Test 6 - Complex Animals - Mollusks
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2025-07-29
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What rank are mollusks in terms of which phylum has most numbers of living animals
2nd to arthropods
what does mollis mean
soft
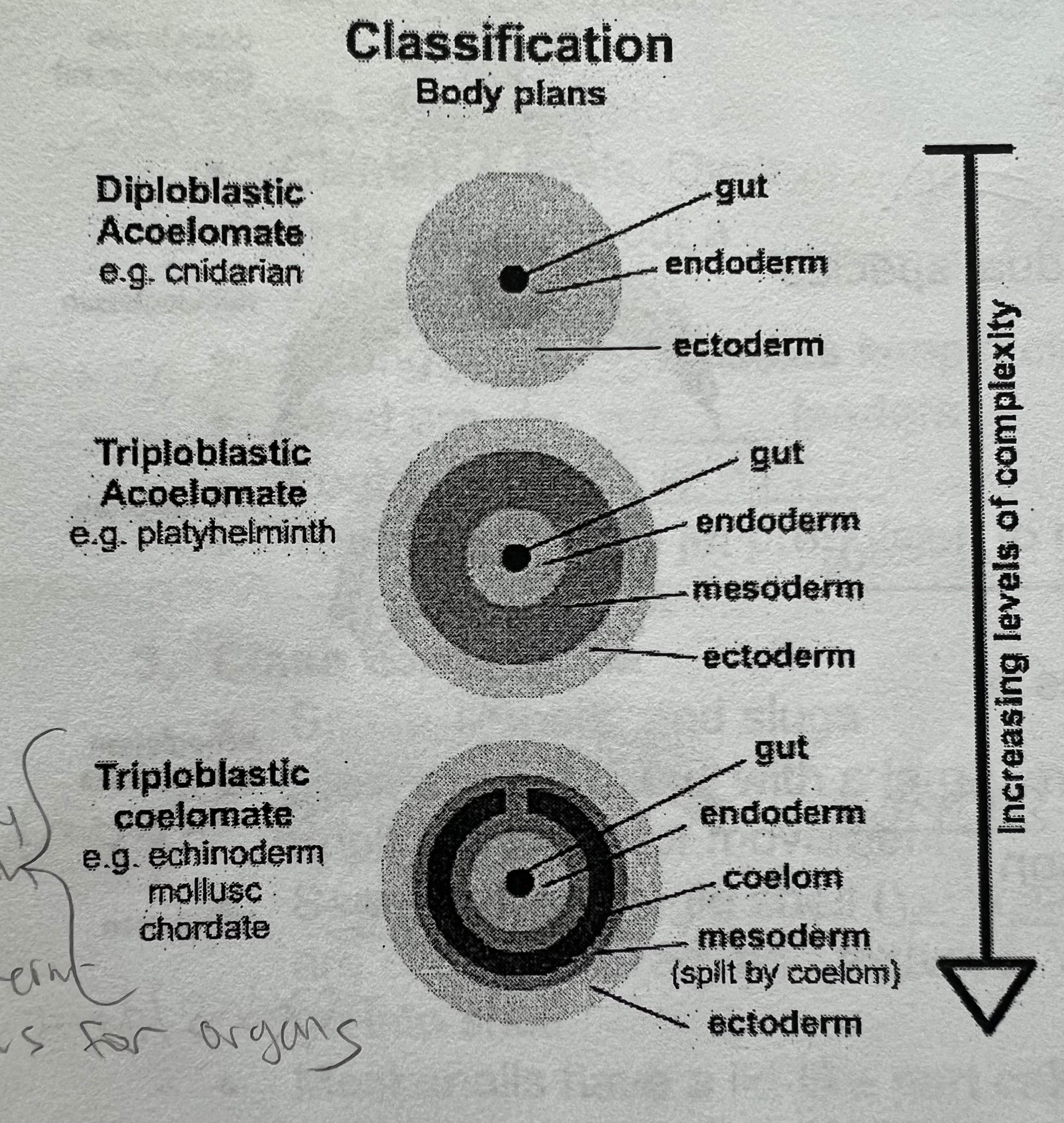
body cavity status and what is it lined with.
