WBC ID and facts
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
myeloblast picture
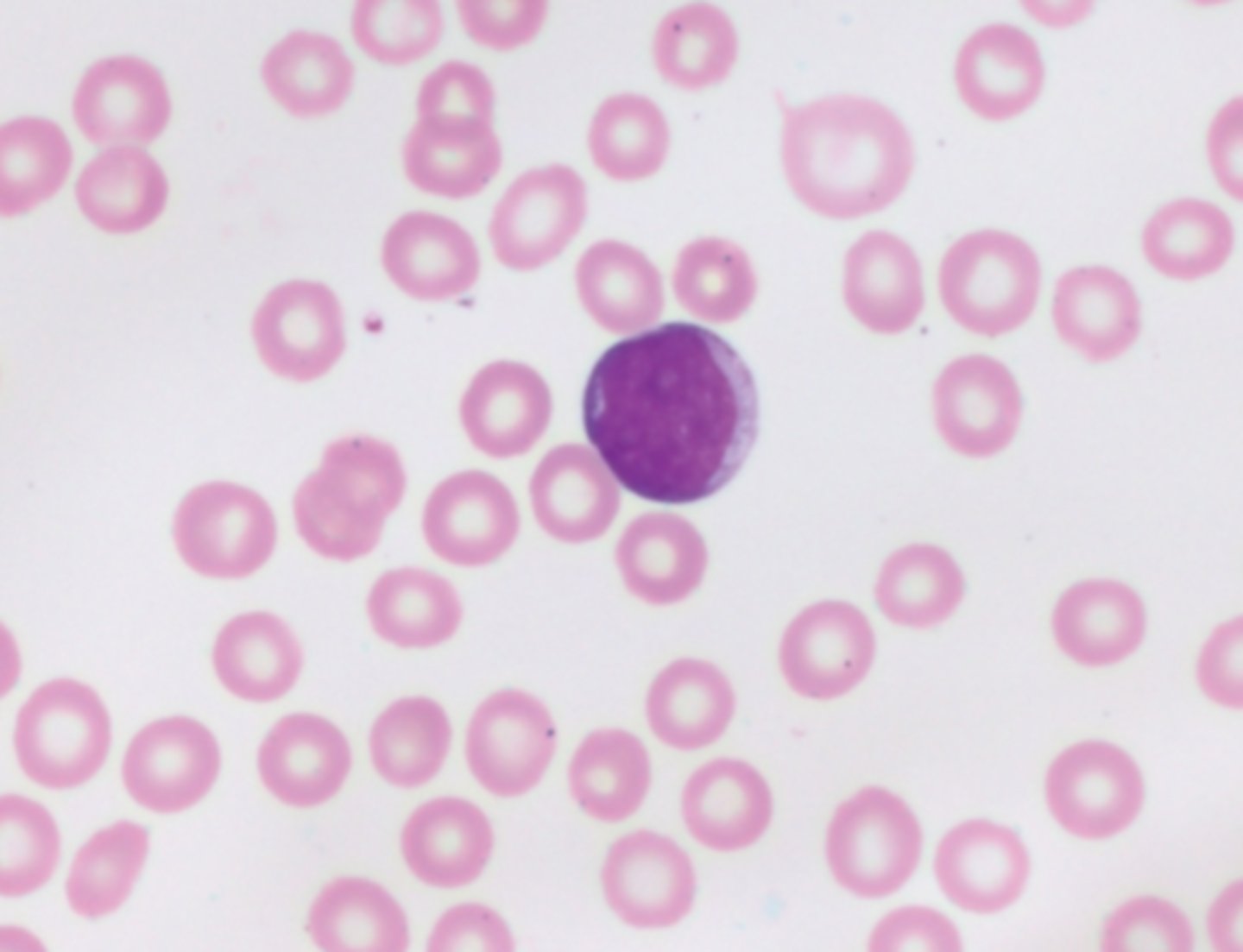
myeloblast
immature bone marrow cell that gives rise to granulocytes
promyelocyte picture
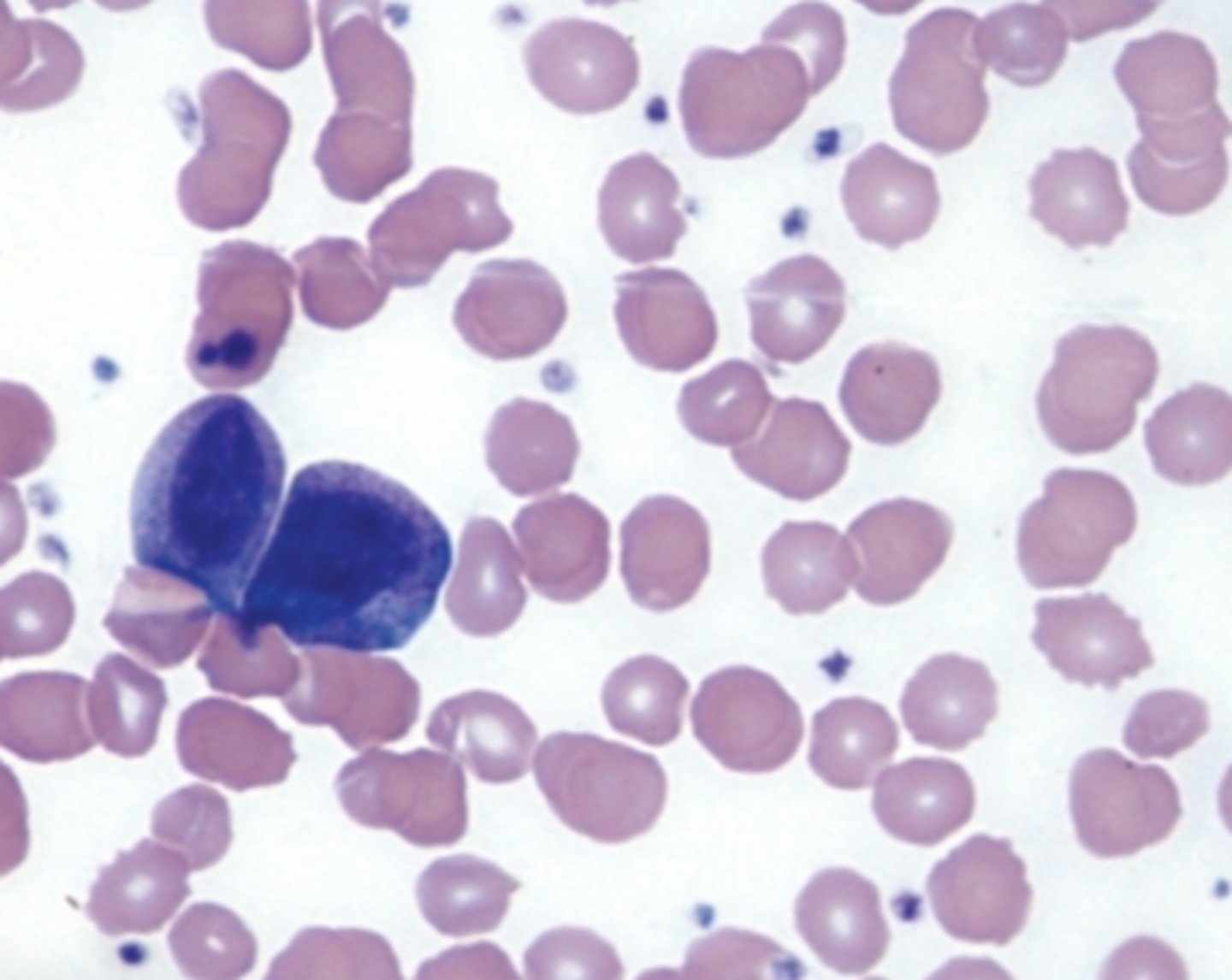
