Lecture 21: Temporal region/Muscles of Mastication and Oral Cavity
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What are the two fossae of the temporal region?
temporal fossa
infratemporal fossa
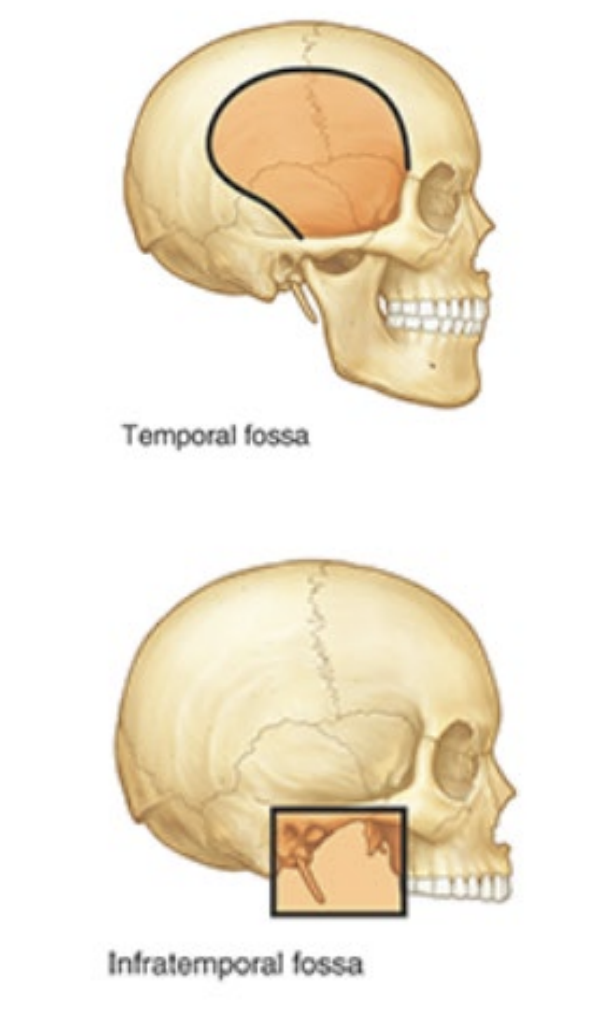
What are the borders of the temporal fossa?
posterior and superior: temporal lines
anterior: frontal and zygomatic bones
lateral: zygomatic arch
What are the contents of the temporal fossa?
Upper part of temporalis muscle
What is the infratemporal fossa inferior to?
zygomatic arch
What are the contents of the infratemporal fossa?
inferior temporalis
lateral and medial pterygoid muscles
maxillary artery
pterygoid venous plexus
V3 (mandibular) —> inferior alveolar, lingual, buccal
CN VII (facial) —> chorda tympani
otic ganglion
Name the four muscles of mastication.
Temporalis
Masseter
Lateral and medial pterygoid
What is the insertion, innervation, and function of the temporalis?
inserts on anterior border of ramus of mandible
innervated by mandibular nerve (V3)
elevates mandible (closes jaw)
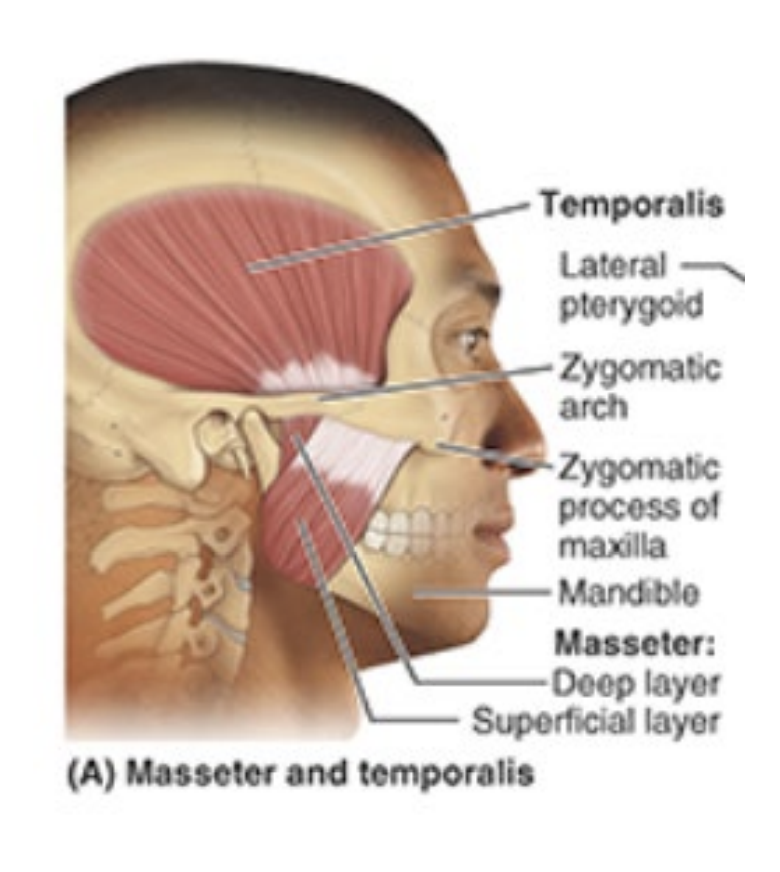
What is the insertion, innervation, and purpose of the masseter?
