PSK4U Unit 2 Test Flashcards
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Periosteum
Membrane covering the entire length of bone (has blood vessels and nerves)
Medullary Cavity
Central bone cavity containing marrow (red marrow - blood cell production & yellow marrow - storing fat cells)
Compact Bone
Hard, dense outer bone layer for strength (can be strengthened with exercise)
Cancellous Bone
Spongy inner part of the bone filled with marrow in its small cavity-like spaces
Diaphysis
Shaft of bone
Epiphysis
Ends of bone
Difference between axial and appendicular skeleton
Axial skeleton (80 bones) - skull, vertebrae, and rib cage
Appendicular skeleton (126 bones) - limbs and girdles (pelvic and pectorial girdles help to articulate the limbs respective to the main axial skeleton)
Why are landmarks important (two reasons)
Landmarks are a specific and easily identifiable point on a bone that serves as a reference point to the location of another body structure.
Tells us where muscles (tendons) and ligaments are attached
Tells us where our nerves and arteries are running through
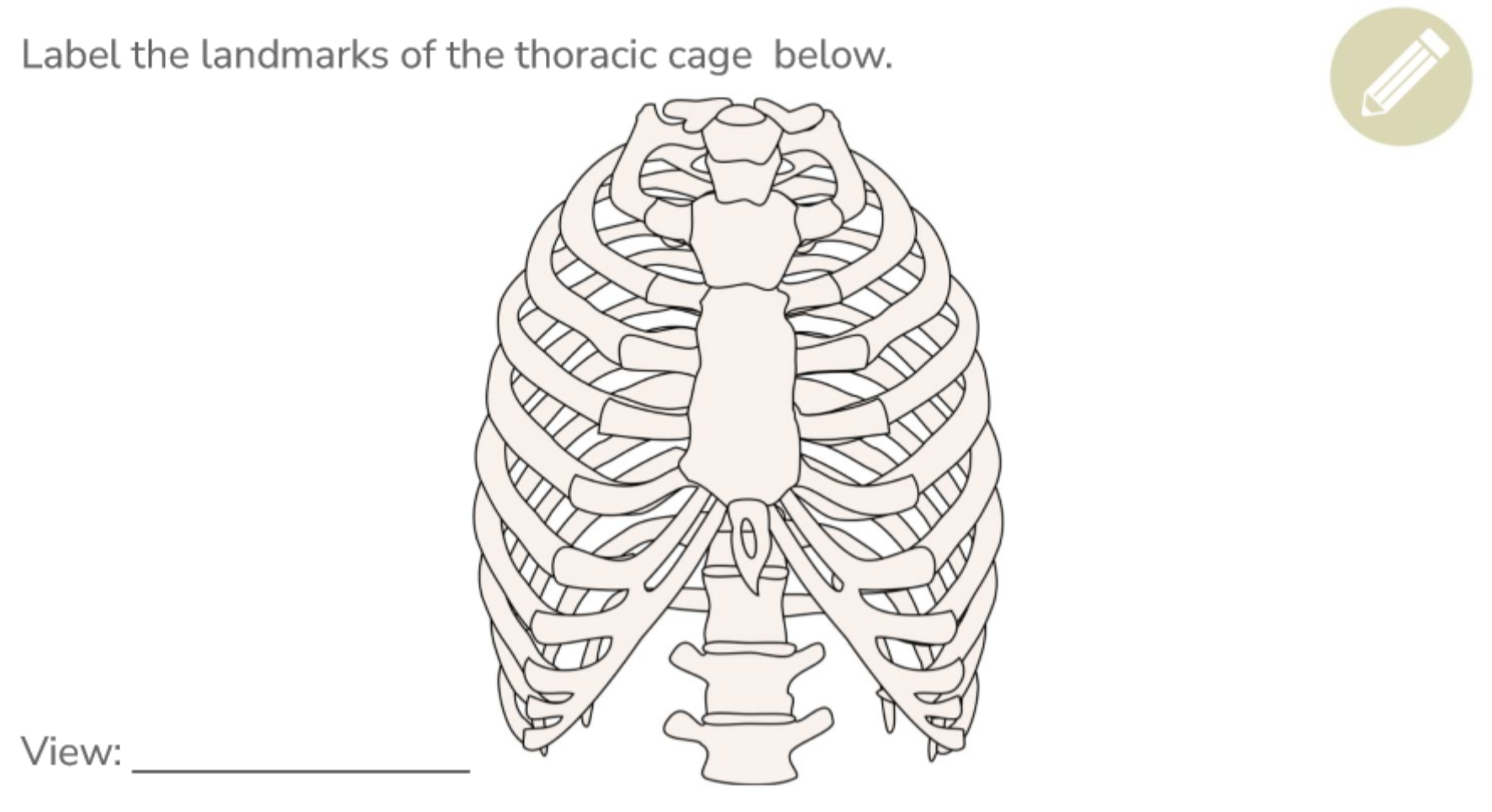
Label all the thoracic cage landmarks (anterior)
All types of fractures
Simple fracture - Crack in bone, no separation
