unit 5 cell cycle and DNA replication
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
What is the cell cycle?
The series of events a cell goes through as it grows, replicates its DNA, and divides.
Why do cells divide?
For growth, repair, replacement, and asexual reproduction.
Interphase
The phase where a cell spends ~90% of its life performing normal functions and preparing to divide.
G0 phase
Resting phase; cell exits the cell cycle and does not divide.
G1 phase
Cell grows and prepares for DNA replication by synthesizing proteins and enzymes.
S phase
DNA synthesis; genetic material is replicated.
G2 phase
Cell grows and prepares for division; doubles contents and checks DNA.
M phase
The phase that includes mitosis and cytokinesis.
Mitosis
Nuclear division producing two identical nuclei.
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm into two daughter cells.
Cleavage furrow
Indentation that forms during cytokinesis in animal cells.
Cell plate
Structure that forms during cytokinesis in plant cells.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death that occurs in a controlled manner.
How is the cell cycle regulated?
By cyclins, checkpoints, and proteins that monitor DNA damage and spindle attachment.
Cyclins
Proteins that regulate the timing and progression of the cell cycle.
Checkpoints
Control points that ensure conditions are favorable before progressing.
G1 checkpoint
Checks cell size, nutrients, growth factors, and DNA damage.
G2 checkpoint
Checks for DNA damage before mitosis begins.
Spindle checkpoint- Metaphase
Ensures chromosomes are properly attached to spindle fibers.
What happens when regulation fails?
The cell may become cancerous due to uncontrolled division.
Cancer
A disease caused by uncontrolled cell division due to gene mutations.
Mutagen
An environmental agent that causes mutations (e.g., radiation).
Carcinogen
An agent that causes cancer (e.g., tobacco tar).
Oncogene
A mutated proto-oncogene that promotes uncontrolled cell division.
Tumor suppressor gene
A gene that normally slows or stops cell division.
Effect of tumor suppressor mutation
Loss of function leads to uncontrolled division.
Effect of oncogene mutation
Gain of function causes checkpoint failure and rapid division.
How is cancer treated?
Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, biologics, immunotherapy, and RNAi.
Why does chemotherapy cause hair loss?
It targets rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles.
Chromatin
Spaghetti-like form of DNA during interphase.
Chromosome
A condensed structure of DNA made of two sister chromatids.
Chromatid
One identical half of a replicated chromosome.
Sister chromatids
Identical DNA strands joined at the centromere.
Centromere
Region where sister chromatids are joined.
Telomere
End regions of a chromosome.
Spindle fibers
Microtubules that move chromosomes during mitosis.
Centriole
Organelle that helps form spindle fibers in animal cells.
Prophase
Chromatin condenses, nuclear membrane breaks down, spindle fibers form.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up at the MIDDLE of the cell.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and move AWAY to opposite poles.
Telophase
TWO Nuclear envelopes reform; chromosomes unwind.
Nucleic acids
Molecules that store and transmit genetic information.
Monomer of nucleic acids
Nucleotide.
Nucleotide components
Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base.
DNA sugar
Deoxyribose.
RNA sugar
Ribose.
DNA bases
A, T, C, G.
RNA bases
A, U, C, G.
Double helix
The twisted ladder structure of DNA.
Complementary base pairing
A-T and G-C.
Anti-parallel DNA
Two strands run in opposite directions (5’→3’ and 3’→5’).
Type of bonds in DNA
Covalent bonds in backbone, hydrogen bonds between bases.
Why DNA replicates
So each daughter cell gets a complete copy of genetic information.
DNA replication model
Semi-conservative.
Semi-conservative replication
Each new DNA molecule contains one old strand and one new strand.
DNA helicase
Unzips DNA strands at the replication fork.
Replication fork
Area where DNA strands separate.
Primase
Adds RNA primer to start replication.
DNA polymerase III
Adds nucleotides in the 5’→3’ direction.
DNA polymerase I
Removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA.
DNA ligase
“glues” Okazaki fragments together.
Leading strand
Continuously synthesized toward the replication fork.
old strand 3’ to 5’ into fork
Lagging strand
Discontinuously synthesized away from the fork.
old strand 5’ to 3’ into fork
Okazaki fragments
Short DNA fragments formed on the lagging strand.
What can go wrong during replication
Mutations from errors or environmental damage.