coelomates with a body cavity lined with mesodermal tissue
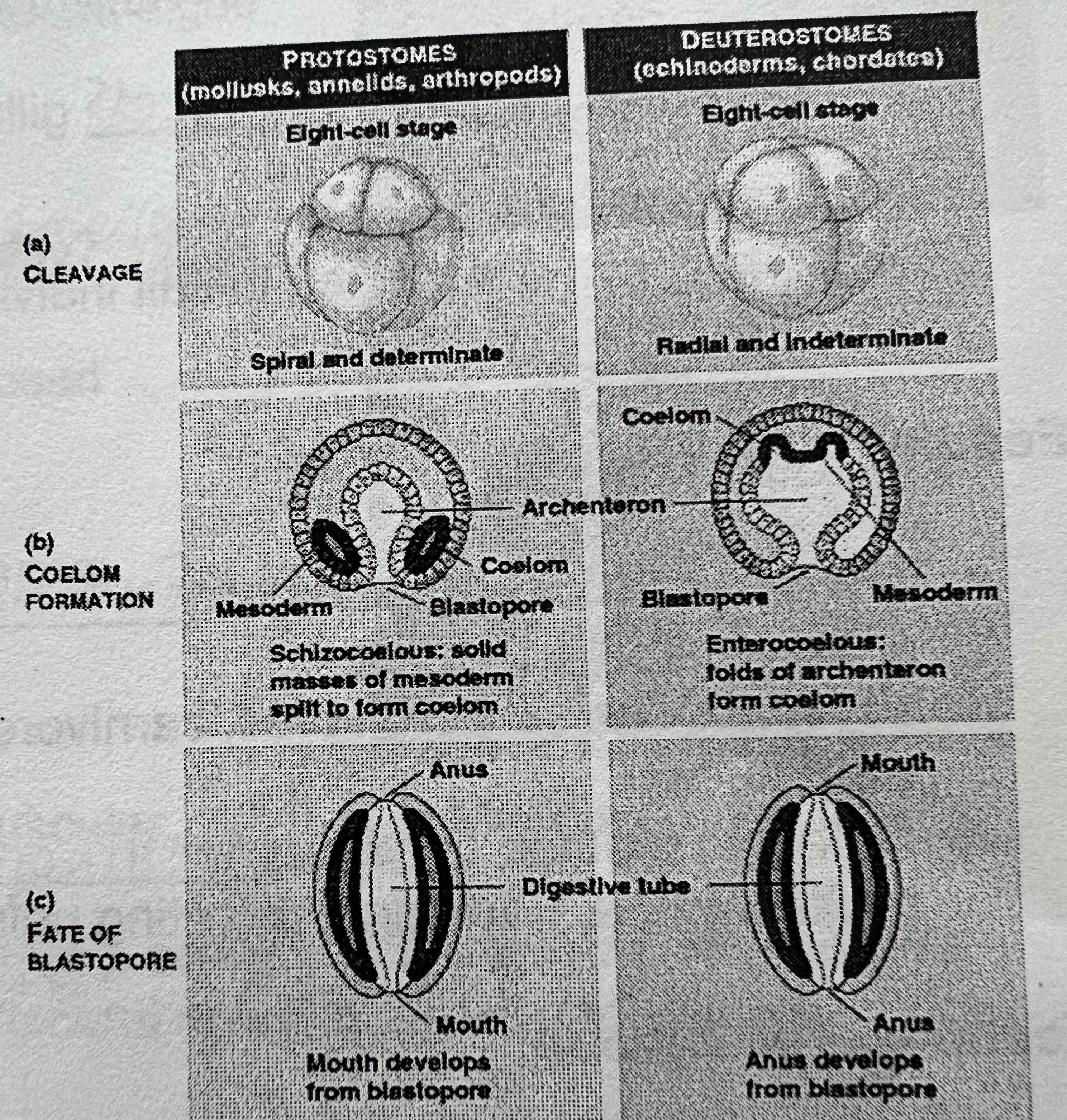
are mollusks protosomes and what are protosomes
Yes, proto(first)some(stoma = mouth), mouth forms before anus. Blastopore becomes the mouth
Look & memorize
good
Look & memorize
good
what three body parts do all mollusks have
mantle foot and visceral mass
Describe digestive system (4)
one way
specialized organs
specialized mouthparts
radule (chitinous tongue)
describe circulatory systm
all open except cephalopods
describe respiration system
gills extract O2 & get rid of nitrogenous waste
What do most mollusks have for protection for their soft bodies
CaCO3 shell, internal shells, or lost to evolution
what type of symmetry
bilateral
nervous system?
