Medicinal Botany Exam 1
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
composition of cell walls
glucose monomers form a network of cellulose microfibril
cellulose synthase
synthesizes cellulose
primary cell wall
formed first right outside of the plasma membrane and primary made of cellulose, it is the thinner and weaker wall made of both cellulose and lignin.
secondary cell wall
formed after cell stops growing, pushes itself between first wall and plasma membrane. the thicker and stronger wall
lignin
concrete filling between cellulose and microfibrils
plasmodesmata
openings connecting to adjacent cells, allow for quick communication and transport
middle lamella
the “glue” that holds cells together and helps the plant hold on to water. composed of pectins
turgor pressure
the pressure that is put on a cell wall
turgid/ hypotonic solution
fewer solutes in the solution compared to inside of the cell. water crosses plasma membrane and goes into cell to balance water: solute concentration
isotonic solution/ flaccid
equal concentration of solutes inside and outside of cell so water moves in and out equally. droopy plant
hypertonic solution/ plasmolyzed
more solutes in the solution outside of the cell than inside the cell so water is actively leaving the cell. results in plasma membrane ripping away from the cell wall.
Chloroplasts (structure)
three membranes: inner, outer and thylakoid
chloroplasts (function)
photosynthesis. in the thylakoid membrane there is chlorophyll a pigment molecule that reflect green light,. responsible for making plants green
chromoplasts
holds pigment molecules responsible for giving plants their color
leucoplasts
stores starch, how plats store their sugars
vacuole (function)
storage for the cell
phytochemicals
used for the plant’s defense and stores in the plant’s vacuole in a non toxic form
calcium oxalate crystals
druses, raphides. sharp crystals inside of plants for defenses
chlorophyll
is the primary pigment in plants and has the primary responsibility of executing photosynthesis. reflects green light
what synthesizes chlorophyll
succinyl-coA and Glycine
Carotenoids
accessory pigments that absorb other wavelengths of light lessening damage on the plant. helps attract pollinators as well as added defense for plants
carotene
a carotenoid. reflects orange light and is found in carrots.
lycopene
a carotenoid. reflects red light and found in tomatoes
lutein
a carotenoid. reflects yellow light and found in lemons, bananas, corn etc.
Anthocyanins
a carotenoid. reflects blue, red or purple light. found in onions. may improve night vision and protect against heart disease
Betalins
a carotenoid. reflects yellow or red and synthesized from tyrosine. found in beets. is an anti-oxidant and may protect against various cancers and heart disease
apical maristems
the tips of shoots and roots. it is an area of growth, lengthens the plant
lateral meristems
in the form of a ring they are in the stems and roots of a plant. they widen the plant.
Parenchyma Cells
alive at maturity, these cells are metabolically active so they are involved with photosynthesis, mitosis and cellular respiration.
Collenchyma Cells
semi-alive at maturity, these cells are structural support cells with an only and thicker cell wall.