insertion: angle of mandible
innervation: mandibular nerve (V3)
elevates mandible (closes jaw)
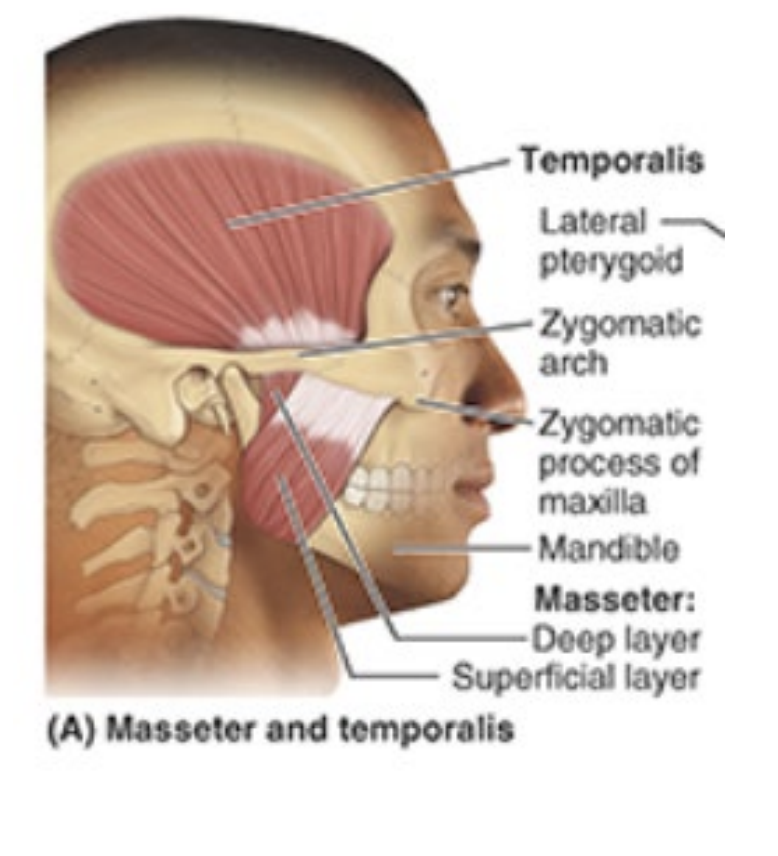
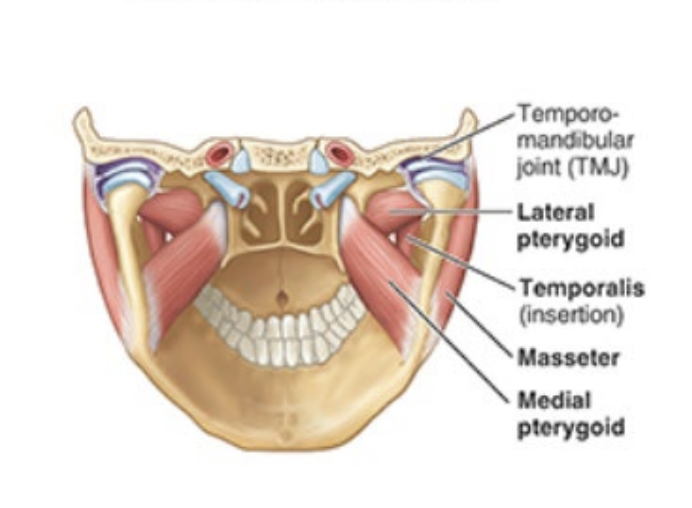
What is the insertion, innervation, and purpose of the lateral pterygoid?
insertion: joint capsule of temporomandibular joint
innervation: mandibular nerve (V3)
depresses chin
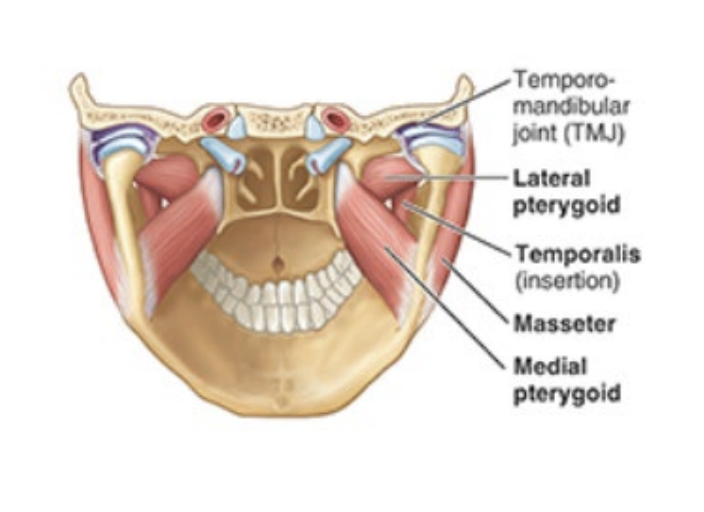
What is the insertion, innervation, and purpose of the medial pterygoid?