cephalized & sensory organs
how reproduce
dioecious, sexual
describe visceral mass
contains gut (mouth&anus), circulatory system, reproductive system, and excretory system with kidneys
describe mantle (6)
thin membrane
covers visceral mass
secretes mass
chemical sensory organs.
cavity encloses and protects gills.
can be lined with chromatophores.
describe strong muscular foot
foot modified to suit individual species lifestyles, e.g. squid = siphon
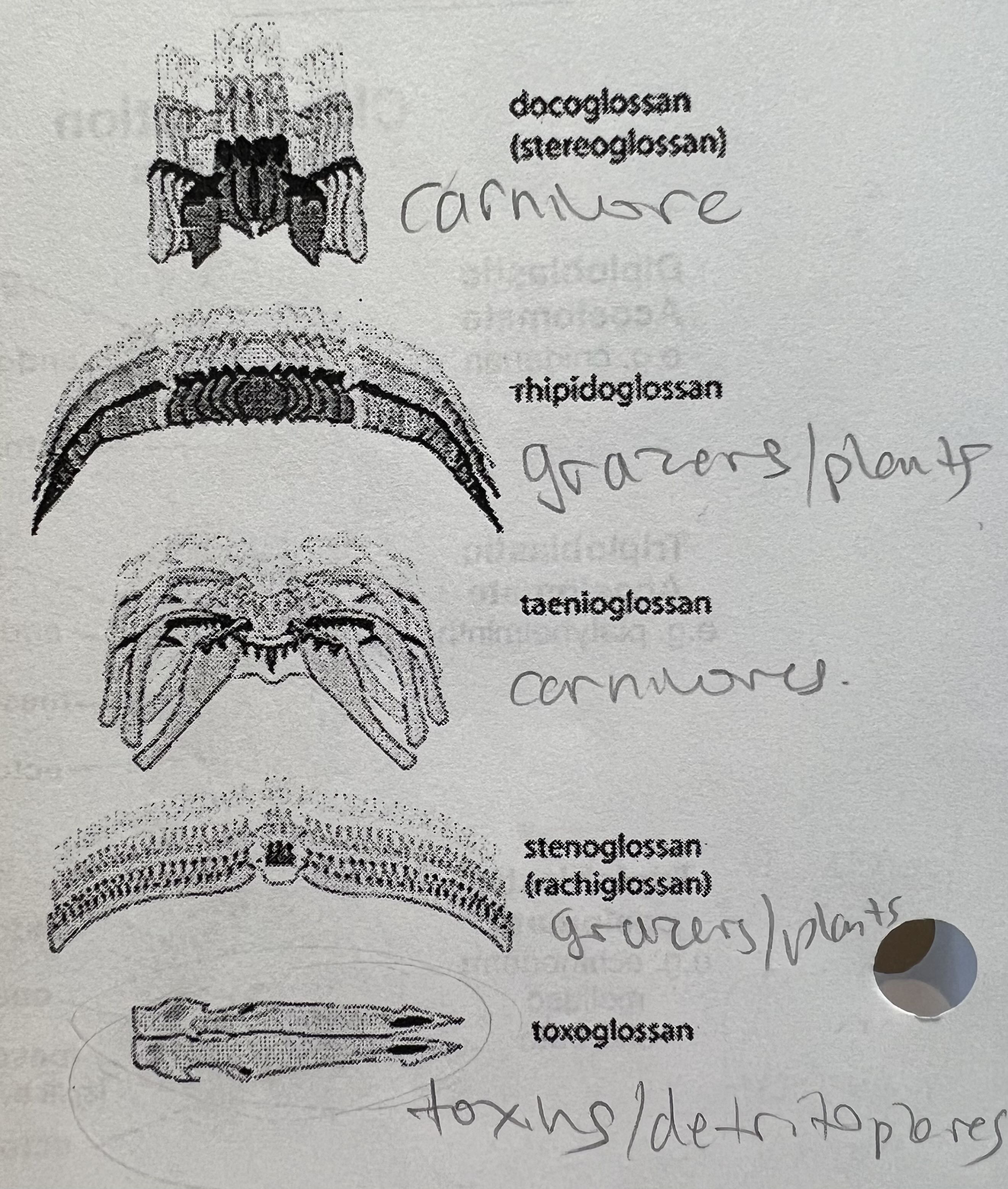
radula feeding (3)
shape depends on feeding method and type of food
herbivores, carnivores, or detritovores
different radulae used for drilling, scraping, multipurpose, darts, and secreting poison
siphon (4)
respiration: brings water to gills
feeding: transports food to digestive system
reproduction: brings in sperm, releases eggs or sperm