Human DNA replication speed
~50 nucleotides per second.
Cancer is contagious
False.
Cancer is a single disease
False; it includes over 100 diseases.
Cancer caused by abnormal genes
True.
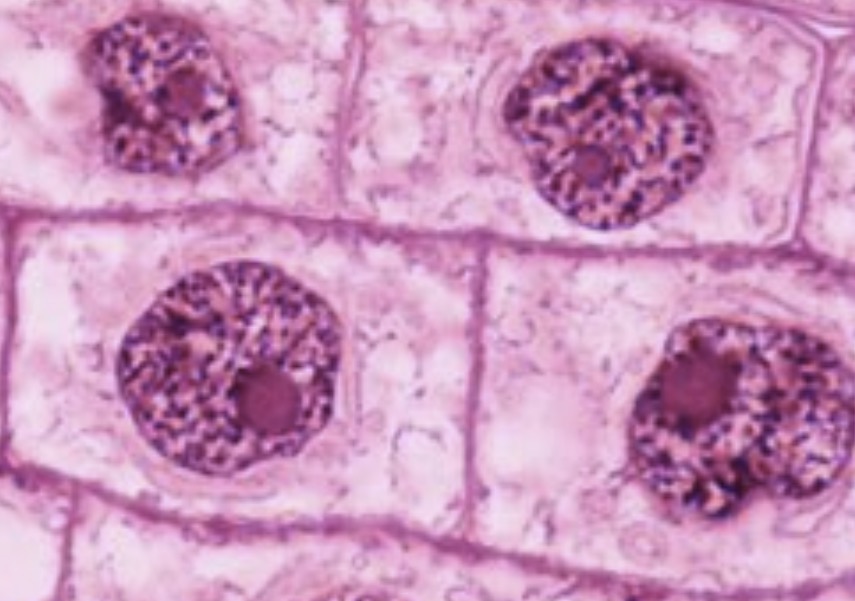
What phase is this?
Interphase
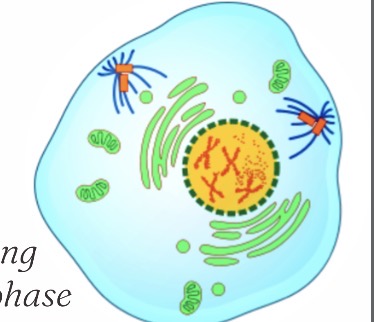
What phase is this?
Prophase
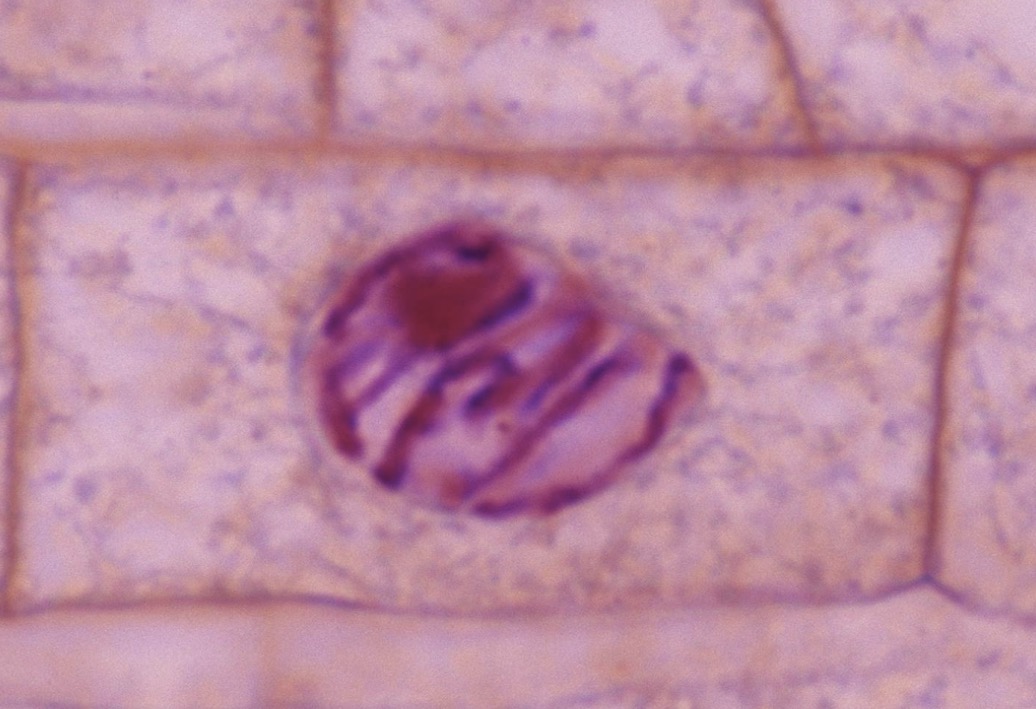

What phase is this?