Insertion: medial ramus of mandible
innervation: mandibular nerve (V3)
elevates mandible
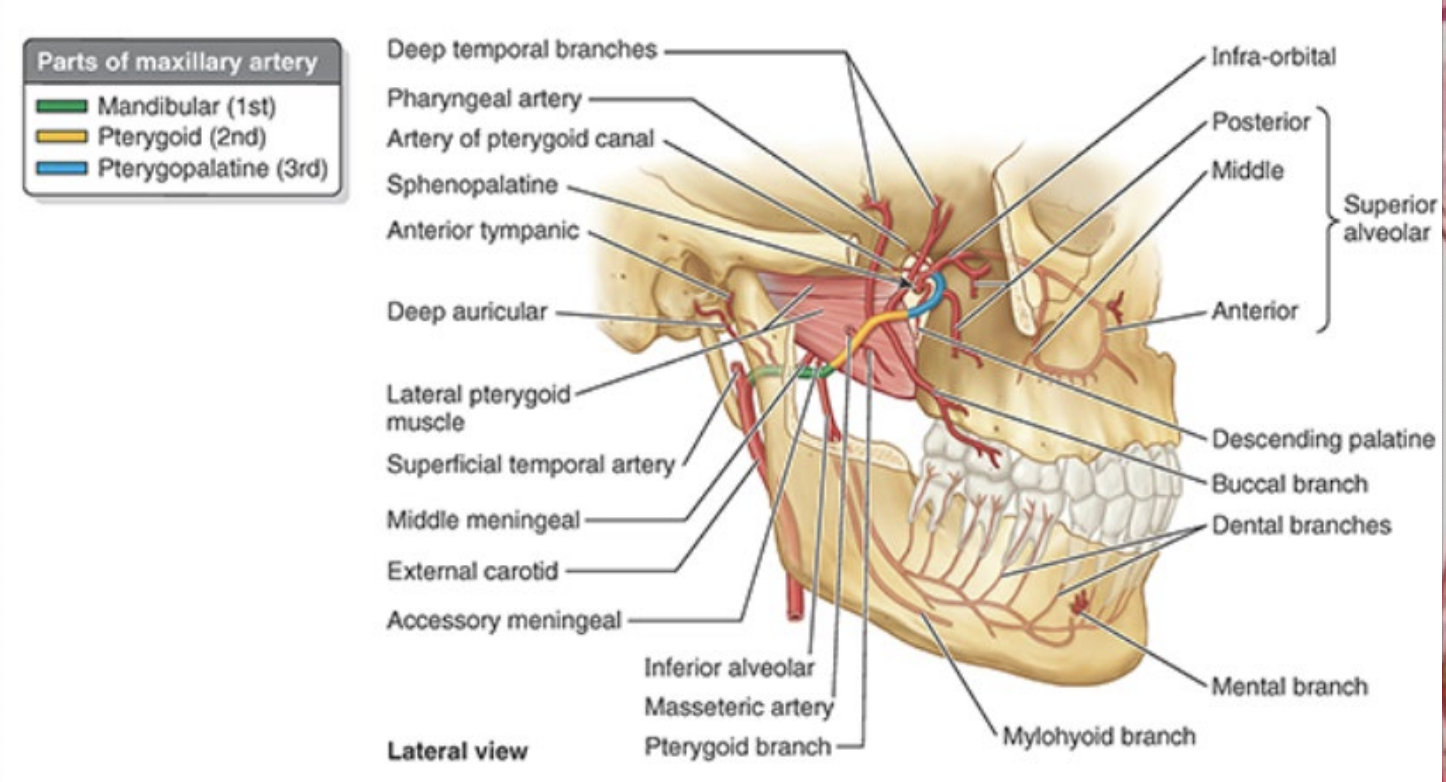
What is the maxillary artery a branch of and what does it supply?
branch of external carotid
supplies lateral-deep face
What are the three parts of the maxillary artery? What are they named in relation to?
mandibular (first) - posterior to lateral pterygoid
pterygoid (second) - adjacent to lateral pterygoid
pterygopalatine (third) - anterior to lateral pterygoid
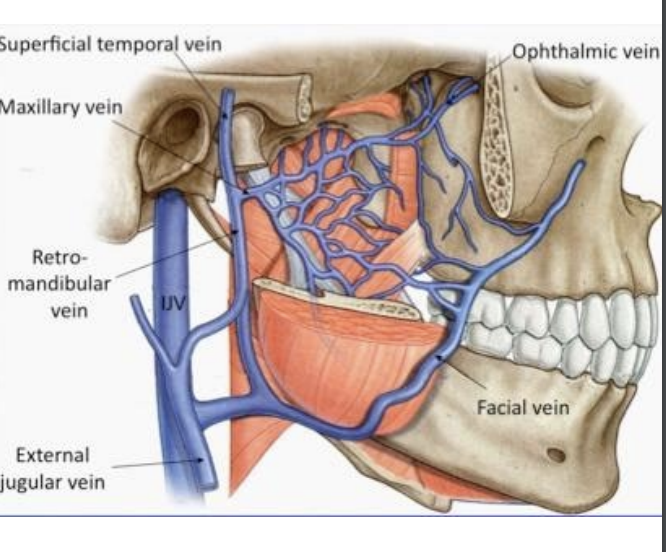
Describe the venous drainage of the infratemporal fossa.