Sclerenchyma Cells
alive when younger and dead when reached maturity, these cells have very thick primary and secondary cell walls and no organelles. just used for transport
Dermal Tissue
skin of the plant
Vascular Tissue
the veins of the plant, used for transport
Ground Tissue
most of the plant, gas exchange, photosynthesis and structural cells are here
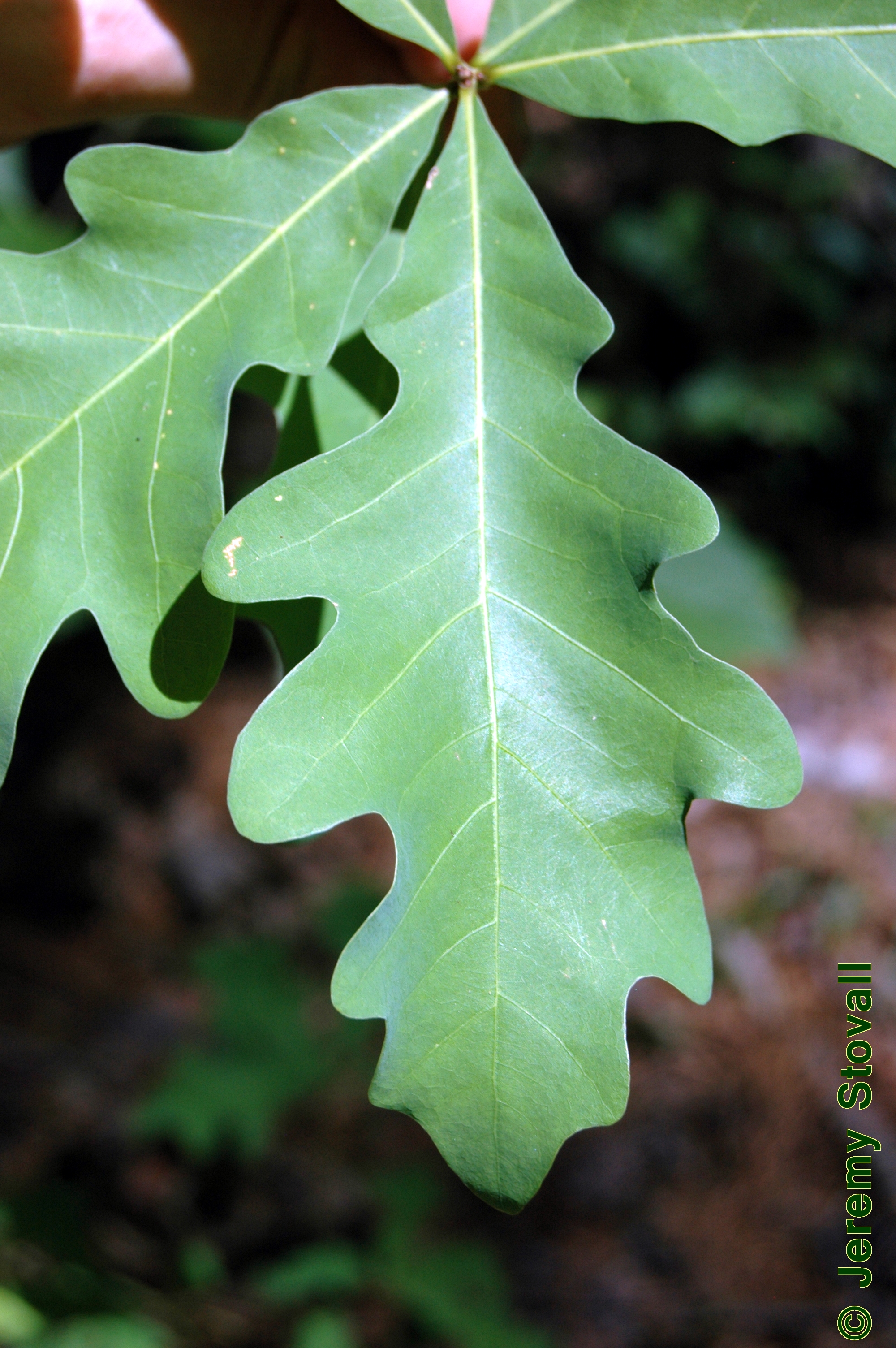

identify the leaf morphology
