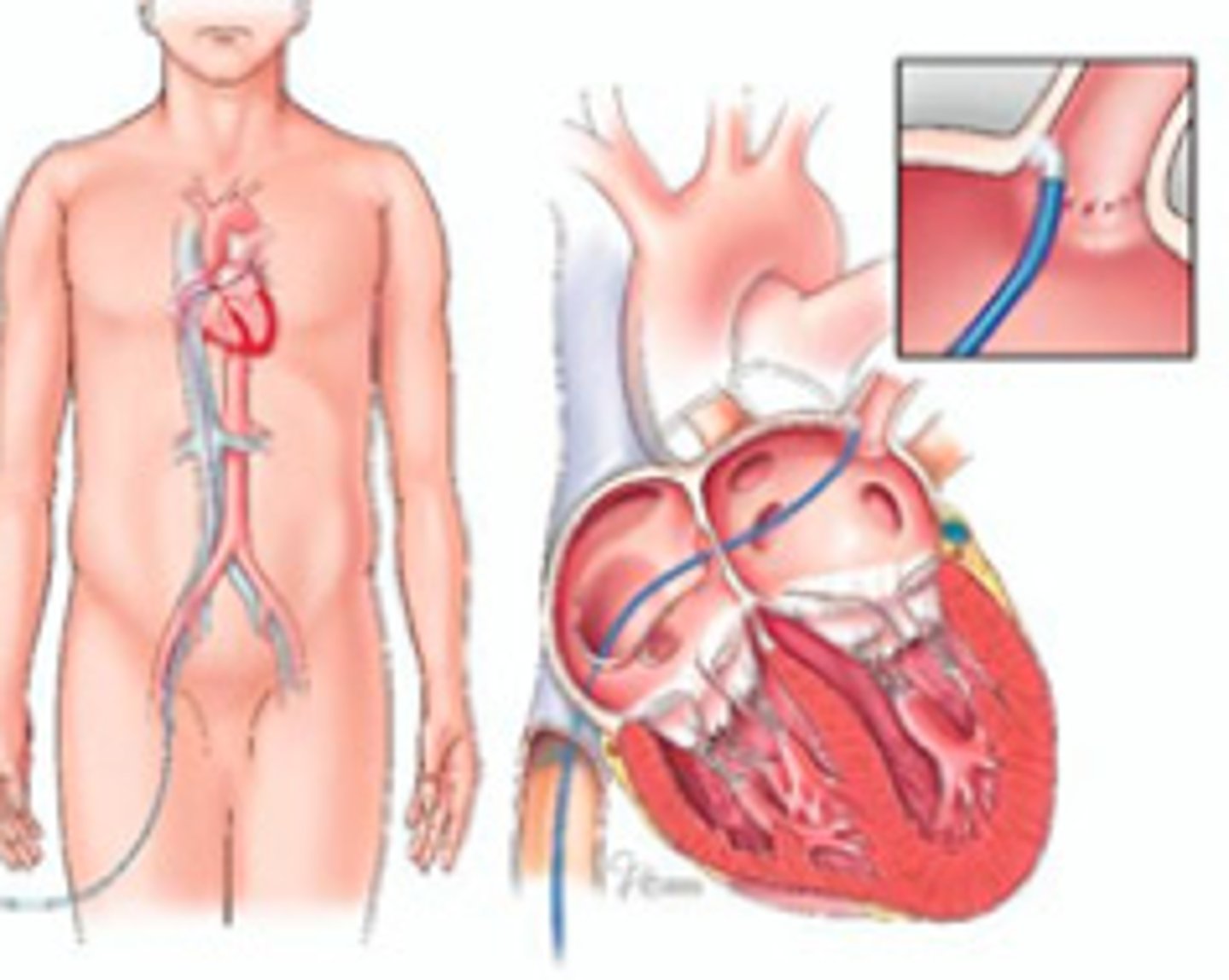
cardiac ablation
procedure in which a catheter is inserted through a vein in the groin and threaded to the heart to correct structural problems in the heart that cause arrhythmia; employs radiofrequency (heat) laser or cryoenergy to cause scarring of abnormal areas
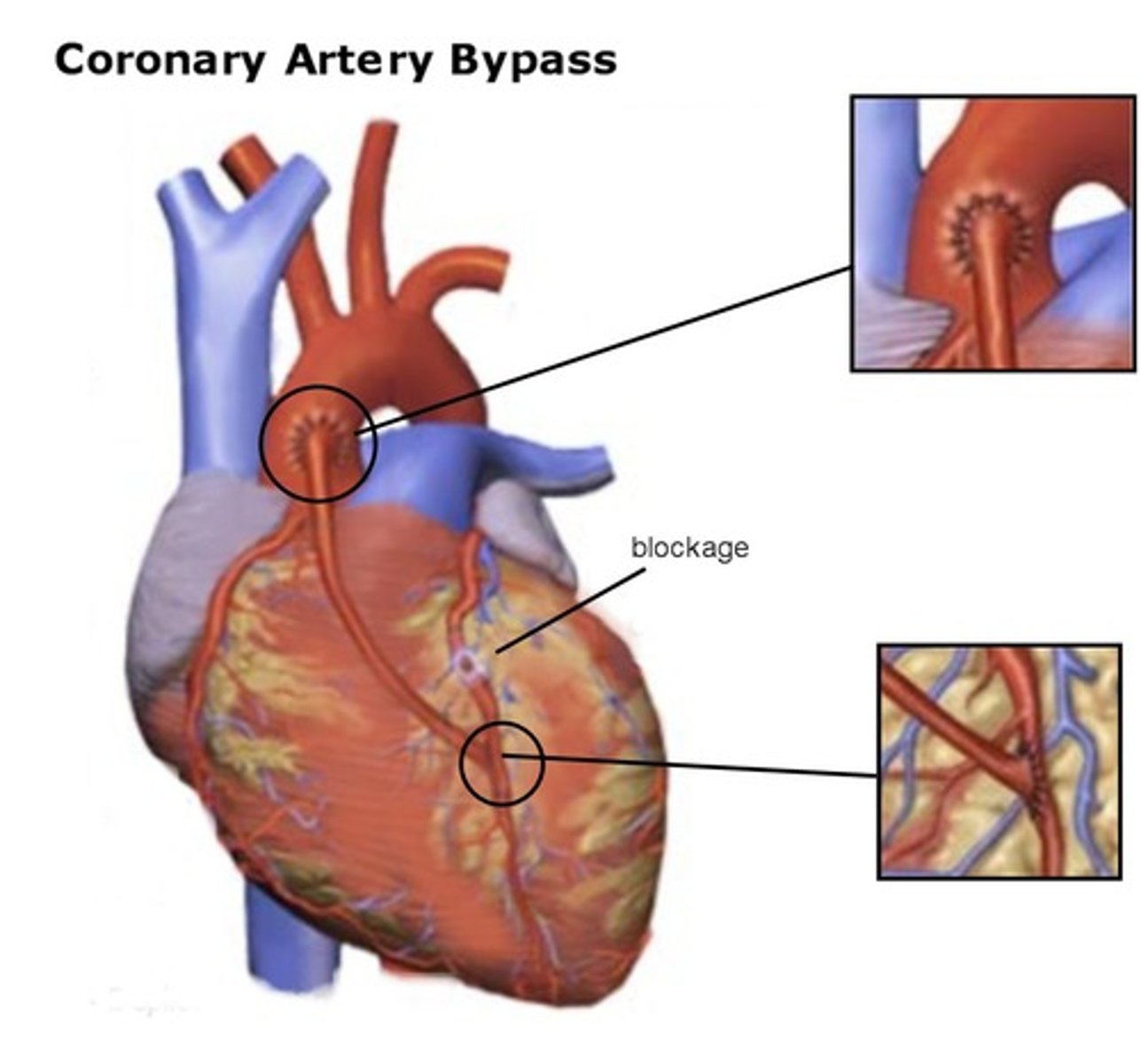
coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
Placement of a vessel graft from another part of the body to bypass the blocked area of a coronary artery and restore blood supply to the heart muscle
implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD)
small, battery-powered device inserted within the chest of a patient who is at high risk for developing an arrhythmia, such as ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, or cardiac arrest; also called automatic implantable cardioverter-defrillator
open heart surgery
surgical procedure in which the sternum is cut in half vertically to open the chest and expose the heart, its valves or the arteries
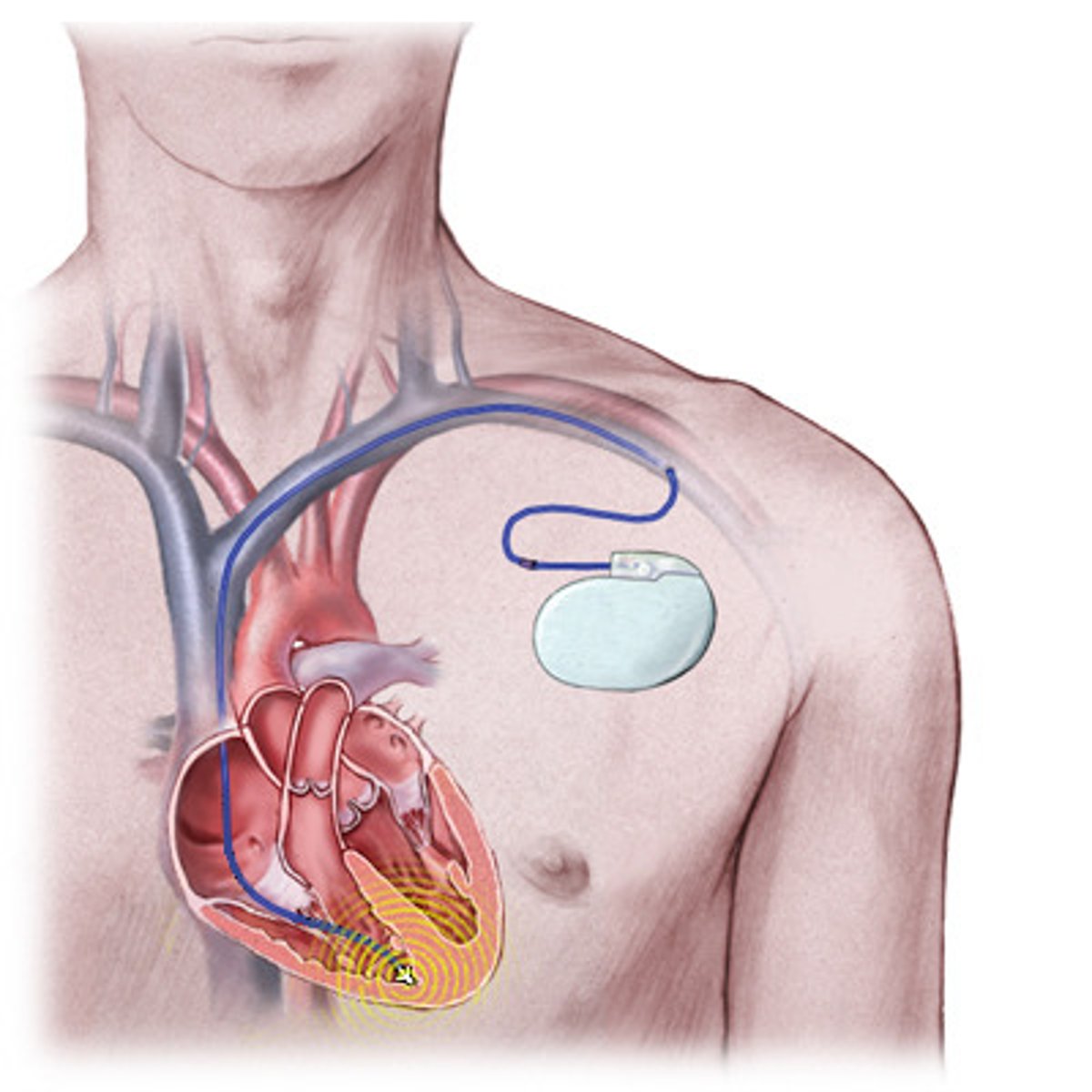
pacemaker insertion
implantation of a battery-powered device inside the chest to control the heart rate and rhythm; coordinates heartbeat with an electrical pulse