Promyelocyte
Appearance of primary/nonspecific granules
myelocyte picture
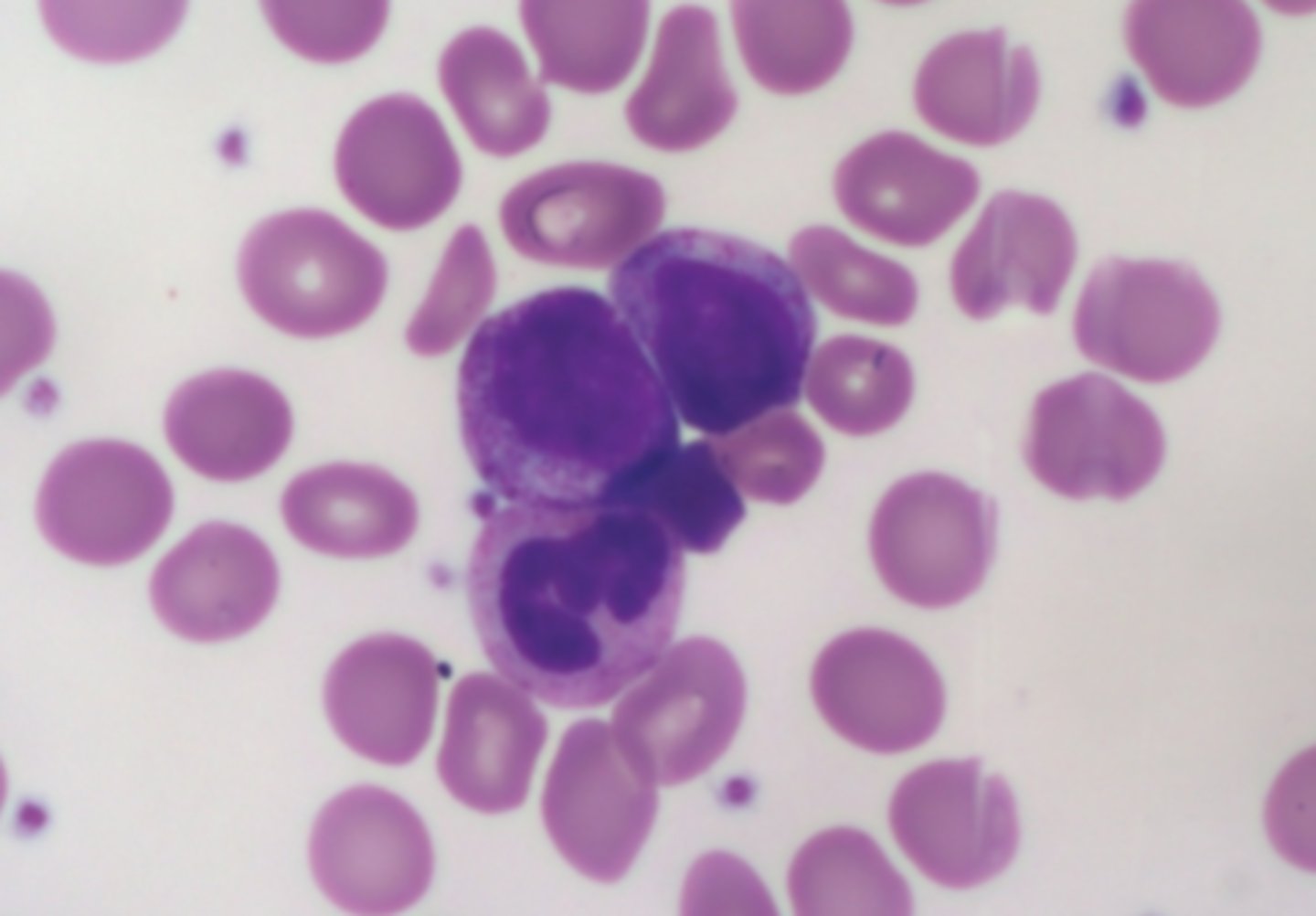
Myelocyte
immature cell that comes from a myeloblast in the red marrow and develops into either a neutrophil, eosinophil, or basophil