Metaphase
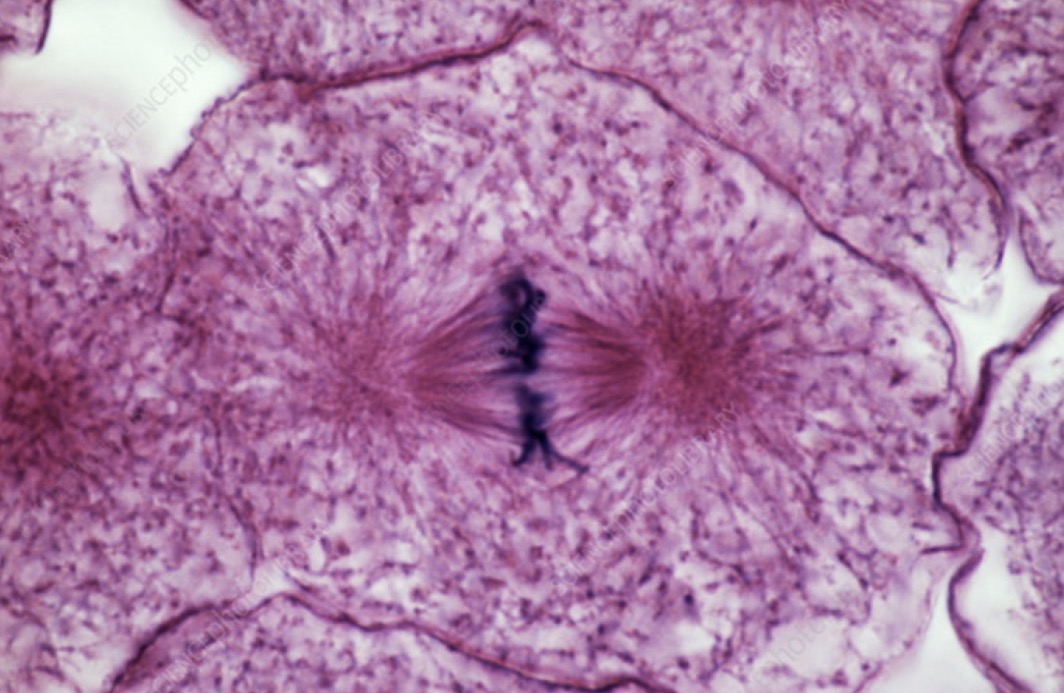

What phase is this?
