CMPP: Sodium and Potassium Disorders
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
water balance
hypo-- water EXCESS
hyper --water DEFICIT
hyponatremia/hypernatremia are primarily disorders of...
increased, dilute
hyponatremia results in _____ intravascular water, and the body is unable to excrete a _____ urine
decreased, concentrated
hypernatremia results in _____ intravascular water, and the body is unable to excrete a _____ urine
Hyponatremia
any process that expands the vascular volume around a fixed total body Na and that limits water excretion may result in THIS condition.
increase in intravascular water
inability of the body to appropriately respond by excreting a dilute urine
--> are the kidneys unable to keep up with the primary problem, or are the kidneys the problem?
two factors required for hyponatremia to occur
H2O content rises due to ingested quantity exceeding the normal physiologic capacity of the kidneys to excrete H2O
how does polydipsia cause hyponatremia?
Psychogenic polydipsia
psychiatric craving for excess water
Beer potomania
Hyponatremia in chronic beer drinkers; >4L
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
primary determinant for renal water handling; secreted by posterior pituitary in response to high serum osmolality
circulating volume
a high serum osmolality indicates a decreased...
euvolemia, normal serum Na
the body prioritizes maintaining _________ over maintaining _________.
the body perceives the decreased effective circulating volume caused by these conditions as a hypovolemic state
--> results in H2O reabsorption and hyponatremia
--> still technically being "appropriately" released
how do diseases with decreased effective circulating volume (CHF, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome) result in secretion of ADH?
Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion
ADH is secreted despite no perfusion or osmotic-related stmiilu
low, low, euvolemia
the net result of SIADH is a ____ serum Na, ___ serum osmolality in the setting of __________.
inappropriately high osmolality (concentrated urine)
--> urine should be dilute because the body should be interpreting low serum Na as the body having too much water
in SIADH, urine studies yield an...
pneumonia, TB, acute respiratory failure, mechanical ventilation
pulmonary disorders that can cause SIADH
meningitis, encephalitis, CVA, head trauma, acute psychosis
neurologic and psychiatric disorders that can cause SIADH
paraneoplastic syndromes
how does malignancy cause SIADH
narcotics, chemo, TCAs, anti-seizure meds, antipsychotics
what drugs are indicated in causing SIADH
neurologic -- since neurons are VERY sensitive to fluid changes
hyponatremia primarily results in what kinds of symptoms?
serum osmolality, serum Na
the development of symptoms in hyponatremia is due to changes in _________ rather than changes in _______.
Pseudohyponatremia
falsely low serum sodium level with no physiologic consequences because the serum osmolality is normal.
elevated plasma proteins (multiple myeloma)
hypertriglyceridemia
hyperglycemia
common causes of pseudohyponatremia
elevated blood glucose transiently increases serum osmolality
elevated blood glucose causes water to be drawn into the vasculature --> additional H2O drawn into the vasculature dilutes the Na, resulting in hyponatremia
how can hyperglycemia cause a pseudohyponatremia?
pseudohyponatremia -- treat underlying cause
if a patient is hyponatremic, and their measured serum osmolality is normal/high, what is their diagnosis/tx?
determine URINE osmolality
if a patient is hyponatremic, and their measured serum osmolality is low, what is your next step?
psychogenic polydipsia and beer potomaina
--> dilute urine in response to hyponatremia is an APPROPRIATE response, so the kidneys are doing their best by excreting as much free water as possible.
--> true hyponatremia
if a patient is hyponatremic, their measured serum osmolality is low, and their urine osmolality is low, what is the likely diagnosis?
determine the patient's volume status!
if a patient is hyponatremic, their measured serum osmolality is low, and their measured urine osmolality is high, what is your next step?
late-stage CHF, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome (body has perceived these conditions as low volume states)
if a patient is hyponatremic, their measured serum osmolality is low, their measured urine osmolality is high, and they are HYPERvolemic, what is their diagnosis?
SIADH
if a patient is hyponatremic, their measured serum osmolality is low, their measured urine osmolality is high, and they are EUvolemic, what is their diagnosis?