Metamyelocyte picture
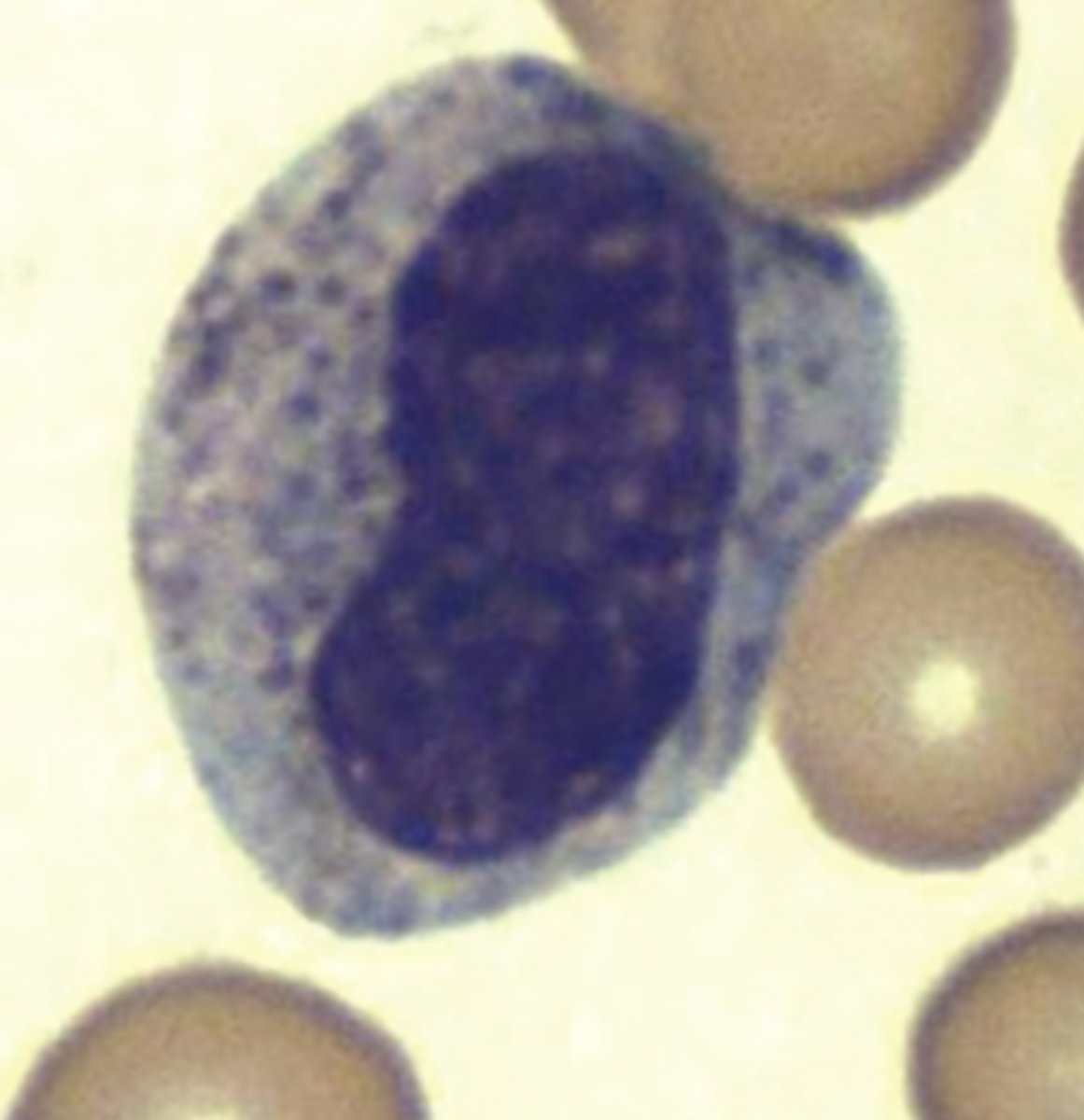
Metamyelocyte
transitional cell intermediate in development between a myelocyte and a mature granular leukocyte
what is the order of granulocyte development?