locomotion: jet propulsion (nautilus)
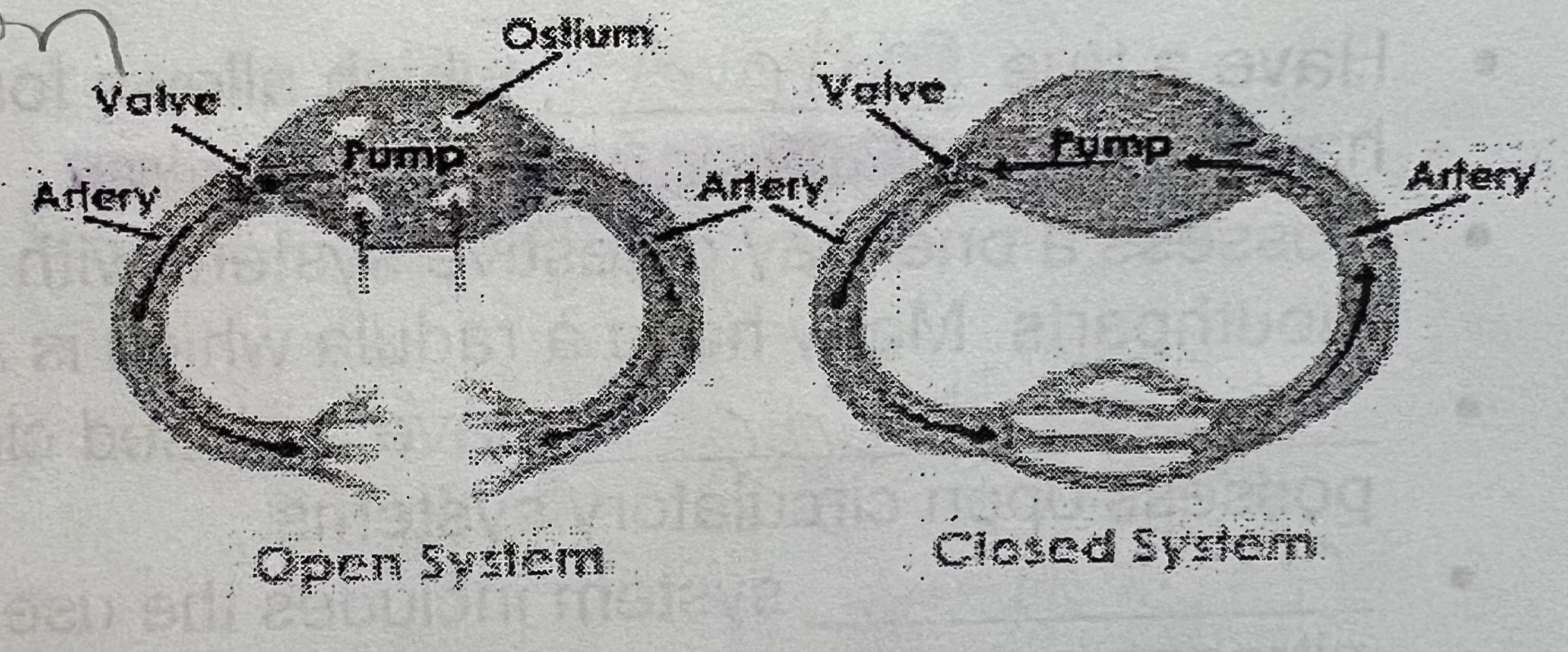
open circulation in mollusks (5)
all but cephalopods
pumps hemolymph throughout body
no veins
drains to and from the gills
slow
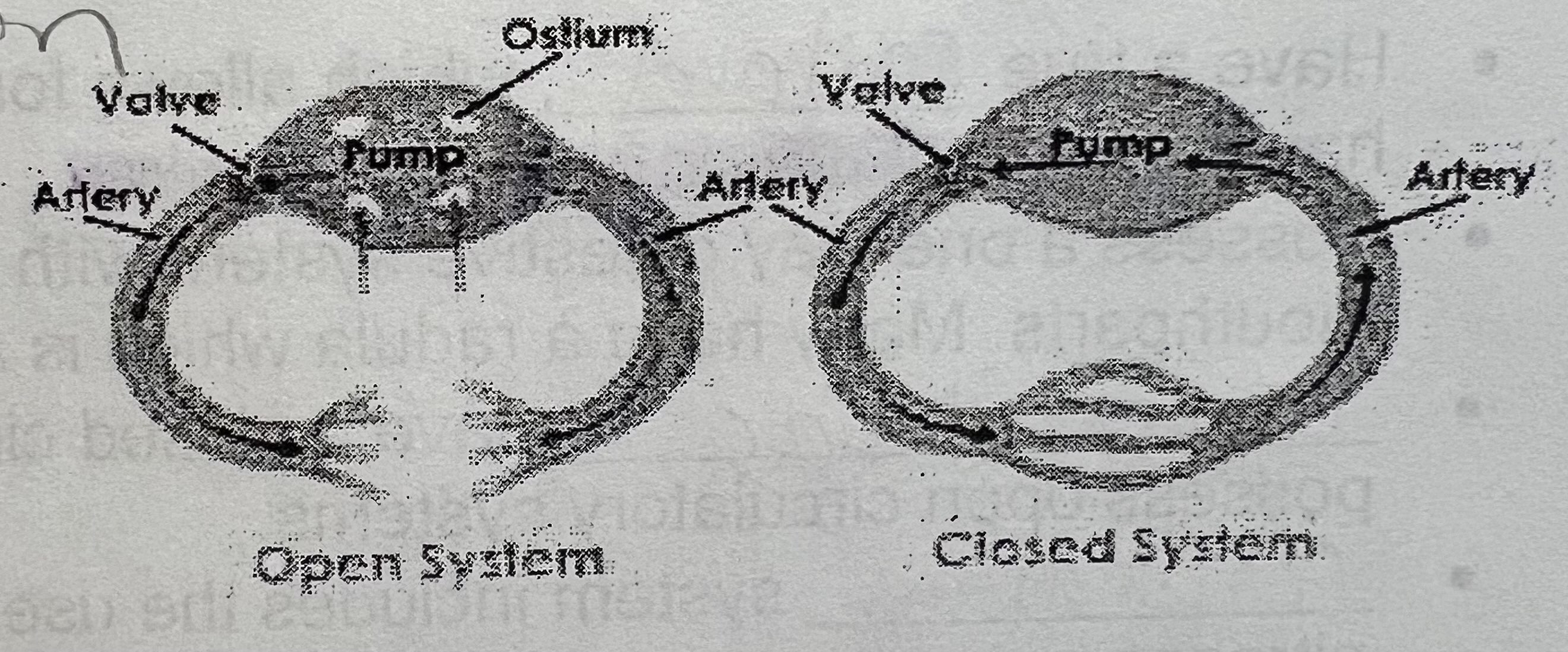
closed circulation in mollusks
cephalopods
pumps hemocyanin through veins using vessels
How many shell plates does polyplacophora have, and what can it do (4)
8:
protection
flexing
ball rolling
sounded by girdle structure
where do polyplacophora live
interidial zone
what is the polyplacophora foot for
adhesion
describe the polyplacophora radula and what it does
radula tipped with magnetide (Fe₃O₄) to eat algae
Examples from class bivalvia
clams, mussels, oysters
example of polyplacophora
chitons
what does valvia mean
shell
Do bivalva have radulas, why or why not
