Opiates (natural, synthetic, and their antagonists)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
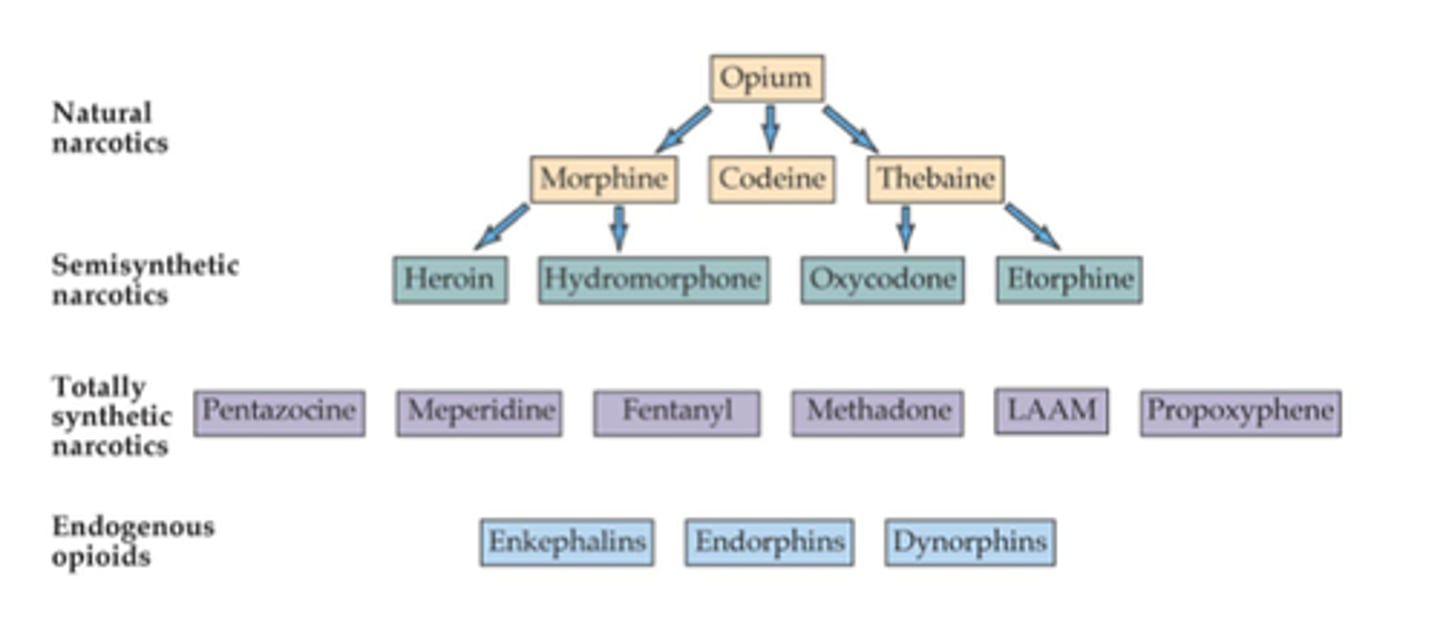
Opiates
-narcotic analgesics
-reduce pain, induce relaxation, don't cause unconsciousness
-high doses can result in coma/death
-leads to tolerance and dependence
-their second creates effect is on the GI tract--> constipation, can treat diarrhea (imodium is a synthetic that does not cross BBB)
-active ingredient=morphine
-also contains codeine, thebaine, narcotine
-heroin was synthesized from morphine-- passes through brain 4x faster, converted to morphine once in the brain