1st Myeloblast
2nd Promyelocyte
3rd Myelocyte
4th Metamyelocyte
End of proliferative phase
Segmented neutrophil picture
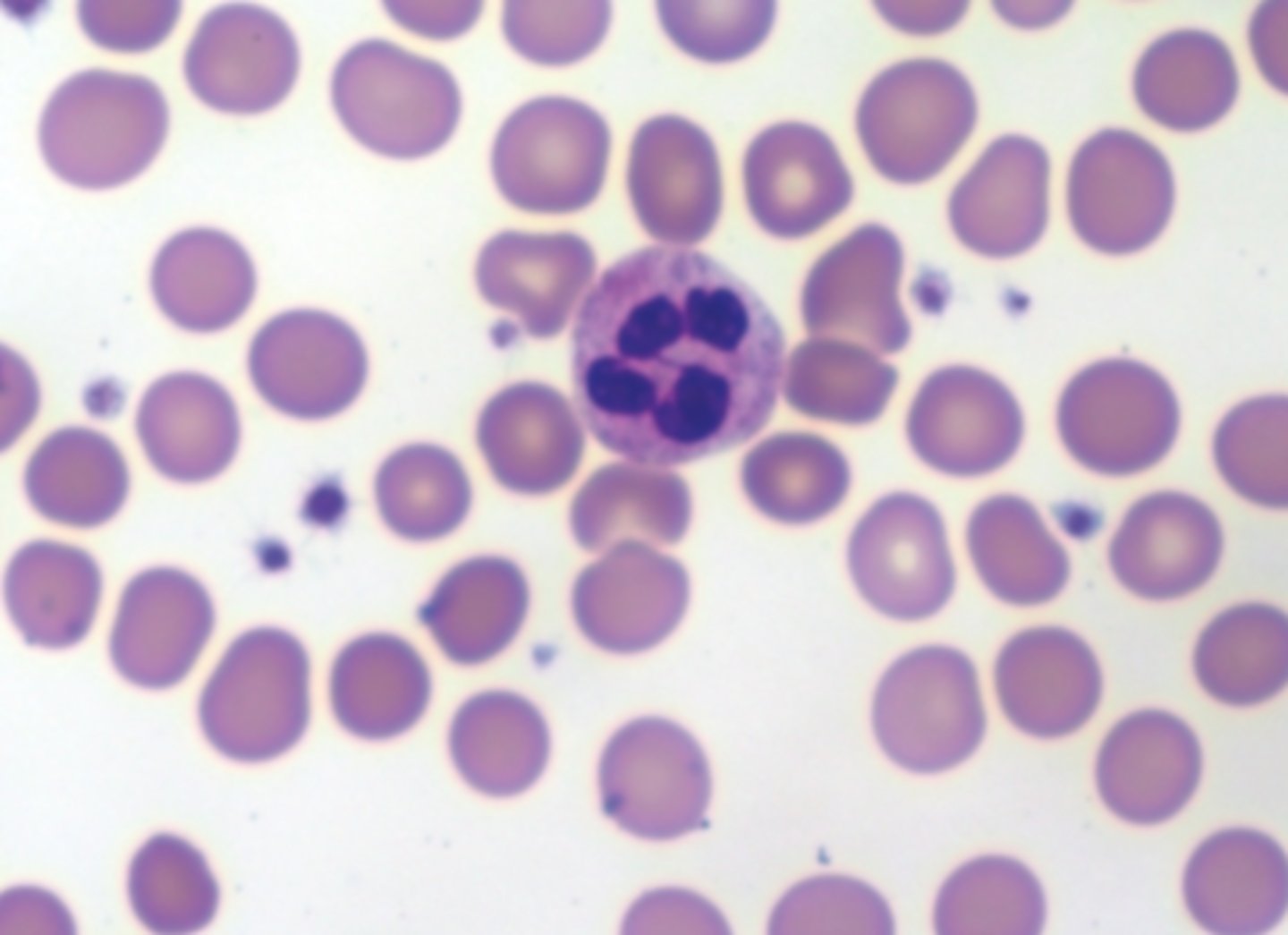
band neutrophil picture
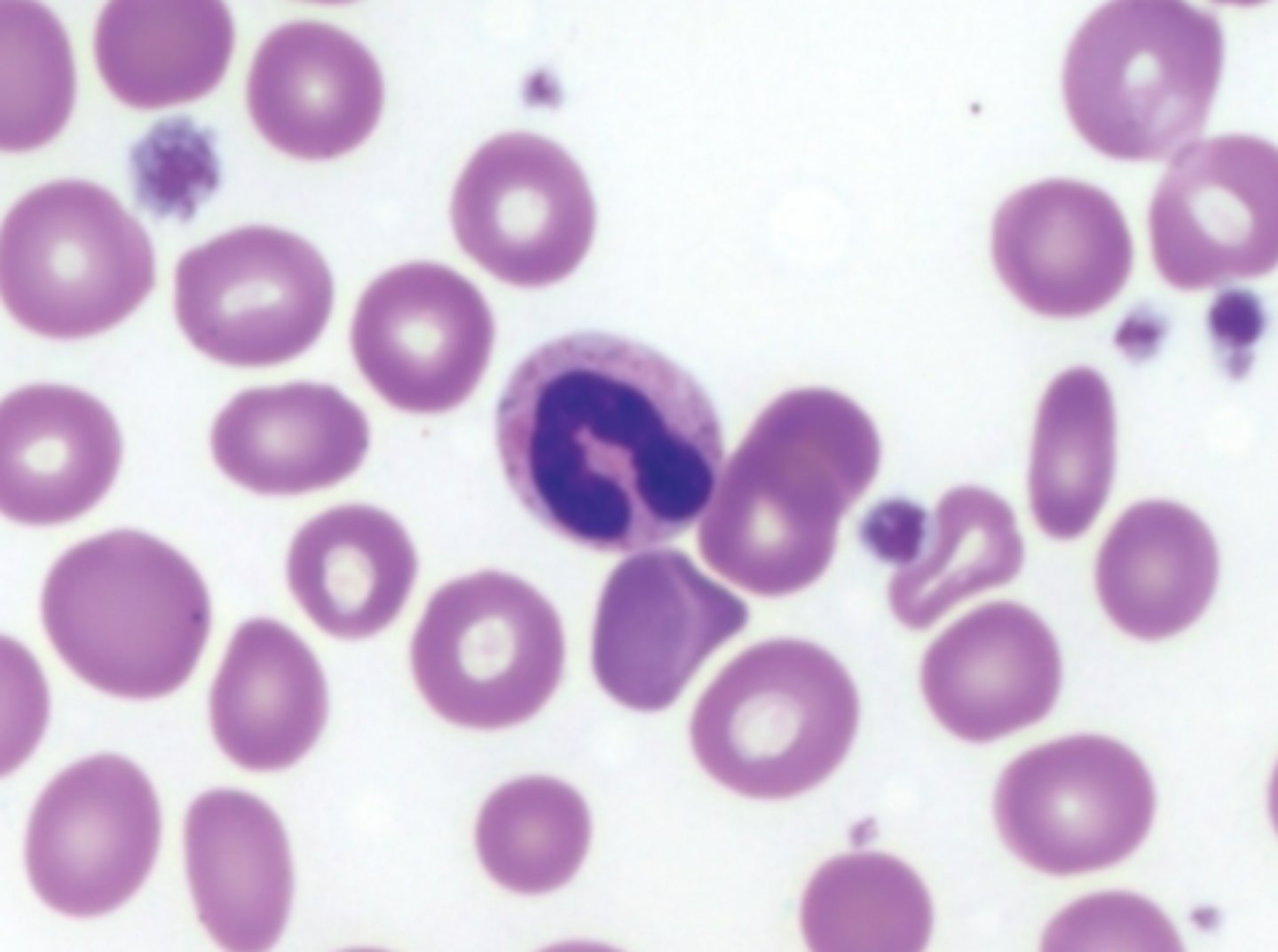
segmented neutrophil characteristics
nucleus: pinched into segments connected with a fine filament, 3-5 lobes distinct lobes, chromatin coarse densely packed,
cytoplasm: abundant, pink
granules: secondary granules fine and specific
10-16 micro meter
most abundant
Band neutrophil characteristics
elongated/curved nucleus
(associated with C, S, or J shape
pink cytoplasm