pinnately lobed leaf
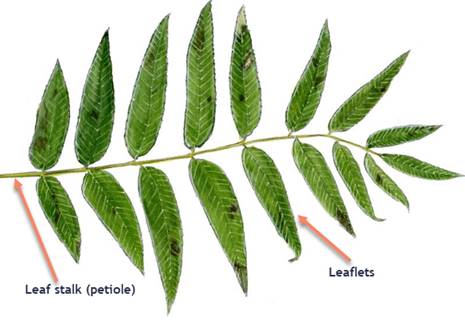
identify the leaf morphology
pinnately compound leaves
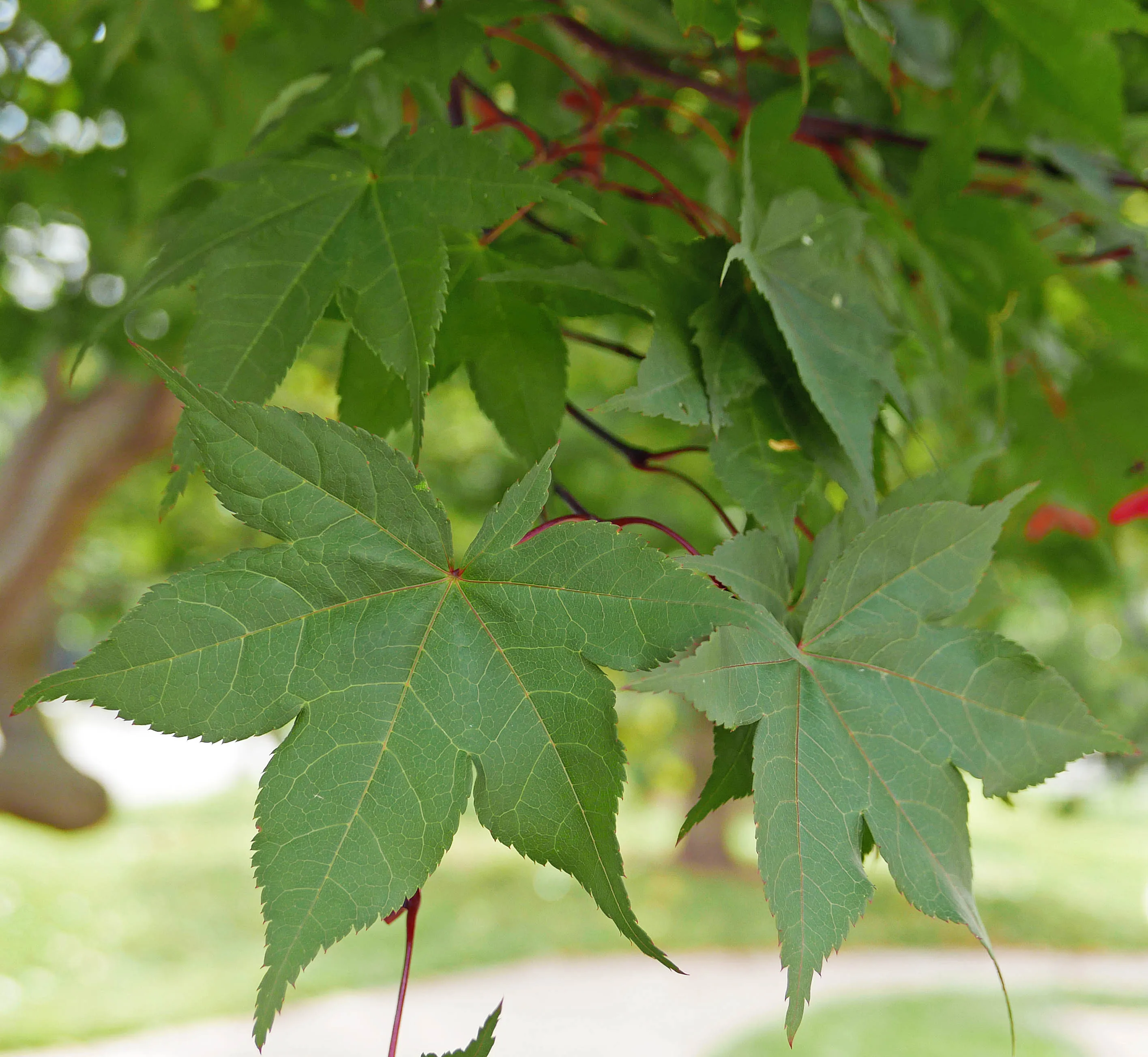

identify the leaf morphology
palmately lobed leaves
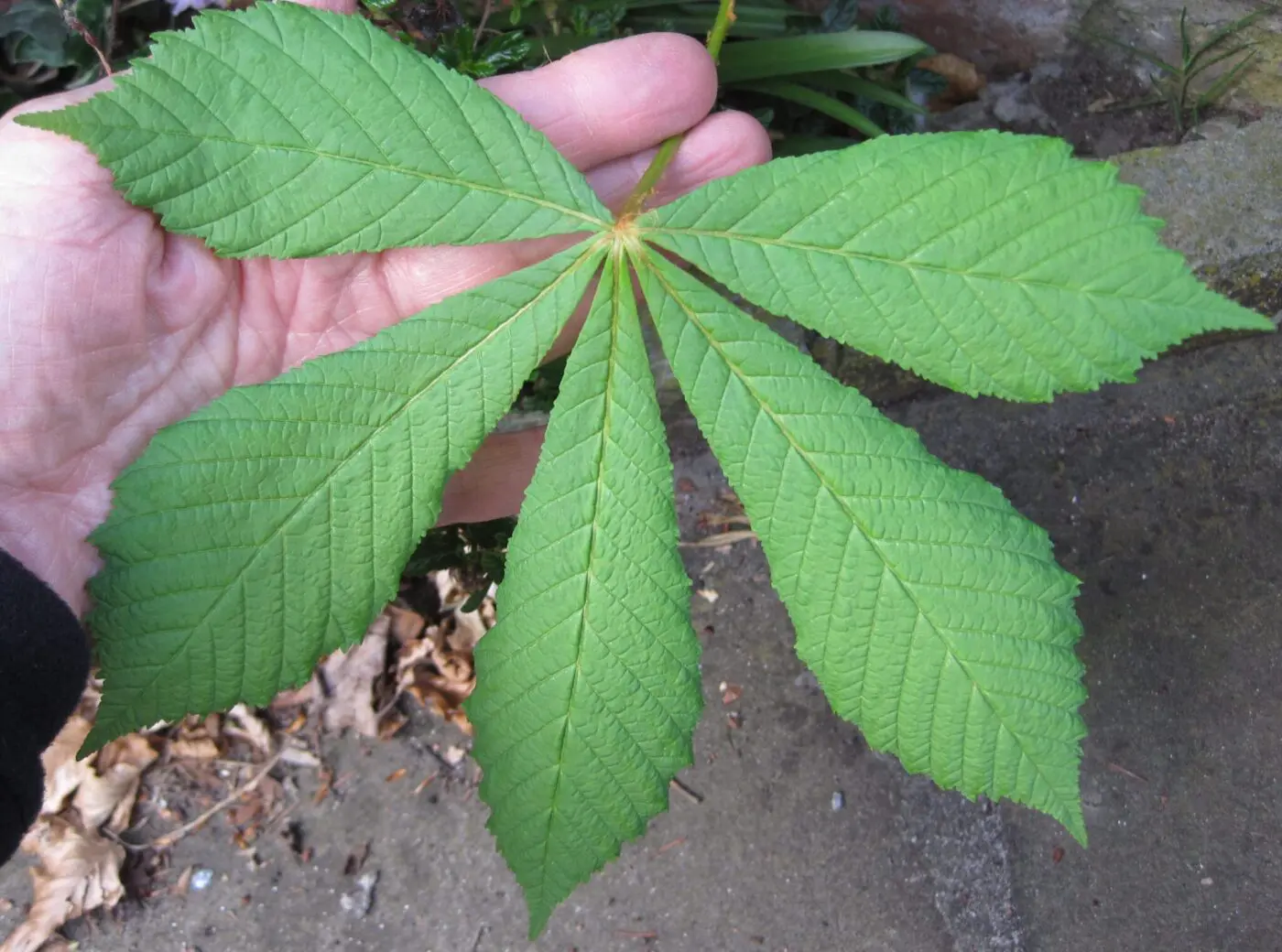

identify the leaf morphology
palmately compound leaf

identify the leaf morphology
modified leaves
Lower and Upper Epidermis
1-2 cell layers thick
produces the cuticle
cuticle
waxy substance produced by the epidermis. coats leaves to act as a defense mechanism as well as helps prevent water loss
stomata
two guard cells that open and close allowing for the leaf to participate in gas exchange between the leaf and the atmosphere.
what is a potential downside to the function of the stomata?
when it is open, it allows for water to escape so it is a tightly regulated process that depends on the water level of the guard cells.