Na losses exceed H2O losses
if a patient is hyponatremic, their measured serum osmolality is low, their measured urine osmolality is high, and they are HYPOvolemic, what is their diagnosis?
fix hyponatremia slowly
pseudohyponatremia -- fix underlying cause
how to treat a hyponatremic pt who is asymptomatic
Central pontine myelinolysis
complication of correcting hyponatremia too rapidly in asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic patients
blood becomes very concentrated --> water moves out of cells --> cells lyse and this causes irreversible neuronal damage
how does overly rapid correction of hyponatremia result in CPM?
irreversible dysarthria, dysphagia, flaccid paralysis, and DEATH
CPM can result in...
chronic asymptomatic hyponatremia
--> if you were to treat, do IT SLOWLY OVER SEVERAL DAYS
what is the most common presentation of hyponatremia?
0.9% NS
tx for hypovolemic hyponatremia
treat underlying cause
H2O restriction and administration of a loop diuretic
tx for hypervolemic hyponatremia
water restriction
identify and treat the underlying cause
tx for SIADH
severe neurologic dysfunction (intractable seizures)
severe symptomatic hyponatremia is defined as...
3% hypertonic saline -- rate of collection is slowed once clinical situation improves
tx for severe symptomatic hyponatremia
free H2O deficit
hypernatremia is most commonly secondary to...
hypothalamic osmoreceptors get stimulated, resulting in increased thirst and ADH secretion --> excretion of maximally concentrated urine
how does the body normally try to compensate for hypernatremia?
hypernatremic dehydration
what is the most common cause of hypernatremia?
skin (evaporations and burns)
respiratory tract insensible losses
GI tract (DIARRHEA)
non-renal causes of hypernatremia
Loop diuretics (due to excretion of excess free water)
Osmotic diuresis (extensive free H2O loss -- usually secondary to glycosuria)
DI (results in ADH deficiency)
renal causes of hypernatremia
Central Diabetes Insipidus
impaired ADH secretion from the posterior pituitary
IDIOPATHIC, brain tumors, cranial surgery, head trauma
causes of central diabetes insipidus
nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
kidneys are unable to respond to ADH
intrinsic renal diseases and various meds (LITHIUM)
causes of nephrogenic DI
physical restrictions (institutionalized, handicapped, post-op, intubated)
mentally impaired (delirium, dementia)
hypothalamic dysfunction (primary hypodipsia)
what are some causes of an impaired thirst response?
depends how quickly Na rises -- shrinking of brain cells if it comes on quickly
Focal neurologic deficits
presentation of hypernatremia
polyuria
renal causes of hypernatremia will have concomitant...
increased aldosterone and increased corticosteroid states
if a patient who is hypernatremia is also hypervolemic, the ddx includes...
they are causing the reabsorption of both water and salt -- so there is a TON of salt and a TON of water being retained
why would increased aldosterone/corticosteroid states cause hypernatremia with hypervolemia?
hypokalemic -- secretes K+
what would you expect your serum potassium level to be in one with hyperaldosteronism and in Cushing's snydrome?
kidneys produce a SMALL amount of highly concentrated during with low Na
if a hypernatremic patient is also hypovolemic, what is the appropriate renal response?
the body wants to hold onto water more than it wants to correct the Na issue --> and the best way to retain water is to also retain salt --> so there is little to no Na in the urine
why is the urine produced by the kidneys in a hypernatremic hypovolemic state low in Na?
insensible fluid losses and GI losses (water losses > Na losses)
primary hypodipsia
what are the primary ddx considerations in one with hypernatremia that is hypovolemic
defect in renal H2O conservation -- DI
if a patient who is hypernatremic and hypovolemic is producing high volumes of dilute urine, what does that indicate?
DDAVP test
test that determines the cause of hypernatremia in the setting of hypovolemia and high urine volume; synthetic form of ADH is given intramurally, and it helps to differentiate central DI from nephrogenic DI
increased urine osmolality -- central DI
unchanged urine osmolality -- nephrogenic DI
what are the different results of the DDAVP test what what do these results indicate?
osmotic diuresis -- kidneys are doing their best to put out a concentrated urine in a a highly concentrated environment, but they cannot keep up with the osmotic load (high volume)
if a patient is hypernatremic, what diagnosis should be considered if the urine volume is inappropriately high but the urine osmolality is appropriately high?
overly aggressive tx can lead to rapid fluid shifts and excess H2O entering the brain cells -- cerebral edema
why is rapid correction of hypernatremia dangerous?