chromatin is clumped
10-16 micro meter
eosinophil picture
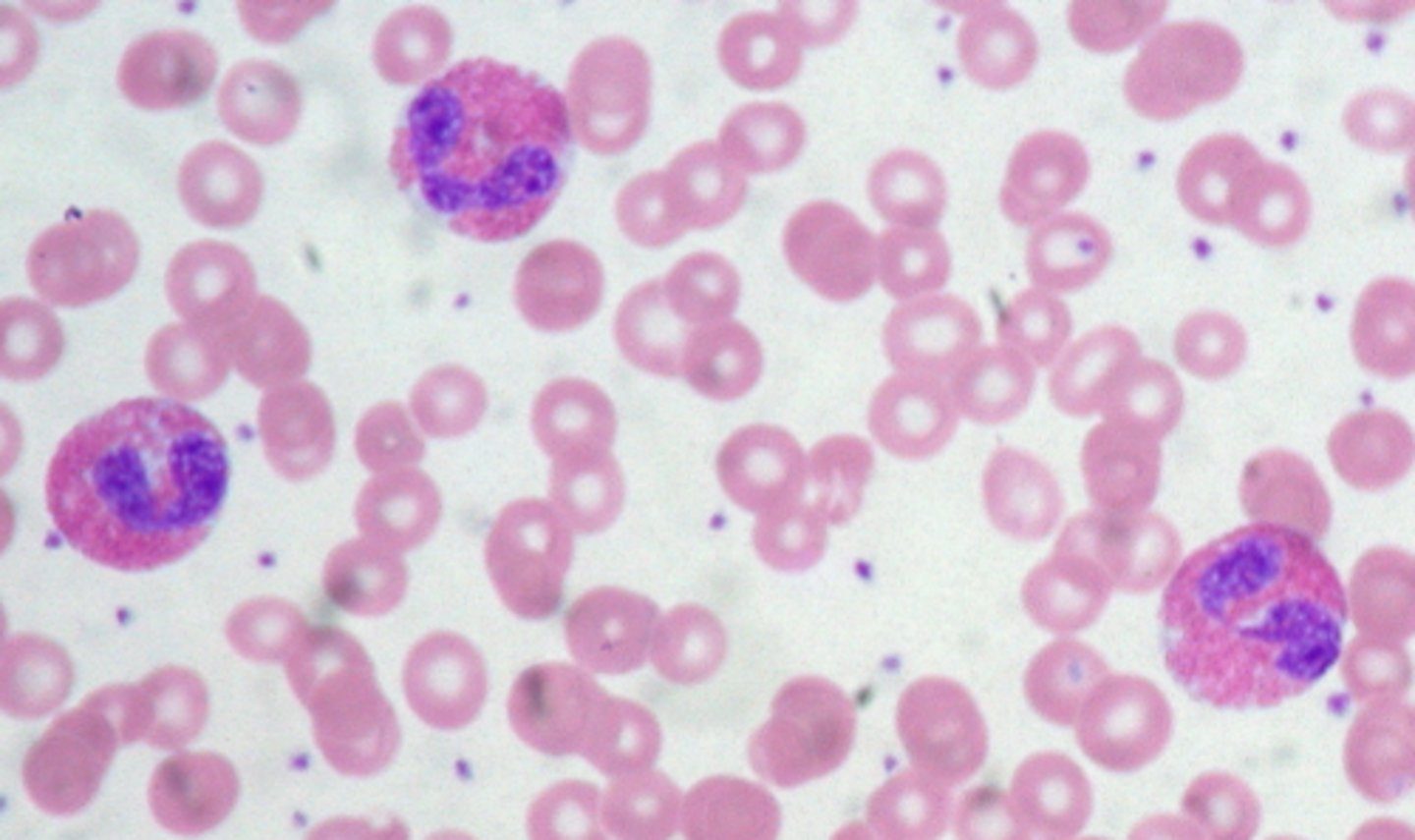
Eosinophil characteristics
nucleus is bilobed,
secondary cytoplasmic granules stain red to orange
cytoplasm is irregular and pink
chromatin is coarse clumped
12-17 micrometers
primary granules rare
bright and colorful
basophil picture
Basophil characteristics
-nucleus 2 lobed no visible chromatin
-cytoplasmic granules stain dark purple
cytoplasm is lavender to colorless
cytoplasm predominates N:C ratio
very dark
steps of monocyte maturation
. Monoblast (same description as myeloblast)