Palisade parenchyma
columnal cells that are photosynthetic
Spongy parenchyma
photosynthetic cells
rounded cells with air gaps that provide a humid environment that transitions incoming CO2 from gas to liquid
Veins
composed of the xylem and phloem.
xylem
transports water and minerals from the soil up to the plant
phloem
transports sugars from “source” (high amt) to “sink” (low amt)
terminal buds
buds at the very tip of the stem
internode
spaces between nodes
node
location where anything is coming off of the stem
stolons
above ground stems that grow along the soil surface. leaves grow at the nodes from roots that dig into the soil
strawberries
rhizome
below ground stems that root at the nodes and send up leaves to the surface. above ground they look like different plants
iris
corm
dense and hard on the inside, made up of stem tissue. bulbs
crocus
thorn
composed of leaf and stem tissue
gleditsia
tubers
rhizomes that are modified for storage of starch
potatoes
cladode
stem tissue, thorns are leaf tissue
cactus fruit
tendrils
made up of stem tissue or leaf tissue
climbing plants
pith
inner portion of the stem, can be empty or filed with cells
vascular bundle
includes the xylem and phloem
xylem is closer to the middle and the phloem is more on the outside
tap root
large primary root that goes deep into the soil to access water and minerals
Fibrous Root/ Adventious Root
secondary roots that stay near the surface to access water and minerals art the soil surface

identify the modified stem and give an example
stolon, strawberries

identify the modified stem and give an example
rhizome, iris

identify the modified stem and give an example
corm, crocus

identify the modified stem and give an example
tuber, potatoes

identify the modified stem and give an example
thorn, gleditsia

identify the modified stem and give an example
cladode, cactus fruit

identify the modified stem and give an example
tendrils, vines and other climbing plants
tuberous roots
modified roots for storage of starch
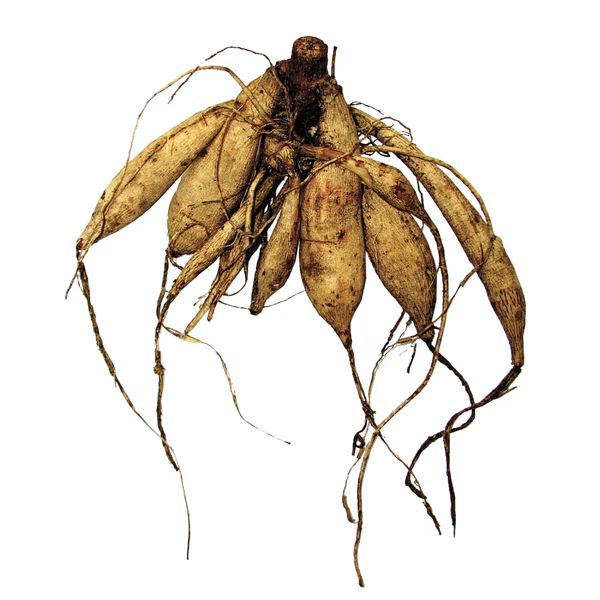

identify the root
tuberous
prop roots
roots that grow out of the soil to help prop the plant up/ anchor it down
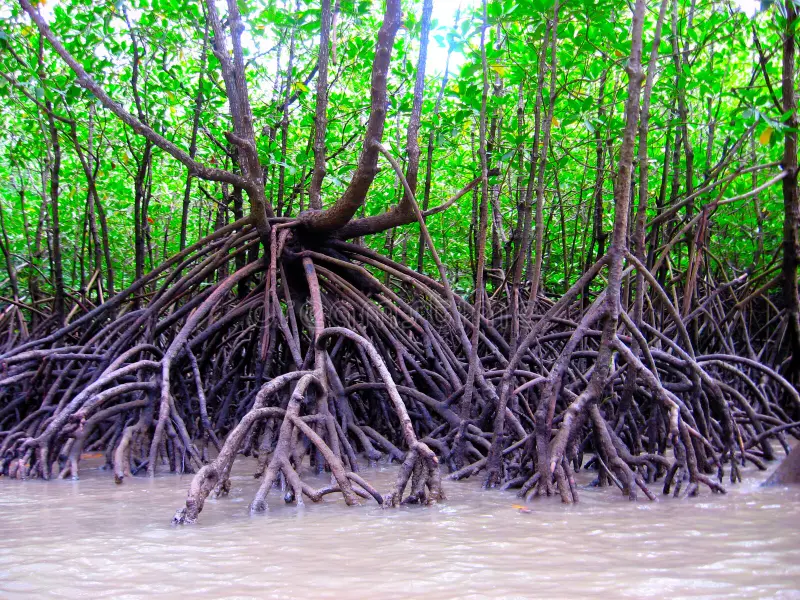

identify the roots
prop roots
pneumatophores
“knee” roots that come up out of the ground to breathe in wetland areas for gas exchange
identify the root

pneumatophores
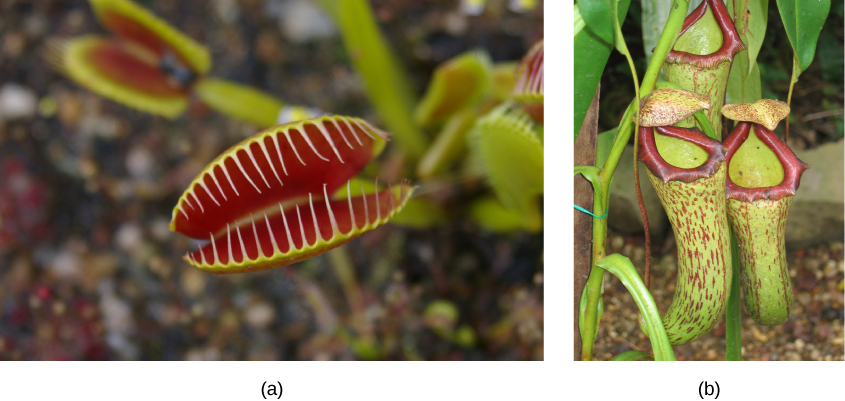
what organism forms a symbiotic relationship with legumes? what is the reasoning for this relationship?
legumes gives rhizobium bacteria sugars to live, rhizobium gives the plant nitrogen
how do ants form symbiotic relationships with the myrmecodia plant?