Pterygoid plexus
drains posteriorly into maxillary vein
drains anteriorly into facial vein
What does the mandibular nerve split into? Name the function of each branch.
buccal nerve (cheek sensation)
inferior alveolar nerve (innervates mandibular teeth)
lingual nerve (innervates sensory TO anterior 2/3 tongue)
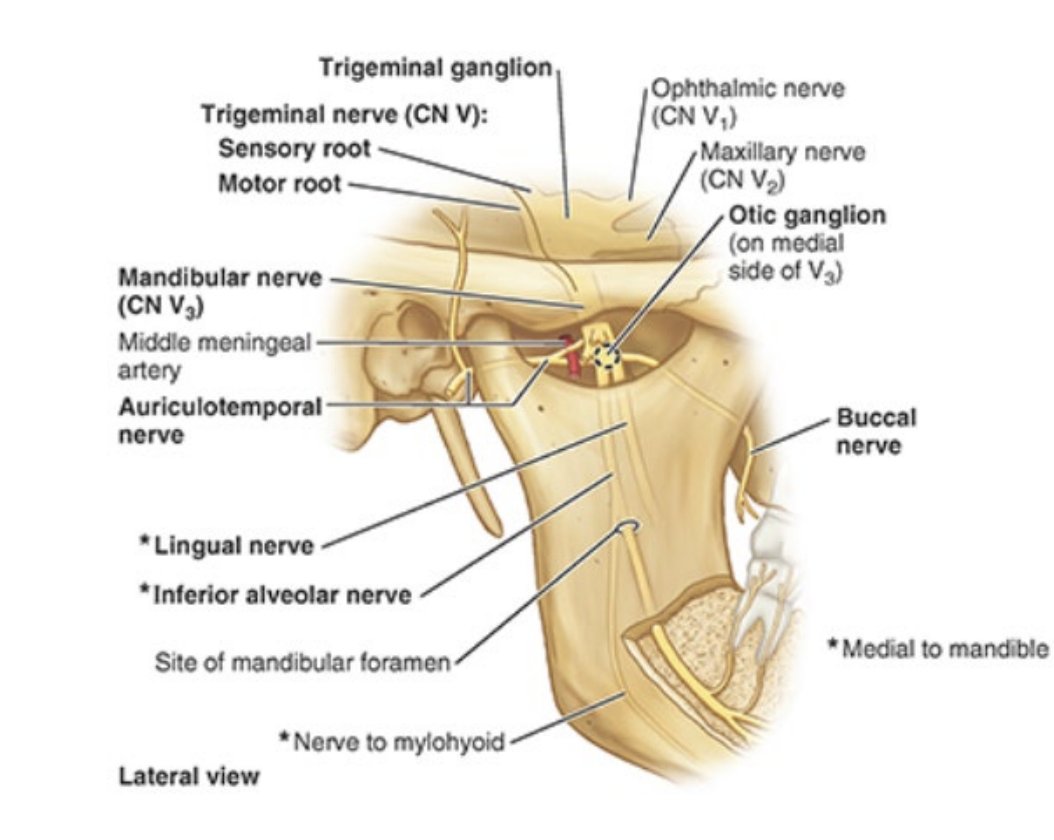
What is the chorda tympani nerve a branch of? What is its purpose? What other nerve does it join in the infratemporal fossa?
branch of CN VII (facial)
taste sensation FROM anterior 2/3 tongue → joins lingual nerve in fossa
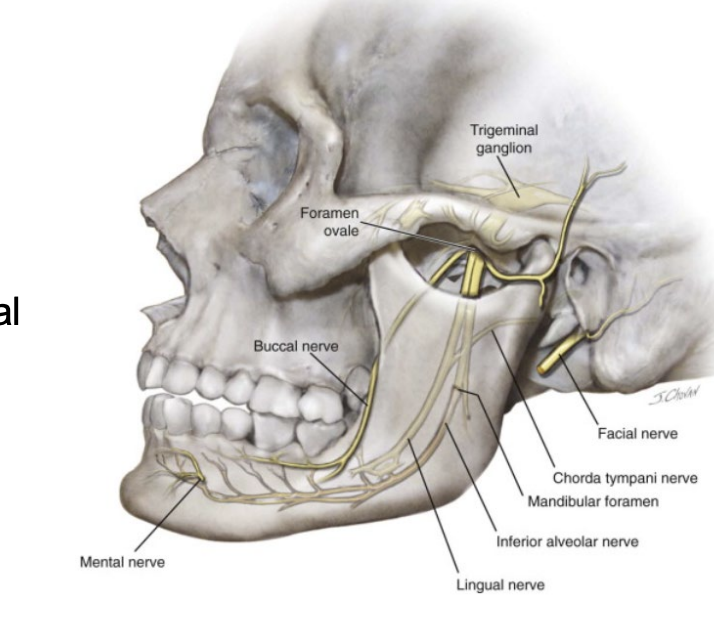
The temporomandibular joint is the articulation between…
mandibular fossa of temporal bone and head of mandible
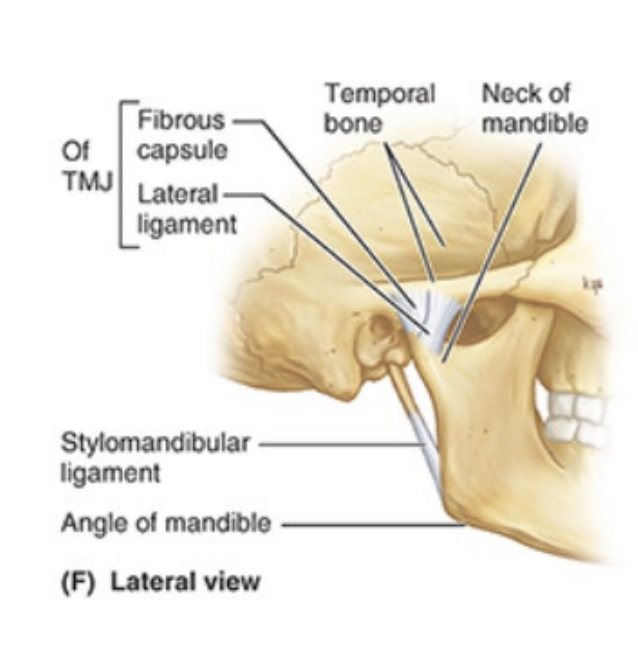
Name the three ligaments of the TMJ
intrinsic lateral ligament
stylomandibular ligament
sphenomandibular ligament
What forms the lateral ligament of the TMJ?