2. Promonocyte◦Size: 12 to 20 micrometers◦Irregular and indented chromatin; gray-blue cytoplasm
3. Monocyte◦Chromatin is loosely weaved, lacy, open, and thin;cytoplasm may have numerous vacuoles
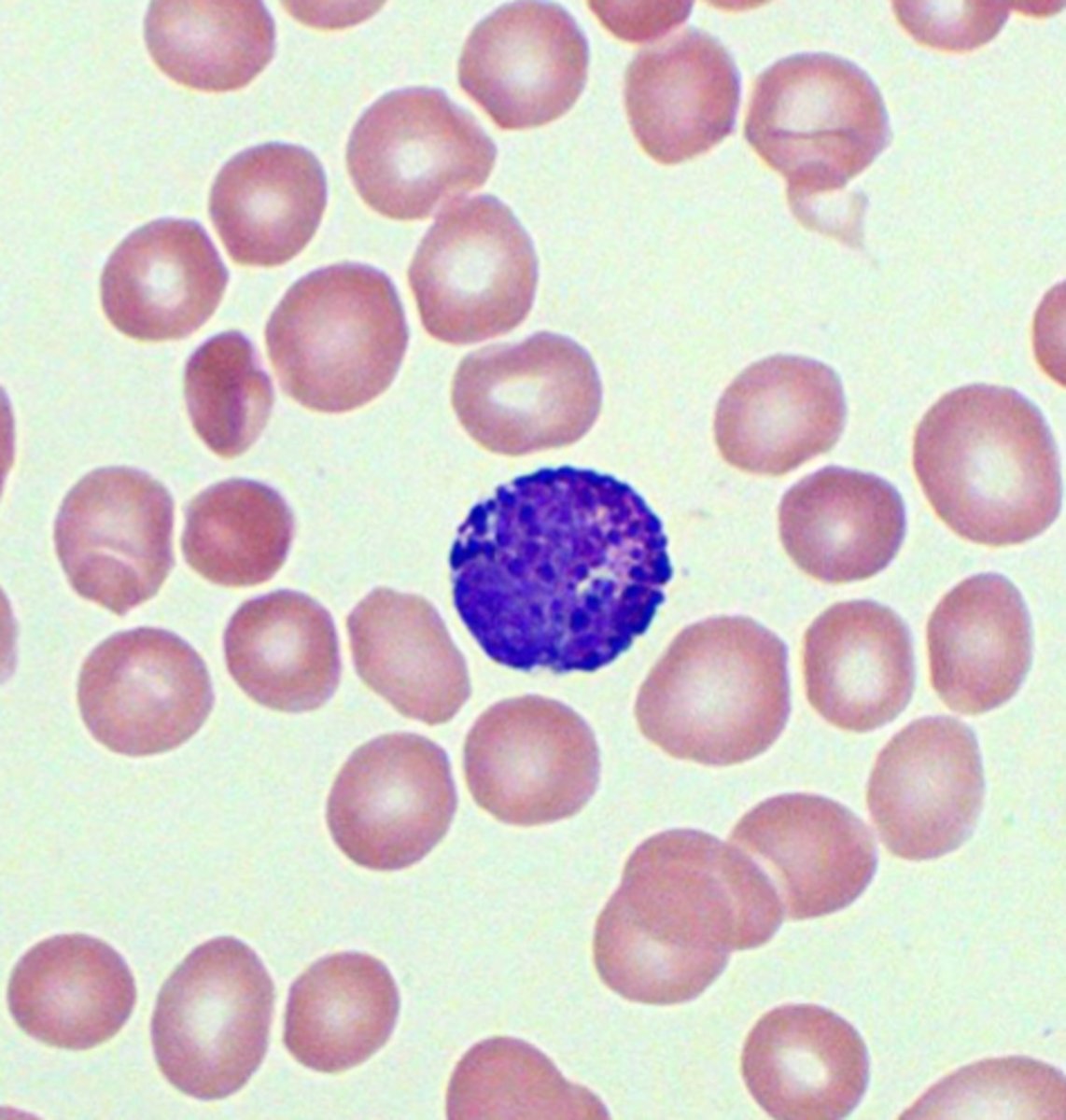
Monocyte characteristics
-Largest WBC
-Have "U"-shaped nucleus
chromatin is lace like
can have vacuoles
color is blue grey for cytoplasm can be irregular shaped
granuoles fine dispered and abundant
monocyte picture
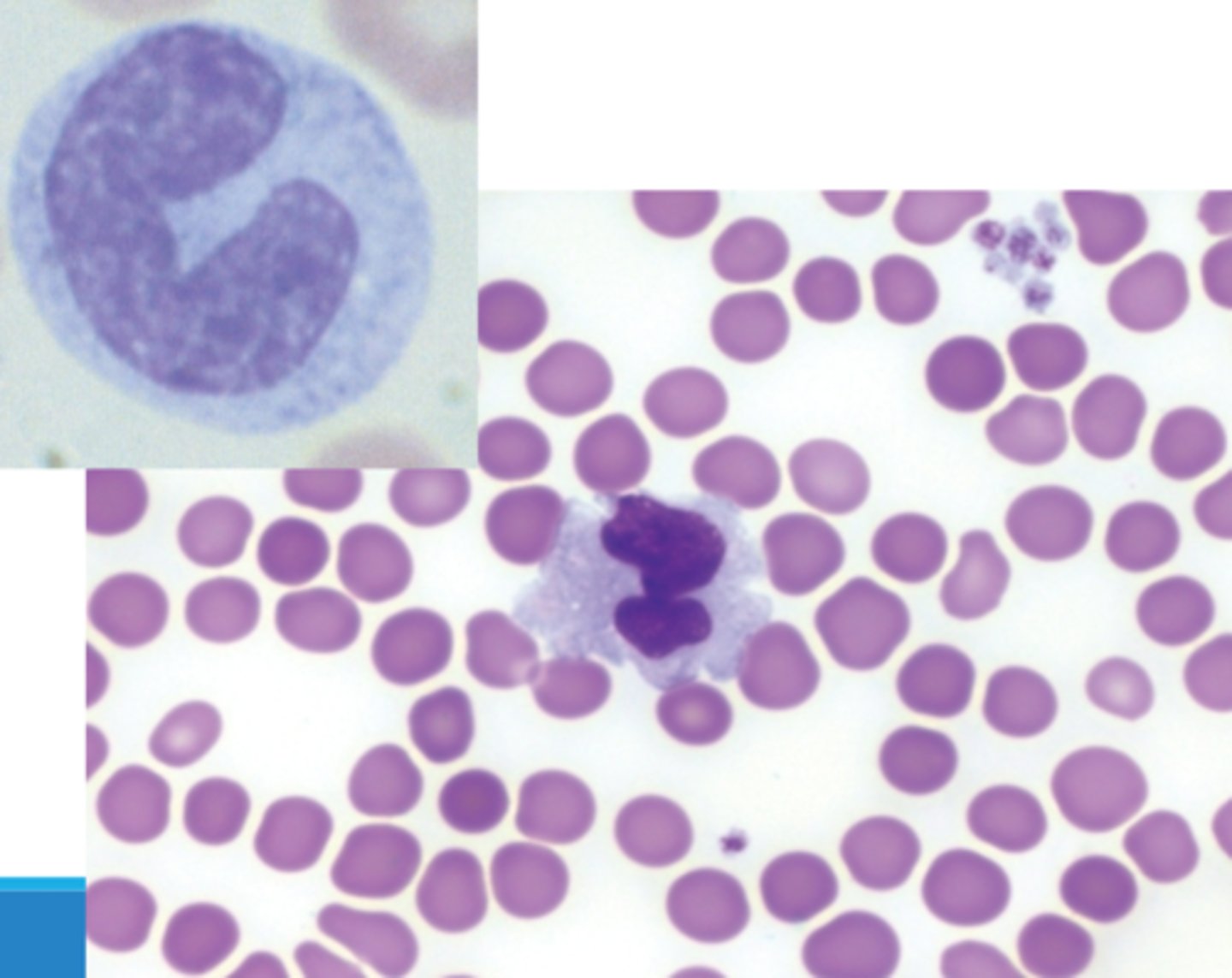
Neutrophil function
phagocytize bacteria
eosinophil function
Kill parasitic worms and is important in chronic allergeries
Smaller round granules rich in acid phosphatase◦Larger containing acid phosphatase
Basophil function
release histamines + herperine (inflammatory response)
acute allergies like anaphylaxis
Contain heparin and histamine
Monocytes/Macrophages function
Ingest and kill microorganisms
Inhibit the growth of intracellular microorganisms
Removal of senescent RBCs, dead cells, and debris
Maintain storage for iron
Synthesize proteins
what cells are myeloid
neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils
what cells are granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
what is the lymphatic cell population?