defibrillation
lifesaving emergency treatment to restart the heart in cardiorespiratory arrest by delivering high-voltage electoral current through the heart; an AED anaylzes heart rhythm and delivers an electrical shock to stimulate a heart in cardiac arrest
cardioversion
defibrillation technique using low-energy shocks to reset the heart's rhythm back to its normal pattern; helps treat arrhythmias that antiarrhythmic drugs can't treat
angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
lower blood pressure by inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I (an inactive enzyme) to angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor)
ex. Benazepril (Lotensin), lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril)
angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
lower blood pressure by blocking the angiotensin II enzyme from causing vasoconstriction
ex. losartan (Cozaar), valsartan (Diovan)
antiarrhythmics
prevent, alleviate, or correct cardiac arrhythmias (dysrhythmias) by stabilizing the electrical conduction of the heart
ex. amiodarone (Cordarone), digoxin (Lanoxin)
anticoagulants
inhibit the body's natural coagulation response to prevent the formation of clots in blood vessels
ex. warfarin (Coumadin), dabigatran (Pradaxa)
beta blockers
block the effect of adrenaline, which slows nerve pulses through the heart, causing a decrease in heart rate
ex. atenolol (Tenormin), metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol-XL)
calcium channel blockers
block movement of calcium (required for blood vessel contraction) into myocardial cells and arterial walls, causing heart rate and blood pressure to decrease
ex. amlodipine (Norvasc), diltiazem (Cardizem CD), nifedipine (Adalat CC, Procardia)
diuretics
act on kidneys to increase excretion of water and sodium; help reduce fluid build up in the body
ex. furosemide (Lasix), hydrochlorothiazide (Hydrodiuril)
nitrates
dilate blood vessels of the heart, causing an increase in the amount of oxygen delivered to the myocardium, and widen blood vessels of the body, allowing more blood flow to the heart
ex. nitroglycerin (Nitrostat, Nitrogard, Nitrolingual), isosorbide mononitrate (Imdur)
statins
lower cholesterol in the blood and reduce its production in the liver by blocking the enzyme that produces it
ex. atrovastatin (Lipitor), simvastatin (Zocor), simvastatine and ezetimibe (Vytorin)