thickened part of joint capsule
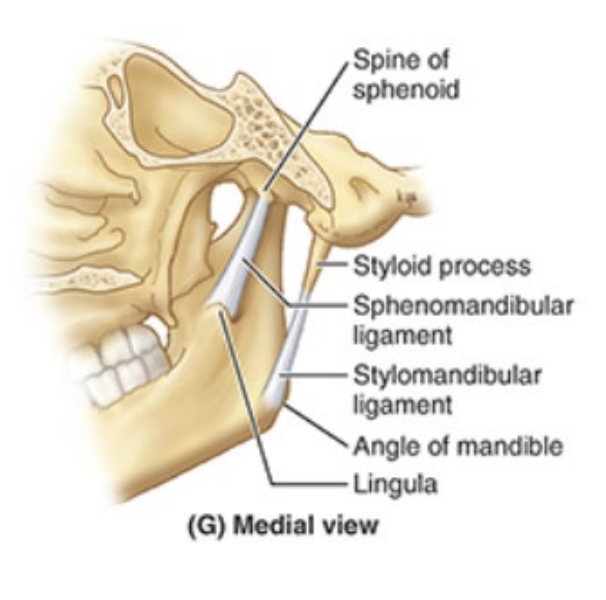
What does the stylomandibular ligament run from/to? The sphenomandibular ligament?
stylomandibular: runs from styloid process of temporal bone to angle of mandible
sphenomandibular: runs from spine of sphenoid bone to lingula of mandible
What are the two parts of the oral cavity?
oral vestibule - slit-like space between teeth/gums and lips/cheeks
oral cavity proper - space between upper and lower dental arches
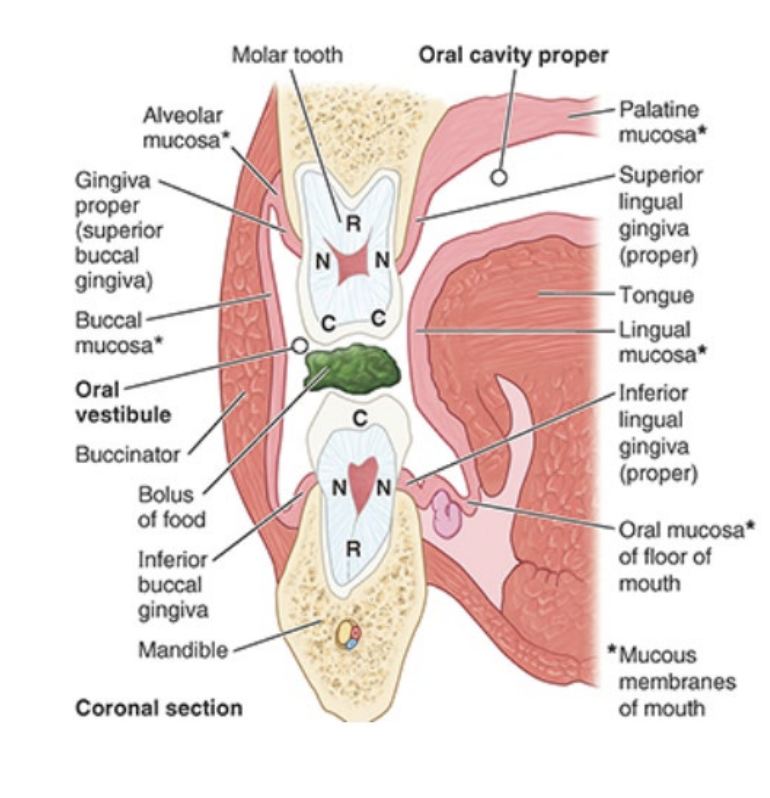
What are the gingivae composed of? What is the gingiva proper attached to?
fibrous tissue covered with mucus membrane
attached to alveolar (containing roots of teeth) parts of mandible and maxilla and necks of teeth
What are the two different types of gingiva proper (location-based)?
superior/inferior lingual gingivae: adjacent to the tongue (inner gums)
buccal gingivae: adjacent to lips and teeth (outer gums)
How many teeth do children have? Adults?