Anaphase
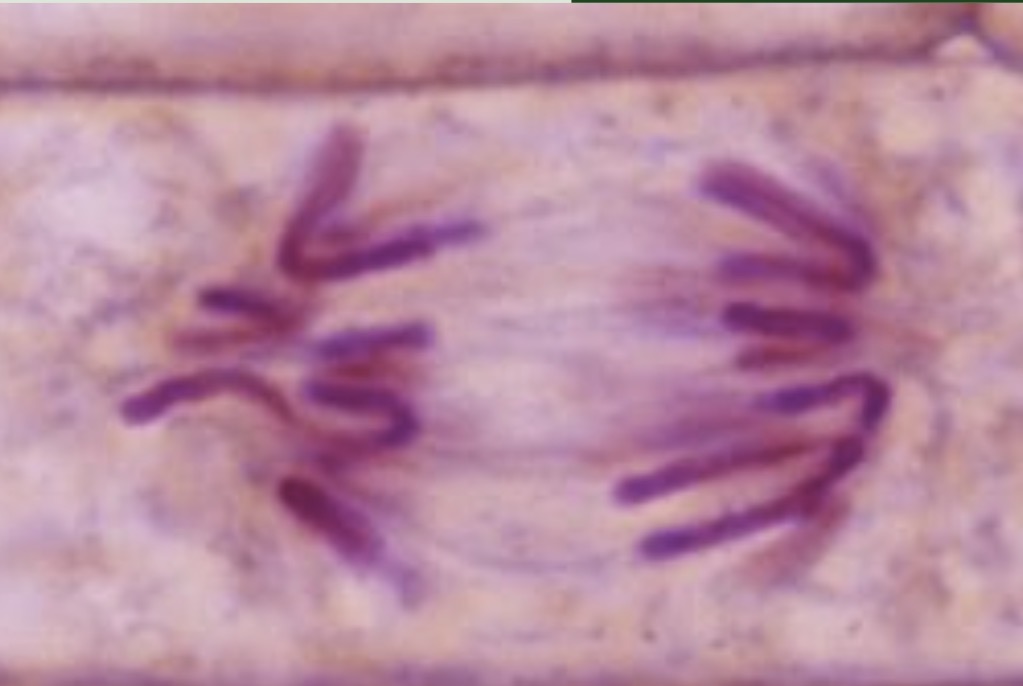
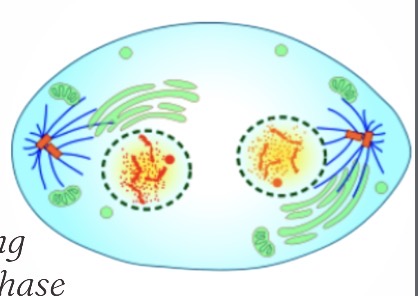
What phase is this?
Telophase
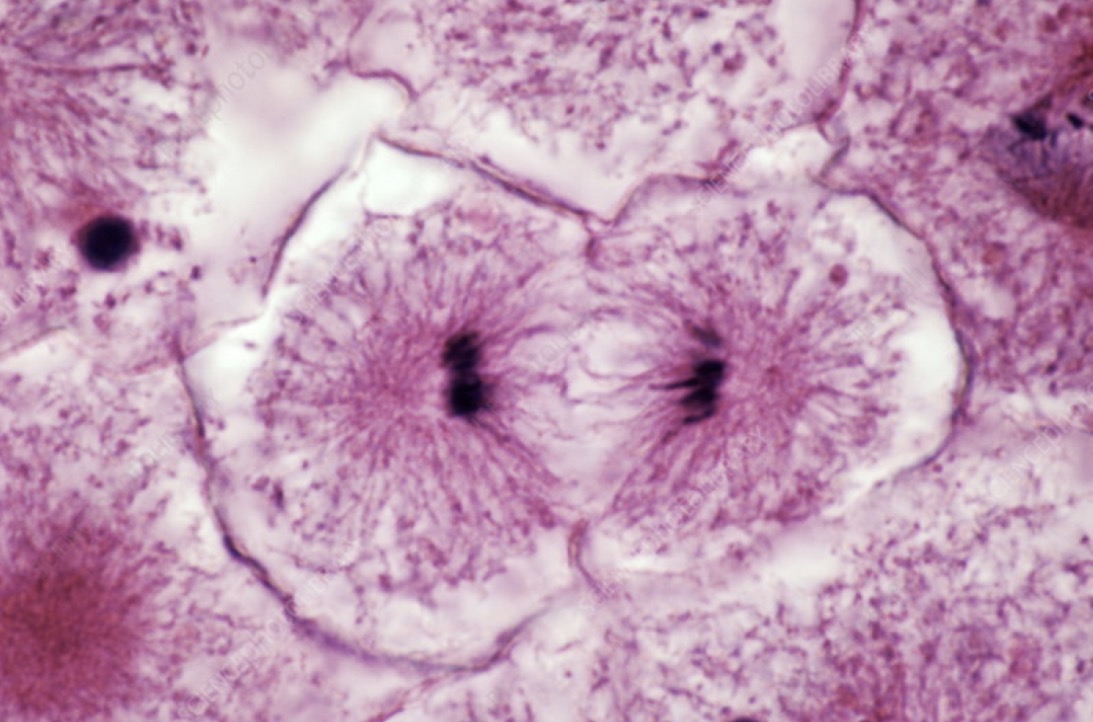

What is this phase called?
Cytokinesis
RNA
helps convert DNA message into proteins
DNA
stores genetic information