ants dig tunnels into the roots of the plant providing them a home and in return the ants will defend the plant when attacked
describe the apoplastic route
water and minerals from the soil go into the root hair and travel between cell walls ONLY until they reach the endodermis. Water and nutrients are unable to pass through the casparian strip so water is forced into the cell
casparian strip
a structure in the cell wall that is impermeable to water. acts as a filter
describe the symplastic route
water and nutrients go right into the root hair, crosses the plasma membrane immediately and goes into the cell
carpels
female whorl, produces the eggs
stamens
male whorl, produces the sperm
petals
neither male or female, sterile whorl who’s job is to attract pollinators
sepals
leaf looking parts that are at the base of the flower
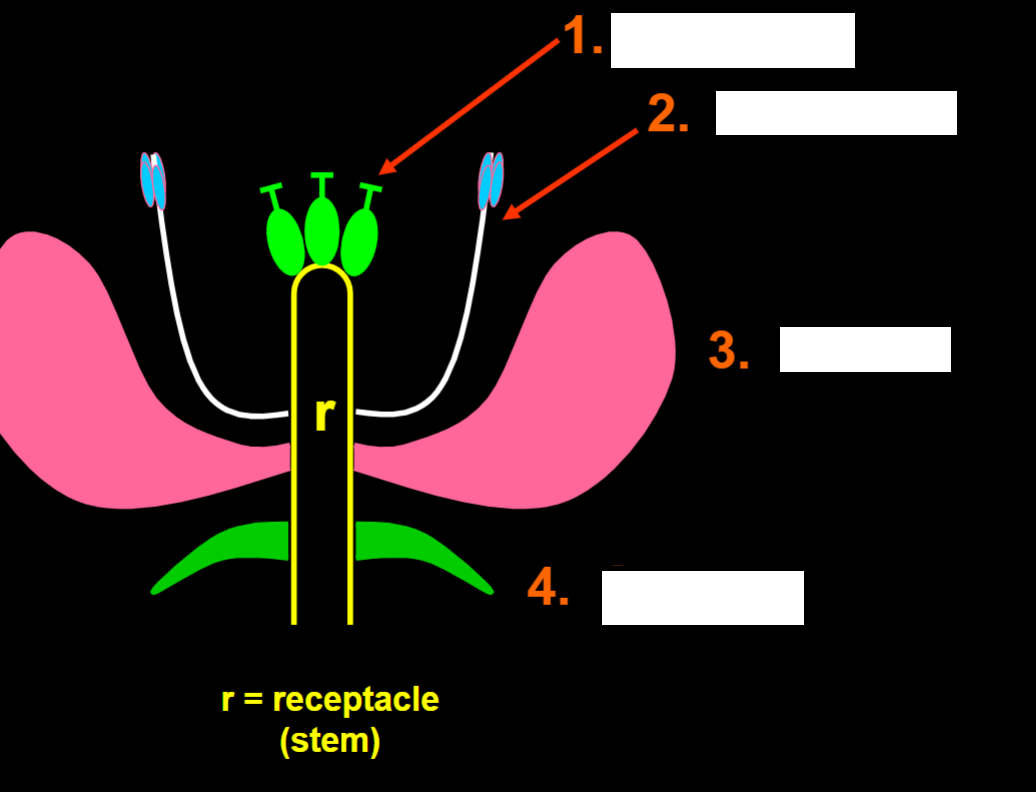
identify the plant anatomy
carpels
stamens
petals
sepals
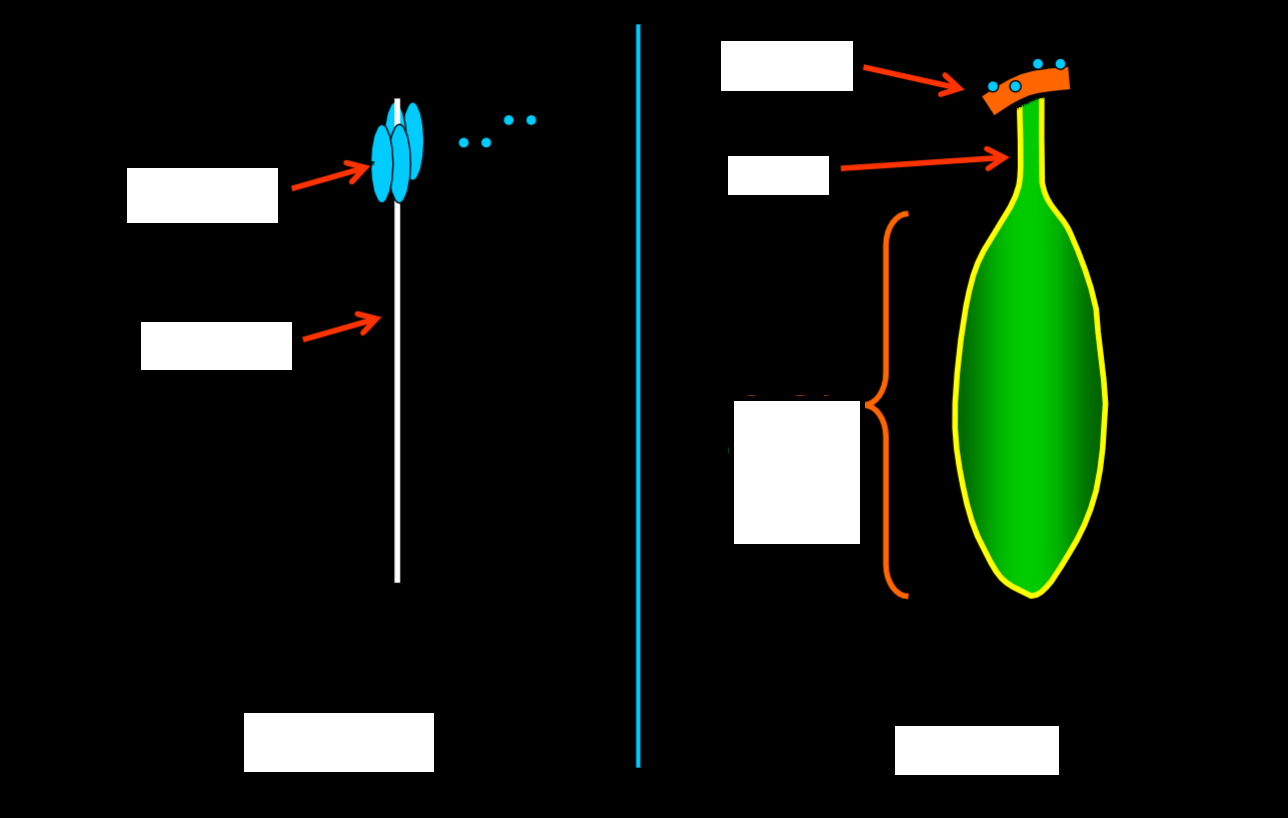
identify the plant anatomy
stamen
anthers
filament
carpel
stigma
style
ovary
define a dehiscent fruit
fruits that open up when they’re mature to release their seeds
identify the characteristics of follicle fruits
open at maturity to release seeds and only have one carpel and one suture
identify the characteristics of legume fruits
from the bean and pea family. Only has one carpel but two sutures
identify the characteristics of Capsule fruits. give an example