Compound fracture - Separation of bone
Comminuted fracture - Shattering of bone into multiple pieces
How are stress fractures connected to shin splints
Stress fractures - when muscles are too fatigued to absorb shock which transfers to the bone underneath causing tiny cracks in the bone (poor footwear or rapid increase in activity on hard flooring)
Shin splints - inflammation of the muscle and tissue around the lateral or medial side of the tibia which can lead to stress fractures if not treated (overuse of tibia)
Types of muscle tissue
Smooth - walls of internal organs
Cardiac - heart chambers
Skeletal - attached to bones for movement
Types of joint
Fibrous, catilaginous, and synovial joints
Types of synovial joints
Ball-and-socket joint - most mobile out of all the synovial joints with “the ball” of the bone attaching into the “socket” of another
Shoulder or hip joint
Gliding joint - connects flat or slightly curved bone surfaces as they glide against each other
Intercarpal or intertarsal joints
Hinge joint - convex portion of a bone fits to a concave portion of another and can only move in one plane
Phalanx or ulna joints
Pivot joint - rounded portion of a bone fits into the groove of another and rotates in a single axis
Atlanoxial in neck joint
Saddle joint - allows movement in two planes (front to back & side to side) but has no rotation
Thumb joint
Condyloid joint - allow movements in two planes (front to back & side to side) but has no rotation
Wrist joint
What are synovial fluids for
Used to lubricate in synovial joints for smooth movement instead of harsh grinding against the bones
What joints are the most prone to dislocation
The ball-and-socket joints such as the shoulder and hip joints are frequently dislocated due to their unstable nature for wide mobility.
All movements (9)
Flexion ↔ Extension
Abduction ↔ Adduction
Pronation ↔ Supination
Protraction ↔ Retraction
Eversion ↔ Inversion
Reposition ↔ Opposition
Elevation ↔ Depression
Dorsiflexion ↔ Plantarflexion
What are agonist and antagonist movements
agonist - main movement action
antagonist - the counteraction of agonist
The planes and axes
Sagittal → horizontal
Frontal → Antero-posterior
Transverse → longitudinal
The differences between the muscle tissues
Location
Striations
Control
Nuclei
Function
Fibrous joints and example
immovable joints made up of dense fibrous tissue primarily for protection (skull)
Cartilaginous joints and example