no radula, because filter feeders
what keeps bivalva closed
abs
what is the bivalva foot used for
burrowing
how do scallops move
jet propulsion
examples from class gastropoda
snails, limpets, slugs
How are gastropoda and Papua New Guinea similar
most diverse class
describe gastropoda foot and muscle movement
large muscular foot, muscles move in rippling motion
gastropoda shells
some univalves, some no-valved
most shells coiled, coloured, textures
visceral mass of gastropoda description
visceral mass is turned 180, and allows head to go into shell
Most snails have a lid-like part called an…
operculum on the back of the foot, so they can draw their bodies into their shell and close off the opening
physical description of gastropoda
well defined head
2-4 tentacles
eyes or sensory cells
reproduction in gastropodas
dioecious, external fertilization
respiratory system of gastropodas
most gills, some lungs
gastropoda radula
specialized, to get food
symmetry of cephalopoda
bilateral
physical components & structures of cephalopoda
prominent head
arms
tentacles
what are cephalopoda known for…
intelligence, developed brain, only other than chordates that have true brains
what do cephalopoda arms do
take in food surounding a hard, strong, beak-like jaw that tears the prey and secrete a poison to paralyze it
how does cephalopoda move
jet propulsion
unique adaptations of cephalopoda
chromatophores
advanced vision
ink cloud when in danger
what is jet propulsion
a method of movement where an animal expels fluid forcefully in one direction to propel itself in the opposite direction
based on Newton’s Third Law (for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction).