Opioid receptors
-metabotropic, G-coupled
-when activated it opens K+ channels (hyper polarized cell, blocking action potential from happening) and closes Ca++ channels (which inhibits vesicle release)
-located supraspinally, spinally, and in the peripheral
-three major subtypes: mu, delta and kappa. Each have distinct distributions in the brain and spinal cord-- must mediate different effects
Opioid receptor ligands
Endogoneous= endorphins, enjephalins, dynorphins
-released in exercise so you don't feel pain and can keep running (good survival advantage)
-Exogenous= opiates
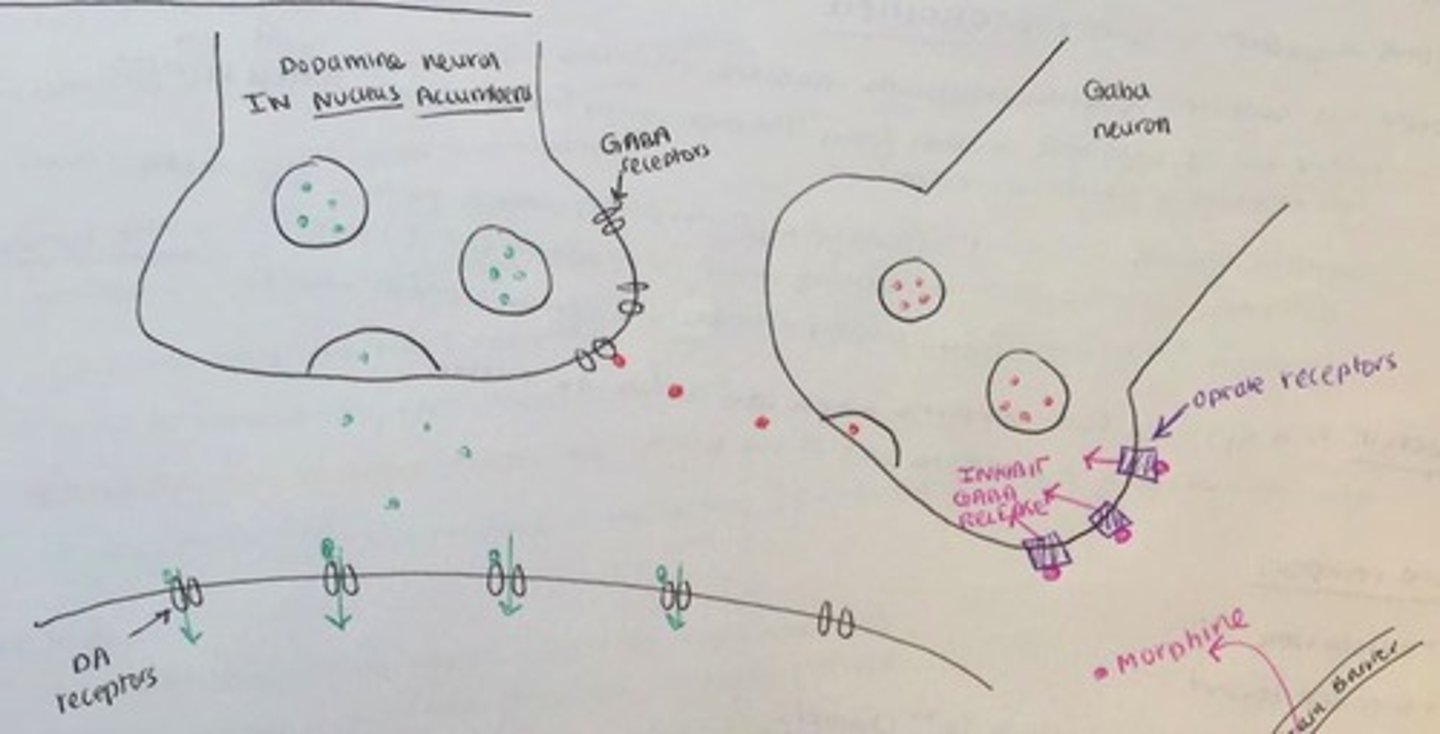