Idiogenic osmoles
Osmotically active substances generated in neurons. The neuron can increase or decrease the number of idiogenic osmoles to balance its osmolarity against that of plasma and the extracellular fluid; can occur when hypernatremia develops gradually.
manage underlying disease
tx for hypervolemic hypernatremia
by mouth/NG tube -- reduces risk of iatrogenic complications
it is safest to administer H2O...
0.9 NS (properly functioning kidneys will excrete the excess Na)
tx for unstable hypernatremia
once hemodynamic status is stablized
in one with unstable hypernatremia, when should fluid be changed to 0.45 NS
intranasal DDAVP
tx for central DI
low Na diet + thiazide diuretic
tx for nephrogenic DI
within the cells
where is most potassium located in the body?
aldosterone allows for K+ to get secreted at the collecting duct in exchange for Na
how does aldosterone help to maintain K homeostasis?
They INCREASE the serum K, since it blocks the component of the RAAS system that allows for K+ to be secreted
how do ACEi/ARBs affect the serum K?
decreased K intake
increased net K loss
shift of K from intravascular space into the cells
what are the three general causes of hypokalemia?
GI losses (N/V/D)
Evaporative losses
what are some non-renal causes of increased net K loss?
MORE COMMON!
--> diuretic use or osmotic diuresis (glycosuria)
--> primary hyperaldosteronism
--> secondary hyperaldosteronism
--> Cushing's syndrome
what are some renal causes of increased net K loss?
alkalemia (HCO3)
exogenous insulin
SABA
what are some causes of transcellular shift in hypokalemia?
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis
rare genetic disease that result in transcellular K shifts and episodic weakness
prominent effects on muscles (cramps) and cardiac rhythm (dysrhythmias)
--> can lead to hypoventilation, paralysis, ileus, constipation
presentation of hypokalemia
the body tries to correct metabolic alkaloses by exchanging H ions for K ions
H ions enter vasculature in exchange for K ions which enter the cell
--> primary hypokalemia can also result in a metabolic alkalosis
how does the body's method of compensation for metabolic alkaloses lead to hypokalemia?
Mg
low K and low __ often occur together.
increased urinary K excretion
what would indicate an inappropriate renal response to hypokalemia?