Why are feathery gills good for diffusion
increase surface area for gas exchange
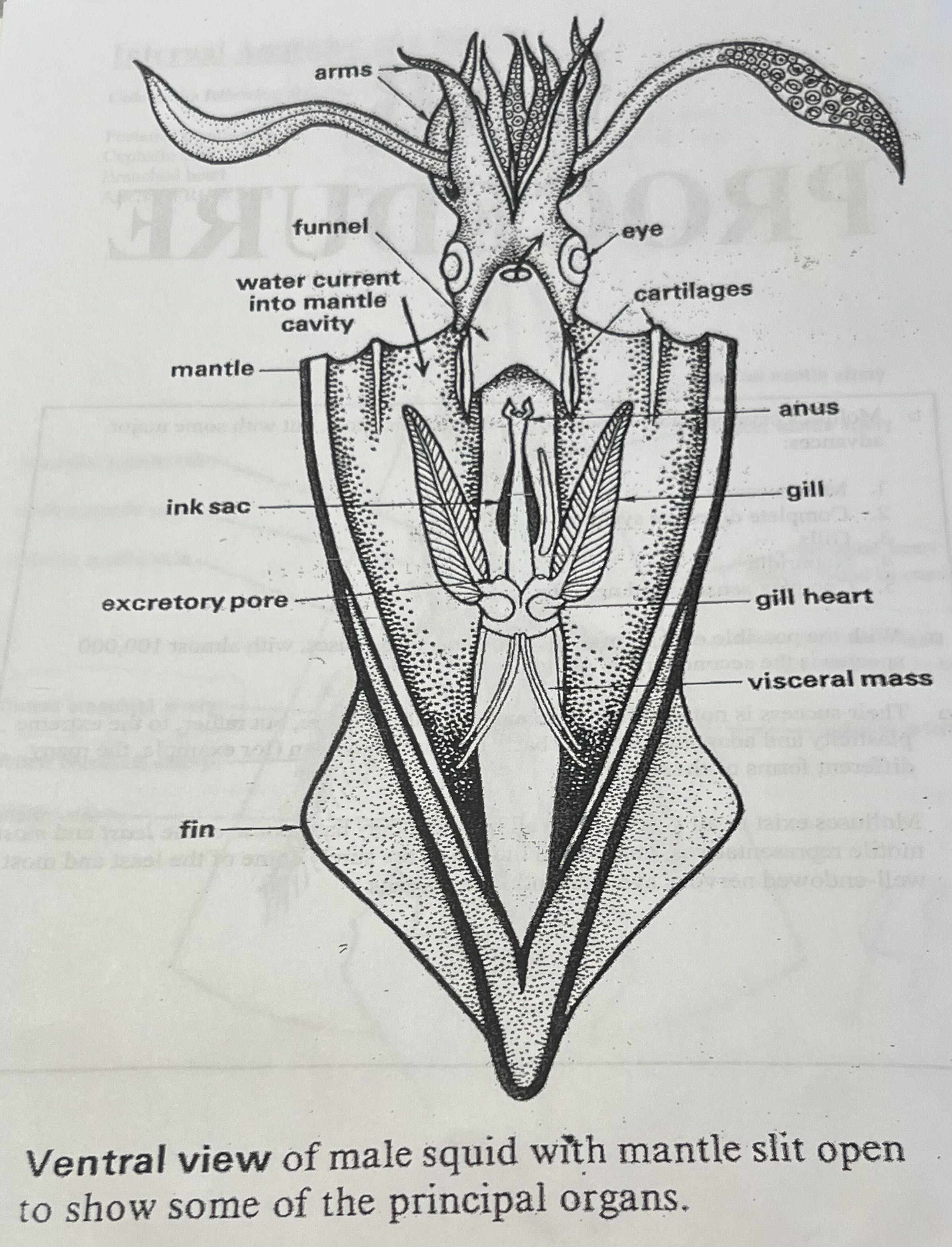
List all functions of parts
Arms – Grasp and manipulate prey; covered with suckers.
Funnel (Siphon) – Expels water for jet propulsion and removes waste.
Mantle – Muscular body wall; encloses organs and helps draw in and expel water for movement.
Ink Sac – Releases ink through the funnel to distract predators.
Excretory Pore – Releases waste from the body.
Fin – Stabilizes and steers while swimming.
Eye – Detects light, shape, and movement; enables advanced vision.
Cartilages – Provide support and structure for the head and eyes.
Anus – Expels digestive waste into the mantle cavity.
Gill – Site of gas exchange (oxygen in, CO₂ out).
Gill Heart (Branchial Heart) – Pumps blood to the gills for oxygenation.
Visceral Mass – Contains internal organs (digestive, reproductive, excretory systems).