children 20, adults 32
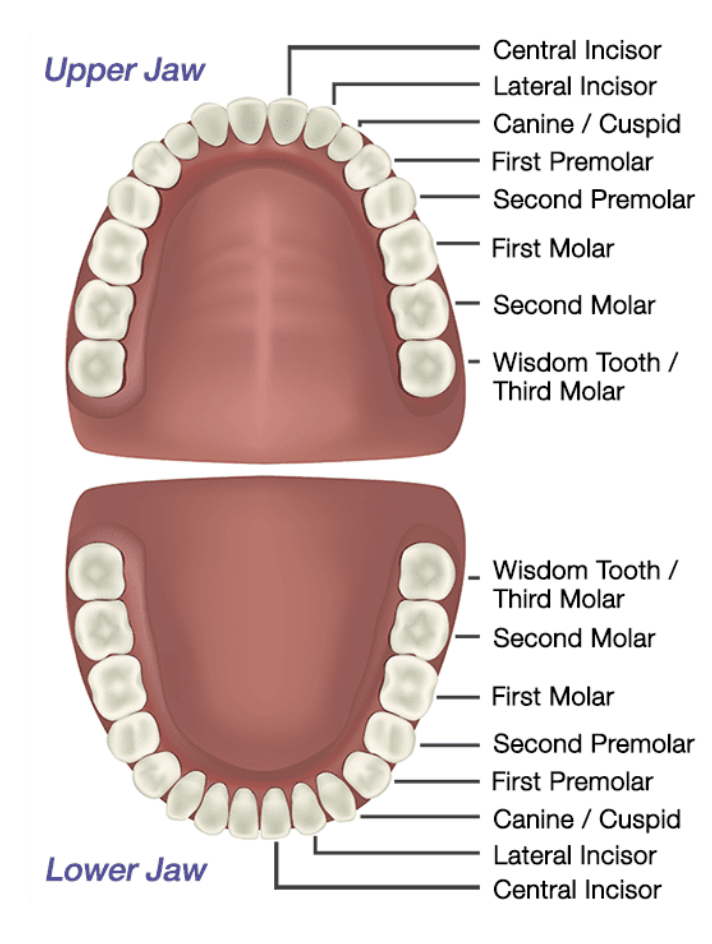
Identify the types of teeth on this diagram. (options: incisors, canine, premolars, molars)
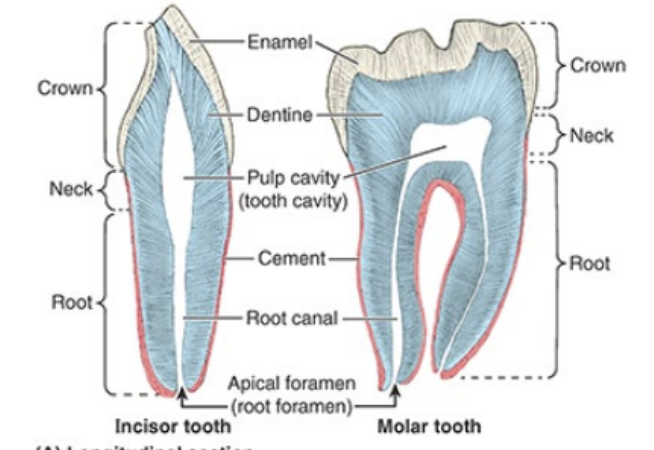
Name the three main sections of a tooth. What does a tooth sit in and what secures it htere?
crown (projects from gingivae)
neck (connects crown and root)
root (fixed in tooth socket/dental alveolus by connective tissue called periodontium)
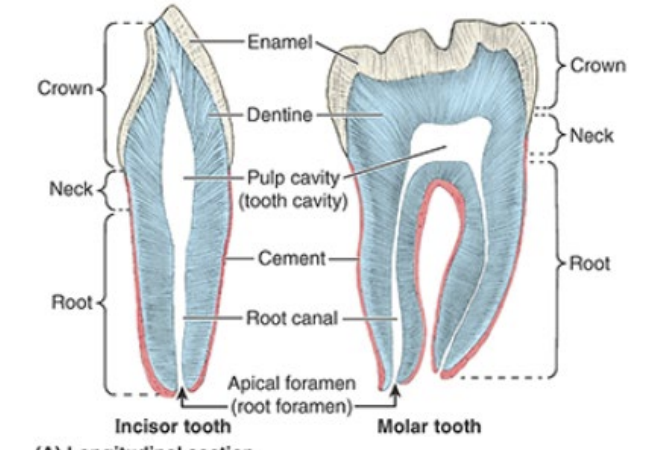
Describe the makeup of a tooth
mostly composed of dentine - covered by enamel over crown and cement over root
What is the pulp cavity/what does it contain? The root canal?
pulp cavity contains connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves
root canal transmits nerves/vessels to pulp cavity via apical foramen
What gives rise to the dental plexuses that innervate teeth?
superior (CN V2/maxillary) and inferior (CN V3/mandibular) alveolar nerves
What arteries supply the maxillary teeth? The mandibular teeth? What are these arteries both branches of?
Maxillary teeth: superior alveolar arteries
Mandibular teeth: inferior alveolar arteries
Both superior and inferior alveolar are branches of maxillary
What is the importance of the palate?