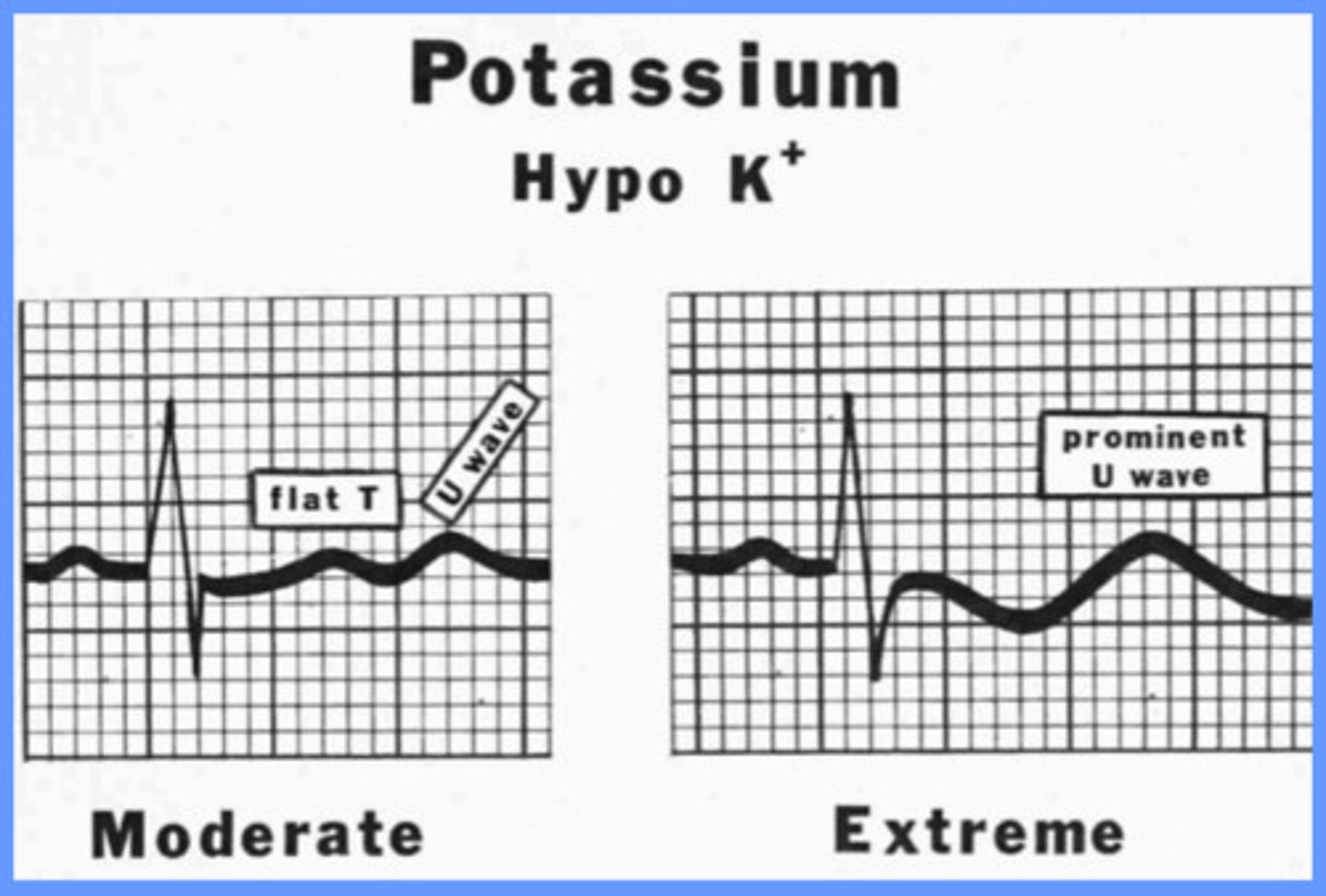
prominent U wave
what is the EKG change associated with hypokalemia?
replace potassium -- oral is safer, but sometimes may HAVE to give IV
--> SLOWLY, as rapid administration can lead to fatal dysrhythmias
tx for hypokalemia
if imminently life-threatening or oral route not possible
--> do not mix with dextrose
when is IV K+ indicated?
Pseudohyperkalemia
falsely elevated K+ level that is caused by the movement of K out of the cells during a "traumatic" venipuncture "hemolyzed specimen"
movement of K out of the cells during a "traumatic" venipuncture "hemolyzed specimen"
what can cause pseudohyperkalemia?
decreased renal function (#1 cause)
transcellular shift
increased intake of K-rich foods
what are the three major causes of hyperkalemia?
hyperaldosteronism (not properly secreting K+)
adrenal insufficiency
what are some conditions that can cause hyperkalemia due to decreased renal excretion (of K+)?
insulin deficiency, metabolic acidosis, muscle relaxants/paralytics
Rhabdo -- K released from damaged muscles
Tumor lysis syndrome -- lysis always leads to more K
--> These conditions cause a release of K+ from ICF stores to ECF
what are some conditions/meds that can cause transcellular shift/hyperkalemia?
usually only occurs if the pt has concomitant renal dx
when would increased K intake lead to hyperkalemia?
Renin inhibitors, ACEis, ARBs, K-sparing diuretics, NSAIDs (decrease GFR)
--> occurs with these meds b/c most of them prevent aldosterone from secreting K+ in collecting duct
--> usually occurs ONLY in setting of underlying kidney dx
what medications can cause hyperkalemia?
dysrhythmias/cardiac issues -- palpitations, syncope, sudden death!
hyperkalemia presentation
Sine wave (QRS merging with T wave) -- pre-arrest rhythm
peaked T waves
--> can quickly degenerate into Vfib/asystole
EKG findings with hyperkalemia
calcium gluconate
if a hyperkalemic pt's cardiac rhythm is UNSTABLE, what is the initial drug of choice?
decreases membrane excitability
calcium gluconate MOA
Insulin, SABAs, IV HCO3
what are some secondary tx for hyperkalemia
Insulin
if a pt is hyperkalemic and hyperglycemic, what is the only med indicated?
Causes K to shift into the cells -- actively transported with glucose -- temporarily lowering serum level
insulin MOA for hyperkalemia