has more than one carpel and more than one suture. these fruits can open many different ways
ex. poppy
what is an indehiscent fruit?
fruits that when at maturity, they do NOT open up to reveal their seeds
define achene fruits, give an example
dry, indehiscent fruit
only have one seed, thin pericarp and the seed moves freely from the pericarp
sunflower seeds
define samara fruits, give an example
dry, indehiscent fruit
1 seeded with thin pericarp that is winged
“helicopters” off of maple trees
define a caryopsis/ Grain fruit. Give an example
dry, indehiscent fruit
1 seeded, thin pericarp and the seed is FUSED to the pericarp
corn kernel
define nuts as a fruit, give an example
dry, indehiscent fruit
1 seeded, pericarp is thin and stony, often has husks and bracts
ex. acorns, walnut
define schizocarps, give an example
dry, indehiscent fruit
Any fruit that splits into 2 or more subunits
describe/ define berry fruits, give an example
simple, fleshy fruit
has 1 to several seeds
mesocarp fleshy
describe/define hesperidium fruits, give an example
simple fleshy fruit
specialized berry with a leathery rind and oil glands on the outer surface
all citrus fruits
define/ describe Pepo fruits, give an example
simple, fleshy fruit
specialized berry with a hard rind
squash and melon family
define/ describe drupe fruits, give an example
simple, fleshy fruits
specialized berry that has a hard and stony endocarp
has 1 to several seeds
peaches, coconuts