Separates oral cavity from the nasal cavities and nasopharynx
What forms the bony skeleton of the hard palate?
anteriorly: maxillae bones
posteriorly: palatine bones
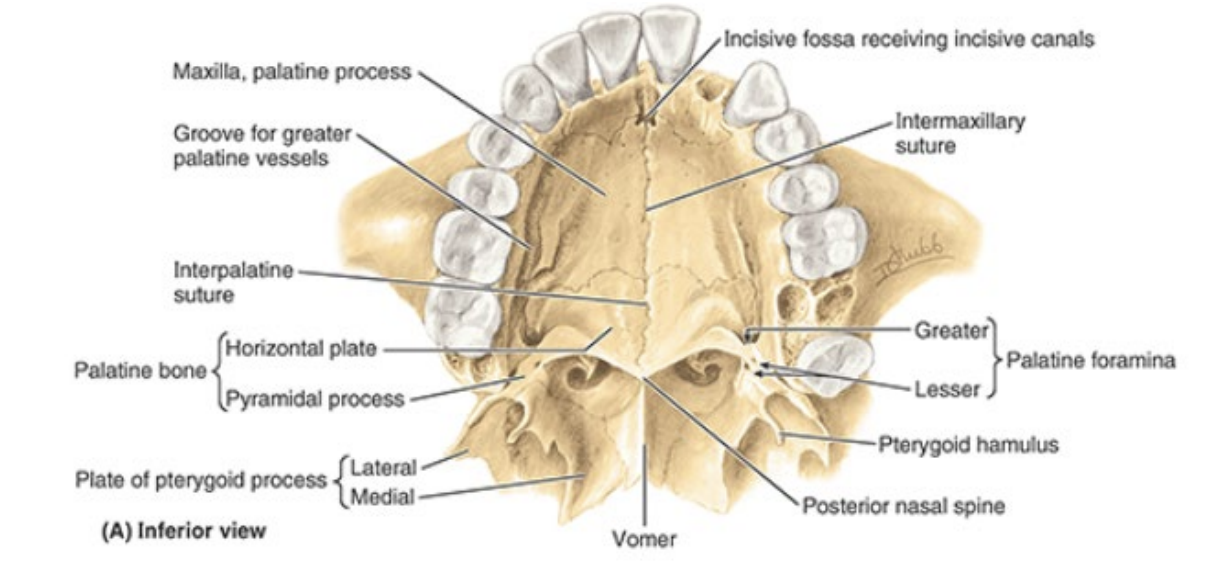
Identify the following features of the hard palate:
incisive fossa
intermaxillary suture
greater palatine foramina
lesser palatine foramina
What is the palatine aponeurosis/its purpose?
Blends posterior edge of hard pallate with posterior muscular part of soft palate —> structural support for soft palate
What is the uvula?
A conical process hanging from the free margin of the posterior soft palate
What are the muscles of the soft palate?
tensor veli palatini
levator veli palatini
palatoglossus
palatopharyngeus
musculus uvulae
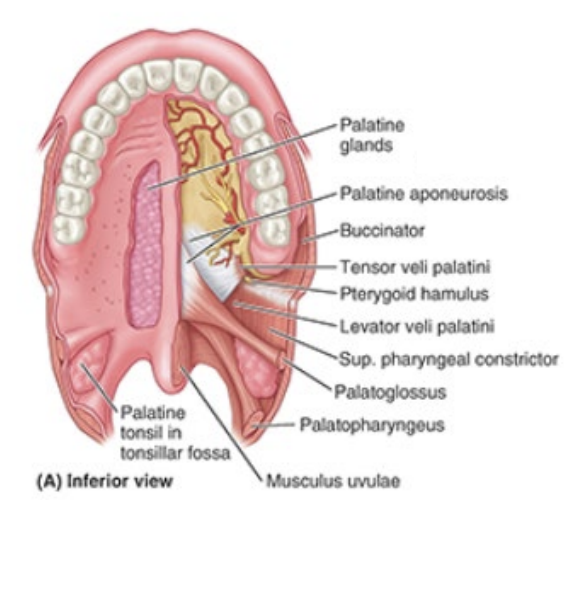
What is the purpose of the muscles of the soft palate?
control air flow through nose, prevent substances in oral cavity from passing to pharynx
What is the innervation of the muscles of the soft palate?
All innervated by CN X (vagus) except tensor veli palatini (CN V3, mandibular)
What arteries supply the palate? What are they branches of?
Greater and lesser palatine arteries (branches of maxillary artery)
What nerves supply the palate? What are they branches of?
Greater and lesser palatine nerves (branches of CN V2, maxillary nerve)
How do arteries and nerves access the palate?