slightly movable joints made up of cartilage connections primarily for shock absorption (vertebrael column)
Synovial joints and example
freely movable joints lubricated by synovial fluids for flexibility and movement (shoulder)
What are the connective tissues
Ligaments (bone to bone) and tendons (muscle to bone)
Striations
Series of ridges, furrows, or linear marks on the muscles to help with contraction and power
Functions of mucoskeletal system
Muscles + Skeleton + Connective Tissue
To support body and stay upright
To allow movement
To protect vital organs
To store minerals (calcium & phosphorus)
Girdle functions
Pectorial and pelvic girdle - for limb articulation respective to the main axial skeleton
Label the regions of a long bone
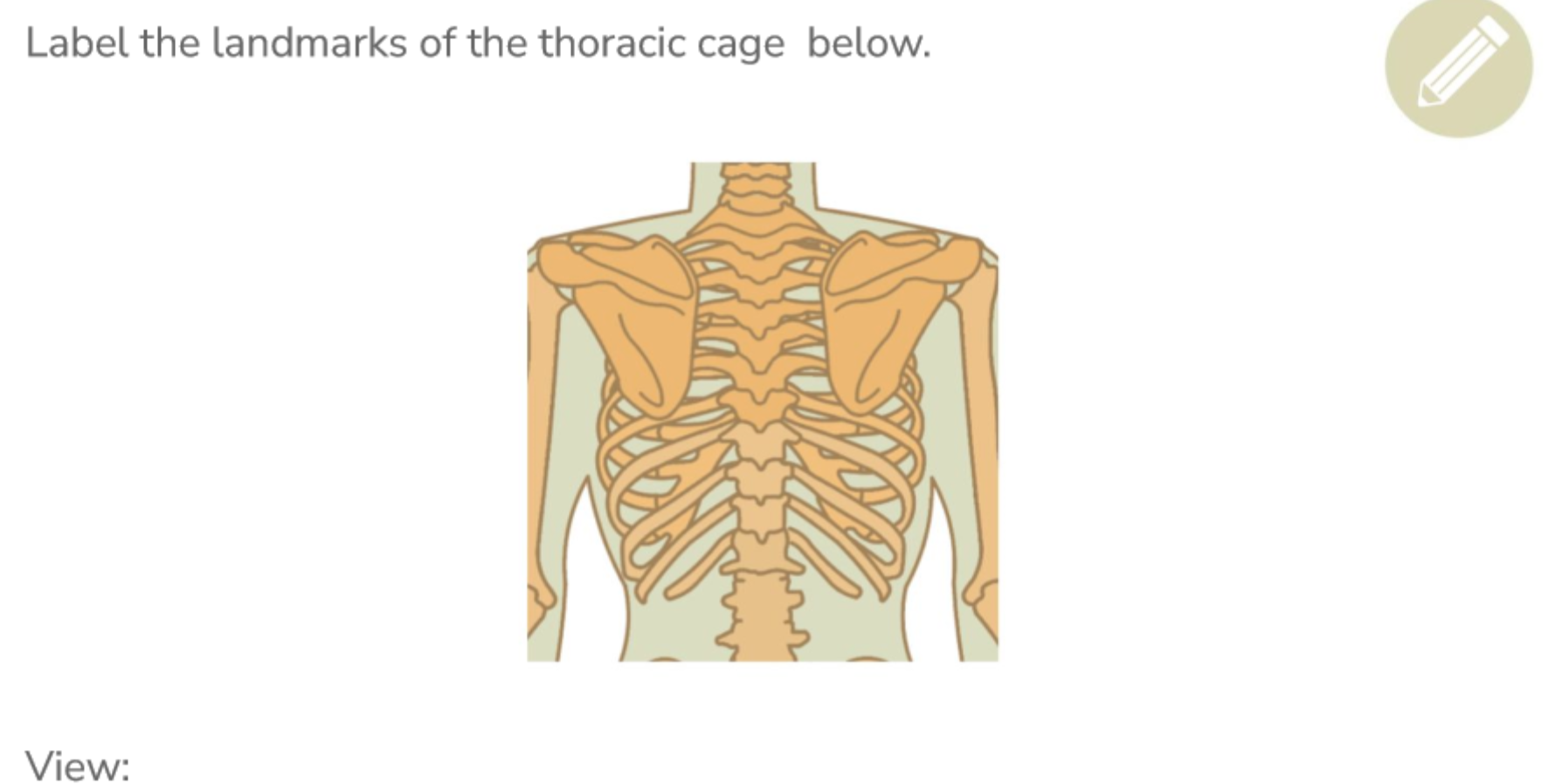
Label all the thoracic cage landmarks (posterior)
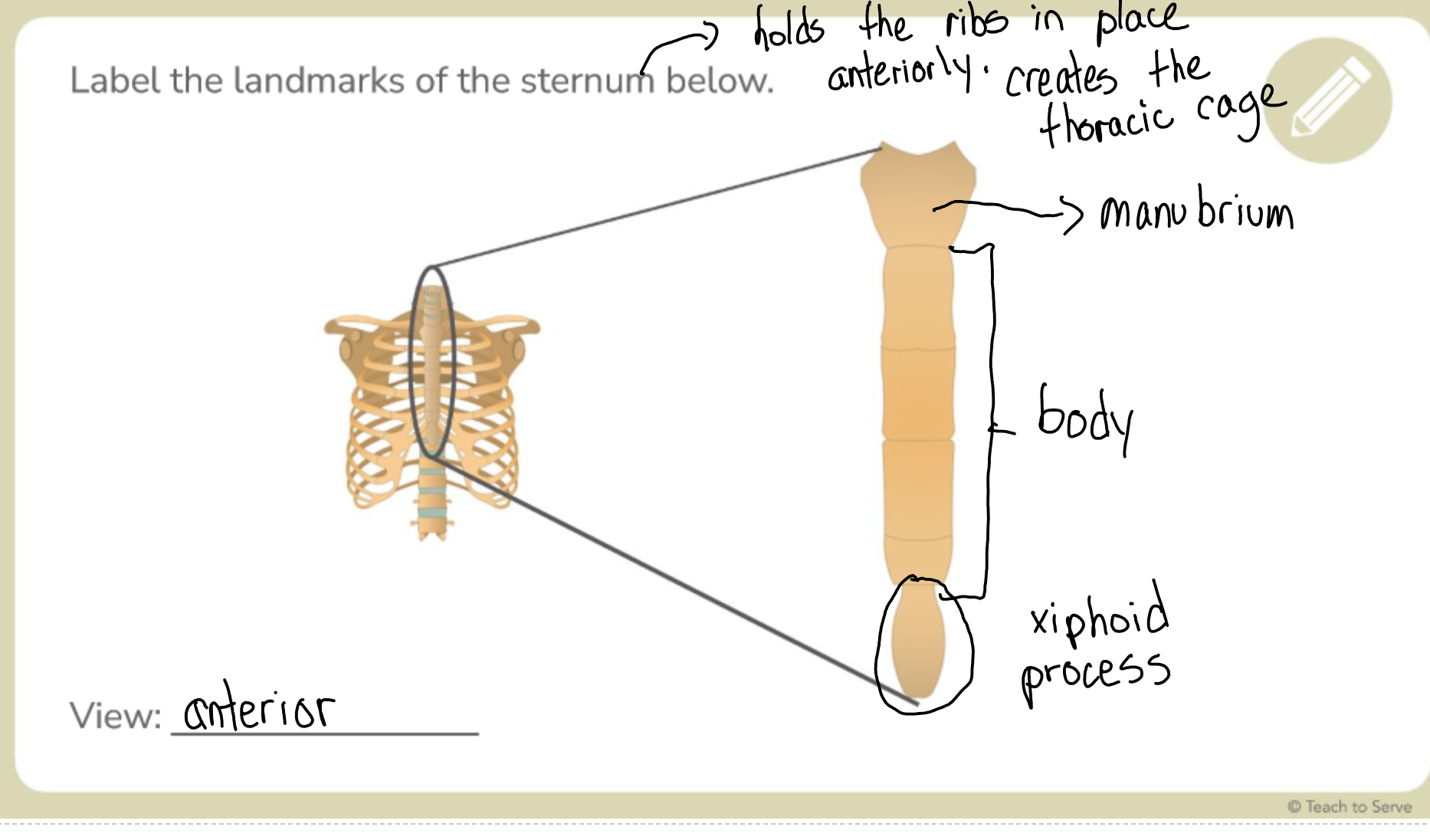
Label the sternum landmarks
Differences between the three types of ribs
True Ribs (7) - directly attached to the sternum and provides protection for lungs
False Ribs (3) - indirectly attached to the costal cartilage which then connects to the sternum and provides elasticity with costal cartilage when breathing
Flotain Ribs (2) - do not attach anteriorly and provides protection for kidney