Mechanism of opiates
-inhibits GABA neurons from firing onto dopamine nuclei in the ventral segmental area (VTA), leading to more dopamine released in the nucleus accumbens
-opiates act on opiate receptors, which are located on the GABA neuron. When they bind to the receptor, they inhibit GABA to fire an action potential, and from releasing their vesicles (of GABA). This means GABA can no longer send out IPSP's to the dopamine neuron it was acting on. This leads to increased dopamine released at the next synapse
Tolerance to opiates
-due to down-regulation of of dopamine receptors at the synapse
-results in diminishing effects of the drug with repeated use
-due to neurons adapting to having the drug present
-leads to withdrawal
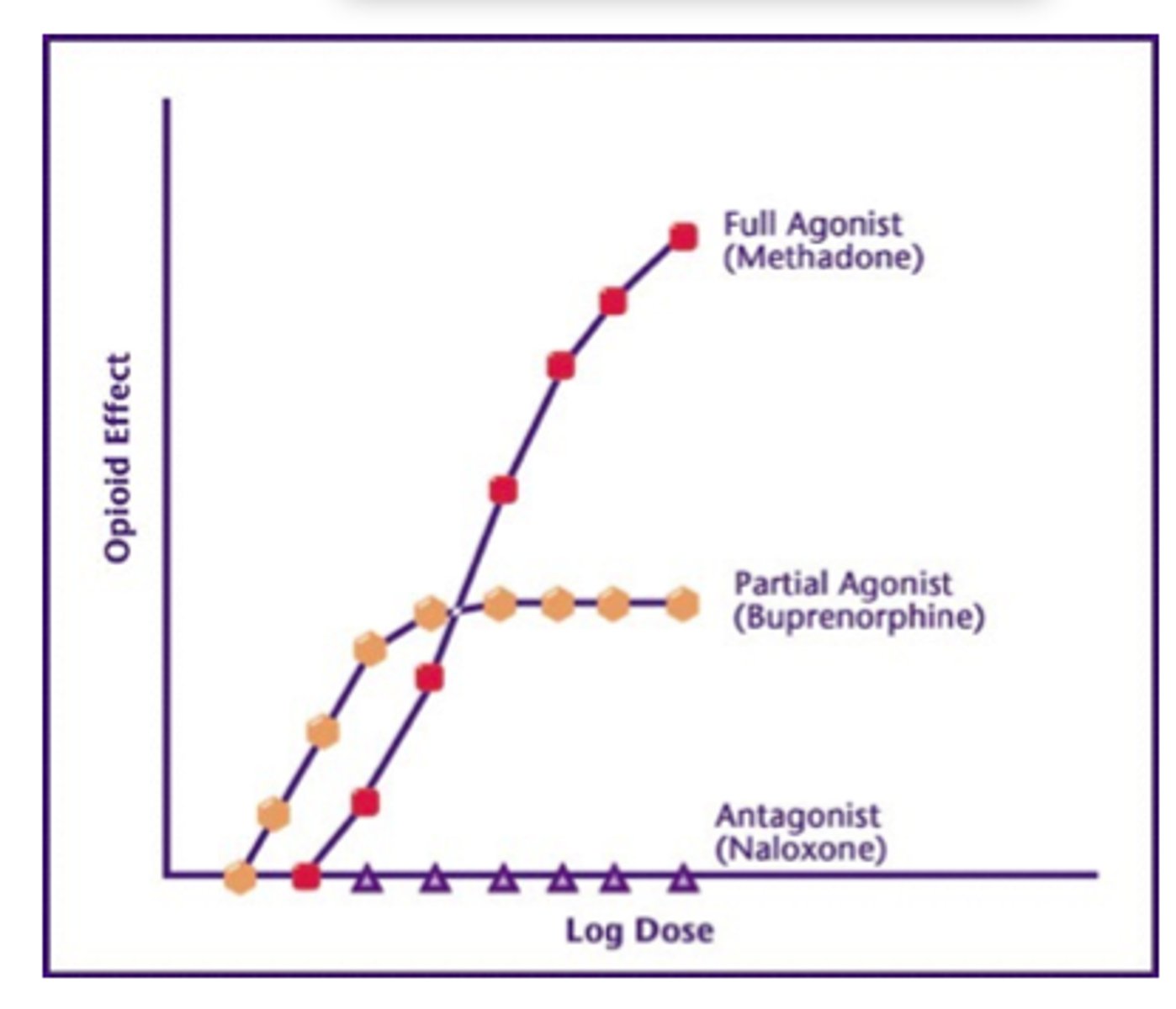
Treating opiate addiction
-three approaches
-methadone= full agonist of opioid receptors
-buprenorphine= partial agonist
-naloxone= antagonist, used to reverse opiate OD's. High affinity for opiate receptors, but no efficacy ligands
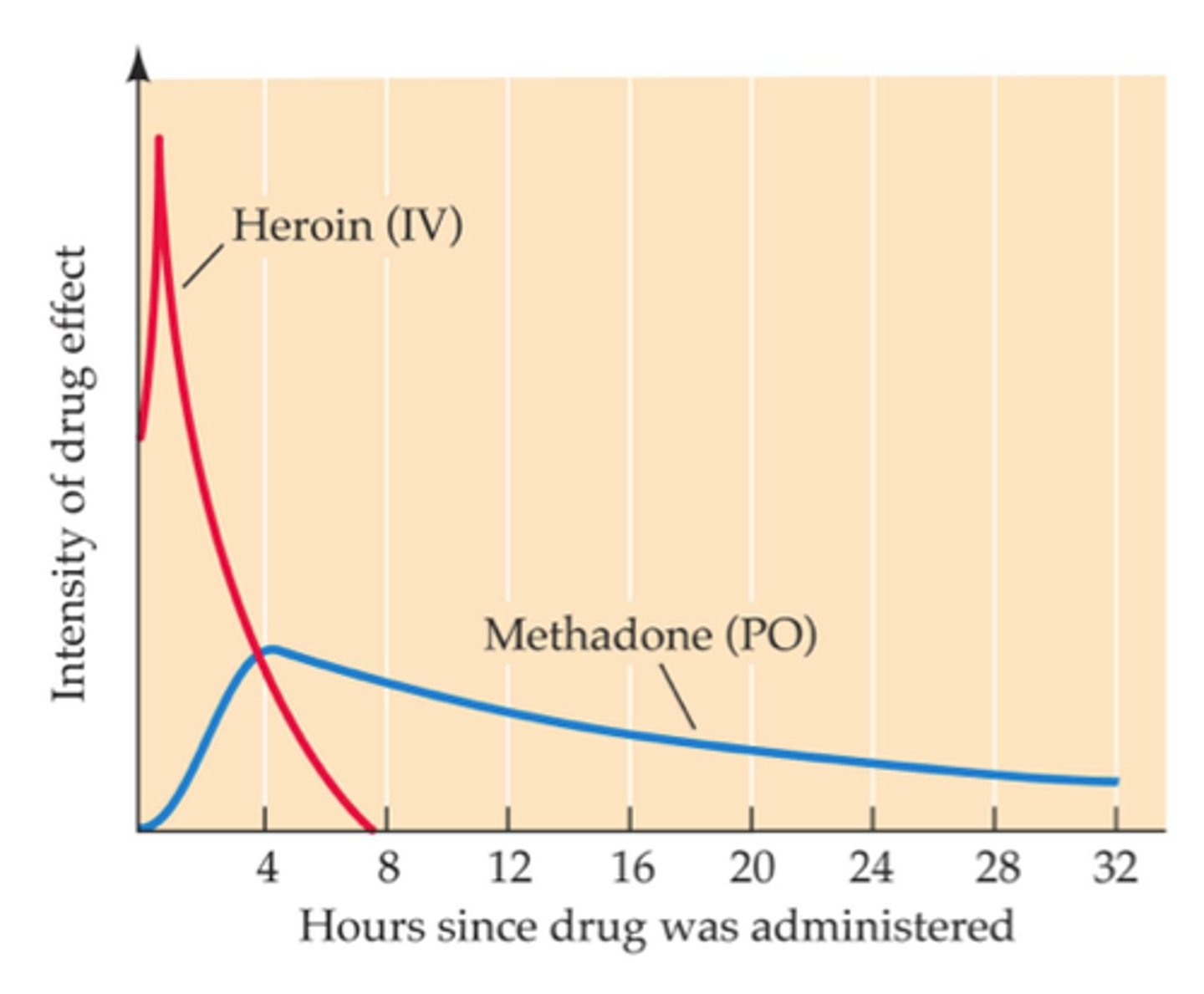
Methadone
-full agonist of opioid receptors
-much longer lasting, but less potent
-has a gradual withdrawal process, no peak high
-much milder withdrawal symptoms
-used to wein people off of opiates