enter via respective greater and lesser palatine foramina
What are the parts of the tongue? Make sure to clarify where they are anatomically
Root: attached posterior portion (between mandible, hyoid, and posterior surface of tongue)
Body: anterior two thirds of tongue
Apex/tip: anterior end)
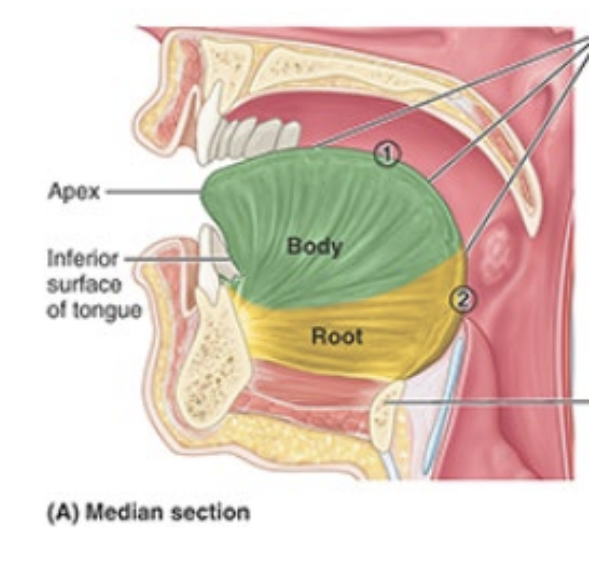
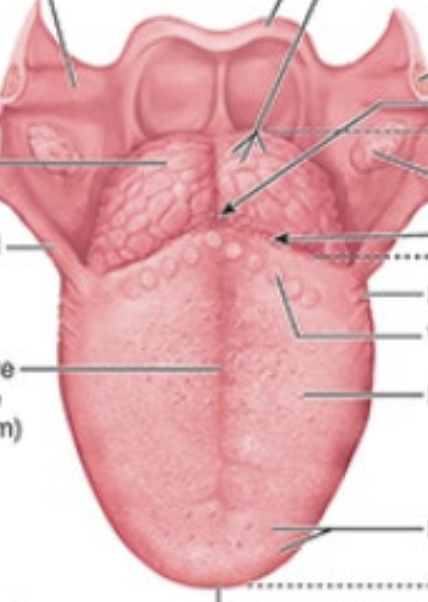
Identify the following features of the tongue:
terminal sulcus
foramen cecum
midline groove
linguinal papillae
notes: terminal sulcus divides oral from phargyngeal part of tongue
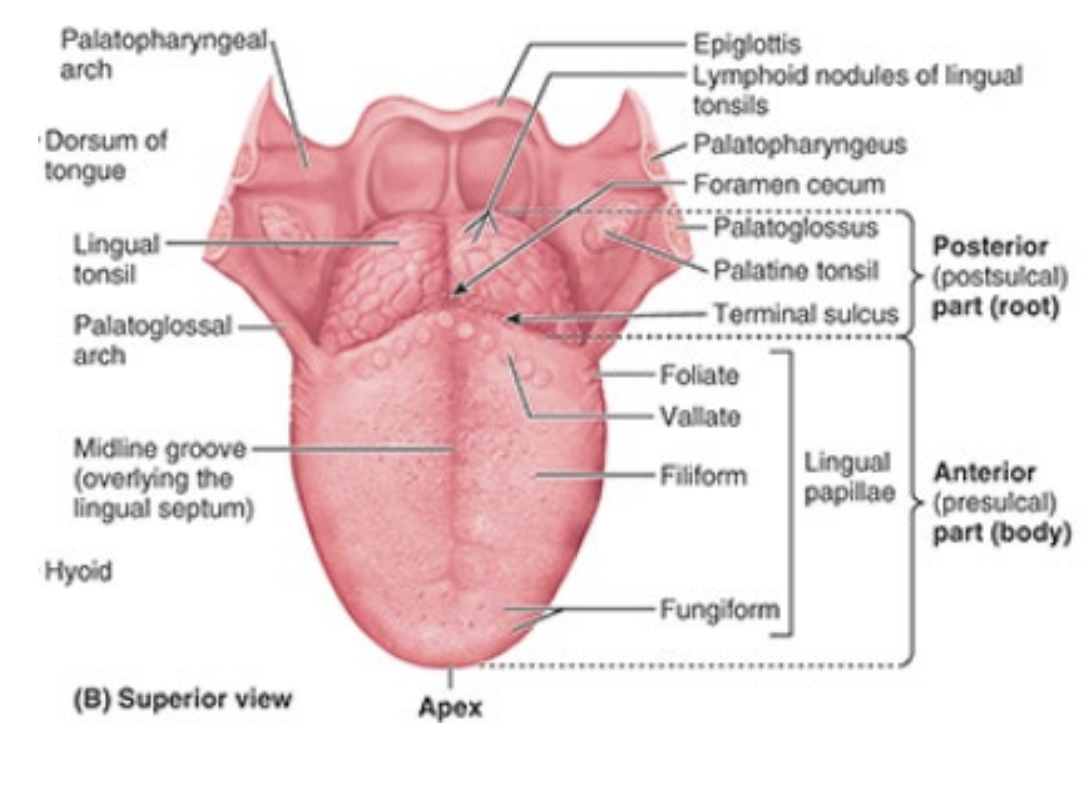
What does the frenulum do?
connects underside of tongue to floor of mouth posteriorly
What is the purpose of the extrinsic vs intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
extrinsic muscles alter position of tongue; originate outside tongue and attach
intrinsic muscles alter tongue’s shape and are confined to tongue
What nerve innervates motor function for all muscles of the tongue but one?
CN XII (hypoglossal)
What is responsible for anterior sensory innervation of the tongue?
general sensory: lingual nerve of CN V3 (mandibular)
taste: CN VII (chorda tympani)
What is responsible for posterior sensory innervation of the tongue?
CN IX (glossopharyngeal)
What are the arteries of the tongue derived from?
lingual artery (branch of external carotid)