T cells 60%-80% B cells 10-20% NK cells <10%
T lymphocyte function
Cellular immune response; destroys virally infected cells and cancer cells
mature in thymus
60-80%
B lymphocyte function
antibody production
mature in BW
10-20%
natural killer cell function
Non-selectively attacks non-self cells, especially body cells that have undergone mutation and become malignant, also attacks grafts and transplanted organs (CELL-MEDIATED)
less than 10%
lymphocyte primary maturation sites
BM and thymus
lymphocyte secodnary maturation sites
Spleen, lymph nodes, Peyer's patches of GI tract, and tonsils
lymphocyte maturation order
Lymphoblast
Prolymphocyte
Lymphocyte
lymphocyte picture
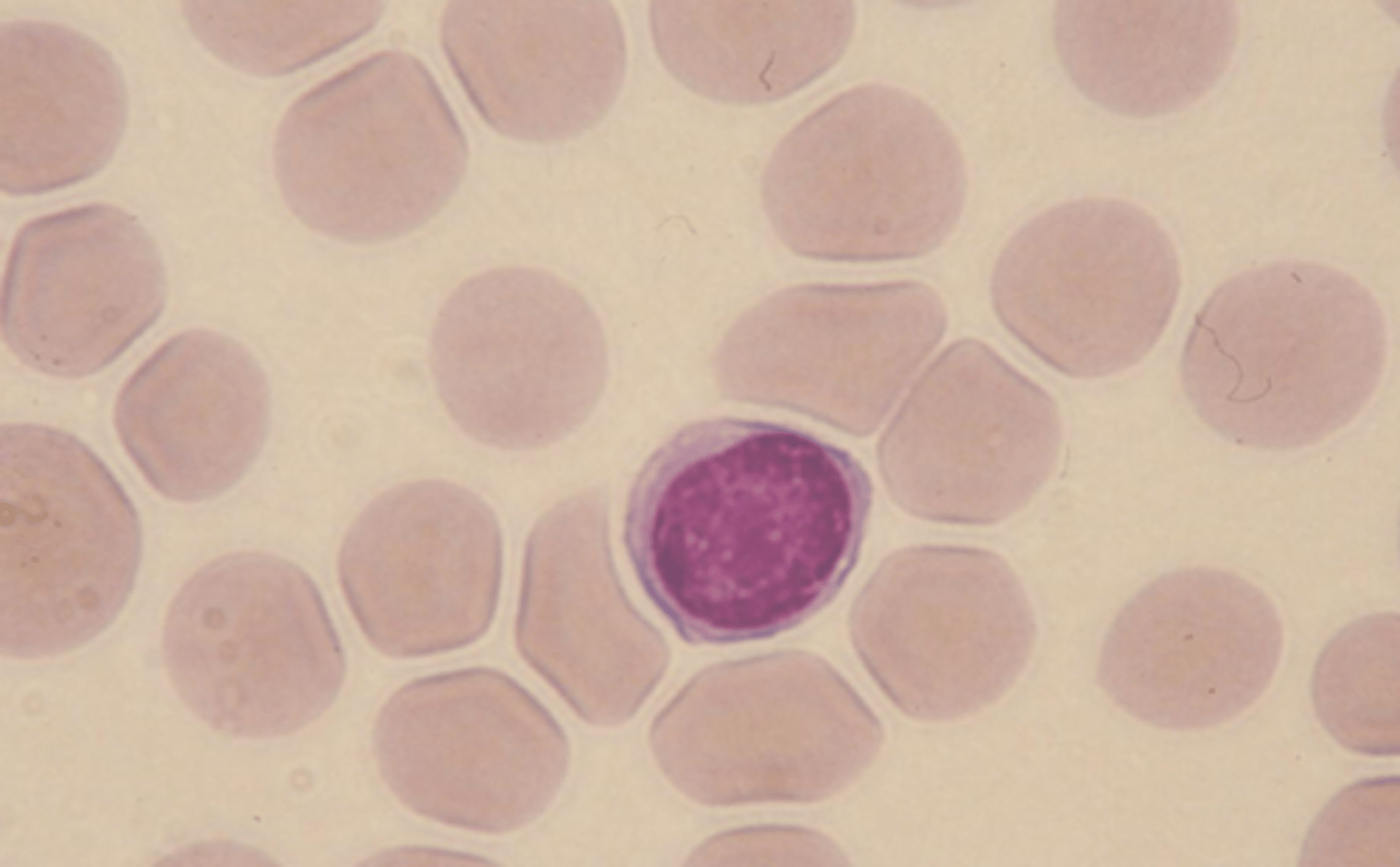
lymphocyte characteristics
small amount of cytoplasm
nucleus is very dark
typically blue
chromatin is dense and clumped
relative percentage lymphocytes at birth
31%
relative percentage lymphocytes at 6 months
61%
relative percentage lymphocytes at 10 yrs
38%
relative percentage lymphocytes at 21 and up
34%
relative percentage of neutrophils
50-70%
relative percentage of lymphocyte
18-42%
relative percentage of monocyte
2-11%
relative percentage of basophil
0-2%
relative percentage of eosinophils
1-3%